SBASAE0A October 2021 – November 2024 ADC12DJ1600 , ADC12QJ1600 , ADC12SJ1600
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Analog Input
- 7.3.2 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 7.3.3 Timestamp
- 7.3.4 Clocking
- 7.3.5
JESD204C Interface
- 7.3.5.1 Transport Layer
- 7.3.5.2 Scrambler
- 7.3.5.3 Link Layer
- 7.3.5.4 8B or 10B Link Layer
- 7.3.5.5 64B or 66B Link Layer
- 7.3.5.6 Physical Layer
- 7.3.5.7 JESD204C Enable
- 7.3.5.8 Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency
- 7.3.5.9 Operation in Subclass 0 Systems
- 7.3.5.10 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Low Power Mode and High Performance Mode
- 7.4.2 JESD204C Modes
- 7.4.3 Power-Down Modes
- 7.4.4 Test Modes
- 7.4.5 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 7.4.6 Offset Calibration
- 7.4.7 Trimming
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- AAV|144
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.1.4.1 ADC Theory of Operation
The differential voltages at the analog inputs are captured by the rising edge of CLK±. After capturing the input signal the ADC converts the analog voltage to a digital value by comparing the voltage to the internal reference voltage. If the voltage on the negative input (that is, INA–) is higher than the voltage on the positive input (that is, INA+) then the digital output is a negative 2's complement value. If the voltage on the positive input is higher than the voltage on the negative input then the digital output is a positive 2's complement value. Equation 1 can calculate the differential voltage at the input pins from the digital output.
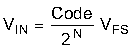
where
- Code is the signed decimal output code (for example, –2048 to +2047)
- N is the ADC resolution
- and VFS is the full-scale input voltage of the ADC as specified in the DC Specifications table, including any adjustment performed by programming FS_RANGE