SLASF43 December 2023 AFE782H1 , AFE882H1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Timing Requirements
- 5.7 Timing Diagrams
- 5.8 Typical Characteristics: VOUT DAC
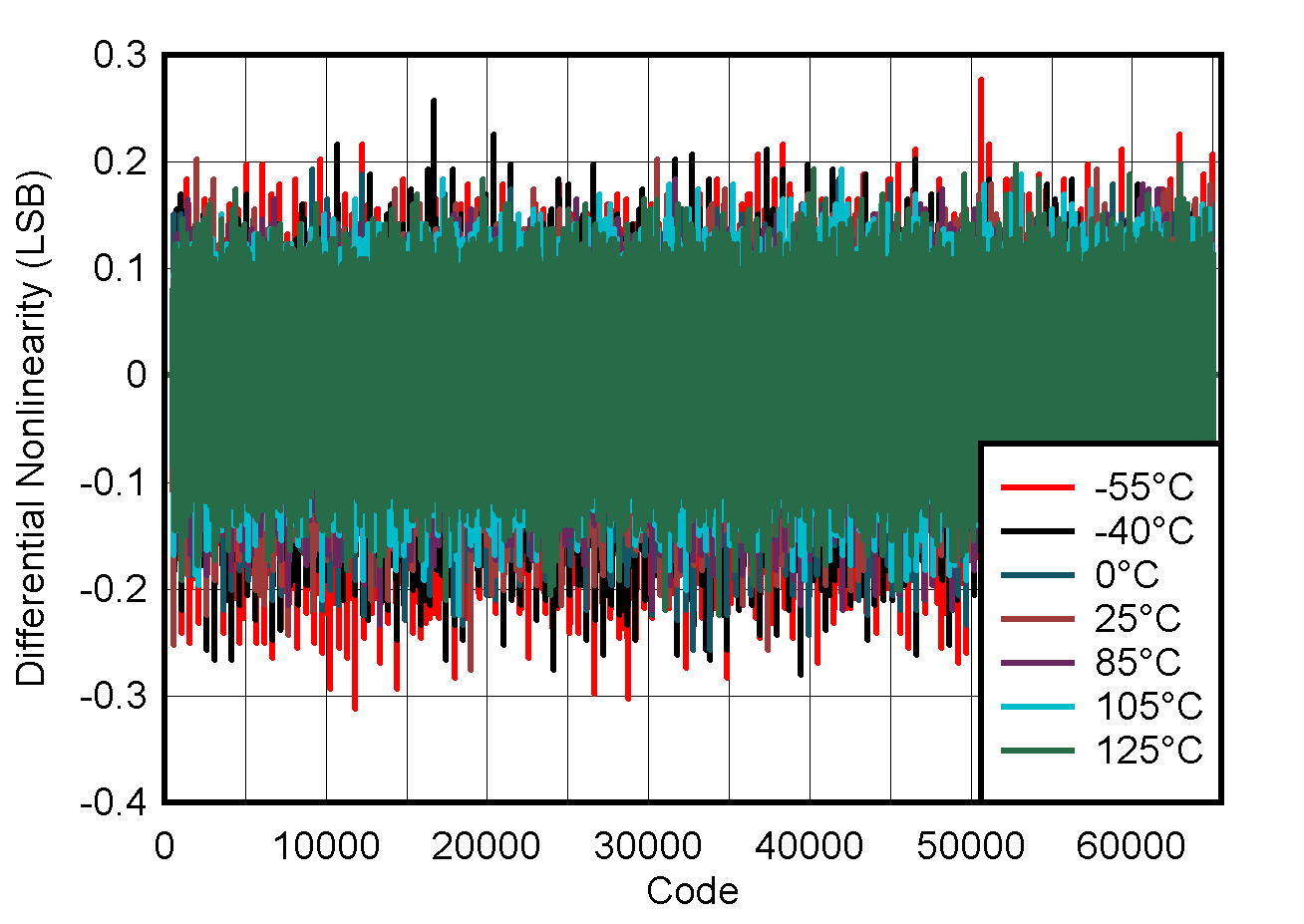
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics: ADC
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics: Reference
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics: HART Modem
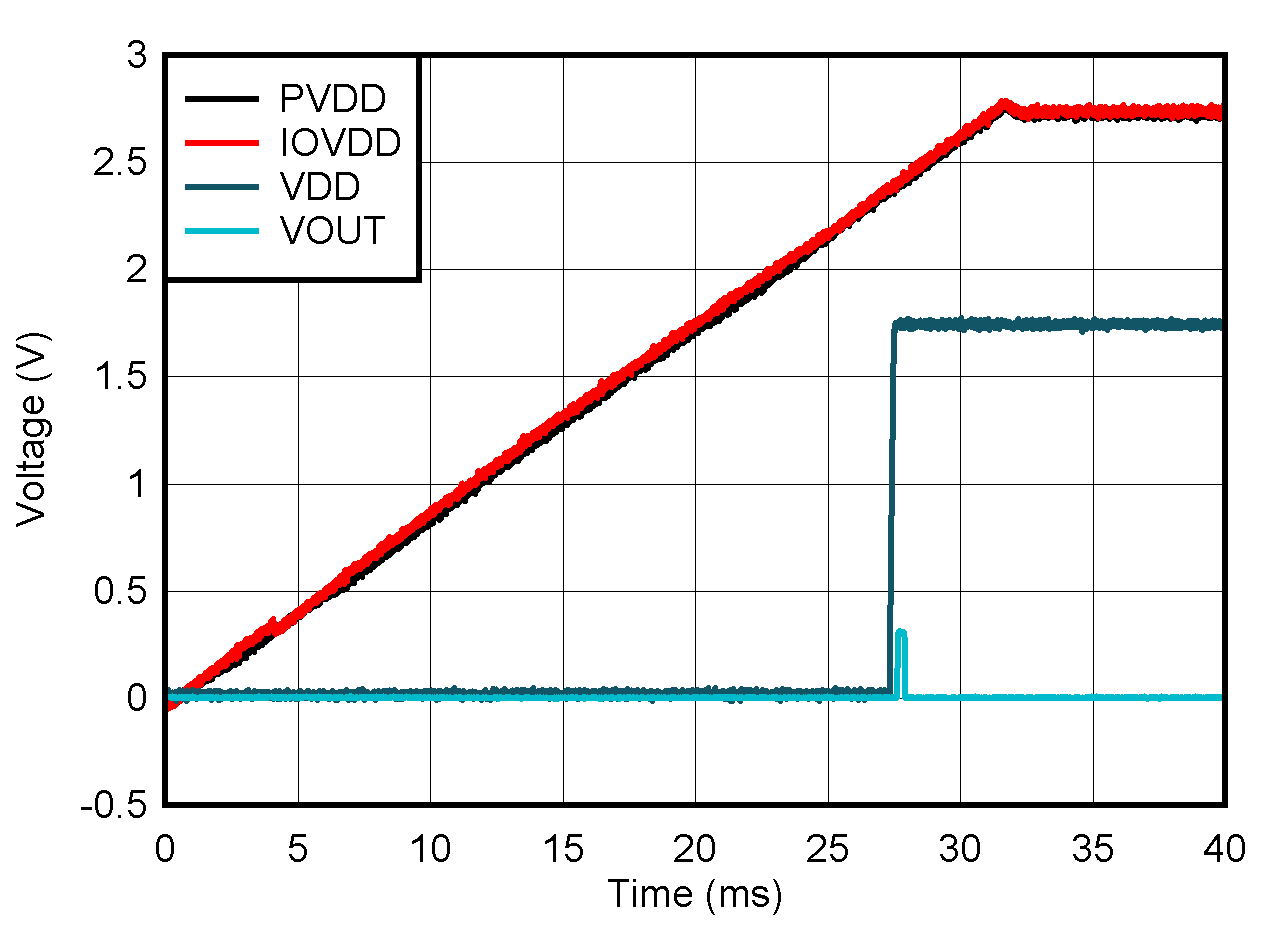
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics: Power Supply
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) Overview
- 6.3.2 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Overview
- 6.3.3 Programmable Out-of-Range Alarms
- 6.3.4 IRQ
- 6.3.5
HART Interface
- 6.3.5.1 FIFO Buffers
- 6.3.5.2 HART Modulator
- 6.3.5.3 HART Demodulator
- 6.3.5.4 HART Modem Modes
- 6.3.5.5 HART Modulation and Demodulation Arbitration
- 6.3.5.6 HART Modulator Timing and Preamble Requirements
- 6.3.5.7 HART Demodulator Timing and Preamble Requirements
- 6.3.5.8 IRQ Configuration for HART Communication
- 6.3.5.9 HART Communication Using the SPI
- 6.3.5.10 HART Communication Using UART
- 6.3.5.11 Memory Built-In Self-Test (MBIST)
- 6.3.6 Internal Reference
- 6.3.7 Integrated Precision Oscillator
- 6.3.8 Precision Oscillator Diagnostics
- 6.3.9 One-Time Programmable (OTP) Memory
- 6.3.10 GPIO
- 6.3.11 Timer
- 6.3.12 Unique Chip Identifier (ID)
- 6.3.13 Scratch Pad Register
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 7 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RRU|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
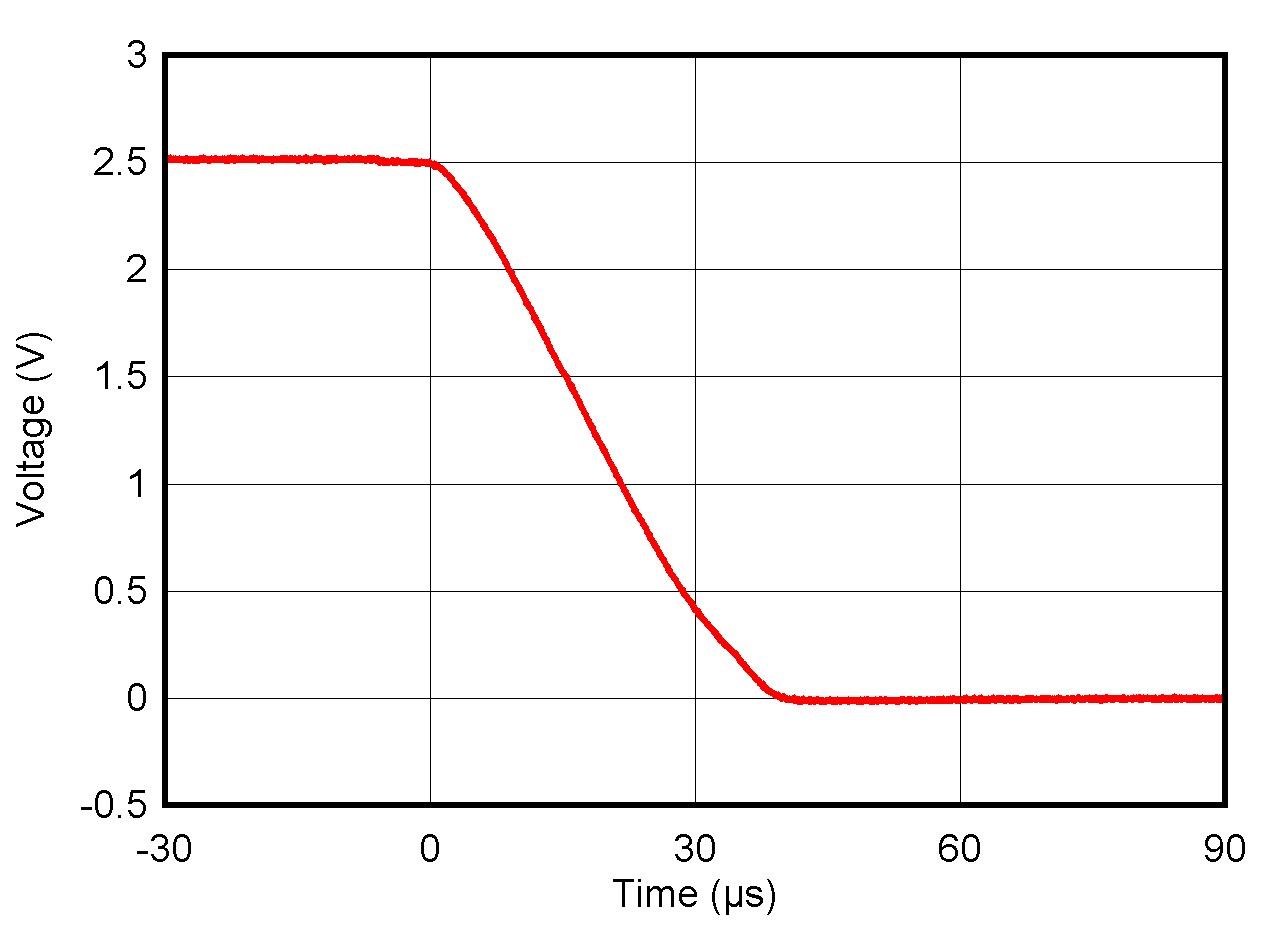
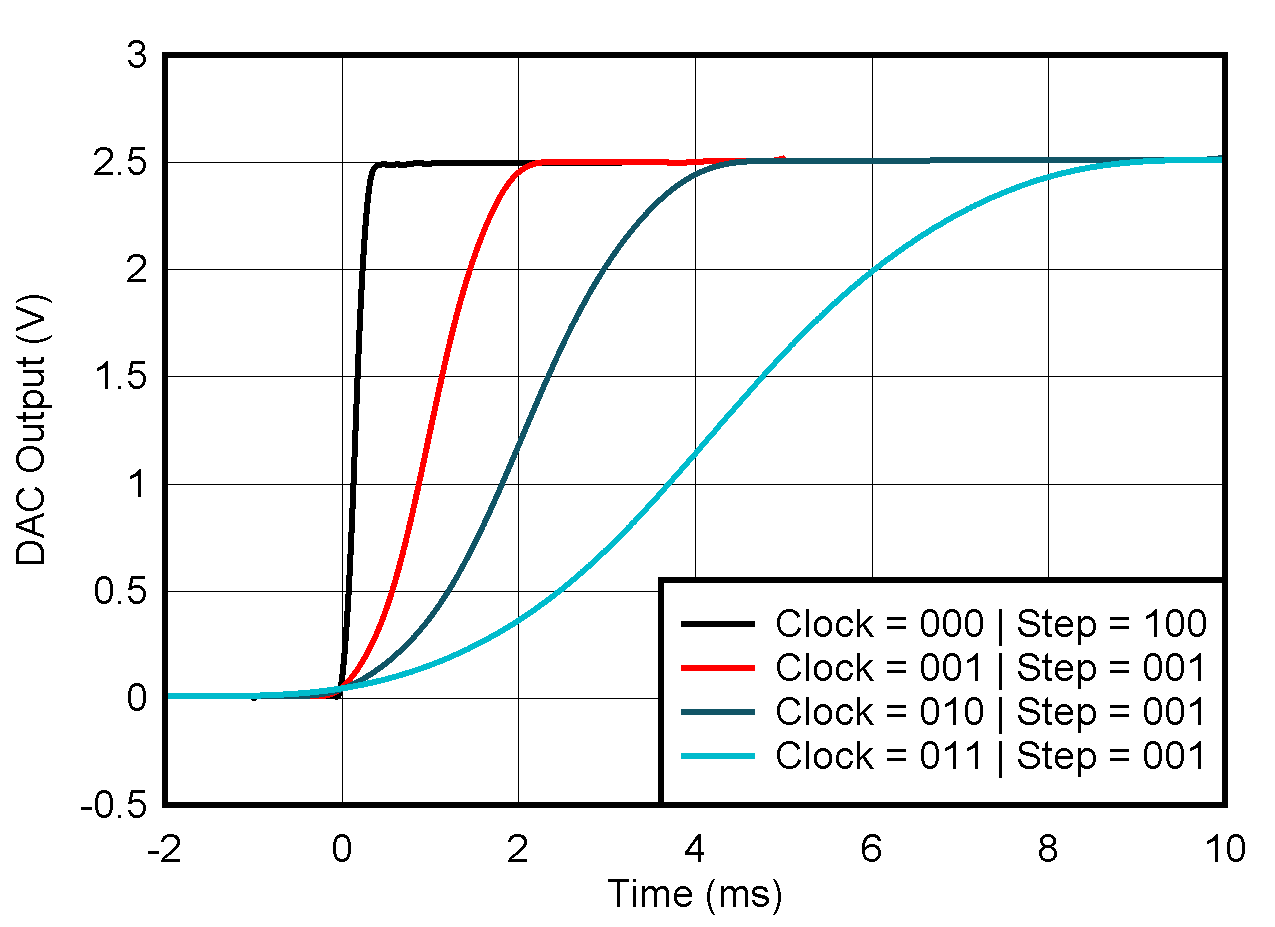
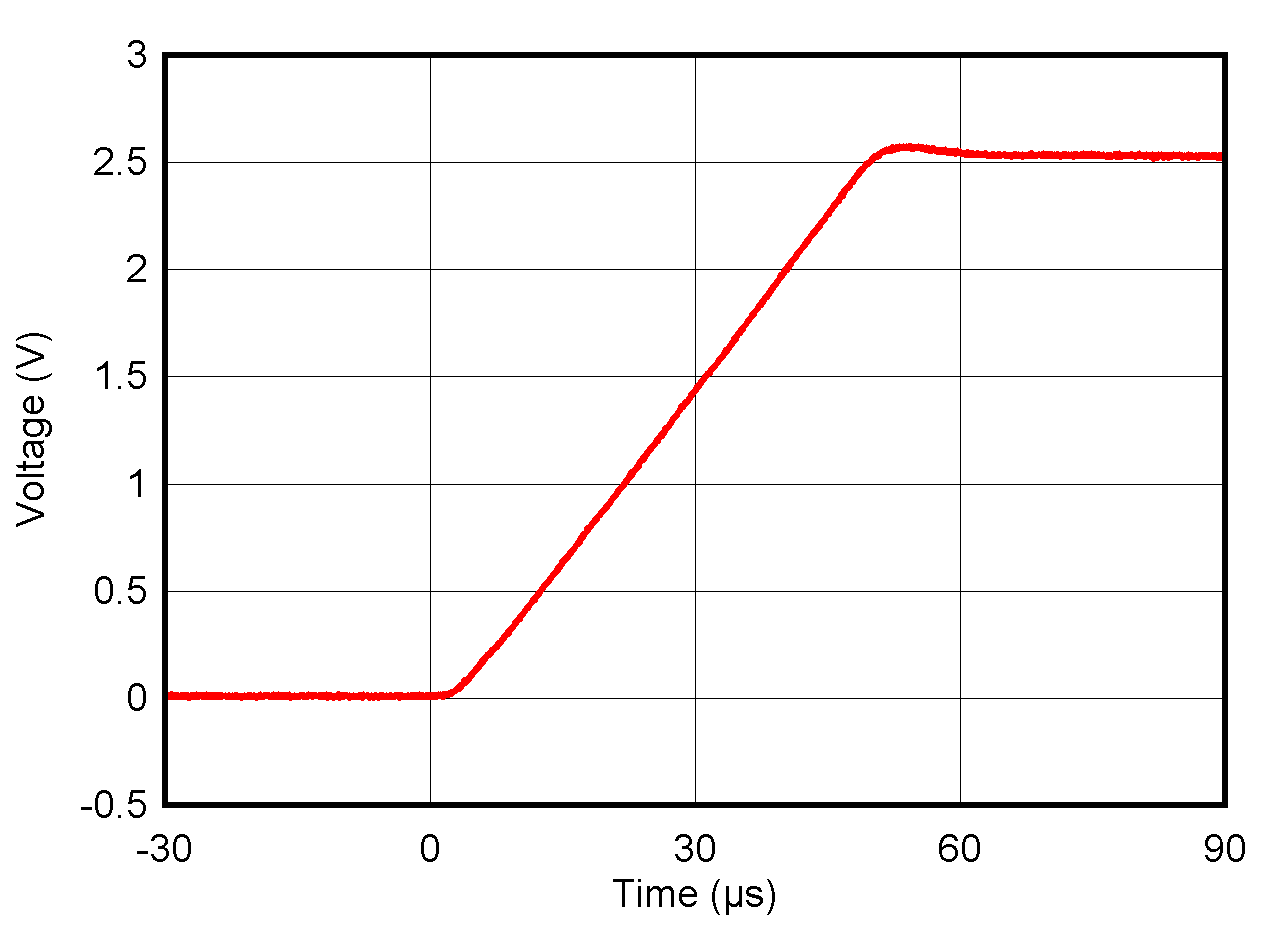
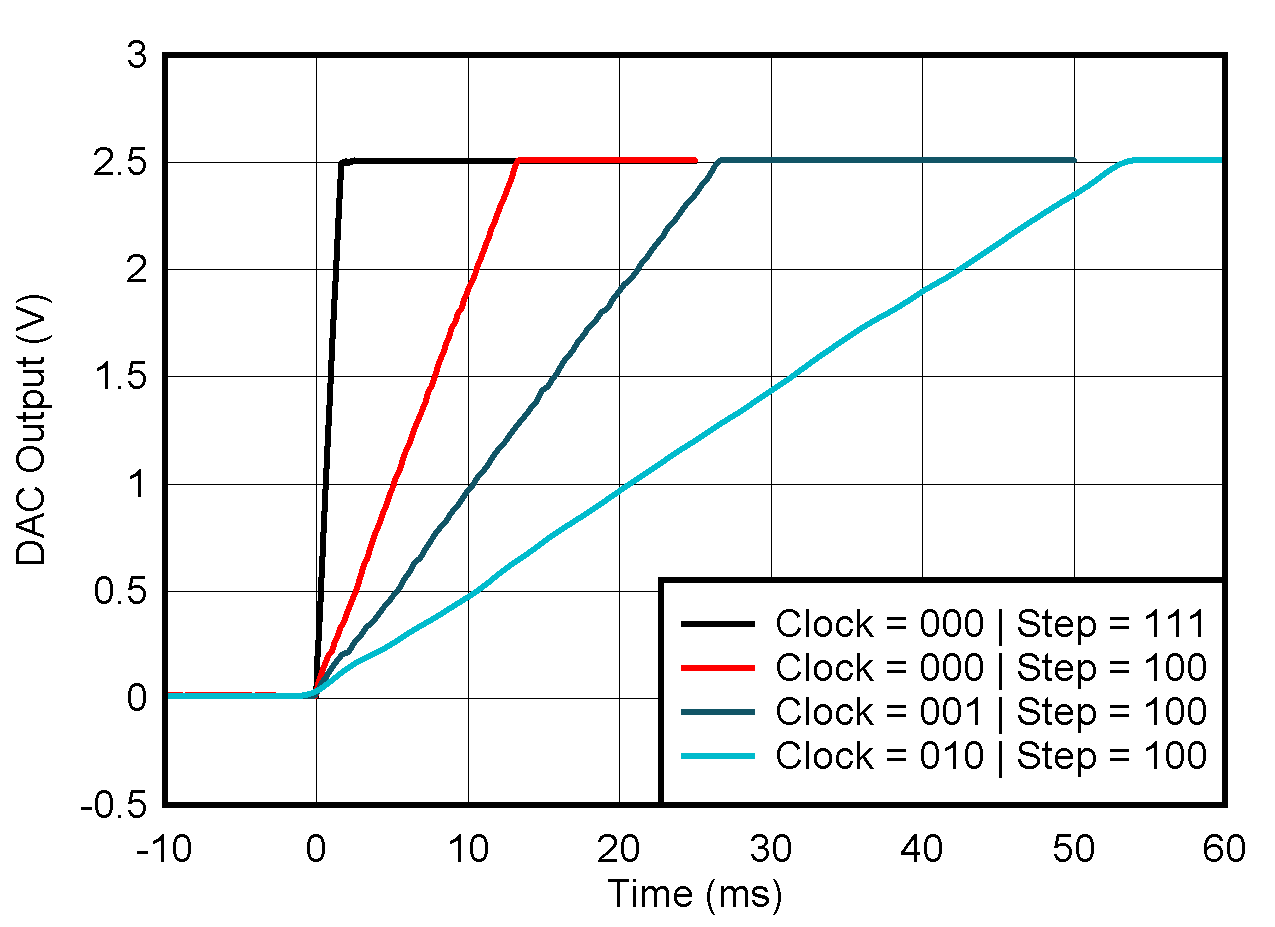
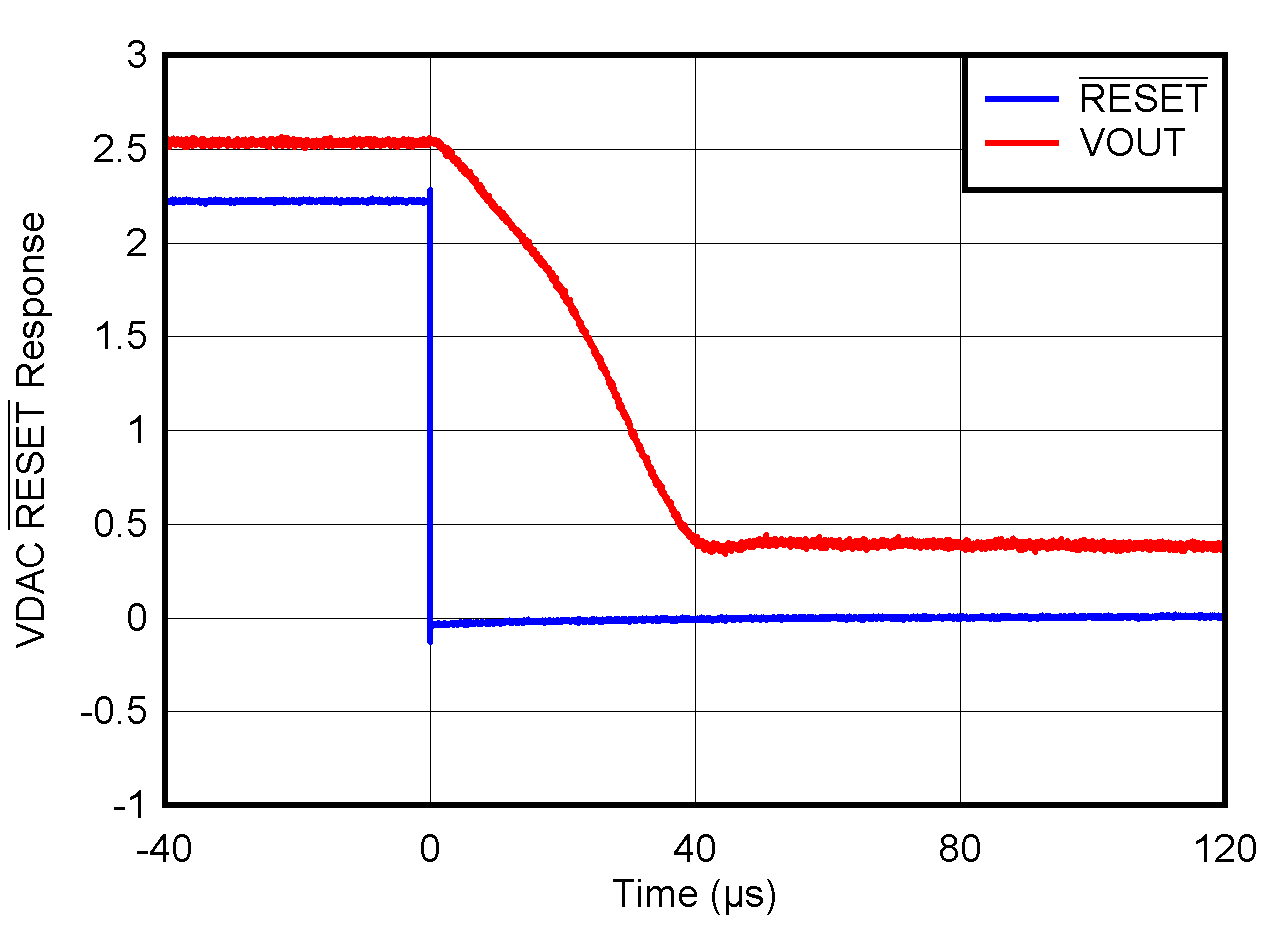
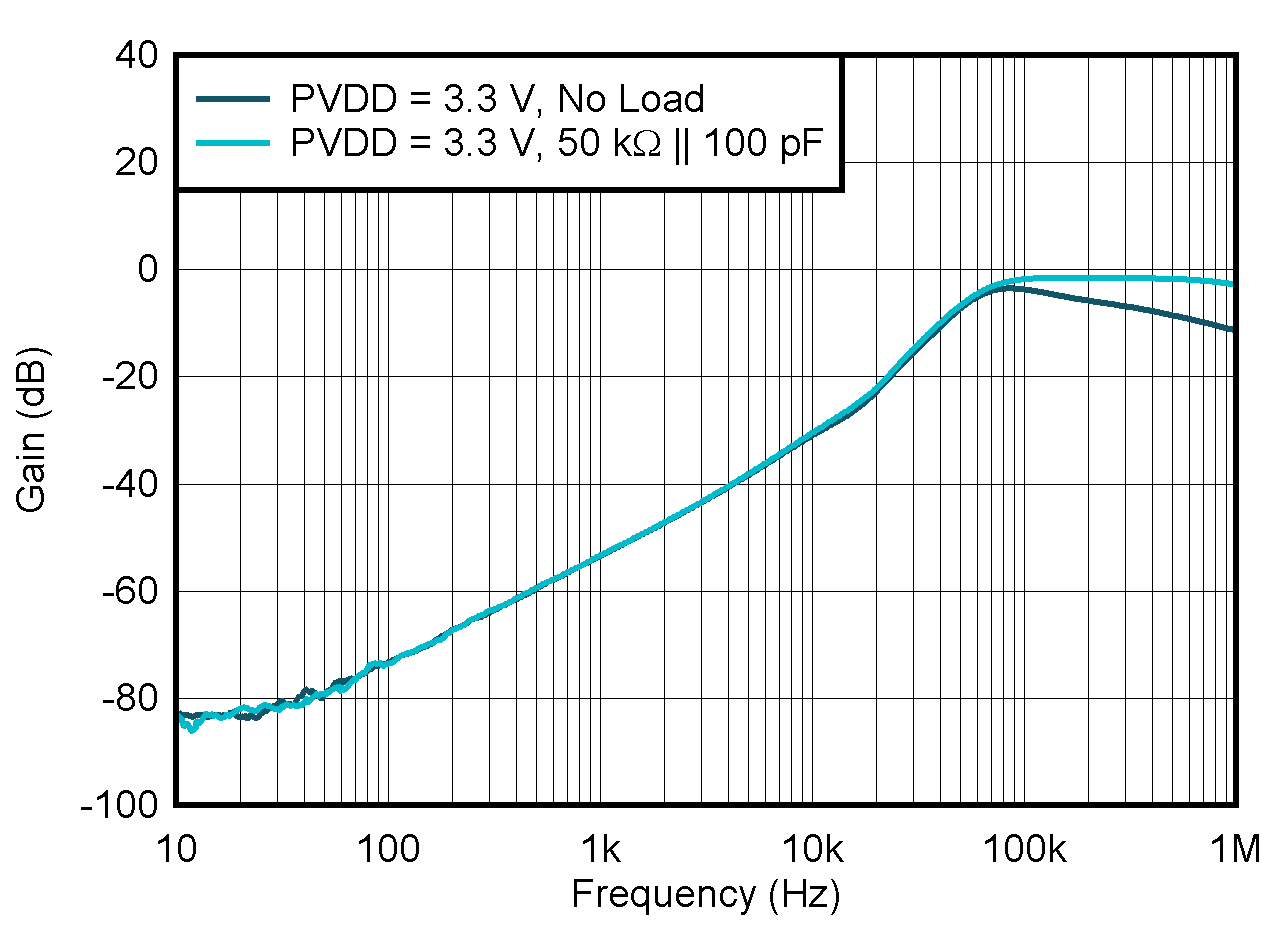
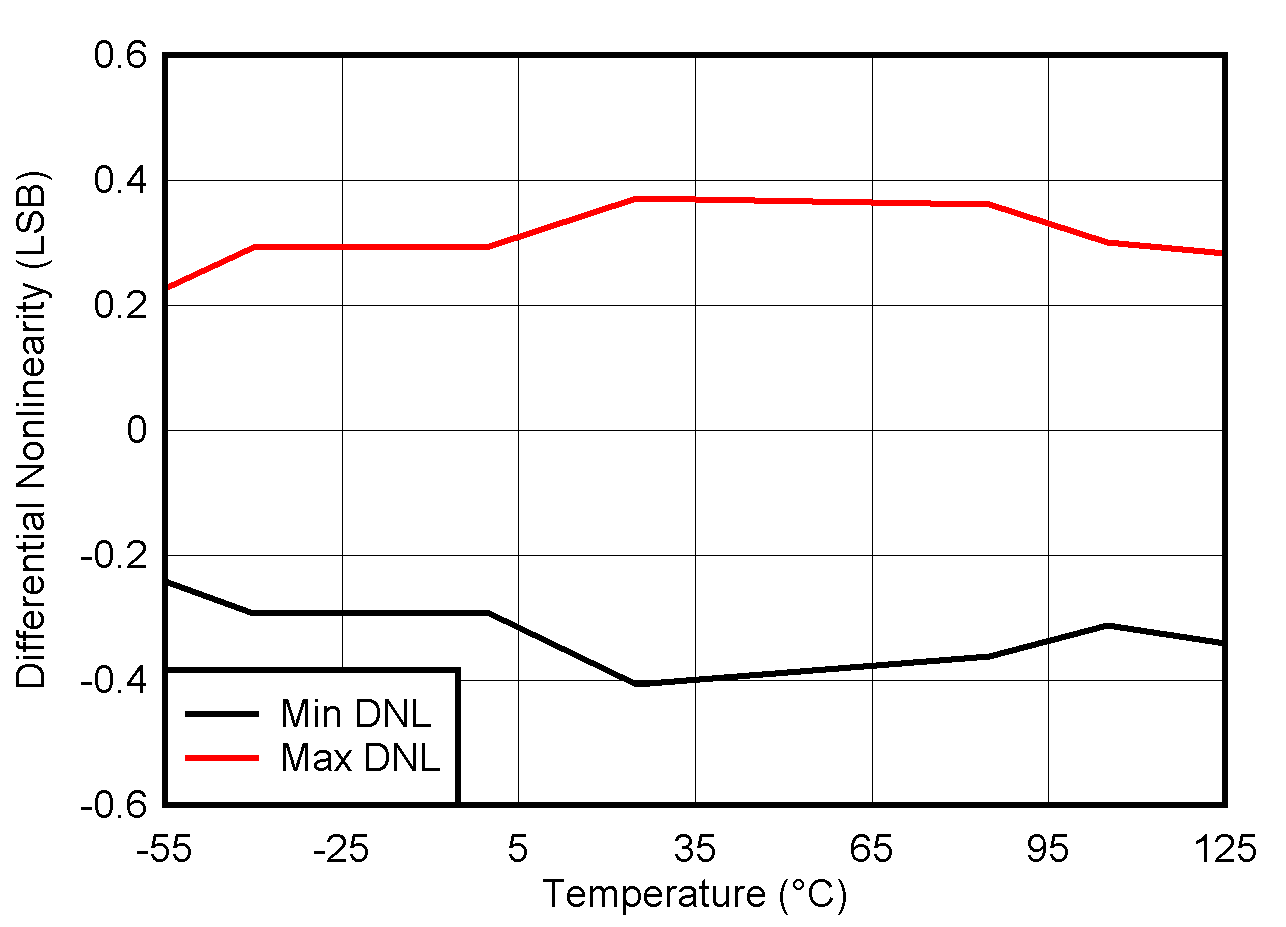
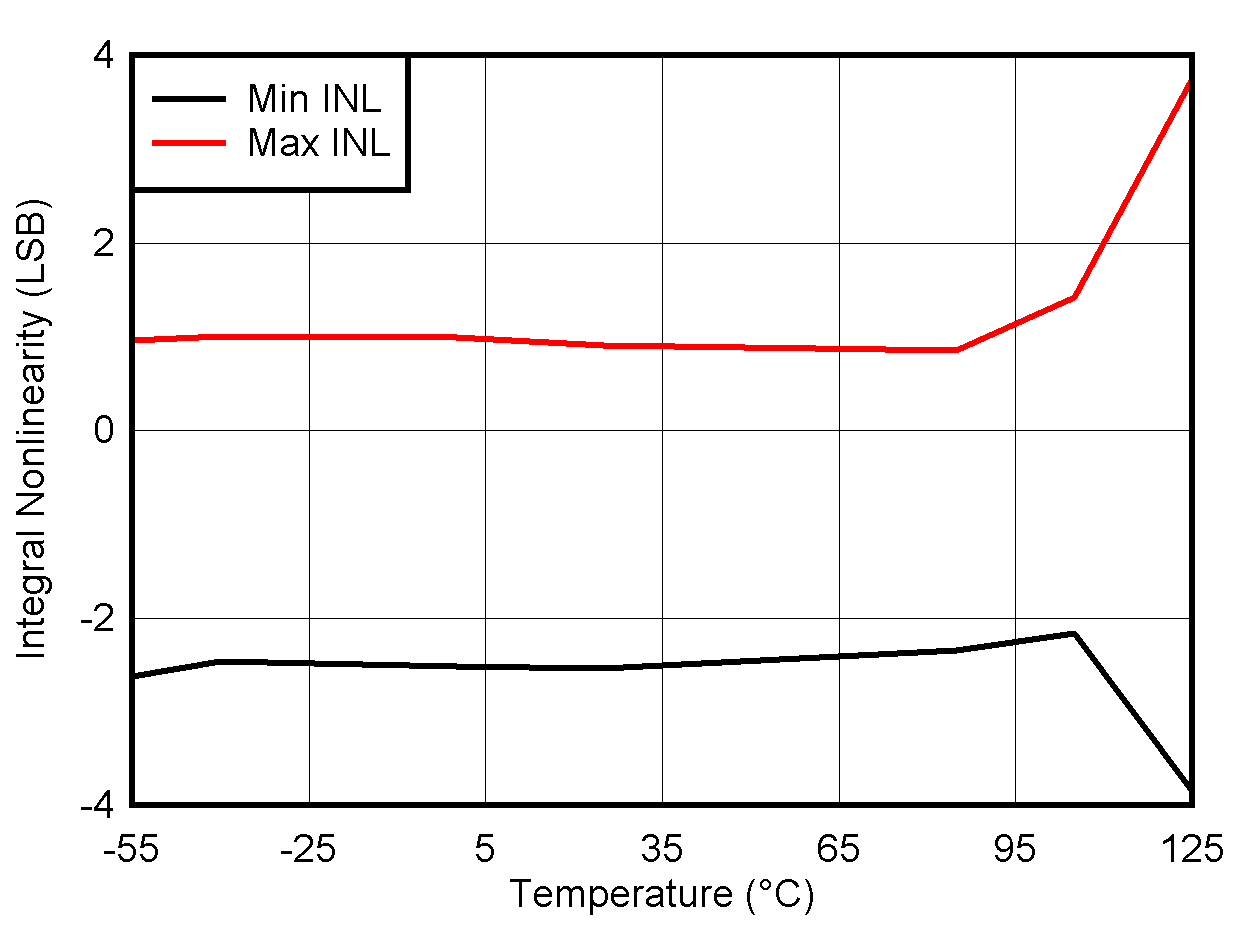
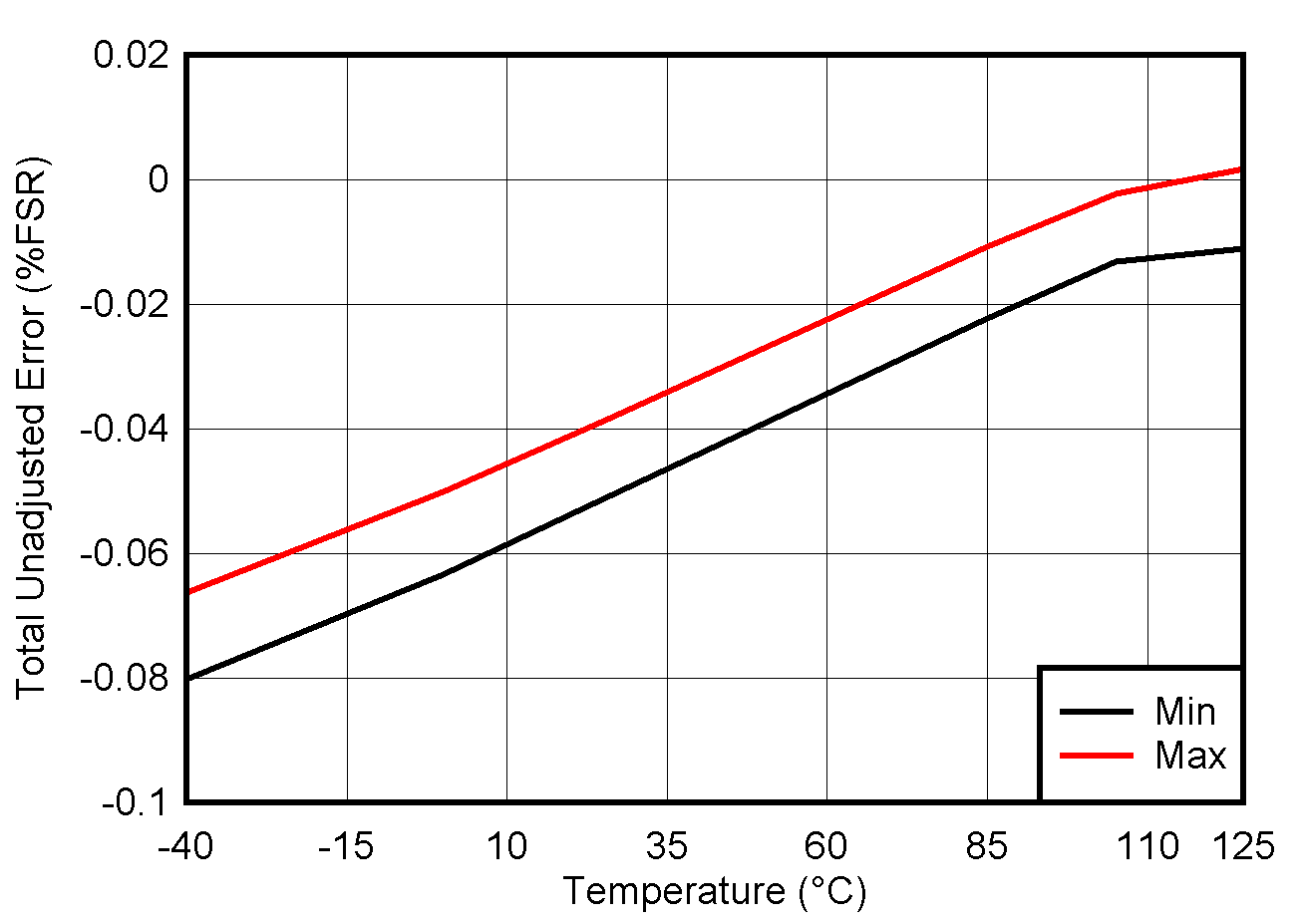
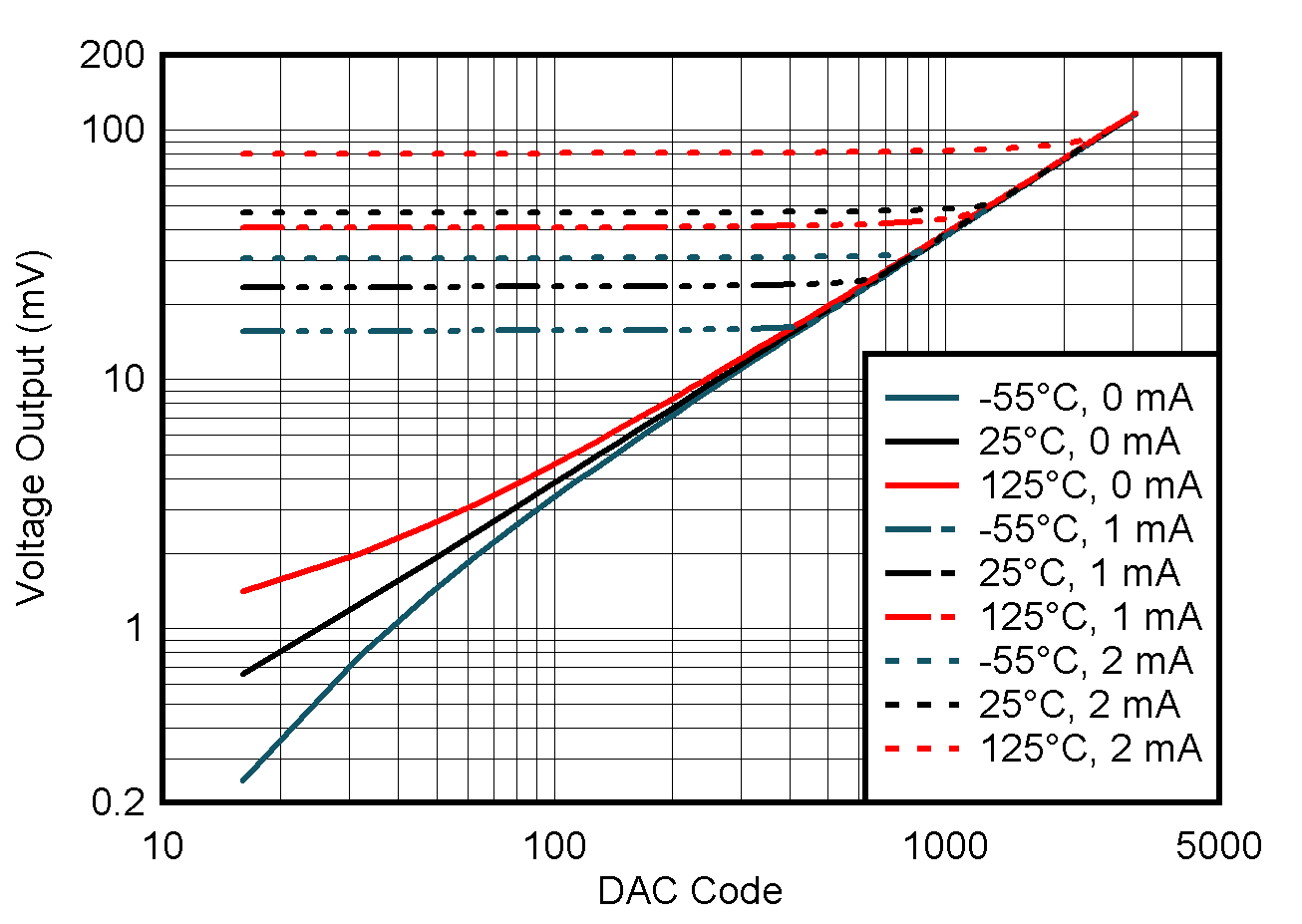
5.8 Typical Characteristics: VOUT DAC
at TA = 25°C, PVDD = 2.7 V, IOVDD = 1.8 V, external or internal VREFIO = 1.25 V, RLOAD = 50 kΩ to GND, CLOAD = 100 pF to GND, and digital inputs at IOVDD or GND (unless otherwise noted)
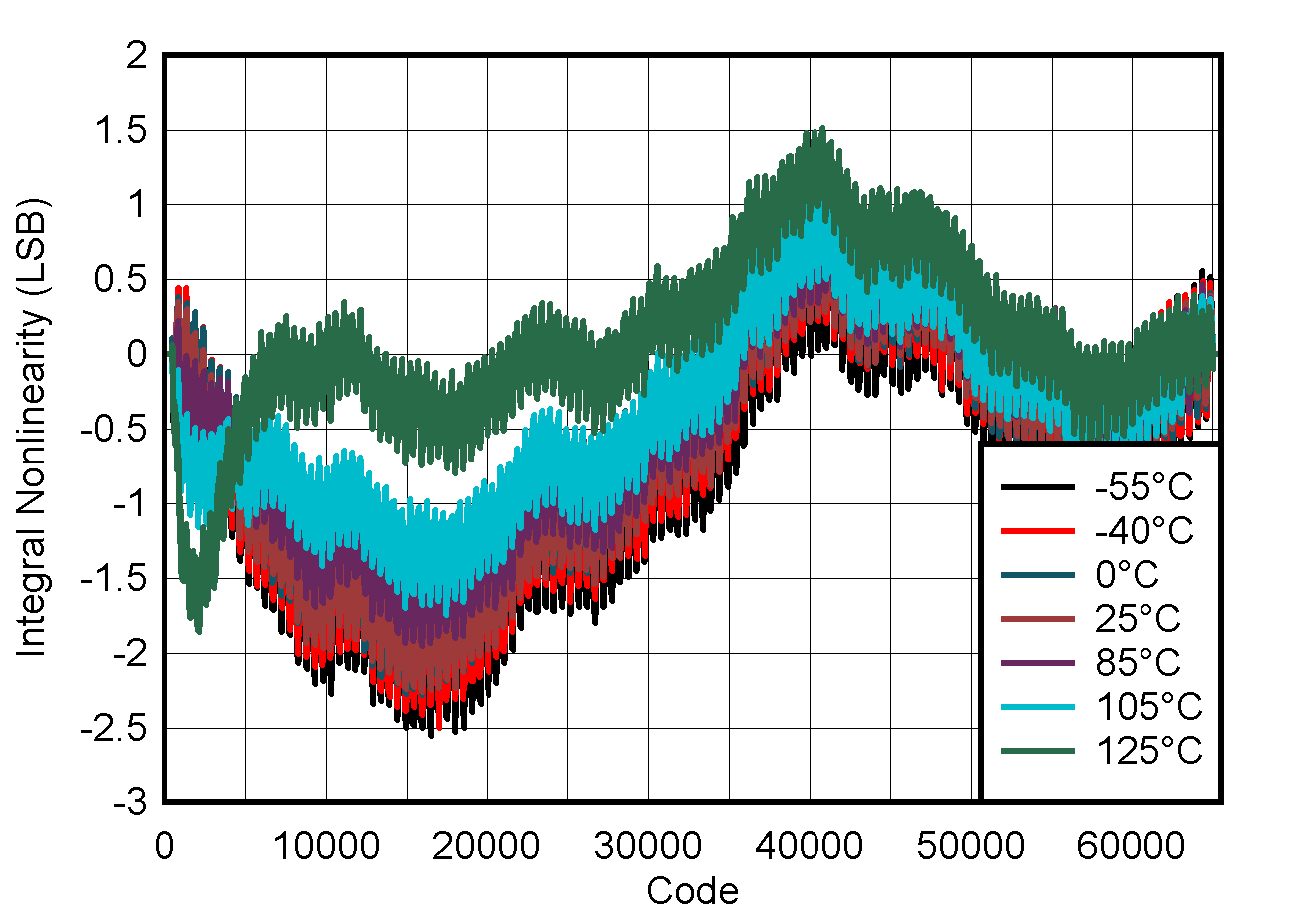
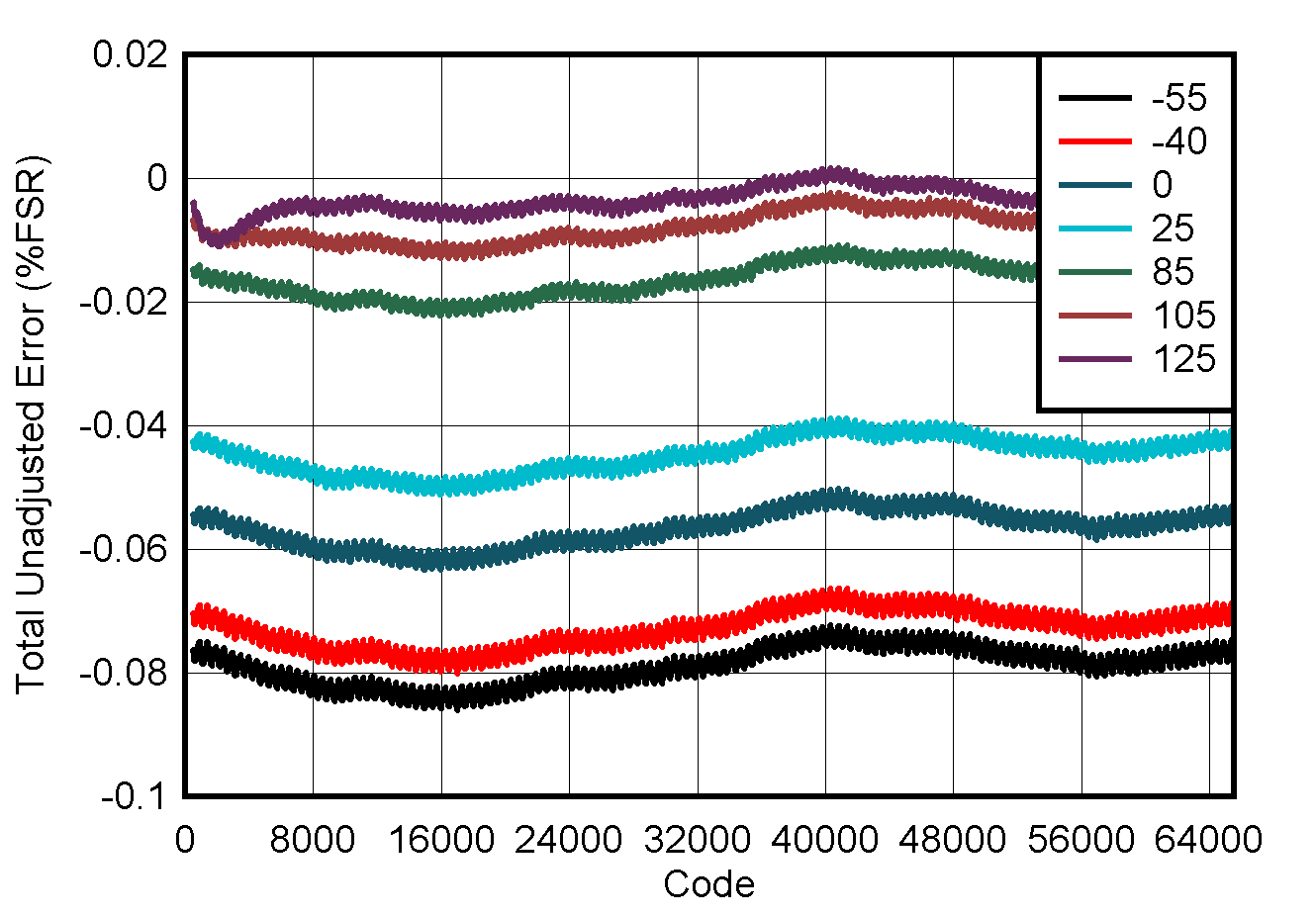
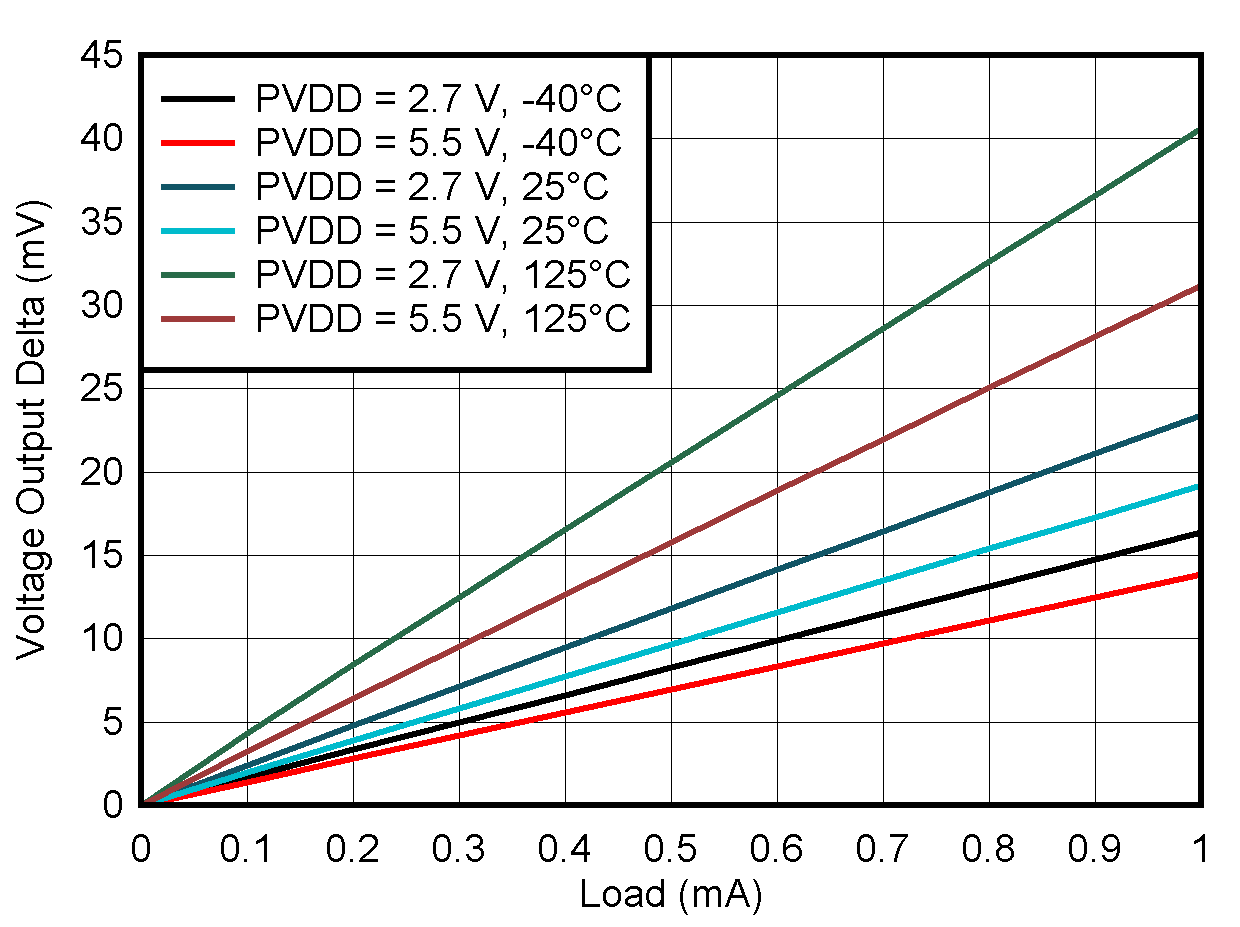
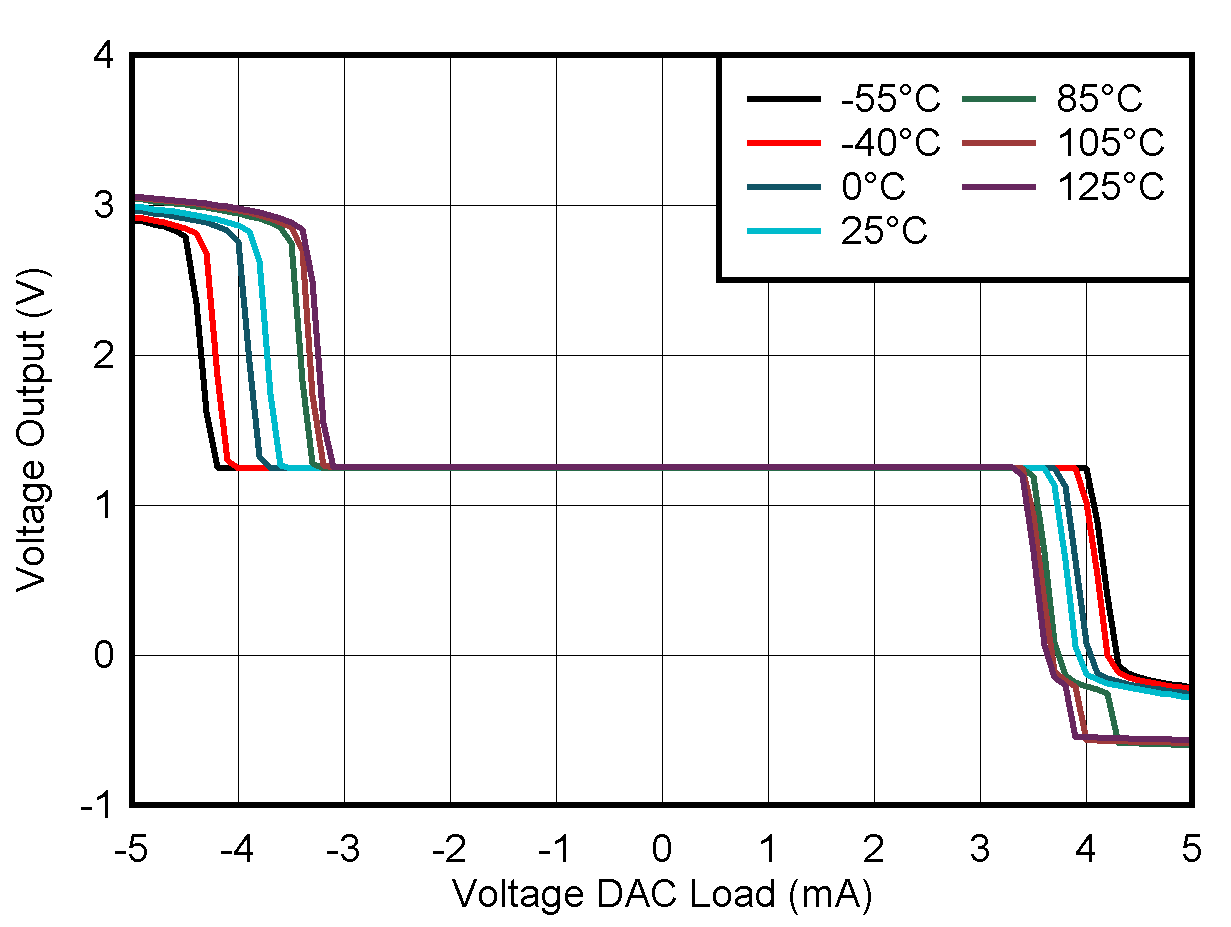
| DAC at midcode | ||
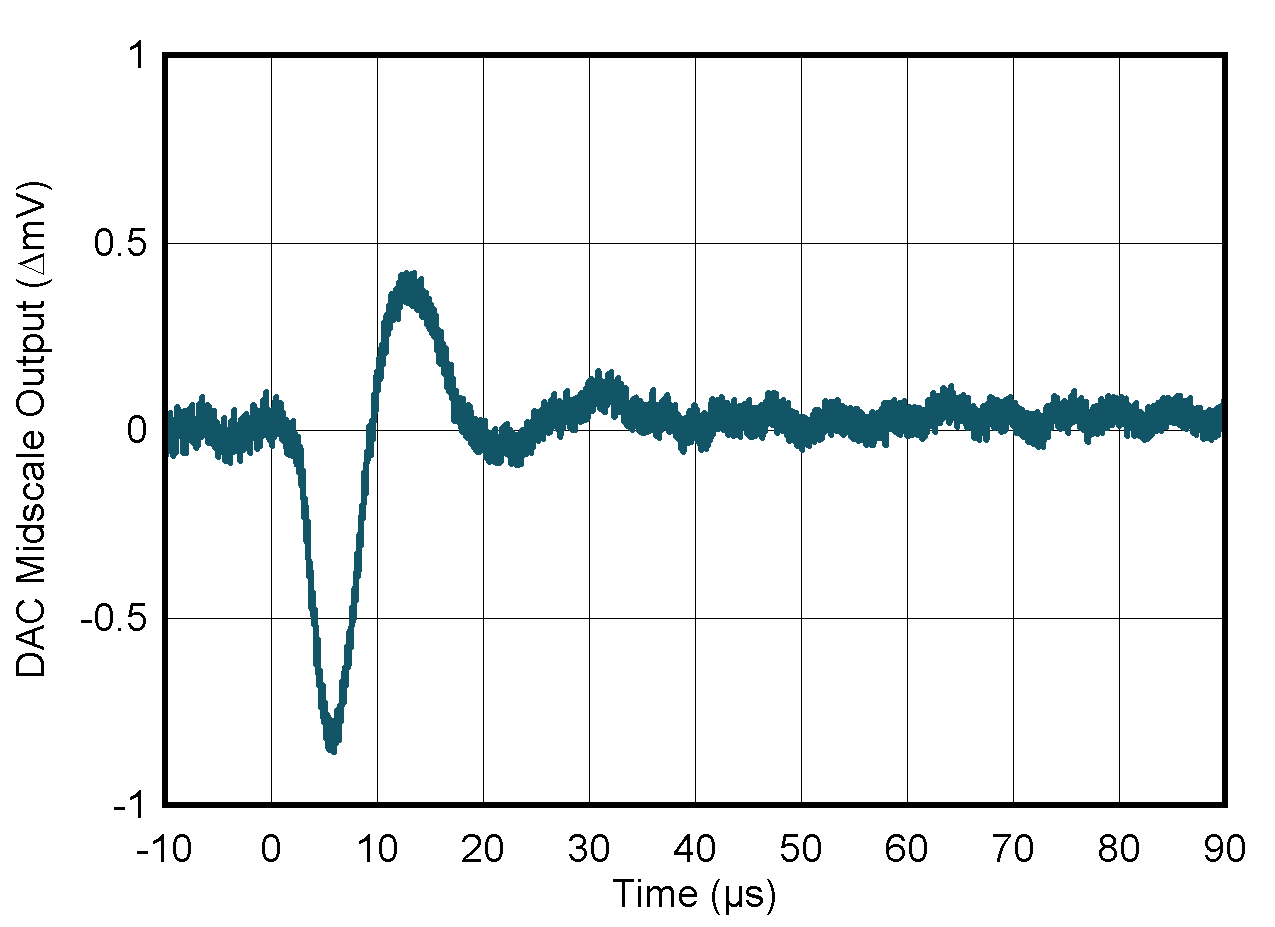
| PVDD = 5.5 V | ||
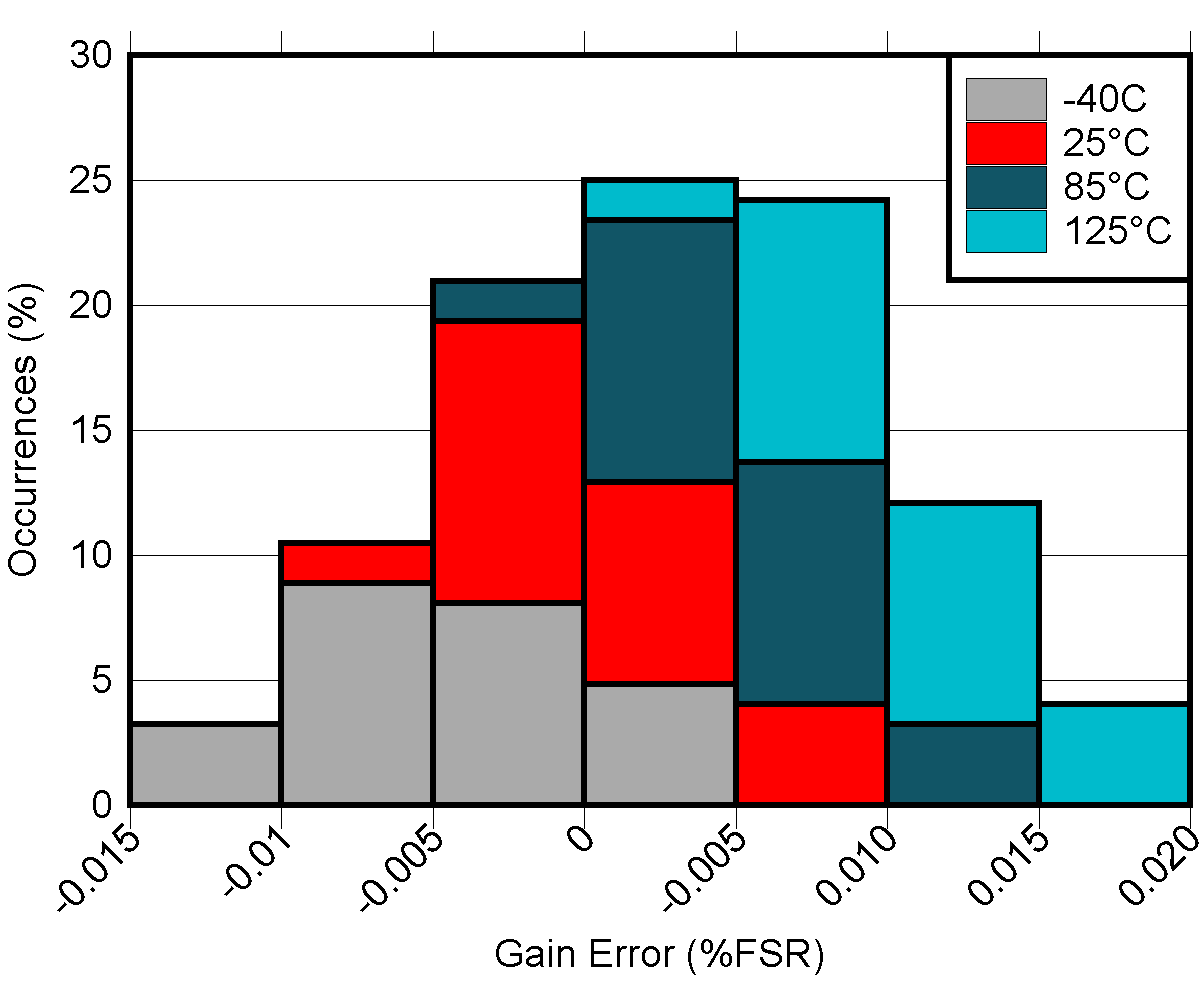 Figure 5-15 DAC
Gain Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-15 DAC
Gain Error vs Temperature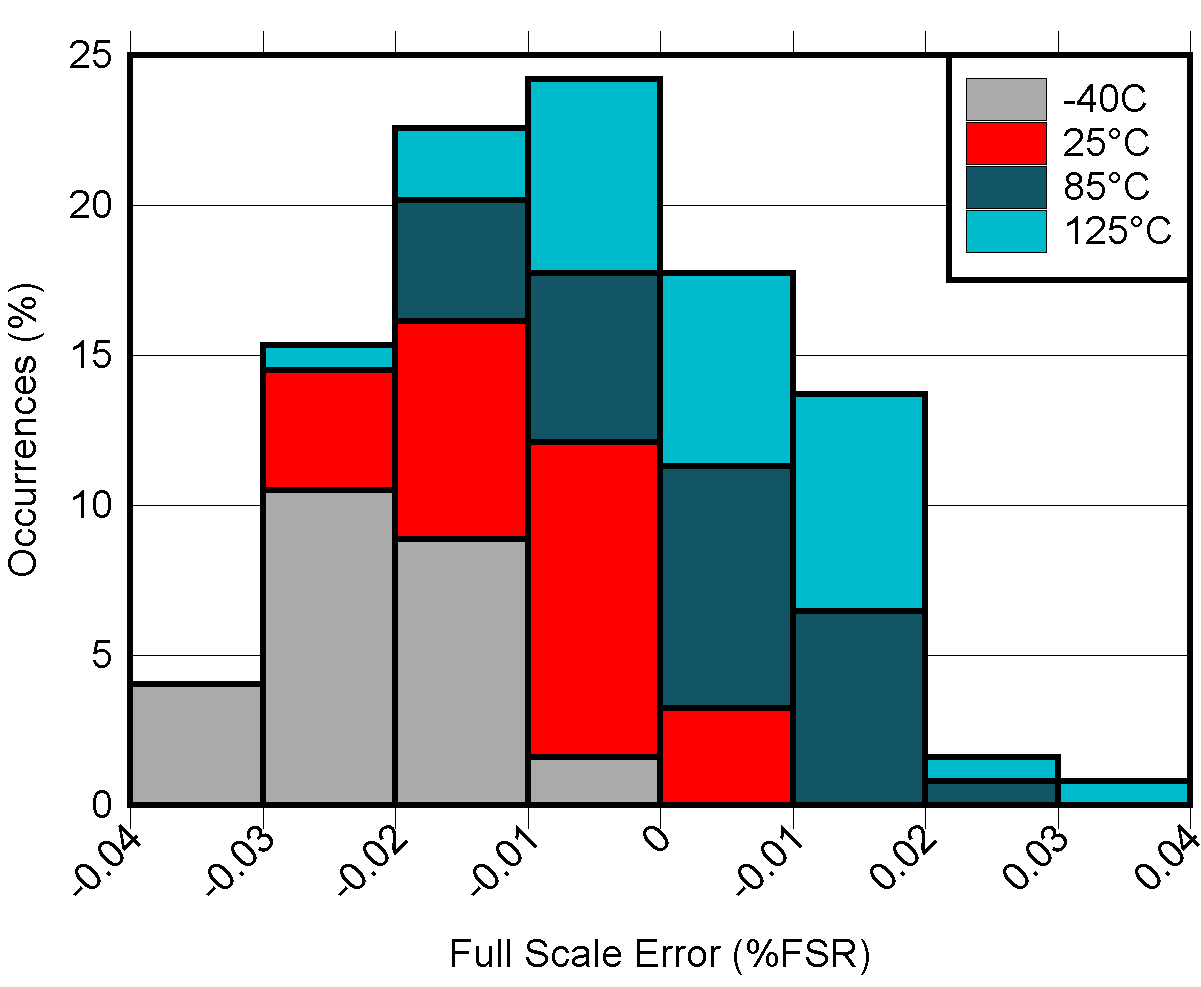 Figure 5-17 DAC
Full Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-17 DAC
Full Scale Error vs Temperature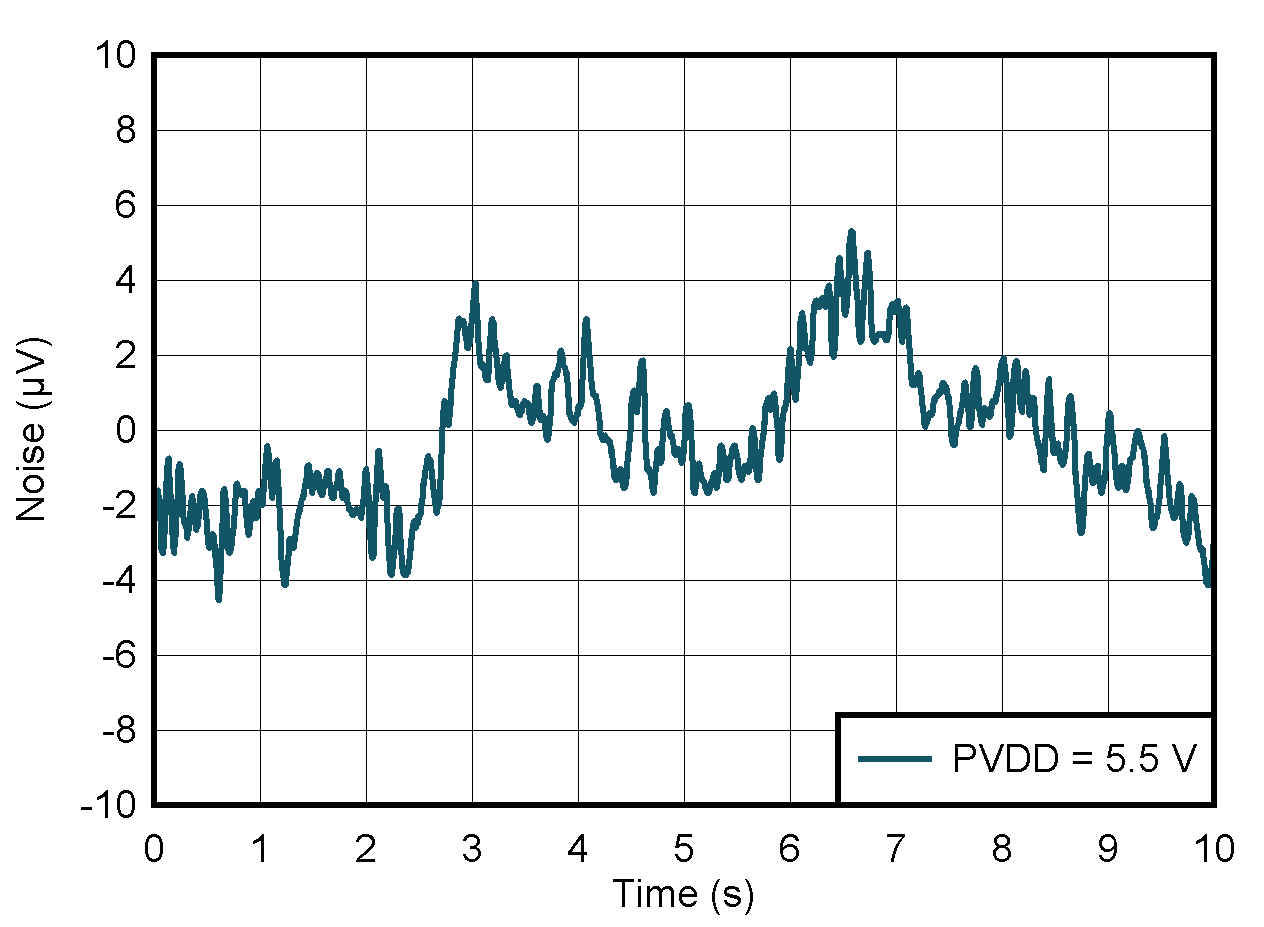
| DAC at midcode | PVDD = 5.5 V | |
| Internal reference | ||
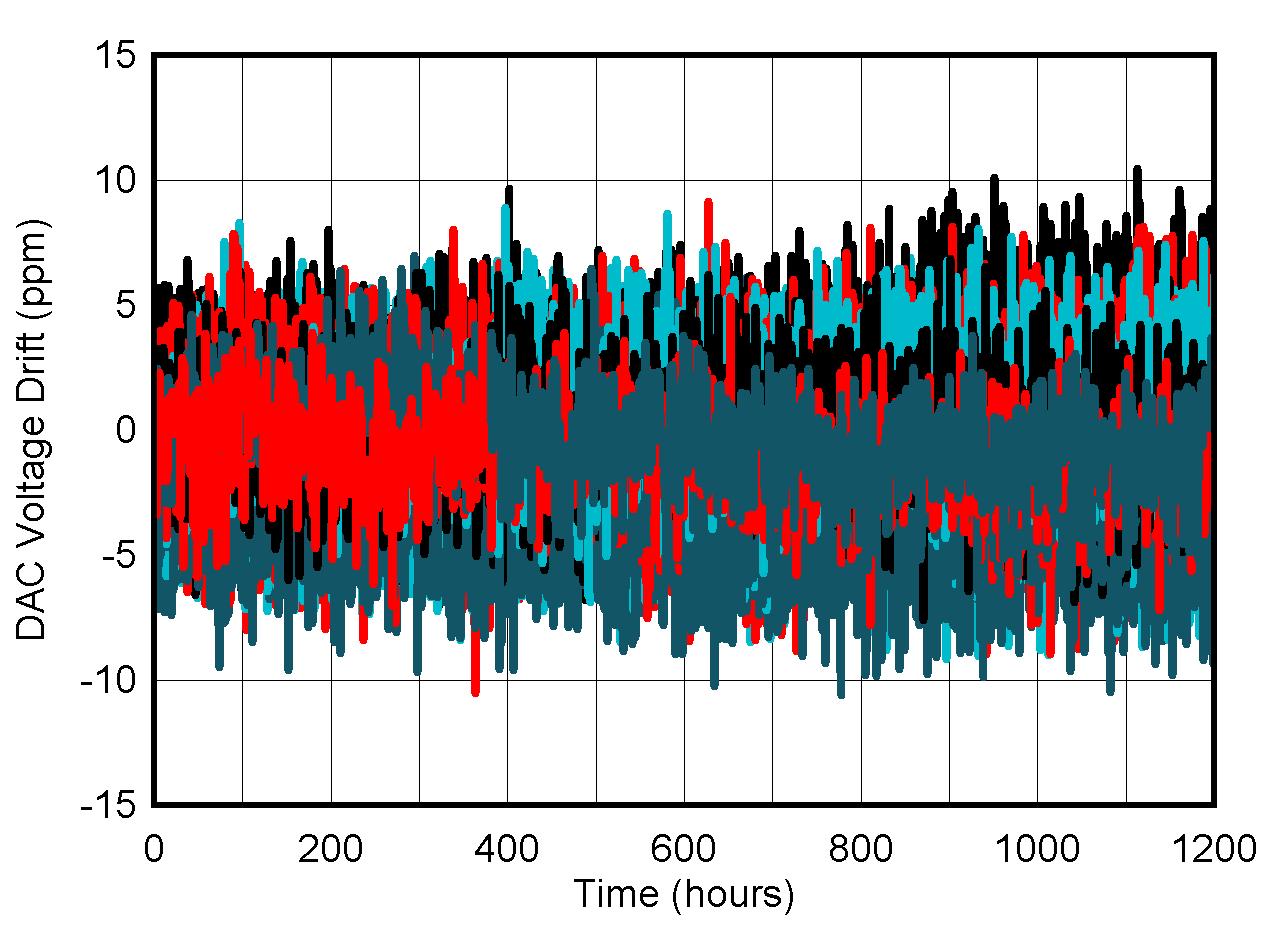
| Ideal reference | ||
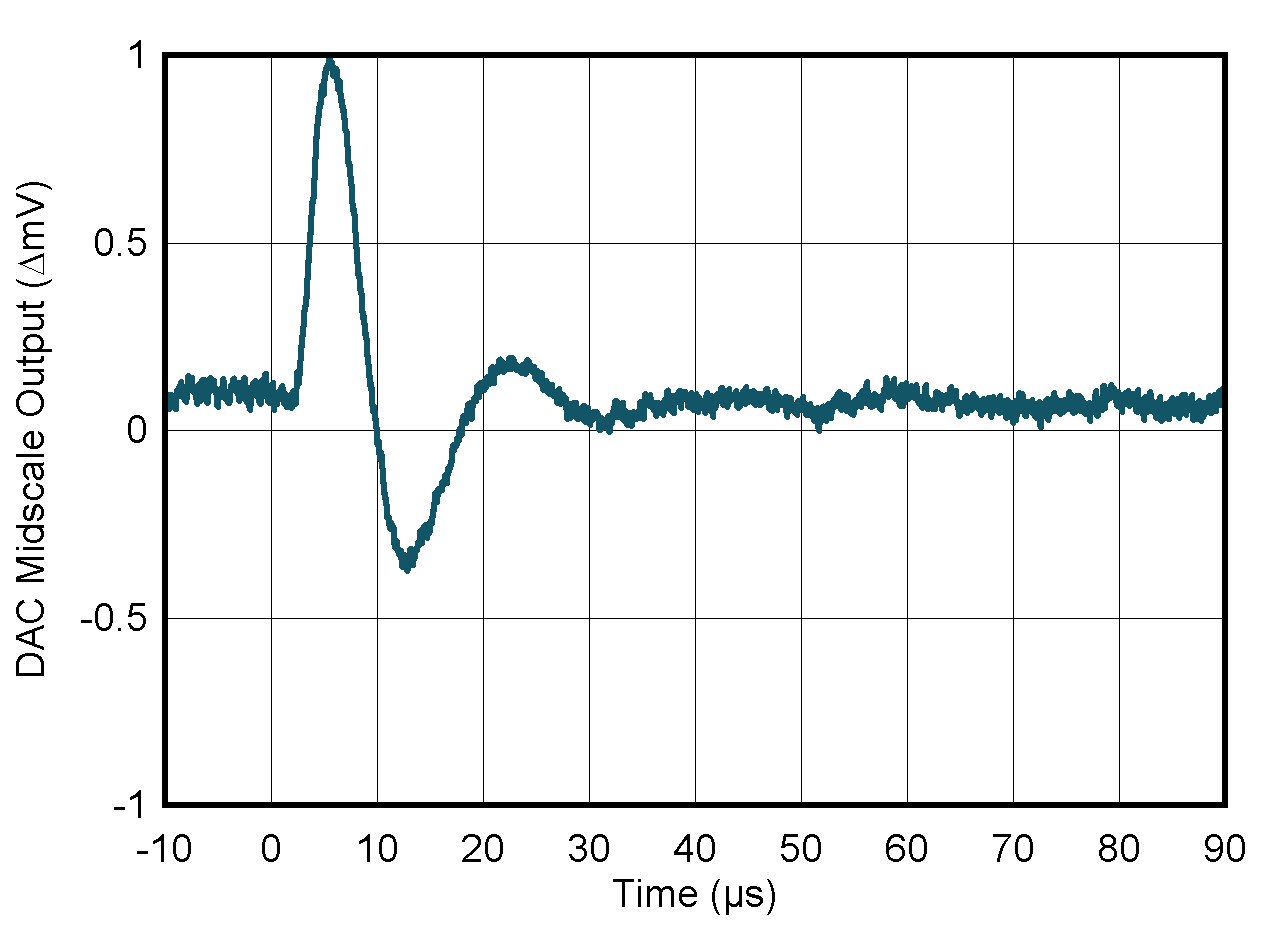
| PVDD = 5.5 V | ||
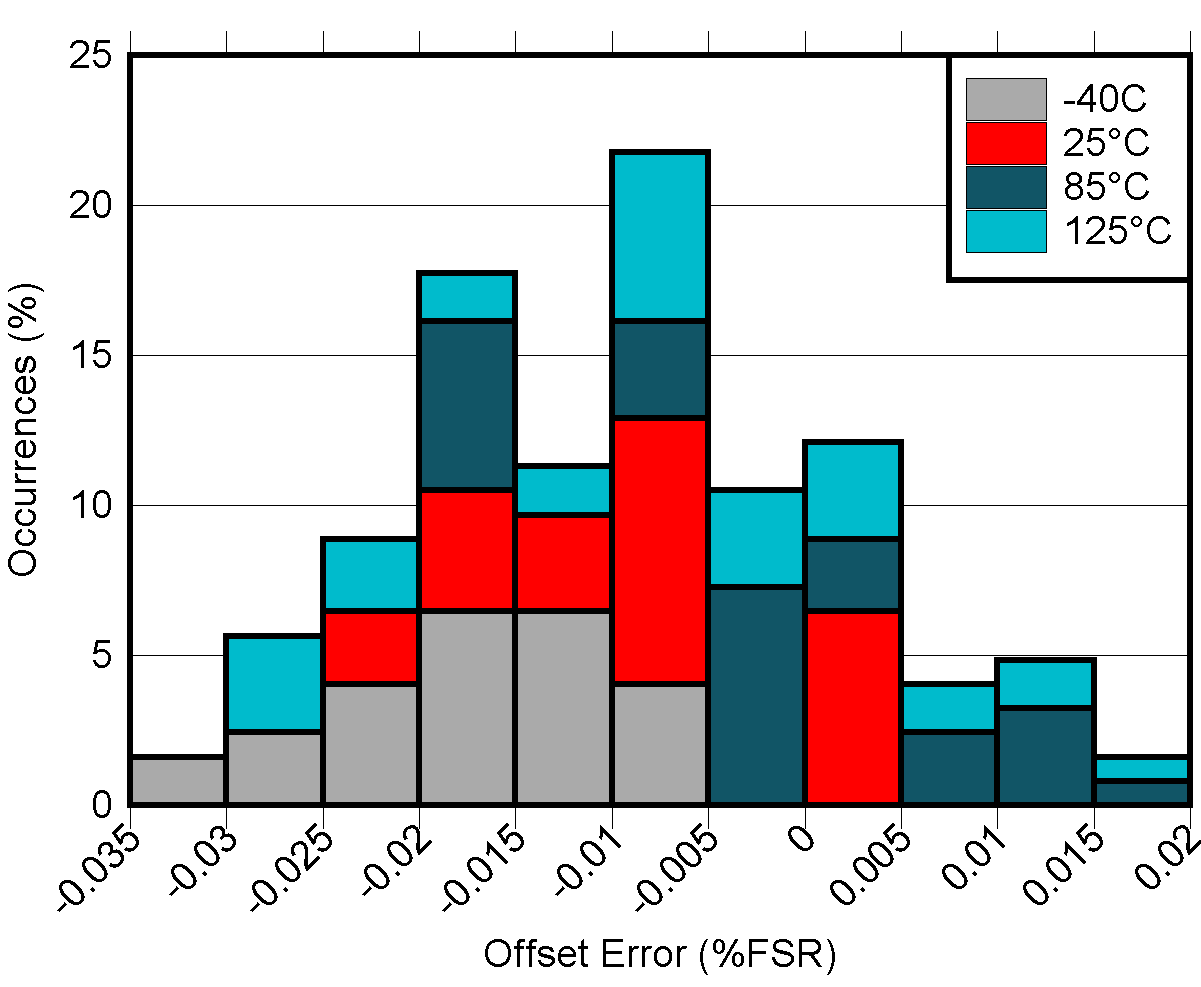 Figure 5-16 DAC
Offset Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-16 DAC
Offset Error vs Temperature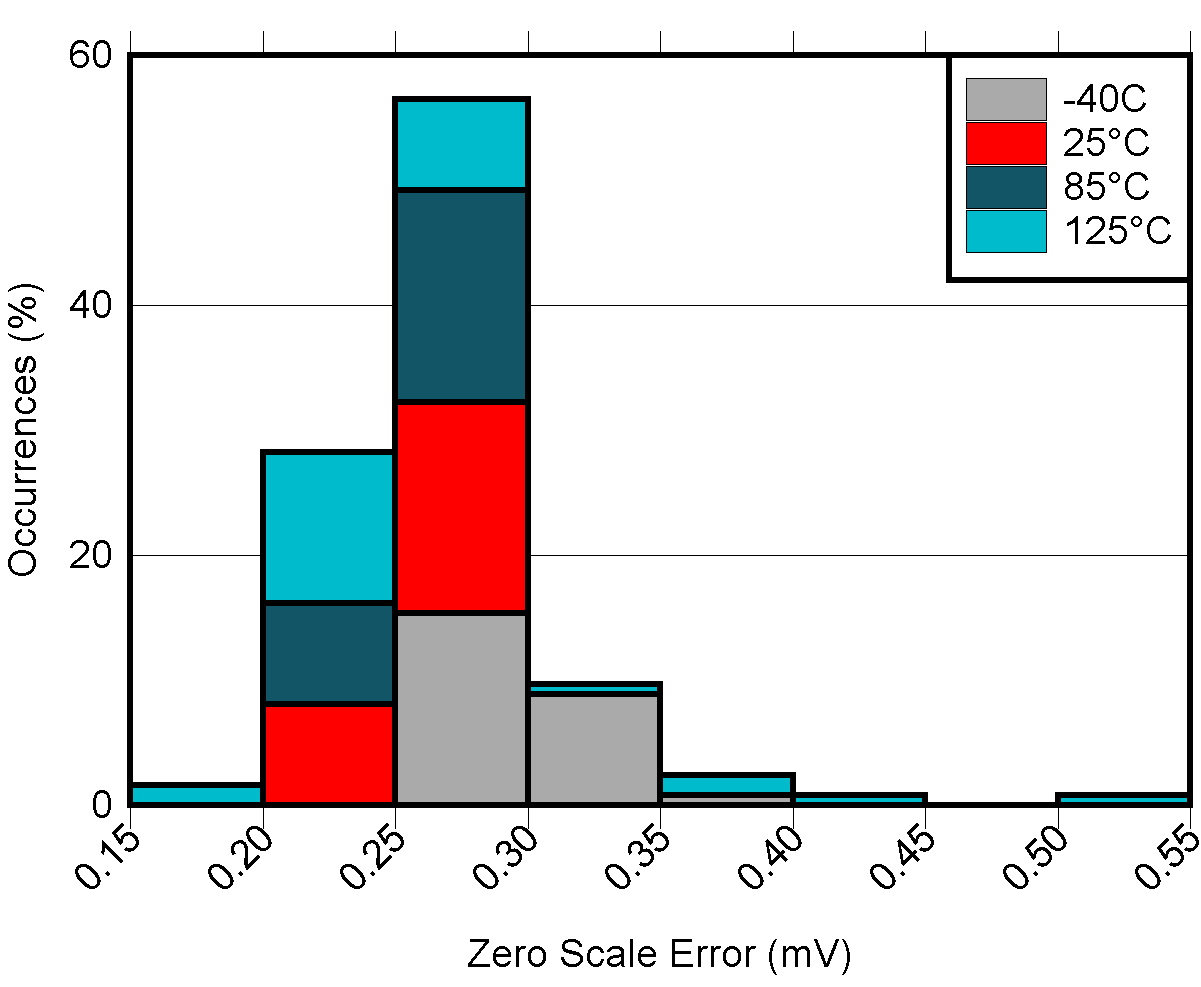 Figure 5-18 DAC
Zero Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-18 DAC
Zero Scale Error vs Temperature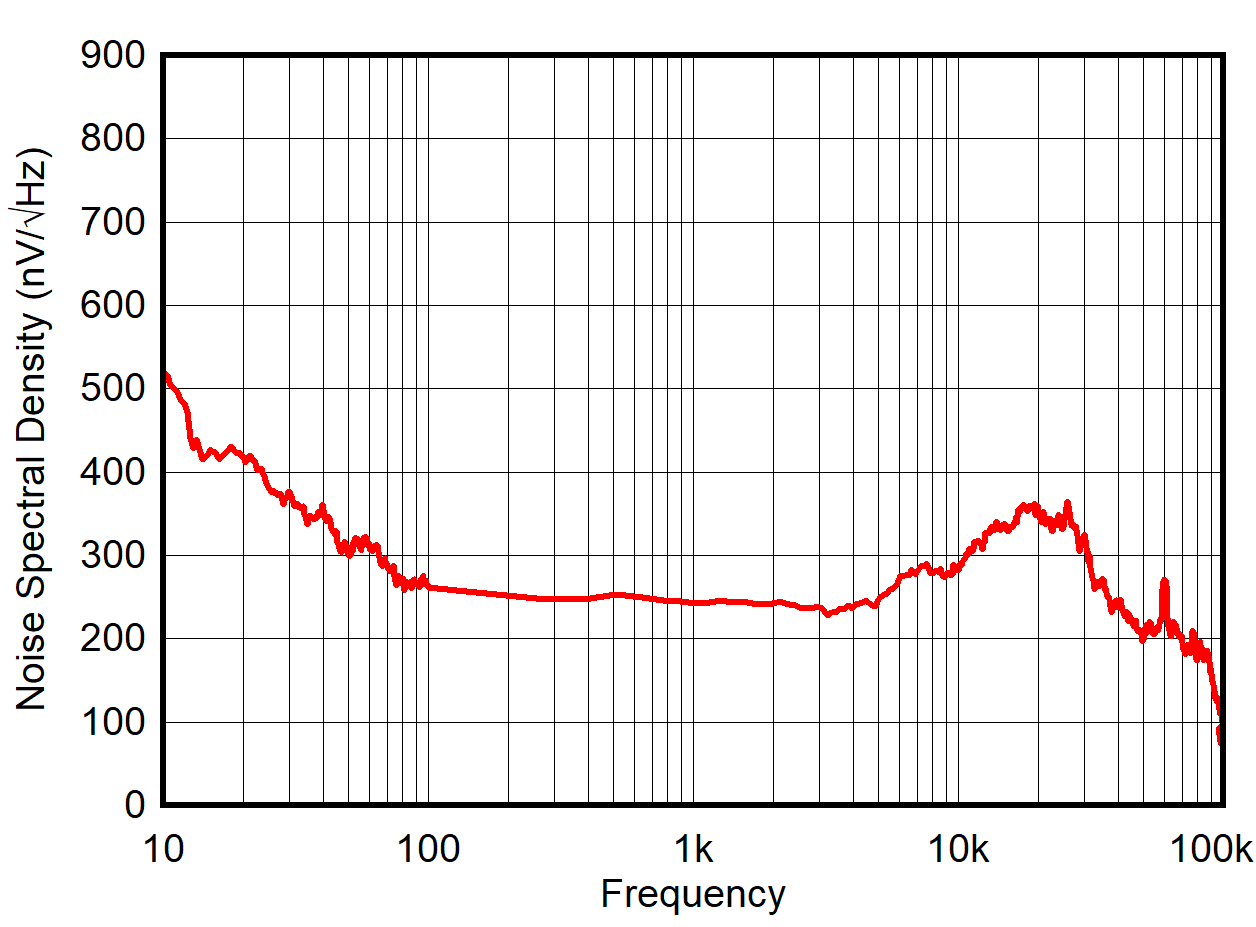
| DAC at midcode | PVDD = 5.5 V | |