SBAS590E March 2016 – June 2020 ADS131A02 , ADS131A04
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Timing Requirements: Asynchronous Interrupt Interface Mode
- 7.7 Switching Characteristics: Asynchronous Interrupt Interface Mode
- 7.8 Timing Requirements: Synchronous Master Interface Mode
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: Synchronous Master Interface Mode
- 7.10 Timing Requirements: Synchronous Slave Interface Mode
- 7.11 Switching Characteristics: Synchronous Slave Interface Mode
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 Interface Protocol
- 9.5.2 SPI Interface
- 9.5.3
SPI Command Definitions
- 9.5.3.1 NULL: Null Command
- 9.5.3.2 RESET: Reset to POR Values
- 9.5.3.3 STANDBY: Enter Standby Mode
- 9.5.3.4 WAKEUP: Exit Standby Mode
- 9.5.3.5 LOCK: Lock ADC Registers
- 9.5.3.6 UNLOCK: Unlock ADC Registers
- 9.5.3.7 RREG: Read a Single Register
- 9.5.3.8 RREGS: Read Multiple Registers
- 9.5.3.9 WREG: Write Single Register
- 9.5.3.10 WREGS: Write Multiple Registers
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1
User Register Description
- 9.6.1.1 ID_MSB: ID Control Register MSB (address = 00h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.2 ID_LSB: ID Control Register LSB (address = 01h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.3 STAT_1: Status 1 Register (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.4 STAT_P: Positive Input Fault Detect Status Register (address = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.5 STAT_N: Negative Input Fault Detect Status Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 STAT_S: SPI Status Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.7 ERROR_CNT: Error Count Register (address = 06h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.8 STAT_M2: Hardware Mode Pin Status Register (address = 07h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.9 Reserved Registers (address = 08h to 0Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.10 A_SYS_CFG: Analog System Configuration Register (address = 0Bh) [reset = 60h]
- 9.6.1.11 D_SYS_CFG: Digital System Configuration Register (address = 0Ch) [reset = 3Ch]
- 9.6.1.12 CLK1: Clock Configuration 1 Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = 08h]
- 9.6.1.13 CLK2: Clock Configuration 2 Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 86h]
- 9.6.1.14 ADC_ENA: ADC Channel Enable Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.15 Reserved Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.2 ADCx: ADC Channel Digital Gain Configuration Registers (address = 11h to 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1
User Register Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PBS|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PBS|32
Orderable Information
10.3 What To Do and What Not To Do
- Do partition the analog, digital, and power-supply circuitry into separate sections on the printed circuit board (PCB).
- Do use a single ground plane for analog and digital grounds.
- Do place the analog components close to the ADC pins using short, direct connections.
- Do keep the SCLK pin free of glitches and noise.
- Do verify that the analog input voltages are within the specified voltage range under all input conditions.
- Do tie unused analog input pins to GND.
- Do provide current limiting to the analog inputs in case overvoltage faults occur.
- Do use a low-dropout (LDO) regulator to reduce ripple voltage generated by switch-mode power supplies. This reduction is especially true for AVDD where the supply noise can affect performance.
- Do keep the input series resistance low to maximize THD performance.
- Do not cross analog and digital signals.
- Do not allow the analog power supply voltages (AVDD – AVSS) to exceed 3.6 V under any conditions, including during power-up and power-down when the negative charge pump is enabled.
- Do not allow the analog power supply voltages (AVDD – AVSS) to exceed 6 V under any conditions, including during power-up and power-down when the negative charge pump is disabled.
- Do not allow the digital supply voltage to exceed 3.9 V under any conditions, including during power-up and power-down.
Figure 104 and Figure 105 illustrate correct and incorrect ADC circuit connections.
 Figure 104. Correct and Incorrect Circuit Connections
Figure 104. Correct and Incorrect Circuit Connections 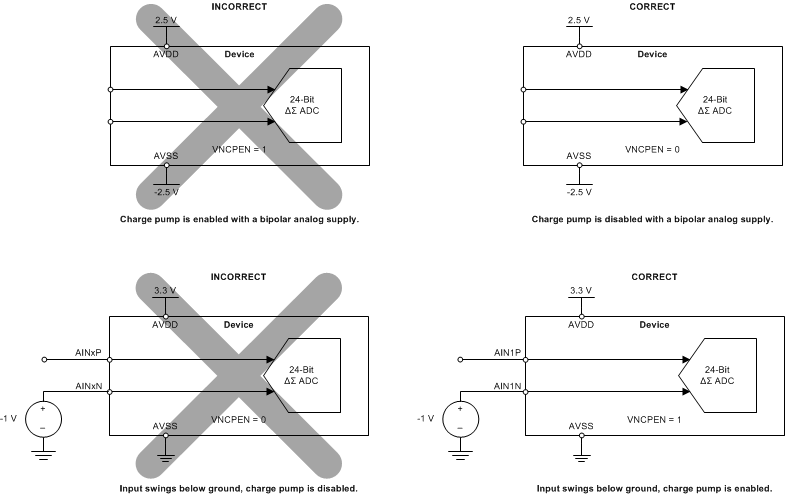 Figure 105. Correct and Incorrect Circuit Connections, Continued
Figure 105. Correct and Incorrect Circuit Connections, Continued