SNOI146C September 2011 – December 2017 ADC141S628-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGS|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
If military/aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments sales office, distributors for availability and specifications.(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VA relative to GND | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| VIO relative to GND | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| Voltage between any two pins(3) | 6 | V | |
| Current in or out of any pin(3) | ±10 | mA | |
| Package input current(3) | ±50 | mA | |
| Power consumption at TA = 25°C | See (4) | ||
| Junction temperature | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are measured with respect to GND = 0 V, unless otherwise specified.
(3) When the input voltage (VIN) at any pin exceeds the power supplies (VIN < GND or VIN > VA), the current at that pin must be limited to 10 mA and VIN must be within the absolute maximum rating for that pin. The 50-mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can safely exceed the power supplies with an input current of 10 mA to five.
(4) The absolute maximum junction temperature (TJmax) for this device is 150°C. The maximum allowable power dissipation is dictated by TJmax, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (θJA), and the ambient temperature (TA), and can be calculated using the formula PDMAX = (TJmax – TA) / θJA. The values for maximum power dissipation listed above are reached only when the ADC141S628-Q1 is operated in a severe fault condition (for example, when input or output pins are driven beyond the power supply voltages, or the power-supply polarity is reversed). These conditions must be avoided.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | ±1250 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±300 | |||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates that HBM stressing shall be in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions(1)(1)(2)
(1) All voltages are measured with respect to GND = 0 V, unless otherwise specified.
(2) For soldering specifications, see the Absolute Maximum Ratings for Soldering application report.
6.4 ADC141S628-Q1 Converter Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for VA = VIO = 5 V, VREF = 4.096 V, and fSCLK = 0.9 MHz to 3.6 MHz; fIN = 20 kHz and CL = 25 pF, unless otherwise noted. All specifications are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STATIC CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| Resolution with no missing codes | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 14 | Bits | |||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | ±0.5 | LSB | |||
| TA = –15°C to +65°C | ±0.95 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | ±1 | |||||
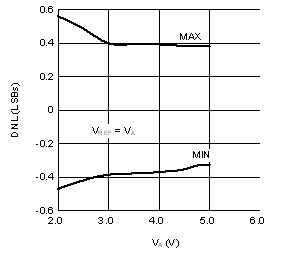
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | ±0.5 | LSB | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | ±0.95 | |||||
| PCTUE | Post calibration total unadjusted error | –15°C ≤ TA ≤ 65°C | ±0.5 | mV | ||
| –40°C ≤ TA ≤ 105°C | –0.85 | 1 | ||||
| OE | Offset error | –1 | LSB | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | ±5 | |||||
| FSE | Full-scale error | –3 | LSB | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | ±7 | |||||
| GE | Gain error | –1.5 | LSB | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | ±6 | |||||
| DYNAMIC CONVERTER CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise and distortion ratio | VIN = –0.1 dBFS | 82 | dBc | ||
| VIN = –0.1 dBFS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
80 | |||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | VIN = –0.1 dBFS | 82 | dBc | ||
| VIN = –0.1 dBFS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
80 | |||||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | VIN = –0.1 dBFS | –97 | dBc | ||
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | VIN = –0.1 dBFS | 98 | dBc | ||
| ENOB | Effective number of bits | VIN = –0.1 dBFS | 13.4 | Bits | ||
| VIN = –0.1 dBFS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
13.0 | |||||
| FPBW | –3-dB full-power bandwidth | Output at 70.7%FS with FS input, single-ended input | 22 | MHz | ||
| ANALOG INPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VIN | (+IN) – (–IN) | TA = –40°C to +105°C | GND | VREF | V | |
| +IN | Noninverting input | TA = –40°C to +105°C | –0.15 | VREF + 0.15 | V | |
| –IN | Inverting input | TA = –40°C to +105°C | –0.15 | 0.15 | V | |
| IDCL | DC leakage current | VIN = VREF or VIN = 0, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
±1 | µA | ||
| CINA | Input capacitance | In acquisition mode | 14 | pF | ||
| In conversion mode | 3.4 | |||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | See the Specification Definitions section for the test condition | 76 | dB | ||
| DIGITAL INPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VIH | Input high voltage | 1.9 | V | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | 2.3 | |||||
| VIL | Input low voltage | 1.0 | V | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | 0.7 | |||||
| IIN | Input current | VIN = 0 V or VA, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
±1 | µA | ||
| CIND | Input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||
| TA = –40°C to +105°C | 4 | |||||
| DIGITAL OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VOH | Output high voltage | ISOURCE = 200 µA | VA – 0.05 | V | ||
| ISOURCE = 200 µA, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
VA – 0.2 | |||||
| ISOURCE = 1 mA | VA – 0.16 | |||||
| VOL | Output low voltage | ISINK = 200 µA | 0.01 | V | ||
| ISINK = 200 µA, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
0.4 | |||||
| ISINK = 1 mA | 0.05 | |||||
| IOZH, IOZL | Tri-state leakage current | Force 0 V or VA, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
±1 | µA | ||
| COUT | Tri-state output capacitance | Force 0 V or VA | 2 | pF | ||
| Force 0 V or VA, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
4 | |||||
| Output coding | Straight binary | |||||
| POWER-SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VA | Analog supply voltage range | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 4.5 | 5.5 | V | |
| VIO | Digital input/output supply voltage range(2) | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 4.5 | 5.5 | V | |
| VREF | Reference voltage range | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 1.0 | VA | V | |
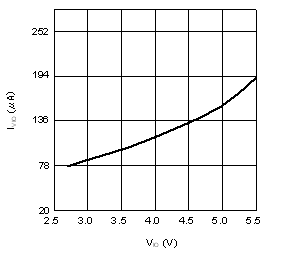
| IVA (Conv) | Analog supply current, conversion mode | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS | 740 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
970 | |||||
| IVIO (Conv) | Digital I/O supply current, conversion mode | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS | 170 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
260 | |||||
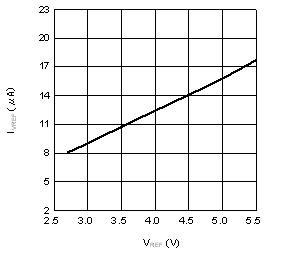
| IVREF (Conv) | Reference current, conversion mode | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS | 45 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
80 | |||||
| IVA (PD) | Analog supply current, power-down mode (CS high) | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz | 8 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = low | 2 | |||||
| fSCLK = low, TA = –40°C to +105°C | 3 | |||||
| IVIO (PD) | Digital I/O supply current, power-down mode (CS high) | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz | 3 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = low | 0.1 | |||||
| fSCLK = low, TA = –40°C to +105°C | 0.7 | |||||
| POWER-SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS (continued) | ||||||
| IVREF (PD) | Reference current, power-down mode (CS high) | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz | 0.1 | µA | ||
| fSCLK = low | 0.1 | |||||
| fSCLK = low, TA = –40°C to +105°C | 0.2 | |||||
| PWR (Conv) | Power consumption, conversion mode | fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS | 4.8 | mW | ||
| fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fS = 200 kSPS, TA = –40°C to +105°C |
6.5 | |||||
| PWR (PD) | Power consumption, power-down mode (CS high) | fSCLK = 0, VA = VIO = VREF = 5.0 V | 11 | µW | ||
| fSCLK = 0, VA = VIO = VREF = 5.0 V, TA = –40°C to +105°C | 19.5 | |||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | See the Specification Definitions section for the test condition | –85 | dB | ||
| AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| fSCLK | Minimum clock frequency | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 3.6 | 0.9 | MHz | |
| fS | Maximum sample rate | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 200 | kSPS | ||
| tACQ | Acquisition, track time | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 833 | ns | ||
| tCONV | Conversion, hold time | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 15 | SCLK cycles | ||
| tAD | Aperture delay | See the Specification Definitions section | 6 | ns | ||
(1) Typical values are at TJ = 25°C and represent most likely parametric norms. Test limits are specified to TI's average outgoing quality level (AOQL).
(2) The value of VIO is independent of the value of VA. For example, VIO can be operating at 5 V while VA is operating at 4.5 V or VIO can be operating at 4.5 V while VA is operating at 5 V.
6.5 ADC141S628-Q1 Timing Requirements
The following specifications apply for VA = VIO = 5 V, VREF = 4.096 V, fSCLK = 0.9 MHz to 3.6 MHz, and CL = 25 pF, unless otherwise noted. All specifications are at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.(1)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tCSS | CS setup time prior to an SCLK rising edge | 3 | ns (min) | |||
| –40°C to +105°C | 6 | ns | ||||
| 1 / fSCLK – 3 | ns (max) | |||||
| –40°C to +105°C | 1 / fSCLK – 6 | ns | ||||
| tDH | DOUT hold time after an SCLK falling edge | 10 | ns (min) | |||
| –40°C to +105°C | 6 | ns | ||||
| tDA | DOUT access time after an SCLK falling edge | 28 | ns (max) | |||
| –40°C to +105°C | 40 | ns | ||||
| tDIS | DOUT disable time after the rising edge of CS(2) | 10 | ns (max) | |||
| 20 | ns | |||||
| tCS | Minimum CS pulse duration | 5 | ns (min) | |||
| –40°C to +105°C | 20 | ns | ||||
| tEN | DOUT enable time after the falling edge of CS | 32 | ns (max) | |||
| 51 | ns | |||||
| tCH | SCLK high time | –40°C to +105°C | 111 | ns | ||
| tCL | SCLK low time | –40°C to +105°C | 111 | ns | ||
| tr | DOUT rise time | 7 | ns | |||
| tf | DOUT fall time | 7 | ns | |||
(1) Typical values are at TJ = 25°C and represent most likely parametric norms. Test limits are specified to TI's average outgoing quality level (AOQL).
(2) tDIS is the time for DOUT to change 10% while being loaded by the timing test circuit (see Figure 2).
 Figure 1. ADC141S628-Q1 Single Conversion Timing Diagram
Figure 1. ADC141S628-Q1 Single Conversion Timing Diagram
 Figure 2. Timing Test Circuit
Figure 2. Timing Test Circuit
 Figure 3. DOUT Rise and Fall Times
Figure 3. DOUT Rise and Fall Times
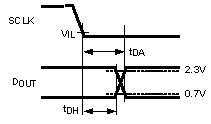 Figure 4. DOUT Hold and Access Times
Figure 4. DOUT Hold and Access Times
 Figure 5. Valid CS Assertion Times
Figure 5. Valid CS Assertion Times
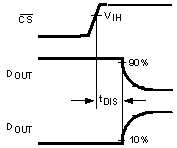 Figure 6. Voltage Waveform for tDIS
Figure 6. Voltage Waveform for tDIS
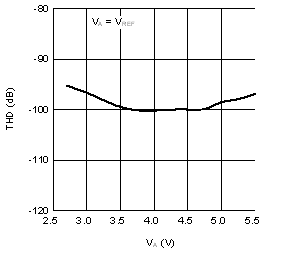
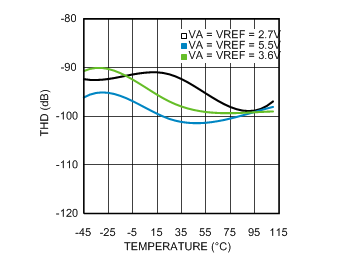
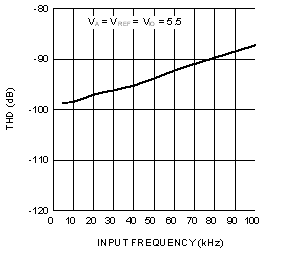
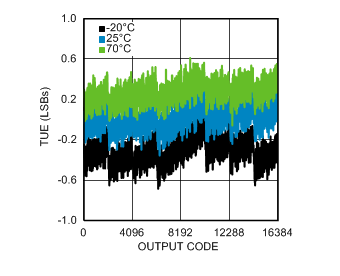
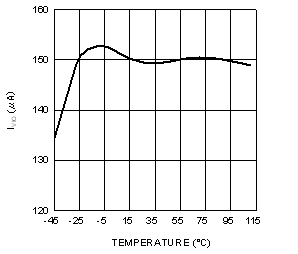
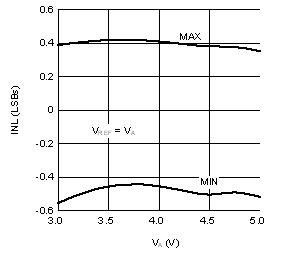
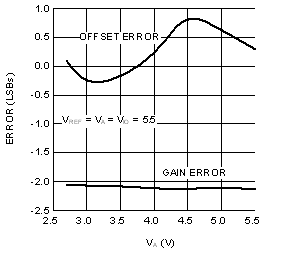
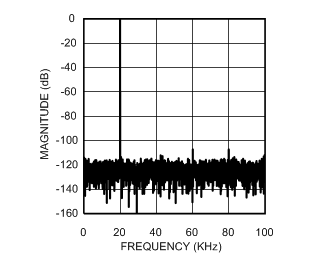
6.6 Typical Characteristics
VA = VIO = VREF = 5 V, fSCLK = 3.6 MHz, fSAMPLE = 200 kSPS, TA = +25°C, and fIN = 20 kHz (unless otherwise noted)