SLVSEO0C August 2021 – June 2024 ADC12DJ4000RF
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Dual-Channel Mode)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Single-Channel Mode)
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Analog Inputs
- 7.3.2 ADC Core
- 7.3.3 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 7.3.4 Timestamp
- 7.3.5 Clocking
- 7.3.6 Programmable FIR Filter (PFIR)
- 7.3.7 Digital Down Converters (DDC)
- 7.3.8
JESD204C Interface
- 7.3.8.1 Transport Layer
- 7.3.8.2 Scrambler
- 7.3.8.3 Link Layer
- 7.3.8.4 8B/10B Link Layer
- 7.3.8.5
64B/66B Link Layer
- 7.3.8.5.1 64B/66B Encoding
- 7.3.8.5.2 Multiblocks, Extended Multiblocks and the Local Extended Multiblock Clock (LEMC)
- 7.3.8.5.3 Block, Multiblock and Extended Multiblock Alignment using Sync Header
- 7.3.8.5.4 Initial Lane Alignment
- 7.3.8.5.5 Block, Multiblock and Extended Multiblock Alignment Monitoring
- 7.3.8.6 Physical Layer
- 7.3.8.7 SerDes Pre-Emphasis
- 7.3.8.8 JESD204C Enable
- 7.3.8.9 Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency
- 7.3.8.10 Operation in Subclass 0 Systems
- 7.3.9 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Dual-Channel Mode
- 7.4.2 Single-Channel Mode (DES Mode)
- 7.4.3 Dual-Input Single-Channel Mode (DUAL DES Mode)
- 7.4.4 JESD204C Modes
- 7.4.5 Power-Down Modes
- 7.4.6 Test Modes
- 7.4.7 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 7.4.8 Offset Calibration
- 7.4.9 Trimming
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 SPI Register Map
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZEG|144
- AAV|144
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.8 JESD204C Interface
The ADC12DJ4000RF uses a JESD204C high-speed serial interface for data converters to transfer data from the ADC to the receiving logic device. Many of the available JESD204C output formats are backwards compatible with existing JESD204B receivers, including many of the JESD204B modes in the ADC12DJ2700 and ADC12DJ3200. The device serialized lanes are capable of operating with both 8B/10B encoding and 64B/66B encoding. A maximum of 16 lanes can be used to lower lane rates for interfacing with speed-limited logic devices. There are a few differences between 8B/10B and 64B/66B encoded JESD204C, which will be described throughout this section. Figure 7-19 shows a simplified block diagram of the 8B/10B encoded JESD204C interface and Figure 7-20 shows a simplified block diagram of the 64B/66B encoded JESD204C interface.
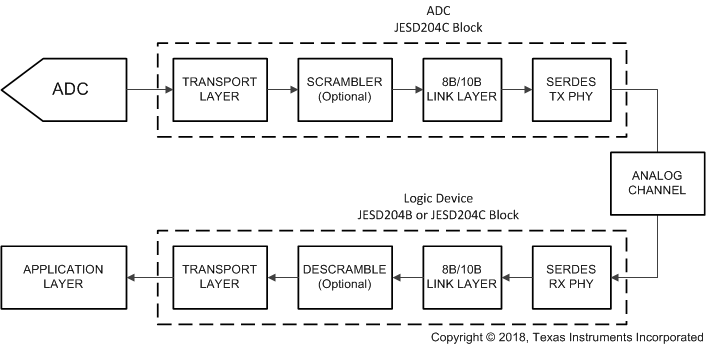 Figure 7-19 Simplified 8B/10B Encoded JESD204C Interface Diagram
Figure 7-19 Simplified 8B/10B Encoded JESD204C Interface Diagram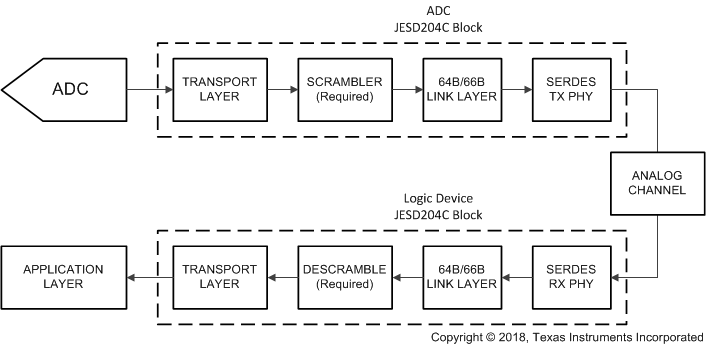 Figure 7-20 Simplified 64B/66B Encoded JESD204C Interface Diagram
Figure 7-20 Simplified 64B/66B Encoded JESD204C Interface DiagramThe various signals used in the JESD204C interface and the associated the device pin names are summarized briefly in Table 7-16 for reference. Most of the signals are common between 8B/10B and 64B/66B encoded JESD204C, except for SYNC which is not needed to achieve block synchronization for 64B/66B encoding. The sync header encoded into the data stream is used for block synchronization instead of the SYNC signal.
| SIGNAL NAME | PIN NAMES | 8B/10B | 64B/66B | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | DA[7:0]+, DA[7:0]–, DB[7:0]+, DB[7:0]–) | Yes | Yes | High-speed serialized data after 8B/10B or 64B/66B encoding |
| SYNC | SYNCSE, TMSTP+, TMSTP– | Yes | No | Link initialization signal (handshake), toggles low to start code group synchronization (CGS) process. Not used for 64B/66B encoding modes, unless it is used for NCO synchronization purposes. |
| Device clock | CLK+, CLK– | Yes | Yes | ADC sampling clock, also used for clocking digital logic and output serializers |
| SYSREF | SYSREF+, SYSREF– | Yes | Yes | System timing reference used to deterministically reset the internal local multiframe clock (LMFC) or local extended multiblock clock (LEMC) counters in each JESD204C device |
Not all optional features of JESD204C are supported by the device. The list of features that are supported and the features that are not supported is provided in Table 7-17.
| LETTER IDENTIFIER | REFERENCE CLAUSE | FEATURE | SUPPORT IN ADC12DJ4000RF |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | clause 8 | 8B/10B link layer | Supported |
| b | clause 7 | 64B/66B link layer | Supported |
| c | clause 7 | 64B/80B link layer | Not supported |
| d | clause 7 | The command channel when using the 64B/66B or 64B/80B link layer | Not supported |
| e | clause 7 | Forward error correction (FEC) when using the 64B/66B or 64B/80B link layer | Supported |
| f | clause 7 | CRC3 when using the 64B/66B or 64B/80B link layer | Not supported |
| g | clause 8 | A physical SYNC pin when using the 8B/10B link layer | Supported |
| h | clause 7, clause 8 | Subclass 0 | Not supported, but subclass 1 transmitter is compatible with subclass 0 receiver |
| i | clause 7, clause 8 | Subclass 1 | Supported |
| j | clause 8 | Subclass 2 | Not supported |
| k | clause 7, clause 8 | Lane alignment within a single link | Supported |
| l | clause 7, clause 8 | Subclass 1 with support for a lane alignment on a multipoint link by means of the MULTIREF signal | Not supported |
| m | clause 8 | SYNC interface timing is compatible with JESD204A | Supported |
| n | clause 8 | SYNC interface timing is compatible with JESD204B | Supported |