SBAS671C July 2014 – March 2016 ADC3241 , ADC3242 , ADC3243 , ADC3244
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADC3241, ADC3242
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADC3243, ADC3244
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 7.8 AC Performance: ADC3241
- 7.9 AC Performance: ADC3242
- 7.10 AC Performance: ADC3243
- 7.11 AC Performance: ADC3244
- 7.12 Digital Characteristics
- 7.13 Timing Requirements: General
- 7.14 Timing Requirements: LVDS Output
- 7.15 Typical Characteristics: ADC3241
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics: ADC3242
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics: ADC3243
- 7.18 Typical Characteristics: ADC3244
- 7.19 Typical Characteristics: Common
- 7.20 Typical Characteristics: Contour
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Summary of Special Mode Registers
- 9.6.2
Serial Register Description
- 9.6.2.1 Register 01h
- 9.6.2.2 Register 03h
- 9.6.2.3 Register 04h
- 9.6.2.4 Register 05h
- 9.6.2.5 Register 06h
- 9.6.2.6 Register 07h
- 9.6.2.7 Register 09h
- 9.6.2.8 Register 0Ah
- 9.6.2.9 Register 0Bh
- 9.6.2.10 Register 0Eh
- 9.6.2.11 Register 0Fh
- 9.6.2.12 Register 13h (address = 13h)
- 9.6.2.13 Register 15h
- 9.6.2.14 Register 25h
- 9.6.2.15 Register 27h
- 9.6.2.16 Register 41Dh
- 9.6.2.17 Register 422h
- 9.6.2.18 Register 434h
- 9.6.2.19 Register 439h
- 9.6.2.20 Register 51Dh
- 9.6.2.21 Register 522h
- 9.6.2.22 Register 534h
- 9.6.2.23 Register 539h
- 9.6.2.24 Register 608h
- 9.6.2.25 Register 70Ah
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power-Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
9 Detailed Description
9.1 Overview
The ADC324x are a high-linearity, ultra-low power, quad-channel, 14-bit, 25-MSPS to 125-MSPS, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) family. The devices are designed specifically to support demanding, high input frequency signals with large dynamic range requirements. An input clock divider allows more flexibility for system clock architecture design while the SYSREF input enables complete system synchronization. The ADC324x family supports serial LVDS interface in order to reduce the number of interface lines, thus allowing for high system integration density. The serial LVDS interface is two-wire, where each ADC data are serialized and output over two LVDS pairs. An internal phase-locked loop (PLL) multiplies the incoming ADC sampling clock to derive the bit clock that is used to serialize the 14-bit output data from each channel. In addition to the serial data streams, the frame and bit clocks are also transmitted as LVDS outputs.
9.2 Functional Block Diagram

9.3 Feature Description
9.3.1 Analog Inputs
The ADC324x analog signal inputs are designed to be driven differentially. Each input pin (INP, INM) must swing symmetrically between (VCM + 0.5 V) and (VCM – 0.5 V), resulting in a 2-VPP (default) differential input swing. The input sampling circuit has a 3-dB bandwidth that extends up to 540 MHz (50-Ω source driving 50-Ω termination between INP and INM).
9.3.2 Clock Input
The device clock inputs can be driven differentially (sine, LVPECL, or LVDS) or single-ended (LVCMOS), with little or no difference in performance between them. The common-mode voltage of the clock inputs is set to
0.95 V using internal 5-kΩ resistors. The self-bias clock inputs of the ADC324x can be driven by the transformer-coupled, sine-wave clock source or by the ac-coupled, LVPECL and LVDS clock sources, as shown in Figure 136, Figure 137, and Figure 138. See Figure 139 for details regarding the internal clock buffer.

 Figure 137. LVDS Clock Driving Circuit
Figure 137. LVDS Clock Driving Circuit
 Figure 138. LVPECL Clock Driving Circuit
Figure 138. LVPECL Clock Driving Circuit

A single-ended CMOS clock can be ac-coupled to the CLKP input, with CLKM connected to ground with a 0.1-μF capacitor, as shown in Figure 140. However, for best performance the clock inputs must be driven differentially, thereby reducing susceptibility to common-mode noise. For high input frequency sampling, TI recommends using a clock source with very low jitter. Band-pass filtering of the clock source can help reduce the effects of jitter. There is no change in performance with a non-50% duty cycle clock input.
 Figure 140. Single-Ended Clock Driving Circuit
Figure 140. Single-Ended Clock Driving Circuit
9.3.2.1 SNR and Clock Jitter
The signal-to-noise ratio of the ADC is limited by three different factors, as shown in Equation 1. Quantization noise (typically 86 dB for a 14-bit ADC) and thermal noise limit SNR at low input frequencies while the clock jitter sets SNR for higher input frequencies.

The SNR limitation resulting from sample clock jitter can be calculated with Equation 2.

The total clock jitter (TJitter) has two components: the internal aperture jitter (130 fs for the device) which is set by the noise of the clock input buffer and the external clock. TJitter can be calculated with Equation 3.

External clock jitter can be minimized by using high-quality clock sources and jitter cleaners as well as band pass filters at the clock input while a faster clock slew rate improves the ADC aperture jitter. The ADC324x has a typical thermal noise of 73.5 dBFS and internal aperture jitter of 130 fs. Figure 141 shows SNR (from 1 MHz offset leaving the 1/f flicker noise) for different jitter of clock driver.
 Figure 141. SNR vs Frequency for Different Clock Jitter
Figure 141. SNR vs Frequency for Different Clock Jitter
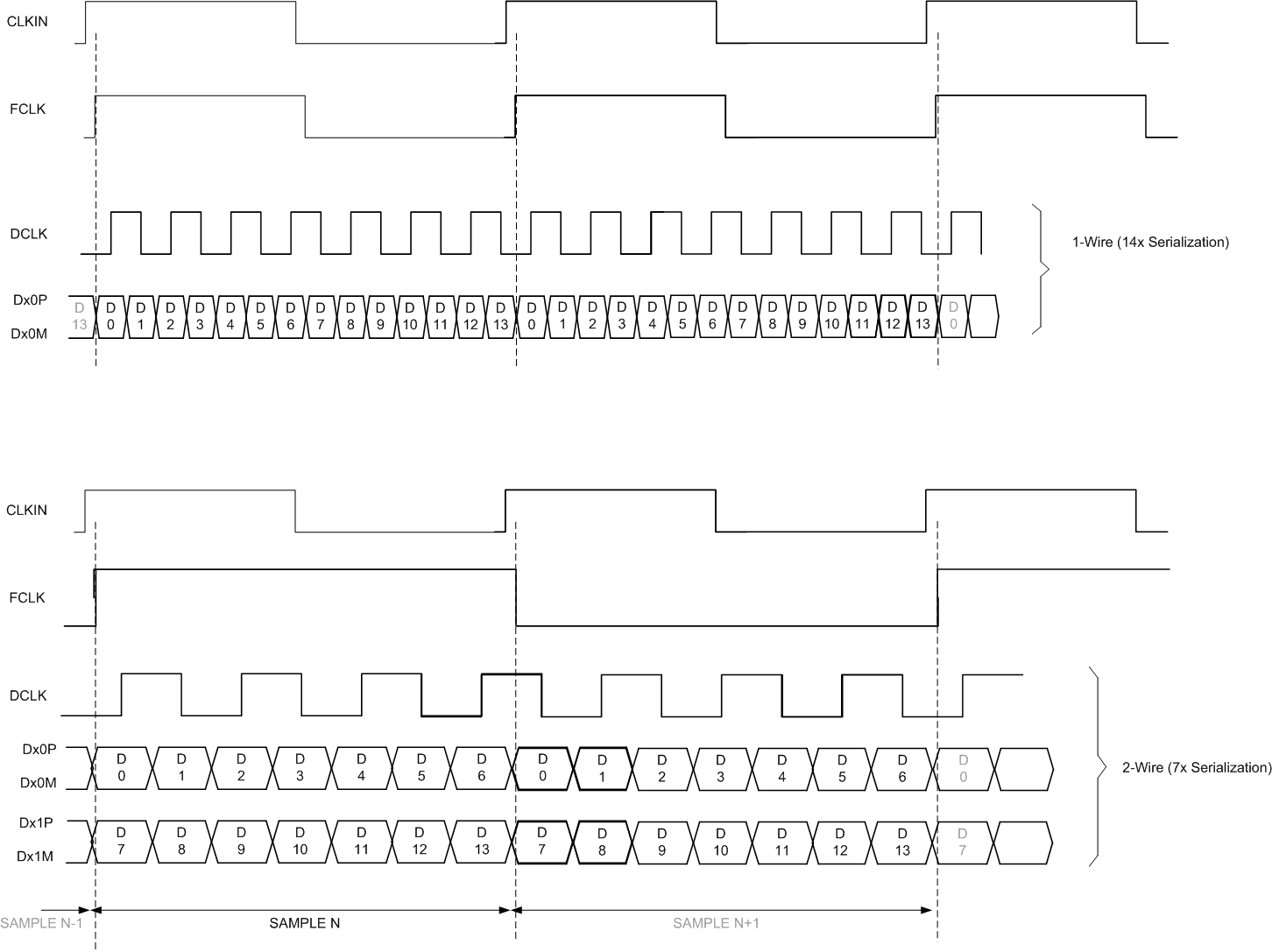
9.3.3 Digital Output Interface
The devices offer two different output format options, thus making interfacing to a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) or an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) easy. Each option can be easily programmed using the serial interface, as shown in Table 3. The output interface options are:
- One-wire, 1x frame clock, 14x serialization with the DDR bit clock and
- Two-wire, 0.5x frame clock, 7x serialization with the DDR bit clock.
Table 3. Interface Rates
| INTERFACE OPTIONS | SERIALIZATION | RECOMMENDED SAMPLING FREQUENCY (MSPS) | BIT CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz) | FRAME CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz) | SERIAL DATA RATE (Mbps) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MINIMUM | MAXIMUM | |||||
| 1-wire | 14x | 15(1) | — | 105 | 15 | 210 |
| — | 80 | 560 | 80 | 1120 | ||
| 2-wire (default after reset) | 7x | 20(1) | — | 70 | 10 | 140 |
| — | 125 | 437.5 | 62.5 | 875 | ||
9.3.3.1 One-Wire Interface: 14x Serialization
In this interface option, the device outputs the data of each ADC serially on a single LVDS pair (one-wire). The data are available at the rising and falling edges of the bit clock (DDR bit clock). The ADC outputs a new word at the rising edge of every frame clock, starting with the MSB. The data rate is 14x sample frequency (14x serialization).
9.3.3.2 Two-Wire Interface: 7x Serialization
The two-wire interface is recommended for sampling frequencies above 65 MSPS. The output data rate is 7x sample frequency because seven data bits are output every clock cycle on each differential pair. Each ADC sample is sent over the two wires with the seven MSBs on Dx1P, Dx1M and the seven LSBs on Dx0P, Dx0M, as shown in Figure 142. Note that in two-wire mode, the frame clock (FCLK) frequency is half of sampling clock (CLKIN) frequency.
9.4 Device Functional Modes
9.4.1 Input Clock Divider
The devices are equipped with an internal divider on the clock input. The clock divider allows operation with a faster input clock, thus simplifying the system clock distribution design. The clock divider can be bypassed for operation with a 125-MHz clock while the divide-by-2 option supports a maximum input clock of 250 MHz and the divide-by-4 option provides a maximum input clock frequency of 500 MHz.
9.4.2 Chopper Functionality
The devices are equipped with an internal chopper front-end. Enabling the chopper function swaps the ADC noise spectrum by shifting the 1/f noise from dc to fS / 2. Figure 143 shows the noise spectrum with the chopper off and Figure 144 shows the noise spectrum with the chopper on. This function is especially useful in applications requiring good ac performance at low input frequencies or in dc-coupled applications. The chopper can be enabled via SPI register writes and is recommended for input frequencies below 30 MHz. The chopper function creates a spur at fS / 2 that must be filtered out digitally.

| fIN = 10 MHz, fS = 125 MHz |

| fIN = 10 MHz, fS = 125 MHz |
9.4.3 Power-Down Control
The power-down functions of the ADC324x can be controlled either through the parallel control pin (PDN) or through an SPI register setting (see register 15h). The PDN pin can also be configured via SPI to a global power-down or standby functionality, as shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Power-Down Modes
| FUNCTION | POWER CONSUMPTION (mW) | WAKE-UP TIME (µs) |
|---|---|---|
| Global power-down | 5 | 85 |
| Standby | 81 | 35 |
9.4.3.1 Improving Wake-Up Time From Global Power-Down
The device has an internal low-pass filter in the sampling clock path. This low-pass filter helps improve the aperture jitter of the device. However, in applications where input frequencies are < 200 MHz, noise from the aperture jitter does not dominate the overall SNR of the device. In such applications, the wake-up time from a global power-down can be reduced by bypassing the low-pass filter using the DIS CLK FILT register bit (write 80h to register address 70Ah). As shown in Table 5, setting the DIS CLK FILT bit improves the wake-up time from a global power-down from 85 µs to 55 µs.
Table 5. Wake-Up Time From Global Power-Down
| DIS CLK FILT REGISTER BIT |
GLOBAL PDN REGISTER BIT | WAKE-UP TIME | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
| 0 | 0→1→0 | 85 | 140 | µs |
| 1 | 0→1→0 | 55 | 81 | µs |
9.4.4 Internal Dither Algorithm
The ADC324x use an internal dither algorithm to achieve high SFDR and a clean spectrum. However, the dither algorithm marginally degrades SNR, creating a trade-off between SNR and SFDR. If desired, the dither algorithm can be turned off by using the DIS DITH CHx registers bits. Figure 145 and Figure 146 show the effect of using dither algorithms.

| SFDR = 95.9 dBc, SNR = 72.7 dBFS, SINAD = 72.7 dBFS, THD = 93.6 dBc, HD2 = –100.6 dBc, HD3 = –95.9 dBc |
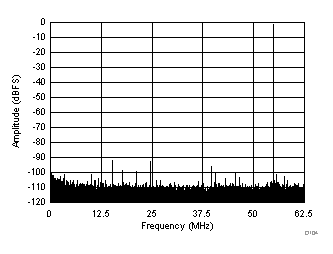
| SFDR = 90.9 dBc, SNR = 73.3 dBFS, SINAD = 73.1 dBFS, THD = 87 dBc, HD2 = –90.9 dBc, HD3 = –94.9 dBc |
9.5 Programming
The ADC324x can be configured using a serial programming interface, as described in this section.
9.5.1 Serial Interface
The device has a set of internal registers that can be accessed by the serial interface formed by the SEN (serial interface enable), SCLK (serial interface clock), SDATA (serial interface data), and SDOUT (serial interface data output) pins. Serially shifting bits into the device is enabled when SEN is low. Serial data SDATA are latched at every SCLK rising edge when SEN is active (low). The serial data are loaded into the register at every 24th SCLK rising edge when SEN is low. When the word length exceeds a multiple of 24 bits, the excess bits are ignored. Data can be loaded in multiples of 24-bit words within a single active SEN pulse. The interface can function with SCLK frequencies from 20 MHz down to very low speeds (of a few hertz) and also with a non-50% SCLK duty cycle.
9.5.1.1 Register Initialization
After power-up, the internal registers must be initialized to their default values through a hardware reset by applying a high pulse on the RESET pin (of durations greater than 10 ns), as shown in Figure 147. If required, the serial interface registers can be cleared during operation either:
- Through a hardware reset, or
- By applying a software reset. When using the serial interface, set the RESET bit (D0 in register address 06h) high. This setting initializes the internal registers to the default values and then self-resets the RESET bit low. In this case, the RESET pin is kept low.
9.5.1.1.1 Serial Register Write
The device internal register can be programmed with these steps:
- Drive the SEN pin low,
- Set the R/W bit to 0 (bit A15 of the 16-bit address),
- Set bit A14 in the address field to 1,
- Initiate a serial interface cycle by specifying the address of the register (A13 to A0) whose content must be written, and
- Write the 8-bit data that are latched in on the SCLK rising edge.
Figure 147 and Table 6 show the timing requirements for the serial register write operation.
 Figure 147. Serial Register Write Timing Diagram
Figure 147. Serial Register Write Timing Diagram
Table 6. Serial Interface Timing(1)
| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fSCLK | SCLK frequency (equal to 1 / tSCLK) | > dc | 20 | MHz | |
| tSLOADS | SEN to SCLK setup time | 25 | ns | ||
| tSLOADH | SCLK to SEN hold time | 25 | ns | ||
| tDSU | SDIO setup time | 25 | ns | ||
| tDH | SDIO hold time | 25 | ns | ||
9.5.1.1.2 Serial Register Readout
The device includes a mode where the contents of the internal registers can be read back using the SDOUT pin. This readback mode can be useful as a diagnostic check to verify the serial interface communication between the external controller and the ADC. Given below is the procedure to read contents of serial registers:
- Drive the SEN pin low.
- Set the R/W bit (A15) to 1. This setting disables any further writes to the registers.
- Set bit A14 in the address field to 1.
- Initiate a serial interface cycle specifying the address of the register (A13 to A0) whose content must be read.
- The device outputs the contents (D7 to D0) of the selected register on the SDOUT pin.
- The external controller can latch the contents at the SCLK rising edge.
- To enable register writes, reset the R/W register bit to 0.
When READOUT is disabled, the SDOUT pin is in a high-impedance mode. If serial readout is not used, the SDOUT pin must float. Figure 148 shows a timing diagram of the serial register read operation. Data appear on the SDOUT pin at the SCLK falling edge with an approximate delay (tSD_DELAY) of 20 ns, as shown in Figure 149.
 Figure 148. Serial Register Read Timing Diagram
Figure 148. Serial Register Read Timing Diagram
 Figure 149. SDOUT Timing Diagram
Figure 149. SDOUT Timing Diagram
9.5.2 Register Initialization
After power-up, the internal registers must be initialized to their default values through a hardware reset by applying a high pulse on the RESET pin, as shown in Figure 150 and Table 7.
 Figure 150. Initialization of Serial Registers after Power-Up
Figure 150. Initialization of Serial Registers after Power-Up
Table 7. Power-Up Timing
| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 | Power-on delay: delay from power up to active high RESET pulse | 1 | ms | |||
| t2 | Reset pulse duration: active high RESET pulse duration | 10 | 1000 | ns | ||
| t3 | Register write delay: delay from RESET disable to SEN active | 100 | ns | |||
If required, the serial interface registers can be cleared during operation either:
- Through hardware reset, or
- By applying a software reset. When using the serial interface, set the RESET bit (D0 in register address 06h) high. This setting initializes the internal registers to the default values and then self-resets the RESET bit low. In this case, the RESET pin is kept low.
9.6 Register Maps
Table 8. Register Map Summary
9.6.1 Summary of Special Mode Registers
Table 9 lists the location, value, and functions of special mode registers in the device.
Table 9. Special Modes Summary
| MODE | REGISTER SETTINGS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Special modes | Registers 439h (bit 3) and 539h (bit 3) | Always set these bits high for best performance |
| Disable dither | Registers 1h (bits 5-2), 434h (bits 5 and 3), and 534h (bits 5 and 3) |
Disable dither to improve SNR |
| Disable chopper | Registers 422h (bit 1) and 522h (bit 1) | Disable chopper to shift 1/f noise floor at dc |
| High IF modes | Registers 41Dh (bit 1), 51Dh (bit 1), and 608h (bits 7-6) |
Improves HD3 for IF > 100 MHz |
9.6.2 Serial Register Description
9.6.2.1 Register 01h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | DIS DITH CHA | DIS DITH CHB | 0 | 0 | ||
| W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | ||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 10. Register 01h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 5-4 | DIS DITH CHA | R/W | 0h | These bits enable or disable the on-chip dither. Control this bit with bits 5 and 3 of register 434h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel A. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 3-2 | DIS DITH CHB | R/W | 0h | These bits enable or disable the on-chip dither. Control this bit with bits 5 and 3 of register 434h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel B. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 1-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.2 Register 03h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ODD EVEN |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 11. Register 03h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-1 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 0 | ODD EVEN | R/W | 0h | This bit selects the bit sequence on the output lanes (in 2-wire mode only). 0 = Bits 0, 1, and 2 appear on lane 0; bits 7, 8, and 9 appear on lane 1 1 = Bits 0, 2, and 4 appear on lane 0; bits 1, 3, and 5 appear on lane 1 |
9.6.2.3 Register 04h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FLIP WIRE |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
9.6.2.4 Register 05h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1W-2W |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 13. Register 05h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-1 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 0 | 1W-2W | R/W | 0h | This bit transmits output data on either one or two wires. 0 = Output data are transmitted on two wires (Dx0P, Dx0M and Dx1P, Dx1M) 1 = Output data are transmitted on one wire (Dx0P, Dx0M). In this mode, the recommended fS is less than 62.5 MSPS. |
9.6.2.5 Register 06h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TEST PATTERN EN | RESET |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 14. Register 06h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | TEST PATTERN EN | R/W | 0h | This bit enables test pattern selection for the digital outputs. 0 = Normal output 1 = Test pattern output enabled |
| 0 | RESET | W | 0h | This bit applies a software reset. This bit resets all internal registers to the default values and self-clears to 0. |
9.6.2.6 Register 07h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | OVR ON LSB |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 15. Register 07h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-1 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 0 | OVR ON LSB | R/W | 0h | This bit provides the overrange (OVR) information on the LSB bits. 0 = Output data bit 0 functions as the LSB of the 14-bit data 1 = Output data bit 0 carries the OVR information. |
9.6.2.7 Register 09h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ALIGN TEST PATTERN | DATA FORMAT |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 16. Register 09h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | ALIGN TEST PATTERN | R/W | 0h | This bit aligns the test patterns across the outputs of both channels. 0 = Test patterns of both channels are free running 1 = Test patterns of both channels are aligned |
| 0 | DATA FORMAT | R/W | 0h | This bit programs the digital output data format. 0 = Twos complement 1 = Offset binary |
9.6.2.8 Register 0Ah
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | CHA TEST PATTERN | |||
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 17. Register 0Ah Description
9.6.2.9 Register 0Bh
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CHB TEST PATTERN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | |||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 18. Register 0Bh Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-4 | CHB TEST PATTERN | R/W | 0h | These bits control the test pattern for channel B after the TEST PATTERN EN bit is set. 0000 = Normal operation 0001 = All 0's 0010 = All 1's 0011 = Toggle pattern: data alternate between 10101010101010 and 01010101010101 0100 = Digital ramp: data increment by 1 LSB every clock cycle from code 0 to 16383 0101 = Custom pattern: output data are the same as programmed by the CUSTOM PATTERN register bits 0110 = Deskew pattern: data are 2AAAh 1000 = PRBS pattern: data are a sequence of pseudo random numbers 1001 = 8-point sine-wave: data are a repetitive sequence of the following eight numbers that form a sine-wave: 0, 2399, 8192, 13984, 16383, 13984, 8192, 2399. Others = Do not use |
| 3-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.10 Register 0Eh
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CUSTOM PATTERN[13:6] | |||||||
| R/W-0h | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 19. Register 0Eh Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | CUSTOM PATTERN[13:6] | R/W | 0h | These bits set the 14-bit custom pattern (bits 13-6) for all channels. |
9.6.2.11 Register 0Fh
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CUSTOM PATTERN[5:0] | 0 | 0 | |||||
| R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | |||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 20. Register 0Fh Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | CUSTOM PATTERN[5:0] | R/W | 0h | These bits set the 14-bit custom pattern (bits 5-0) for all channels. |
| 1-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.12 Register 13h (address = 13h)
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | LOW SPEED ENABLE | |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 21. Register 13h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0. |
| 1-0 | LOW SPEED ENABLE | R/W | 0h | Enables low speed operation in 1-wire and 2-wire mode. Depending upon sampling frequency, write this bit as per Table 22. |
Table 22. LOW SPEED ENABLE Register Bit Settings Across fS
| fS (MSPS) | REGISTER BIT LOW SPEED ENABLE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | 1-WIRE MODE | 2-WIRE MODE | |
| 25 | 125 | 00 | 00 | |
| 20 | 25 | 00 | 10 | |
| 15 | 20 | 10 | Not supported | |
9.6.2.13 Register 15h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | CHA PDN | CHB PDN | 0 | STANDBY | GLOBAL PDN | 0 | CONFIG PDN PIN |
| W-0h | R/W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 23. Register 15h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 6 | CHA PDN | R/W | 0h | 0 = Normal operation 1 = Power-down channel A |
| 5 | CHB PDN | R/W | 0h | 0 = Normal operation 1 = Power-down channel B |
| 4 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 3 | STANDBY | R/W | 0h | The ADCs of both channels enter standby. 0 = Normal operation 1 = Standby |
| 2 | GLOBAL PDN | R/W | 0h | 0 = Normal operation 1 = Global power-down |
| 1 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 0 | CONFIG PDN PIN | R/W | 0h | This bit configures the PDN pin as either a global power-down or standby pin. 0 = Logic high voltage on the PDN pin sends the device into global power-down 1 = Logic high voltage on the PDN pin sends the device into standby |
9.6.2.14 Register 25h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| LVDS SWING | |||||||
| R/W-0h | |||||||
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; -n = value after reset |
Table 24. Register 25h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | LVDS SWING | R/W | 0h | These bits control the swing of the LVDS outputs (including the data output, bit clock, and frame clock). For details see Table 25. |
Table 25. LVDS Output Swing
| BITS 7-4 | BITS 3-0 | LVDS OUTPUT SWING |
|---|---|---|
| 0h | 0h | Default (±425 mV) |
| Dh | 9h | Swing reduces by 50 mV |
| Eh | Ah | Swing reduces by 100 mV |
| Fh | Dh | Swing reduces by 300 mV |
| Ch | Eh | Swing increases by 100 mV |
| Others | Others | Do not use |
9.6.2.15 Register 27h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CLK DIV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 26. Register 27h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | CLK DIV | R/W | 0h | These bits set the internal clock divider for the input sampling clock. 00 = Divide-by-1 01 = Divide-by-1 10 = Divide-by-2 11 = Divide-by-4 |
| 5-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.16 Register 41Dh
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | HIGH IF MODE0 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 27. Register 41Dh Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | HIGH IF MODE0 | R/W | 0h | This bit improves HD3 for IF > 100 MHz. 0 = Normal operation For best HD3 at IF > 100 MHz, set HIGH IF MODE[3:0] to 1111. |
| 0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.17 Register 422h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | DIS CHOP CHA | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 28. Register 422h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | DIS CHOP CHA | R/W | 0h | Disable chopper. Set this bit to shift a 1/f noise floor at dc. 0 = 1/f noise floor is centered at fS / 2 (default) 1 = Chopper mechanism is disabled; 1/f noise floor is centered at dc |
| 0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.18 Register 434h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | DIS DITH CHA | 0 | DIS DITH CHA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 29. Register 434h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 5 | DIS DITH CHA | R/W | 0h | Set this bit with bits 5 and 4 of register 01h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel A. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 4 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 3 | DIS DITH CHA | R/W | 0h | Set this bit with bits 5 and 4 of register 01h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel A. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 2-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.19 Register 439h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | SP1 CHA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 30. Register 439h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-4 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 3 | SP1 CHA | R/W | 0h | Special mode for best performance on channel A. Always write 1 after reset. |
| 2-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.20 Register 51Dh
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | HIGH IF MODE1 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 31. Register 51Dh Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | HIGH IF MODE1 | R/W | 0h | This bit improves HD3 for IF > 100 MHz. 0 = Normal operation For best HD3 at IF > 100 MHz, set HIGH IF MODE[3:0] to 1111. |
| 0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.21 Register 522h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | DIS CHOP CHB | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 32. Register 522h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 1 | DIS CHOP CHB | R/W | 0h | Disable chopper. Set this bit to shift a 1/f noise floor at dc. 0 = 1/f noise floor is centered at fS / 2 (default) 1 = Chopper mechanism is disabled; 1/f noise floor is centered at dc |
| 0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.22 Register 534h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | DIS DITH CHA | 0 | DIS DITH CHA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 33. Register 534h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 5 | DIS DITH CHA | R/W | 0h | Set this bit with bits 3 and 2 of register 01h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel B. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 4 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 3 | DIS DITH CHA | R/W | 0h | Set this bit with bits 3 and 2 of register 01h. 00 = Default 11 = Dither is disabled for channel B. In this mode, SNR typically improves by 0.5 dB at 70 MHz. |
| 2-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.23 Register 539h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | SP1 CHB | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 34. Register 539h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-4 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 3 | SP1 CHB | R/W | 0h | Special mode for best performance on channel B. Always write 1 after reset. |
| 0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.24 Register 608h
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| HIGH IF MODE[3:2] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 35. Register 608h Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | HIGH IF MODE[3:2] | R/W | 0h | This bit improves HD3 for IF > 100 MHz. 0 = Normal operation For best HD3 at IF > 100 MHz, set HIGH IF MODE[3:0] to 1111. |
| 5-0 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
9.6.2.25 Register 70Ah
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DIS CLK FILT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | PDN SYSREF |
| R/W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | W-0h | R/W-0h |
| LEGEND: R/W = Read/Write; R = Read only; W = Write only; -n = value after reset |
Table 36. Register 70Ah Description
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | DIS CLK FILT | R/W | 0h | Set this bit to improve wake-up time from global power-down mode; see the Improving Wake-Up Time From Global Power-Down section for details. |
| 6-1 | 0 | W | 0h | Must write 0 |
| 0 | PDN SYSREF | R/W | 0h | If the SYSREF pins are not used in the system, the SYSREF buffer must be powered down by setting this bit. 0 = Normal operation 1 = Powers down the SYSREF buffer |