SBAS565C January 2014 – August 2019 ADS1283
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Synchronization (SYNC PIN and SYNC Command)
- 8.4.2 Reset (RESET Pin and Reset Command)
- 8.4.3 Power-Down (PWDN Pin and STANDBY Command)
- 8.4.4 Power-On Sequence
- 8.4.5 DVDD Power Supply
- 8.4.6 Serial Interface
- 8.4.7 Data Format
- 8.4.8 Reading Data
- 8.4.9 One-Shot Operation
- 8.4.10 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration Registers
- 8.4.11 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
- 8.4.12 User Calibration
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.5.1.1 SDATAC Requirements
- 8.5.1.2 WAKEUP: Wake-Up From Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.3 STANDBY: Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.4 SYNC: Synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- 8.5.1.5 RESET: Reset the Device
- 8.5.1.6 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.7 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.8 RDATA: Read Data by Command
- 8.5.1.9 RREG: Read Register Data
- 8.5.1.10 WREG: Write to Register
- 8.5.1.11 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration
- 8.5.1.12 GANCAL: Gain Calibration
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID_CFG: ID_Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset =x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 HPF0 and HPF1 Registers
- 8.6.1.5 OFC0, OFC1, OFC2 Registers
- 8.6.1.6 FSC0, FSC1, FSC2 Registers
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.3.2 Digital Filter
The digital filter receives the modulator output and decimates the data stream. By adjusting the amount of filtering, tradeoffs can be made between resolution and data rate: filter more for higher resolution, filter less for higher data rate.
The digital filter is comprised of three cascaded filter stages: a variable-decimation, fifth-order sinc filter; a fixed-decimation FIR, low-pass filter (LPF) with selectable phase; and a programmable, first-order, high-pass filter (HPF), as shown in Figure 35.
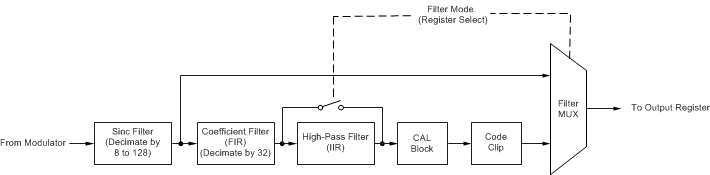 Figure 35. Digital Filter and Output Code Processing
Figure 35. Digital Filter and Output Code Processing The output can be taken from one of the three filter blocks, as Figure 35 shows. For partial filtering by the ADS1283, select the sinc filter output. For complete on-chip filtering, activate both the sinc + FIR stages. The HPF can then be included to remove dc and low frequencies from the data. Table 6 shows the filter options.
Table 6. Digital Filter Selection
| FILTR[1:0] BITS | DIGITAL FILTERS SELECTED |
|---|---|
| 00 | Reserved (not used) |
| 01 | Sinc |
| 10 | Sinc + FIR |
| 11 | Sinc + FIR + HPF
(low-pass and high-pass) |