SBAS785 December 2016 ADS7046
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUG|8
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Figure 50 shows a typical connection diagram for the ADS7046.
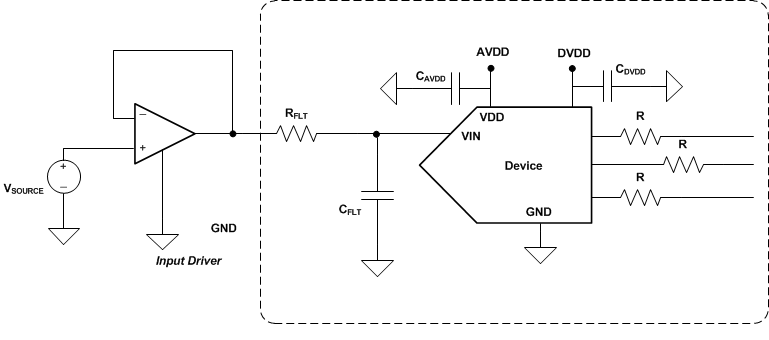 Figure 50. Typical Connection Diagram
Figure 50. Typical Connection Diagram
Figure 51 depicts a board layout example for the device for the typical connection diagram in Figure 50. The key considerations for layout are:
- Use a solid ground plane underneath the device and partition the PCB into analog and digital sections
- Avoid crossing digital lines with the analog signal path and keep the analog input signals and the reference input signals away from noise sources.
- The power sources to the device must be clean and well-bypassed. Use CAVDD decoupling capacitors in close proximity to the analog (AVDD) power-supply pin.
- Use a CDVDD decoupling capacitor close to the digital (DVDD) power-supply pin.
- Avoid placing vias between the AVDD and DVDD pins and the bypass capacitors.
- Connect the ground pin to the ground plane using a short, low-impedance path.
- Place the charge kickback filter components close to the device.
Among ceramic surface-mount capacitors, COG (NPO) ceramic capacitors are recommended because these components provide the most stable electrical properties over voltage, frequency, and temperature changes.
11.2 Layout Example
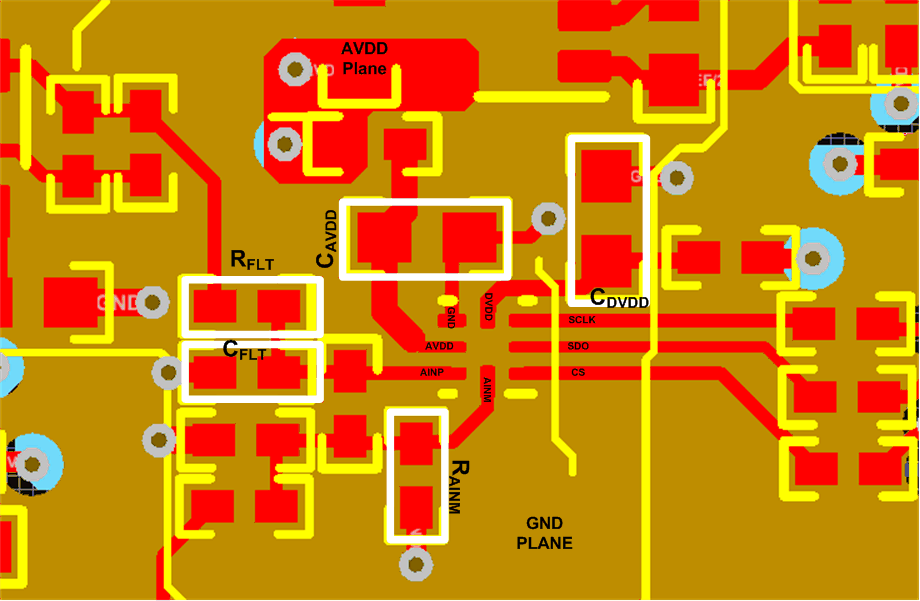 Figure 51. Example Layout
Figure 51. Example Layout