SNAS378L November 2008 – February 2019 ADC14155QML-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 ADC14155 Converter Electrical Characteristics DC Parameters
- 6.6 ADC14155 Converter Electrical Characteristics (Continued) DYNAMIC Parameters
- 6.7 ADC14155 Converter Electrical Characteristics (Continued) Logic and Power Supply Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 ADC14155 Converter Electrical Characteristics (Continued) Timing and AC Characteristics
- 6.9 Timing Diagram
- 6.10 Transfer Characteristic
- 6.11 Typical Performance Characteristics, DNL, INL
- 6.12 Typical Performance Characteristics, Dynamic Performance
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- NBA|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.1.1 Device Nomenclature
APERTURE DELAY is the time after the falling edge of the clock to when the input signal is acquired or held for conversion.
APERTURE JITTER (APERTURE UNCERTAINTY) is the variation in aperture delay from sample to sample. Aperture jitter manifests itself as noise in the output.
CLOCK DUTY CYCLE is the ratio of the time during one cycle that a repetitive digital waveform is high to the total time of one period. The specification here refers to the ADC clock input signal.
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE (VCM) is the common DC voltage applied to both input terminals of the ADC.
CONVERSION LATENCY is the number of clock cycles between initiation of conversion and when that data is presented to the output driver stage. Data for any given sample is available at the output pins the Pipeline Delay plus the Output Delay after the sample is taken. New data is available at every clock cycle, but the data lags the conversion by the pipeline delay.
DIFFERENTIAL NON-LINEARITY (DNL) is the measure of the maximum deviation from the ideal step size of 1 LSB.
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB, or EFFECTIVE BITS) is another method of specifying Signal-to-Noise and Distortion Ratio or SINAD. ENOB is defined as (SINAD – 1.76) / 6.02 and says that the converter is equivalent to a perfect ADC of this (ENOB) number of bits.
FULL POWER BANDWIDTH is a measure of the frequency at which the reconstructed output fundamental drops 3 dB below its low frequency value for a full scale input.
GAIN ERROR is the deviation from the ideal slope of the transfer function. It can be calculated as:
It can also be expressed as Positive Gain Error and Negative Gain Error, which are calculated as:
INTEGRAL NON LINEARITY (INL) is a measure of the deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from negative full scale (½ LSB below the first code transition) through positive full scale (½ LSB above the last code transition). The deviation of any given code from this straight line is measured from the center of that code value.
INTERMODULATION DISTORTION (IMD) is the creation of additional spectral components as a result of two sinusoidal frequencies being applied to the ADC input at the same time. It is defined as the ratio of the power in the intermodulation products to the total power in the original frequencies. IMD is usually expressed in dBFS.
LSB (LEAST SIGNIFICANT BIT) is the bit that has the smallest value or weight of all bits. This value is VFS / 2n, where “VFS” is the full scale input voltage and “n” is the ADC resolution in bits.
MISSING CODES are those output codes that will never appear at the ADC outputs. The ADC14155QML is ensured not to have any missing codes.
MSB (MOST SIGNIFICANT BIT) is the bit that has the largest value or weight. Its value is one half of full scale.
NEGATIVE FULL SCALE ERROR is the difference between the actual first code transition and its ideal value of ½ LSB above negative full scale.
OFFSET ERROR is the difference between the two input voltages [(VIN+) – (VIN–)] required to cause a transition from code 8191 to 8192.
OUTPUT DELAY is the time delay after the falling edge of the clock before the data update is presented at the output pins.
PIPELINE DELAY (LATENCY) See CONVERSION LATENCY.
POSITIVE FULL SCALE ERROR is the difference between the actual last code transition and its ideal value of 1½ LSB below positive full scale.
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO (PSRR) is a measure of how well the ADC rejects a change in the power supply voltage. PSRR is the ratio of the Full-Scale output of the ADC with the supply at the minimum DC supply limit to the Full-Scale output of the ADC with the supply at the maximum DC supply limit, expressed in dB.
SIGNAL TO NOISE RATIO (SNR) is the ratio, expressed in dB, of the rms value of the input signal to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components below one-half the sampling frequency, not including harmonics or DC.
SIGNAL TO NOISE PLUS DISTORTION (S/N+D or SINAD) Is the ratio, expressed in dB, of the rms value of the input signal to the rms value of all of the other spectral components below half the clock frequency, including harmonics but excluding d.c.
SPURIOUS FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR) is the difference, expressed in dB, between the rms values of the input signal and the peak spurious signal, where a spurious signal is any signal present in the output spectrum that is not present at the input.
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION (THD) is the ratio, expressed in dB, of the rms total of the first nine harmonic levels at the output to the level of the fundamental at the output. THD is calculated as
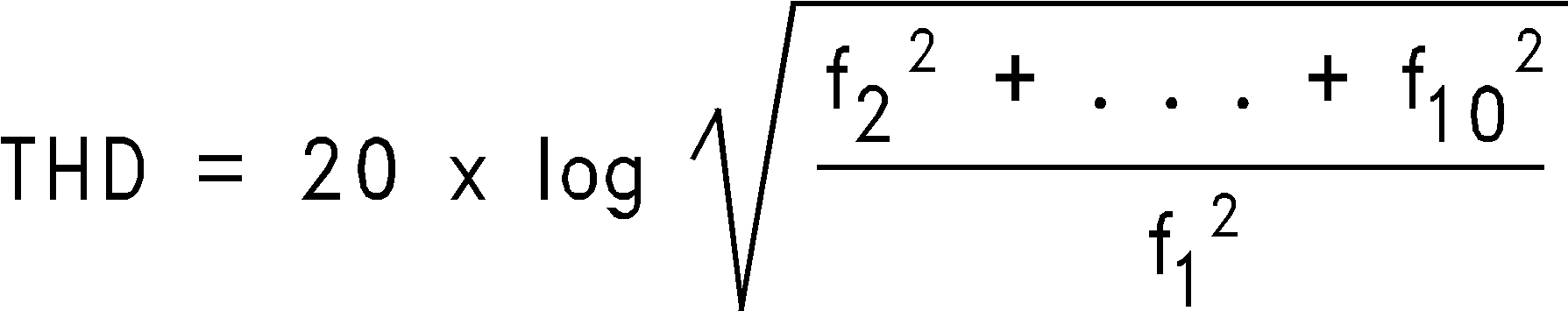
where f1 is the RMS power of the fundamental (output) frequency and f2 through f10 are the RMS power of the first 9 harmonic frequencies in the output spectrum.
SECOND HARMONIC DISTORTION (2ND HARM) is the difference expressed in dB, between the RMS power in the input frequency at the output and the power in its 2nd harmonic level at the output.
THIRD HARMONIC DISTORTION (3RD HARM) is the difference, expressed in dB, between the RMS power in the input frequency at the output and the power in its 3rd harmonic level at the output.