SBOS531E August 2010 – June 2019 AFE031
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description, continued
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Thermal Information
- 8.4 Electrical Characteristics: Transmitter (Tx)
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics: Power Amplifier (PA)
- 8.6 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver (Rx)
- 8.7 Electrical Characteristics: Digital
- 8.8 Electrical Characteristics: Two-Wire Interface
- 8.9 Electrical Characteristics: Internal Bias Generator
- 8.10 Electrical Characteristics: Power Supply
- 8.11 Timing Requirements
- 8.12 Timing Diagrams
- 8.13 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10.2.1.1 Line-Coupling Circuit
The line-coupling circuit is one of the most critical circuits in a powerline modem. The line-coupling circuit has two primary functions: first, to block the low-frequency signal of the mains (commonly 50 Hz or 60 Hz) from damaging the low-voltage modem circuitry; second, to couple the modem signal to and from the ac mains. A typical line-coupling circuit is shown in Figure 49.
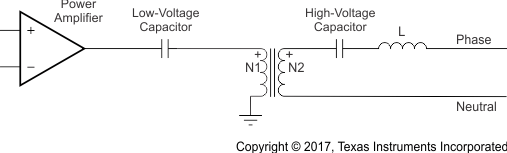 Figure 49. Simplified Line Coupling Circuit
Figure 49. Simplified Line Coupling Circuit For additional information on line-coupling interfaces with the AFE031, refer to Application Report SBOA130, Analog Front-End Design for a Narrowband Power-Line Communications Modem Using the AFE031, available for download at www.ti.com.