SBAS778B June 2017 – August 2019 ADS1287
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1 Serial Interface
- 8.5.2
Commands
- 8.5.2.1 WAKEUP: Wake Up Command
- 8.5.2.2 STANDBY: Standby Mode Command
- 8.5.2.3 SYNC: Synchronize ADC Conversions
- 8.5.2.4 RESET: Reset Command
- 8.5.2.5 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 8.5.2.6 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 8.5.2.7 RDATA: Read Data Command
- 8.5.2.8 RREG: Read Register Data Command
- 8.5.2.9 WREG: Write Register Data Command
- 8.5.2.10 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration Command
- 8.5.2.11 GANCAL: Gain Calibration Command
- 8.6
Register Map
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID/CFG: ID, Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset = x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 High-Pass Filter Corner Frequency (HPFx) Registers (address = 03h, 04h) [reset = 32h, 03h]
- 8.6.1.5 Offset Calibration (OFCx) Registers (address = 05h, 06h, 07h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 8.6.1.6 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCx) Registers (address = 08h, 09h, 0Ah) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHF|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
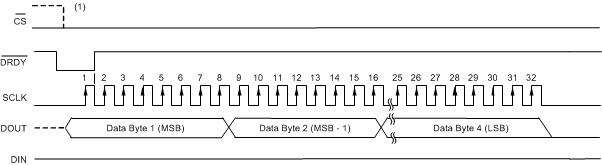
8.4.7.1 Read-Data-Continuous Mode (RDATAC)
In read-data-continuous mode, conversion data are read without the need of a read data command. When DRDY asserts low (indicating new data), the MSB of data appears on DOUT. Read data by applying the serial interface clock on SCLK; see Figure 3 for DRDY to DOUT timing.
As shown in Figure 59, conversion data are read by first driving CS low and then shifting the data by applying the serial interface clock to SCLK. Latch the data on the rising edge of SCLK. On the first falling edge of SCLK, the ADC returns DRDY high. After all 32 bits of conversion data are read, further SCLK transitions result in DOUT driven low. If desired, the read operation can be stopped after 24 bits. A new read cycle is started when new conversion data are available. The data read operation must be completed four CLK periods prior to the next DRDY falling edge, otherwise the data are overwritten with new conversion data.