SBAS565C January 2014 – August 2019 ADS1283
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Synchronization (SYNC PIN and SYNC Command)
- 8.4.2 Reset (RESET Pin and Reset Command)
- 8.4.3 Power-Down (PWDN Pin and STANDBY Command)
- 8.4.4 Power-On Sequence
- 8.4.5 DVDD Power Supply
- 8.4.6 Serial Interface
- 8.4.7 Data Format
- 8.4.8 Reading Data
- 8.4.9 One-Shot Operation
- 8.4.10 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration Registers
- 8.4.11 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
- 8.4.12 User Calibration
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.5.1.1 SDATAC Requirements
- 8.5.1.2 WAKEUP: Wake-Up From Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.3 STANDBY: Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.4 SYNC: Synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- 8.5.1.5 RESET: Reset the Device
- 8.5.1.6 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.7 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.8 RDATA: Read Data by Command
- 8.5.1.9 RREG: Read Register Data
- 8.5.1.10 WREG: Write to Register
- 8.5.1.11 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration
- 8.5.1.12 GANCAL: Gain Calibration
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID_CFG: ID_Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset =x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 HPF0 and HPF1 Registers
- 8.6.1.5 OFC0, OFC1, OFC2 Registers
- 8.6.1.6 FSC0, FSC1, FSC2 Registers
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.4.11 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
Use the calibration commands (OFSCAL or GANCAL) to calibrate the conversion data. The values of the offset and gain calibration registers are internally written to perform calibration. The appropriate input signals must be applied to the ADS1283 inputs before sending the commands. Use slower data rates to achieve more consistent calibration results; this effect is a byproduct of the lower noise that these data rates provide. Also, if calibrating at power-on, be sure the reference voltage is fully settled.
Figure 57 shows the calibration command sequence. After the analog input voltage (and reference) have stabilized, send the SDATAC command, followed by the SYNC and RDATAC commands. DRDY goes low after 64 data periods. After DRDY goes low, send the SDATAC command, then the calibrate command (OFSCAL or GANCAL), followed by the RDATAC command. After 16 data periods, calibration is complete and conversion data can be read at this time. The SYNC input must remain high during the calibration sequence.
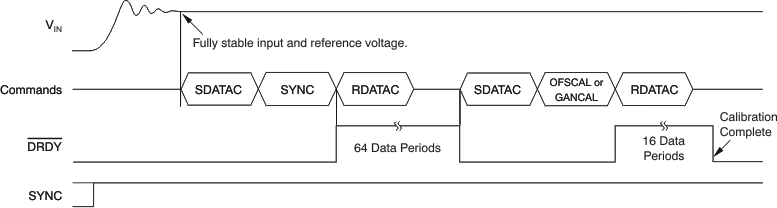 Figure 57. Offset and Gain Calibration Timing
Figure 57. Offset and Gain Calibration Timing The calibration commands apply to specific PGA settings. If the PGA is changed, recalibration is necessary. Calibration is bypassed in the sinc filter mode.