SLASF21 December 2022 AFE78101 , AFE88101
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Timing Requirements
- 6.7 Timing Diagrams
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: VOUT DAC
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: ADC
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: Reference
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: Power Supply
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RRU|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
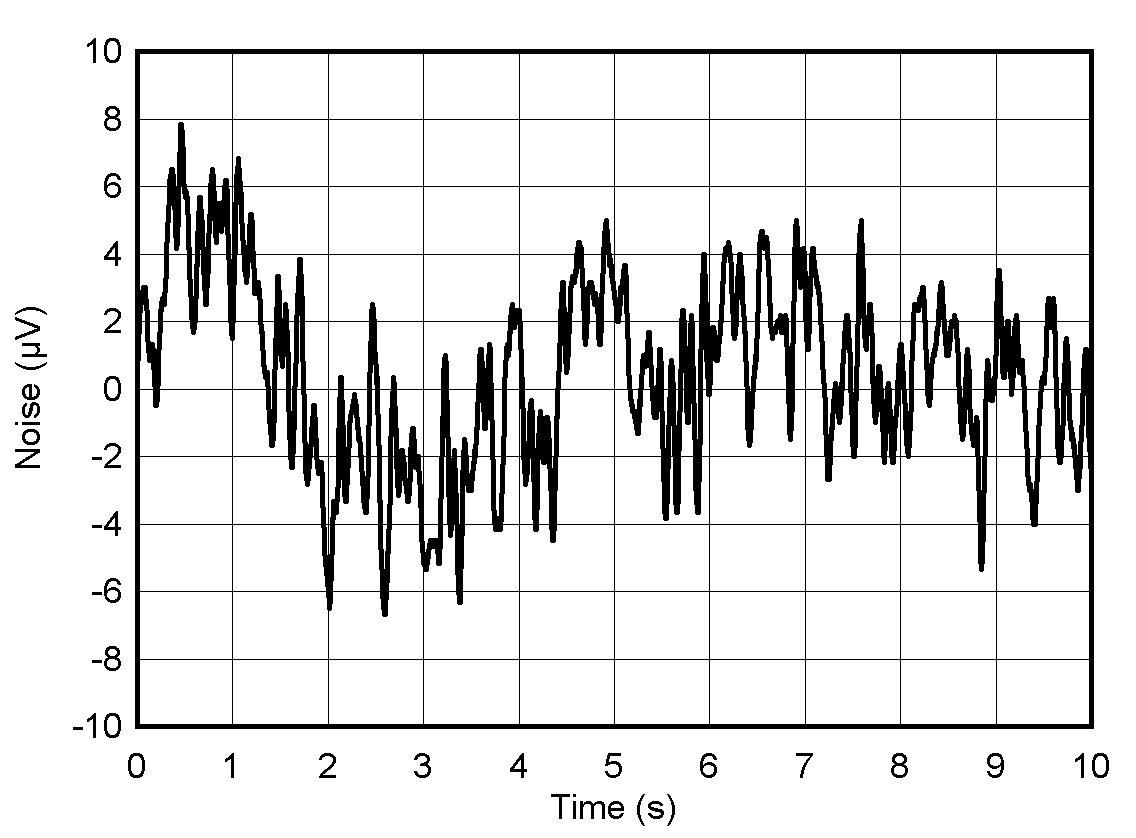
6.10 Typical Characteristics: Reference
at TA = 25°C, PVDD = IOVDD = 3.3 V, external or internal VREFIO = 1.25 V, RLOAD = 50 kΩ to GND, CLOAD = 100 pF to GND, and digital inputs at IOVDD or GND (unless otherwise noted)
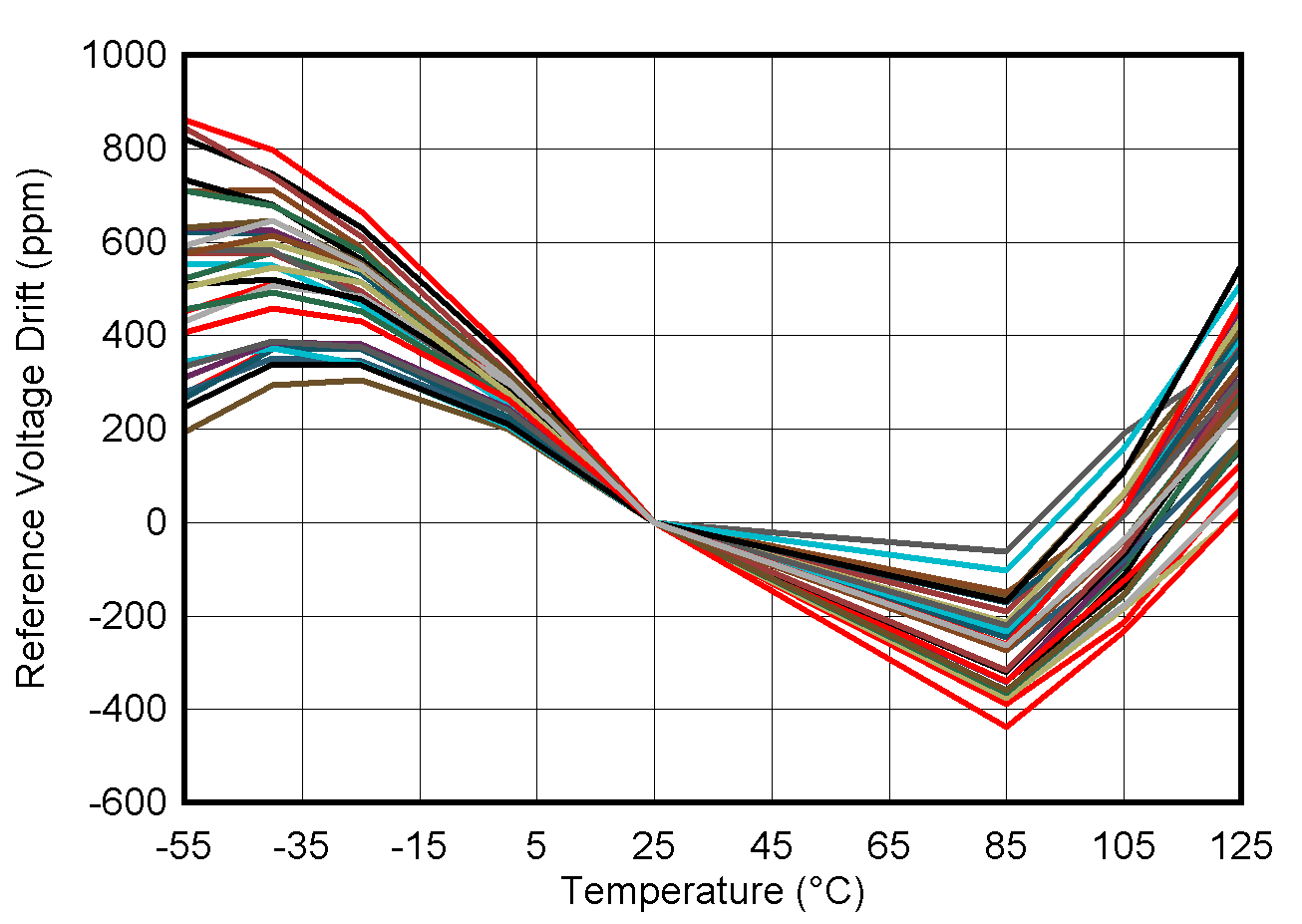
| Pre-soldered | ||
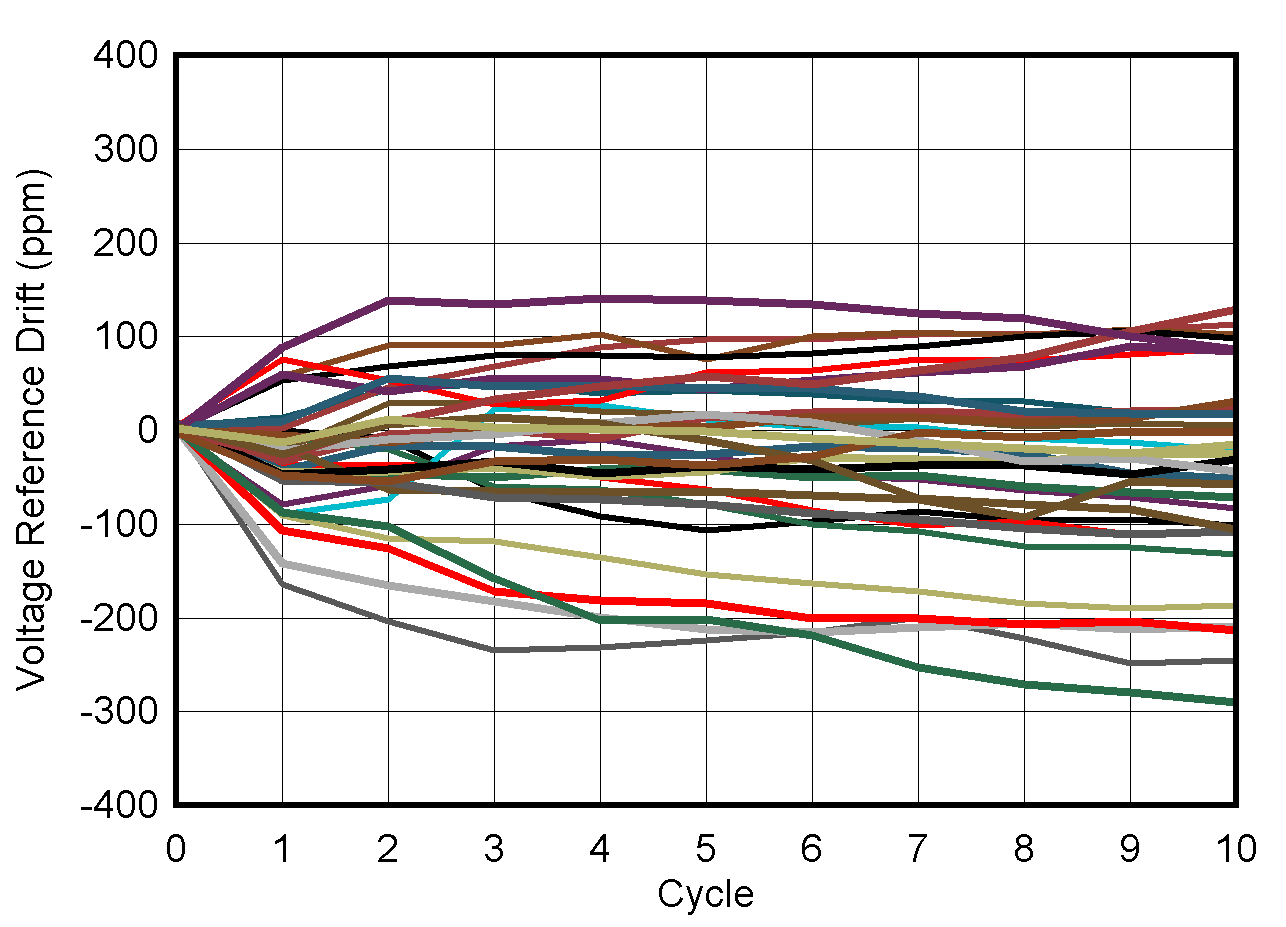
| –40°C to +85°C cycles, 60 minutes per cycle |
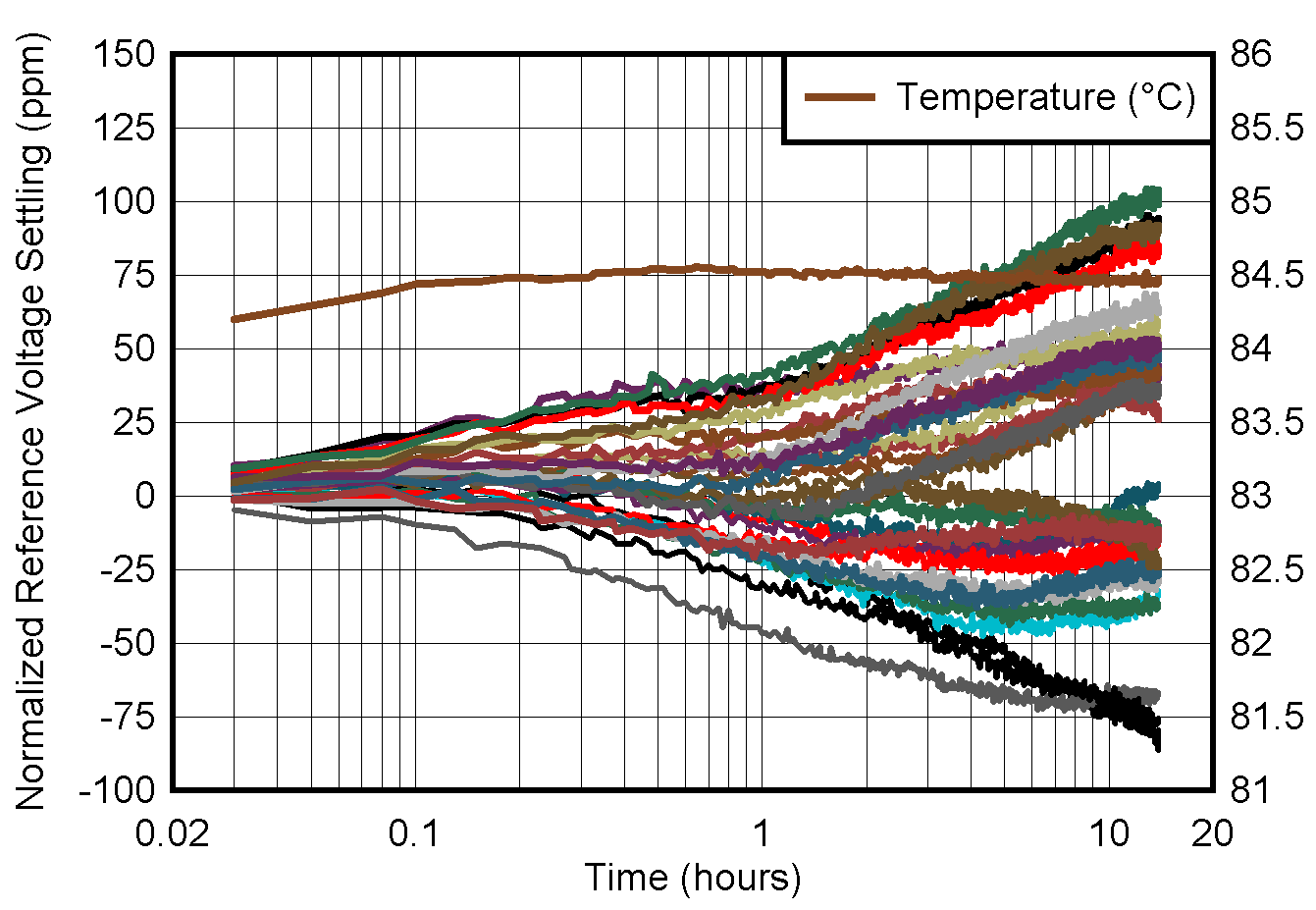
| Two minutes after 25°C to 85°C temperature step |
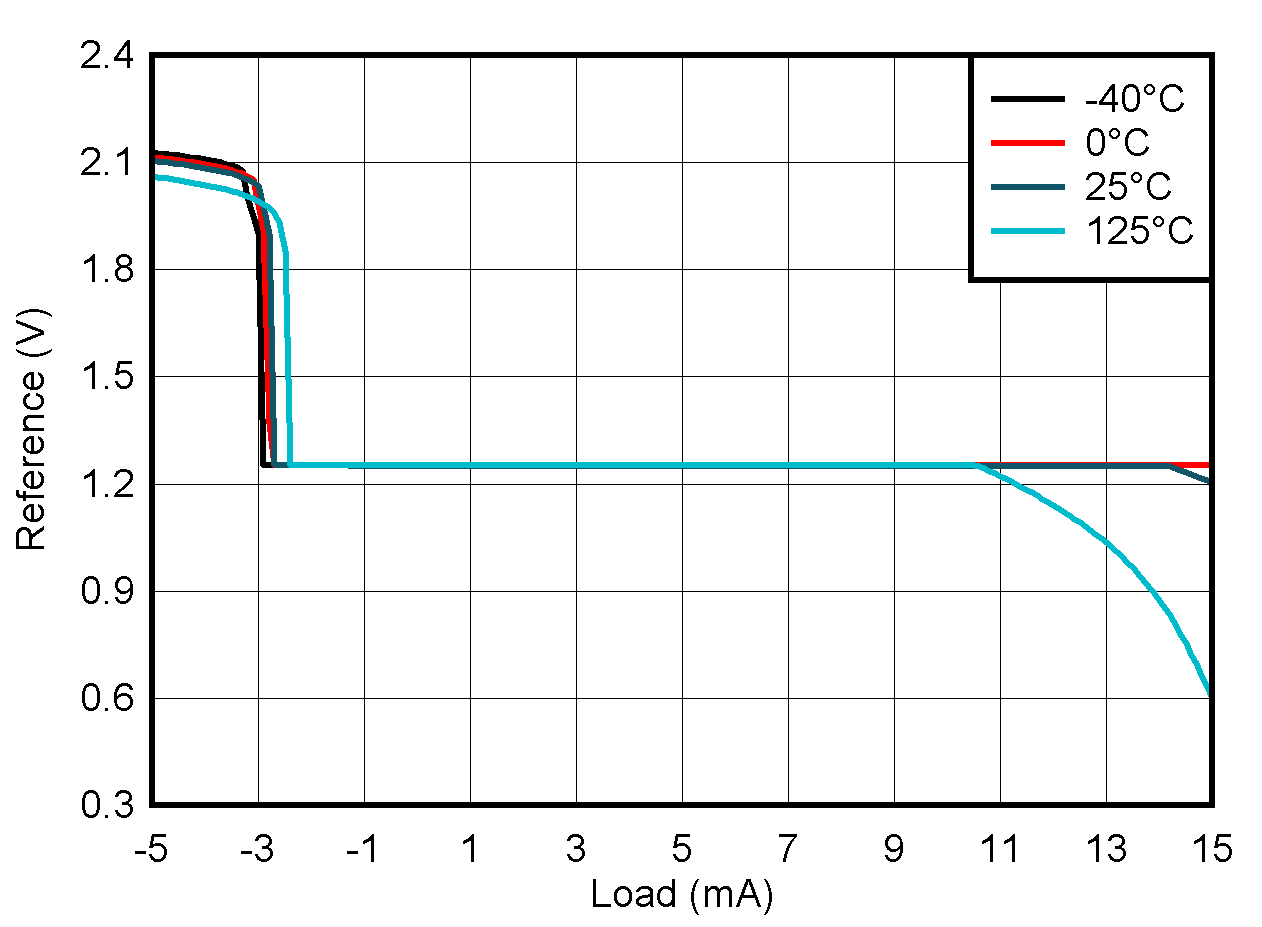
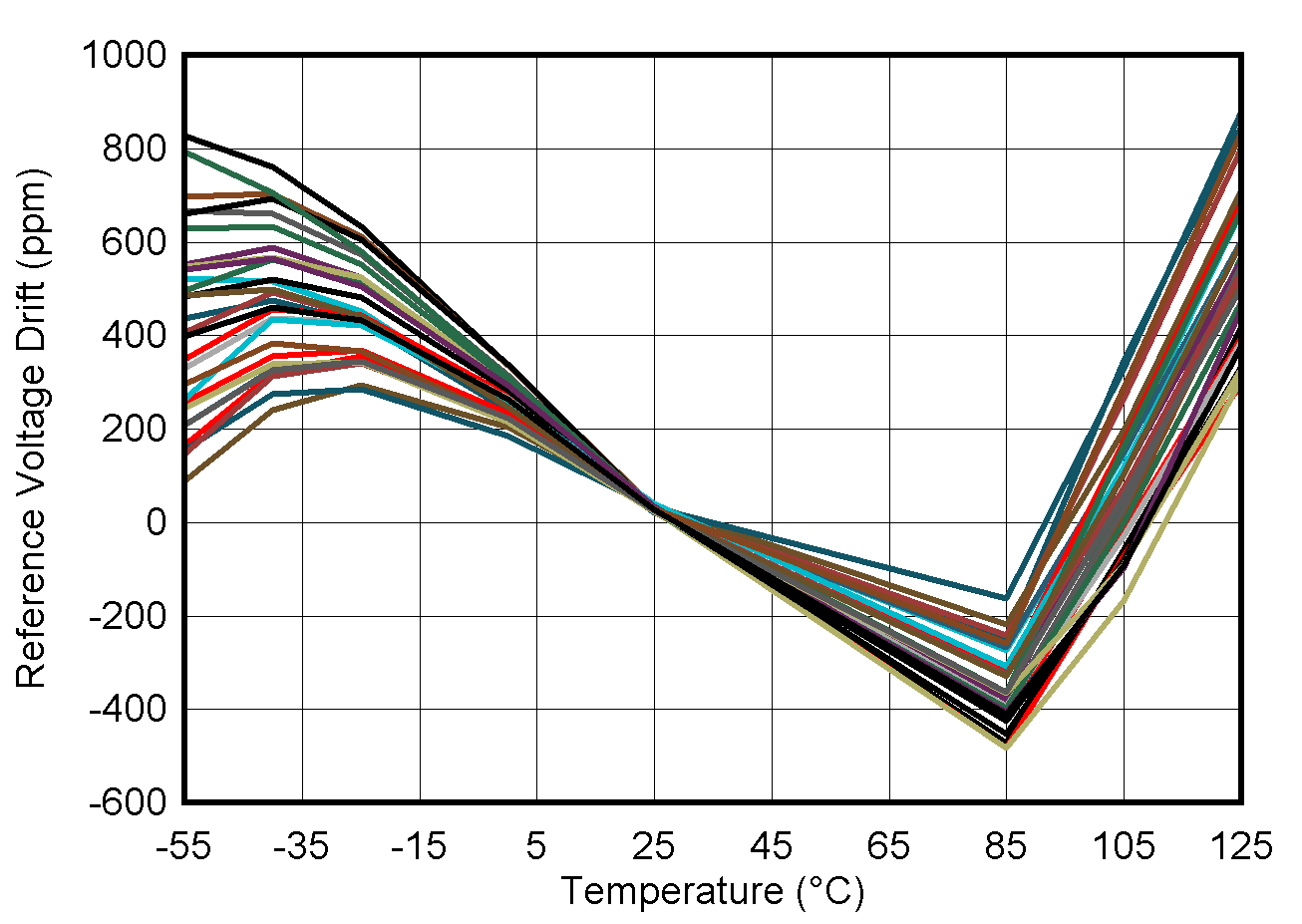
| Post-soldered | ||
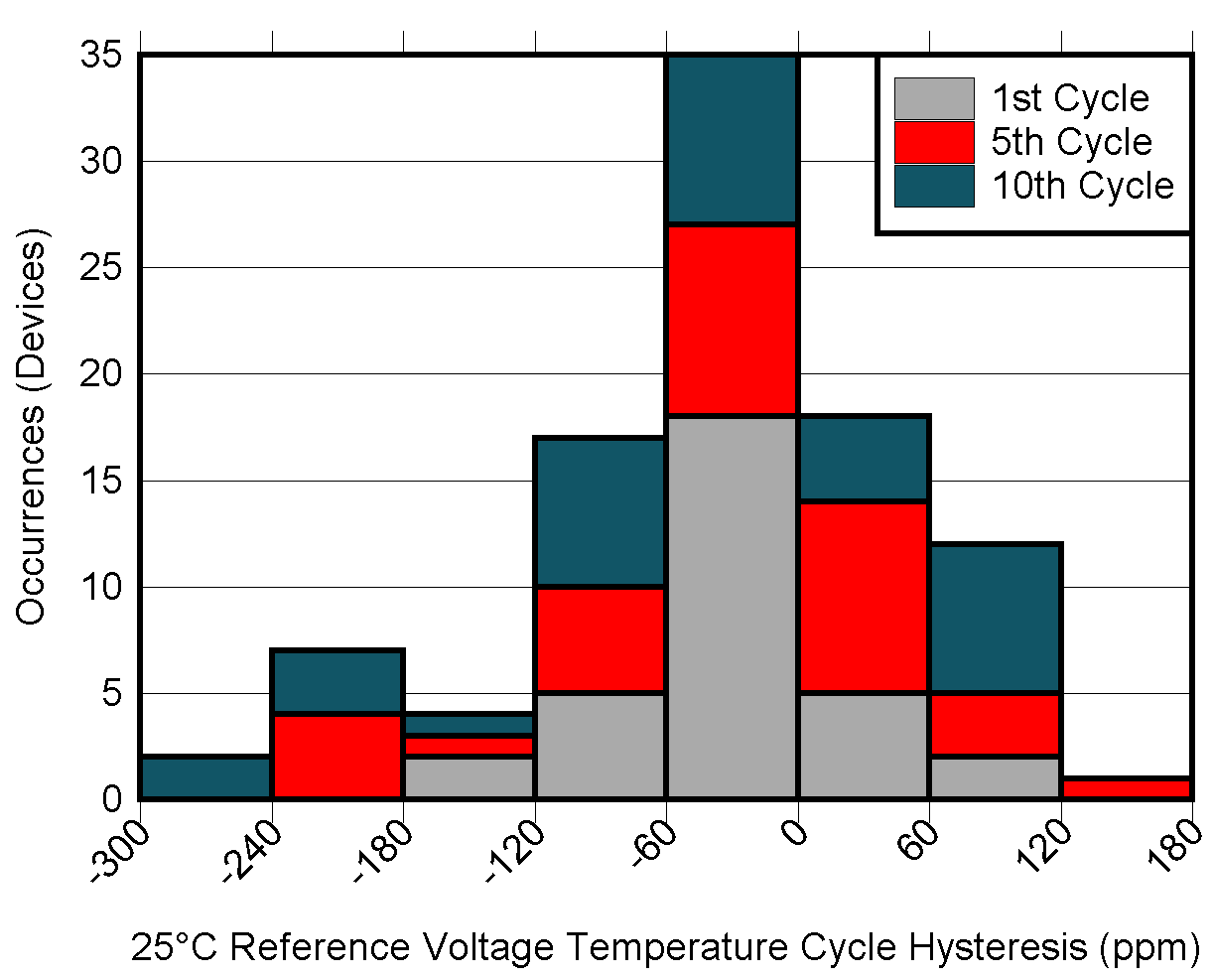
| –40°C to +85°C cycles, 60 minutes per cycle |
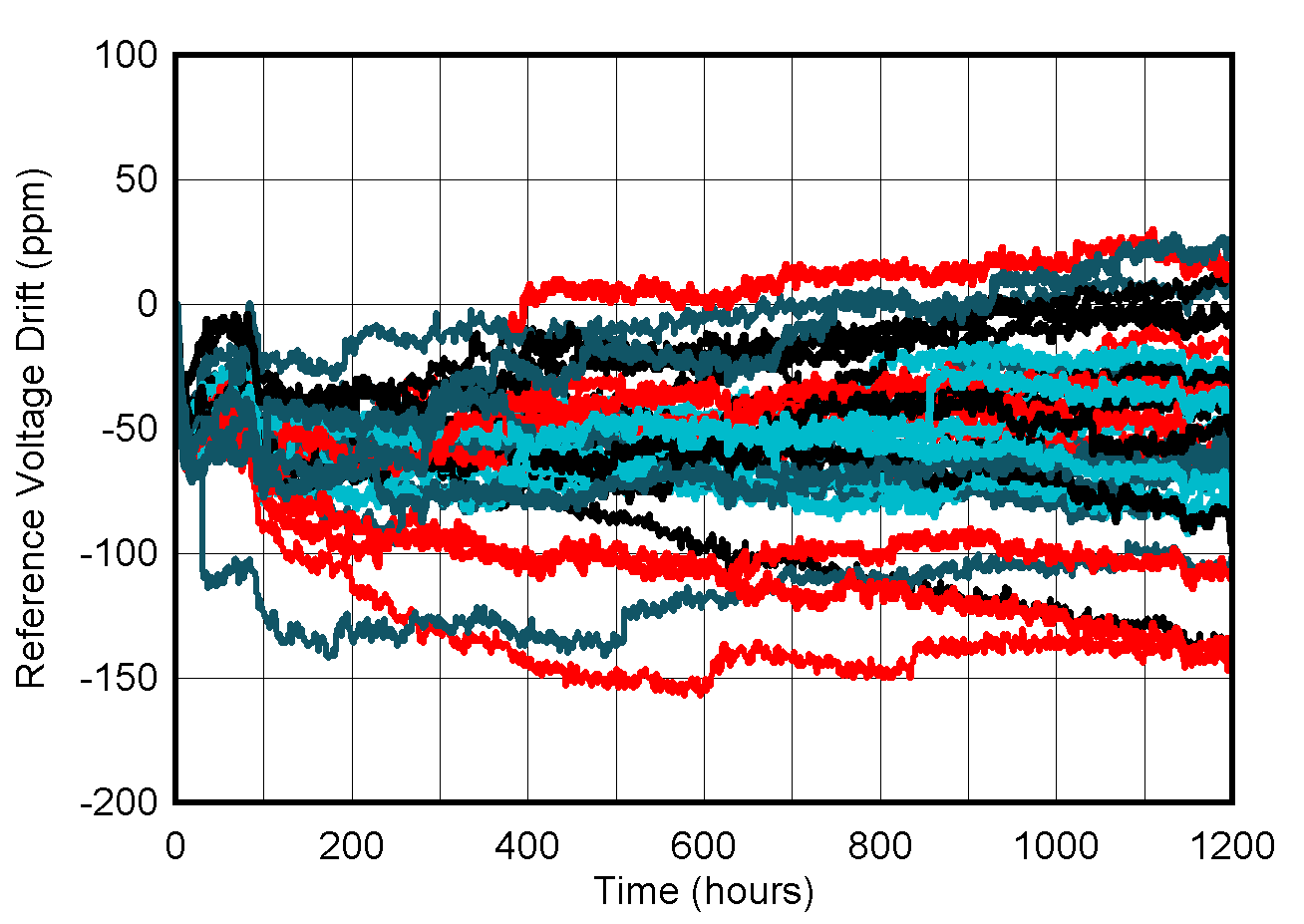
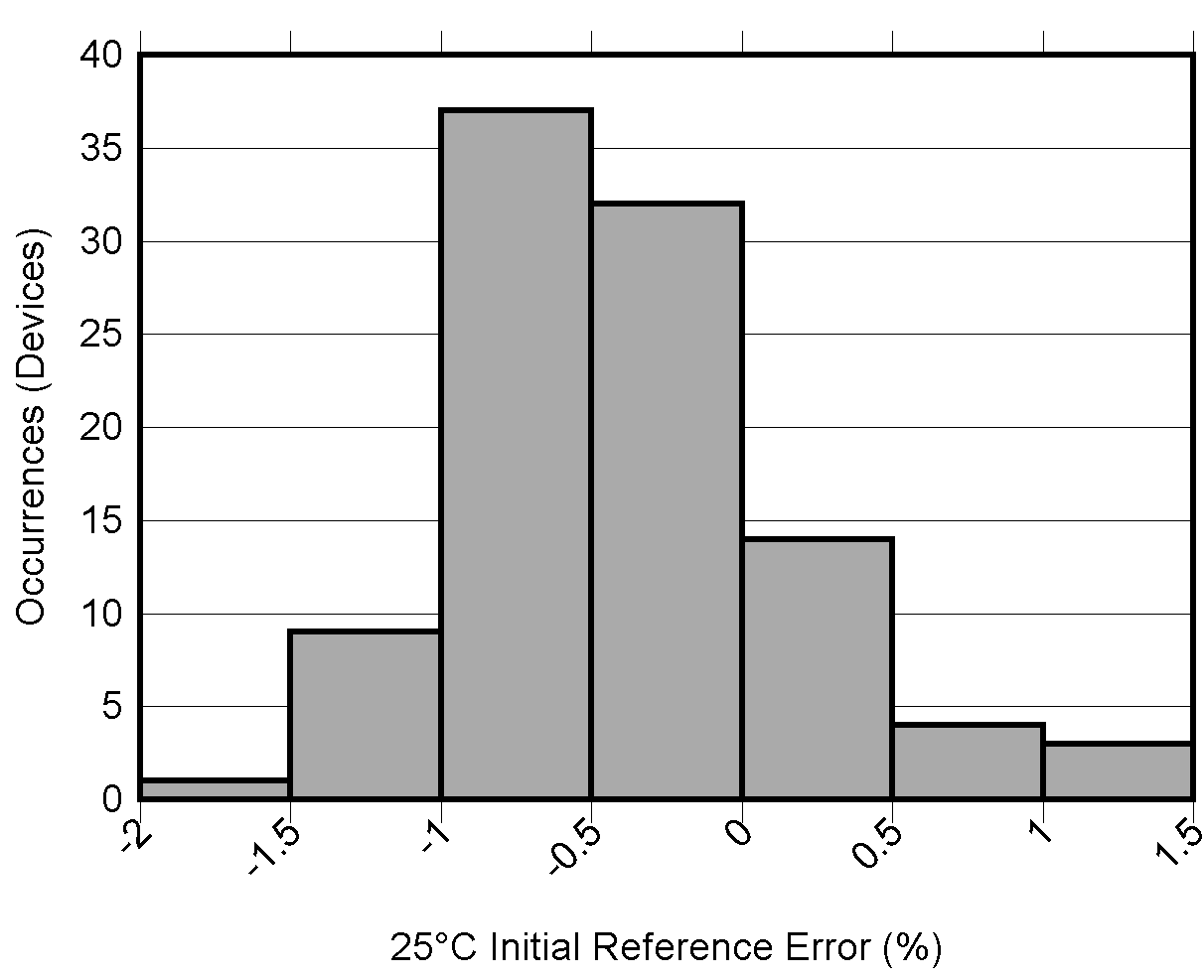 Figure 6-50 Initial Accuracy Distribution
Figure 6-50 Initial Accuracy Distribution