At 25°C, AVDD = 1.9 V, AVDD3V = 3.3 V, DRVDD = 1.8
V, rated sampling frequency, 0-dB gain, sine-wave input clock, 1.5-VPP
differential clock amplitude, 50% clock duty cycle, –1-dBFS differential analog
input, DDR LVDS output interface, and 32k-point FFT, unless otherwise noted.
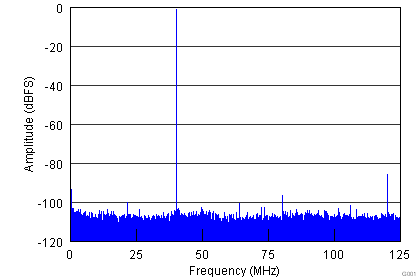
| fIN = 40 MHz | SFDR = 84 dBc | SNR = 71.1 dBFS |
| SINAD = 70.9 dBFS | THD = 84 dBc |
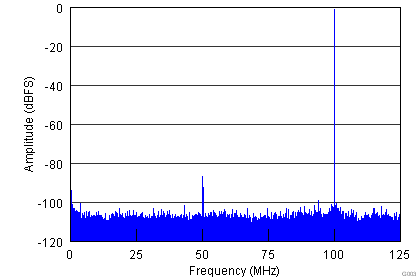
| fIN = 100 MHz | SFDR = 85 dBc | SNR = 70.2 dBFS |
| SINAD = 70.1 dBFS | THD = 84 dBc |

| fIN = 170 MHz | SFDR = 89 dBc | SNR = 69 dBFS |
| SINAD = 68.9 dBFS | THD = 85 dBc |
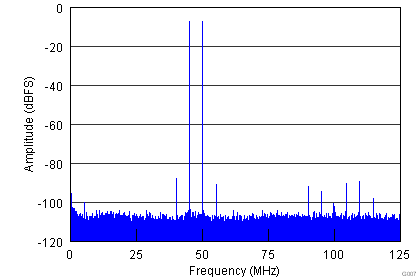
| Each Tone at –7-dBFS Amplitude | |
| fIN1 = 45 MHz | fIN2 = 50 MHz | SFDR = 92 dBFS |
| 2-Tone IMD = 87 dBFS | |
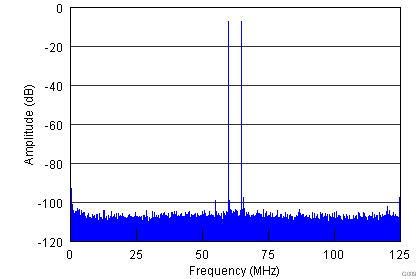
| Each Tone at –7-dBFS Amplitude | |
| fIN1 = 185.1 MHz | fIN2 = 190.1 MHz | SFDR = 102 dBFS |
| 2-Tone IMD = 97 dBFS | |
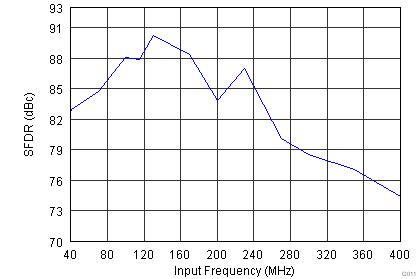 Figure 6-12 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Input Frequency
Figure 6-12 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Input Frequency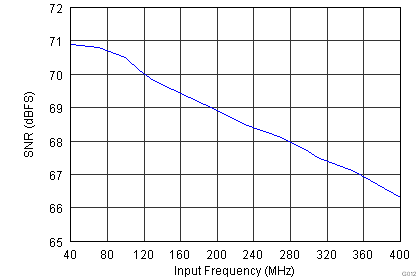 Figure 6-14 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Input Frequency
Figure 6-14 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Input Frequency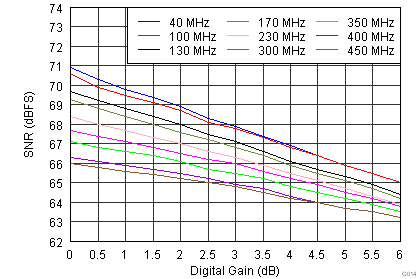 Figure 6-16 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Digital Gain
Figure 6-16 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Digital Gain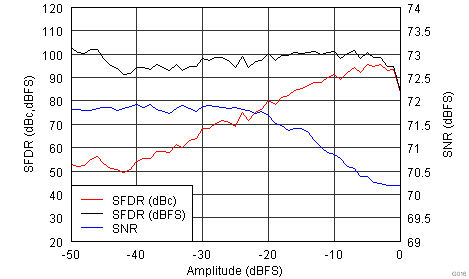
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
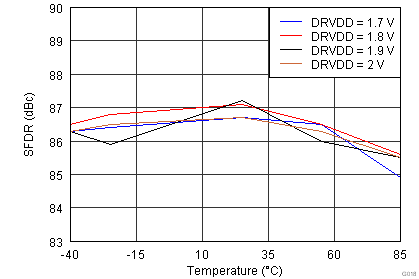
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
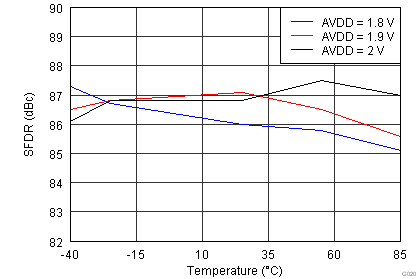
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
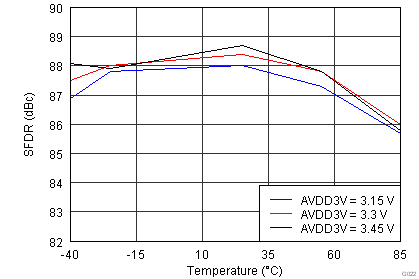
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
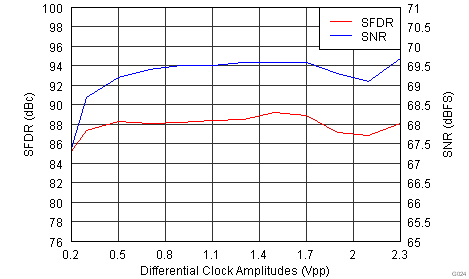
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
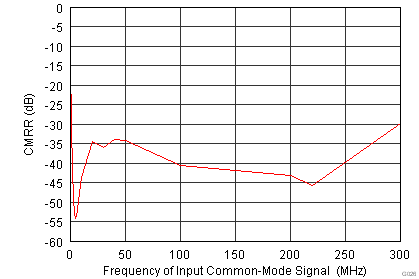
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
| 50-mVPP Signal Superimposed on VCM | |
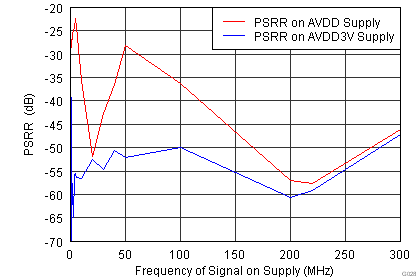
| Input Frequency = 10 MHz | |
| 50-mVPP Signal Superimposed on Supply | |
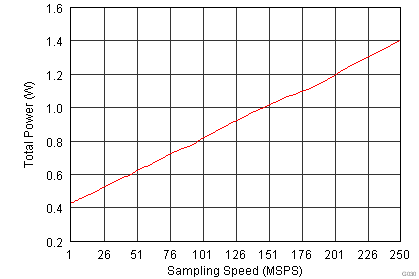
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
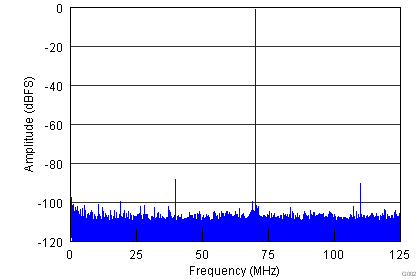
| fIN = 70 MHz | SFDR = 87 dBc | SNR = 70.9 dBFS |
| SINAD = 70.8 dBFS | THD = 84 dBc |
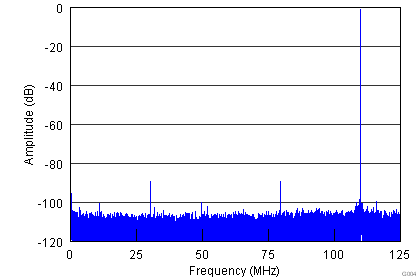
| fIN = 140 MHz | SFDR = 87 dBc | SNR = 69.7 dBFS |
| SINAD = 69.6 dBFS | THD = 84 dBc |

| fIN = 230 MHz | SFDR = 86 dBc | SNR = 68.9 dBFS |
| SINAD = 68.5 dBFS | THD = 84 dBc |
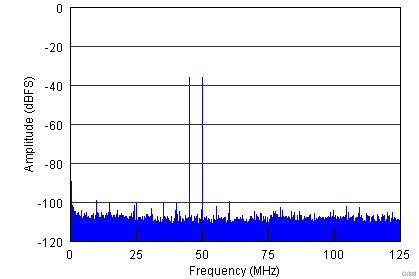
| Each Tone at –36-dBFS Amplitude | |
| fIN1 = 45 MHz | fIN2 = 50 MHz | SFDR = 99 dBFS |
| 2-Tone IMD = 99 dBFS | |
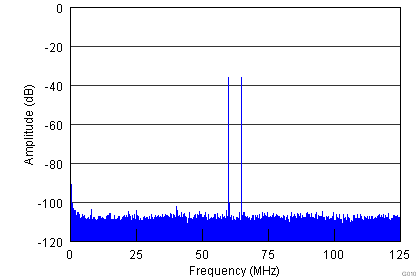
| Each Tone at –36-dBFS Amplitude | |
| fIN1 = 185.1 MHz | fIN2 = 190.1 MHz | SFDR = 100 dBFS |
| 2-Tone IMD = 101 dBFS | |
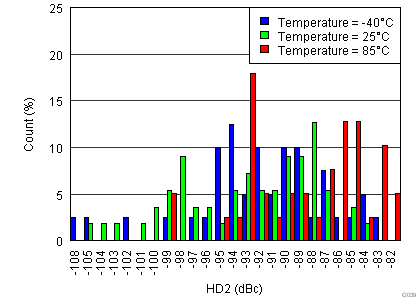
| Input Frequency = 170 MHz | |
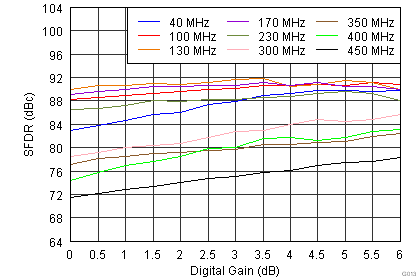 Figure 6-15 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Digital Gain
Figure 6-15 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Digital Gain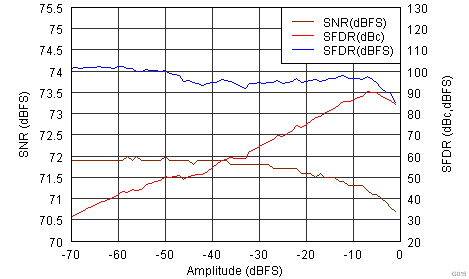 Figure 6-17 Performance vs Input Amplitude
Figure 6-17 Performance vs Input Amplitude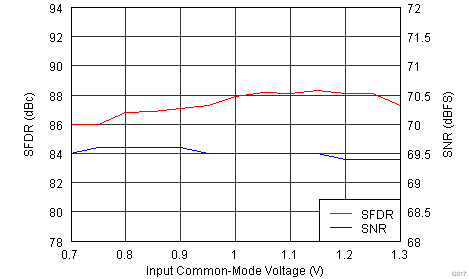
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
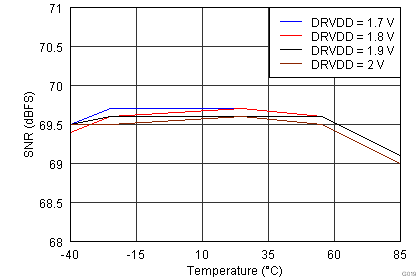
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
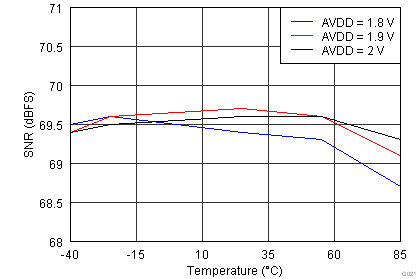
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
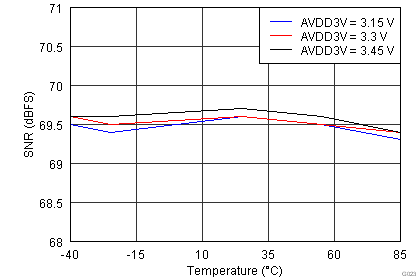
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
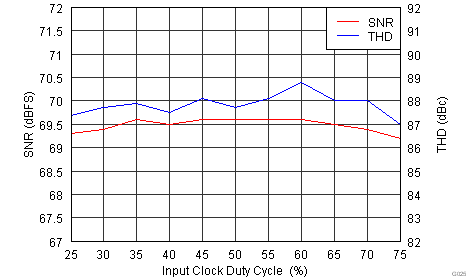
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |
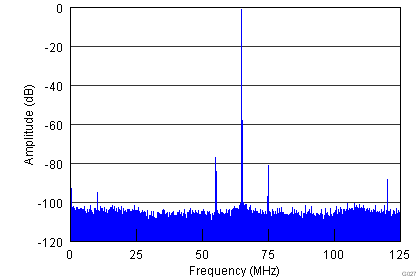
| fIN = 185 MHz | Amplitude (fIN – fCM) = –80.9 dBFS |
| Amplitude (fIN) = –1 dBFS | Amplitude (fCM) = –95 dBFS |
| fCM = 10 MHz, 50 mVPP | Amplitude (fIN + fCM) = –77.2 dBFS |
| SFDR = 76 dBc |
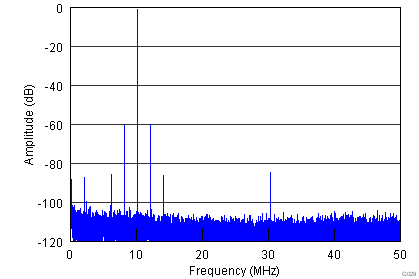
| Amplitude (fIN) = –1 dBFS | Amplitude (fPSRR) = –87 dBFS |
| fIN = 10 MHz | Amplitude (fIN + fPSRR) = –60.6 dBFS |
| fPSRR = 2 MHz, 50 mVPP | Amplitude (fIN – fPSRR) = –60 dBFS |
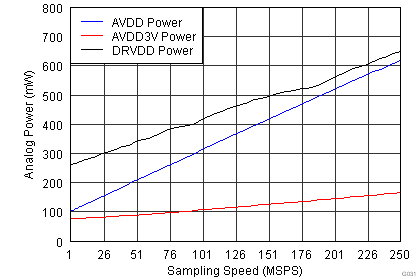
| Input Frequency = 185 MHz | |





 Figure 6-12 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Input Frequency
Figure 6-12 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Input Frequency Figure 6-14 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Input Frequency
Figure 6-14 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Input Frequency Figure 6-16 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Digital Gain
Figure 6-16 Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Digital Gain













 Figure 6-15 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Digital Gain
Figure 6-15 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range vs Digital Gain







