SPRS637E February 2010 – June 2014 AM1707
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 AM1707 ARM Microprocessor
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Characteristics
- 3.2 Device Compatibility
- 3.3 ARM Subsystem
- 3.4 Memory Map Summary
- 3.5 Pin Assignments
- 3.6
Terminal Functions
- 3.6.1 Device Reset and JTAG
- 3.6.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.6.3 Real-Time Clock and 32-kHz Oscillator
- 3.6.4 External Memory Interface A (ASYNC, SDRAM)
- 3.6.5 External Memory Interface B (SDRAM only)
- 3.6.6 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI0, SPI1)
- 3.6.7 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0, eCAP1, eCAP2)
- 3.6.8 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM0, eHRPWM1, eHRPWM2)
- 3.6.9 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module (eQEP)
- 3.6.10 Boot
- 3.6.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
- 3.6.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.6.13 Timers
- 3.6.14 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 3.6.15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1, McASP2)
- 3.6.16 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0, USB1)
- 3.6.17 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.6.18 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.6.19 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCD)
- 3.6.20 Reserved and No Connect
- 3.6.21 Supply and Ground
- 3.6.22 Unused USB0 (USB2.0) and USB1 (USB1.1) Pin Configurations
-
4Device Configuration
- 4.1 Boot Modes
- 4.2 SYSCFG Module
- 4.3 Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
- 4.4 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Junction Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise Noted)
- 4.5 Handling Ratings
- 4.6 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.7 Notes on Recommended Power-On Hours (POH)
- 4.8 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Junction Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted)
-
5Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 5.1 Parameter Information
- 5.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.3 Power Supplies
- 5.4 Reset
- 5.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
- 5.6 Clock PLLs
- 5.7 Interrupts
- 5.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 5.9 EDMA
- 5.10 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 5.11 External Memory Interface B (EMIFB)
- 5.12 Memory Protection Units
- 5.13 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD)
- 5.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 5.15 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 5.16 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1, and McASP2)
- 5.17 Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
- 5.18 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 5.19 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP) Peripheral
- 5.20 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
- 5.21 LCD Controller
- 5.22 Timers
- 5.23 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C0, I2C1)
- 5.24 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 5.25 USB1 Host Controller Registers (USB1.1 OHCI)
- 5.26 USB0 OTG (USB2.0 OTG)
- 5.27 Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 5.28 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 5.29 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 5.30 Emulation Logic
- 5.31 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 5.32 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZKB|256
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
5.1 Parameter Information
5.1.1 Parameter Information Device-Specific Information

Input requirements in this data sheet are tested with an input slew rate of < 4 Volts per nanosecond (4 V/ns) at the device pin and the input signals are driven between 0V and the appropriate IO supply rail for the signal.
The load capacitance value stated is only for characterization and measurement of AC timing signals. This load capacitance value does not indicate the maximum load the device is capable of driving.
5.1.1.1 Signal Transition Levels
All input and output timing parameters are referenced to Vref for both "0" and "1" logic levels. For 3.3 V I/O, Vref = 1.65 V. For 1.8 V I/O, Vref = 0.9 V. For 1.2 V I/O, Vref = 0.6 V.
 Figure 5-2 Input and Output Voltage Reference Levels for AC Timing Measurements
Figure 5-2 Input and Output Voltage Reference Levels for AC Timing Measurements
All rise and fall transition timing parameters are referenced to VIL MAX and VIH MIN for input clocks, VOLMAX and VOH MIN for output clocks.
 Figure 5-3 Rise and Fall Transition Time Voltage Reference Levels
Figure 5-3 Rise and Fall Transition Time Voltage Reference Levels
5.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
All clocks and control signals must transition between VIH and VIL (or between VIL and VIH) in a monotonic manner.
5.3 Power Supplies
5.3.1 Power-on Sequence
The device should be powered-on in the following order:
- RTC (RTC_CVDD) may be powered from an external device (such as a battery) prior to all other supplies being applied or powered-up at the same time as CVDD. If the RTC is not used, RTC_CVDD should be connected to CVDD. RTC_CVDD should not be left unpowered while CVDD is powered.
- Core logic supplies:
- CVDD core logic supply
- Other 1.2V logic supplies (PLL0_VDDA). Groups 2a) and 2b) may be powered up together or 2a) first followed by 2b).
- All 1.8V IO supplies (USB0_VDDA18, USB1_VDDA18).
- All digital IO and analog 3.3V PHY supplies (DVDD, USB0_VDDA33 , USB1_VDDA33). USB0_VDDA33 and USB1_VDDA33 are not required if both USB0 and USB1 are not used) and may be left unconnected.
Group 3) and group 4) may be powered on in either order [3 then 4, or 4 then 3] but group 4) must be powered-on after the core logic supplies.
There is no specific required voltage ramp rate for any of the supplies.
RESET must be maintained active until all power supplies have reached their nominal values.
5.3.2 Power-off Sequence
The power supplies can be powered-off in any order as long as the 3.3V supplies do not remain powered with the other supplies unpowered.
5.4 Reset
5.4.1 Power-On Reset (POR)
A power-on reset (POR) is required to place the device in a known good state after power-up. Power-On Reset is initiated by bringing RESET and TRST low at the same time. POR sets all of the device internal logic to its default state. All pins are tri-stated with the exception of RESETOUT, which remains active through the reset sequence, and RTCK/GP7[14]. If an emulator is driving TCK into the device during reset, then RTCK/GP7[14] will drive out RTCK. If TCK is not being driven into the device during reset, then RTCK/GP7[14] will drive low.RESETOUT is an output for use by other controllers in the system that indicates the device is currently in reset.
While both TRST and RESET need to be asserted upon power up, only RESET needs to be released for the device to boot properly. TRST may be asserted indefinitely for normal operation, keeping the JTAG port interface and device's emulation logic in the reset state.
TRST only needs to be released when it is necessary to use a JTAG controller to debug the device or exercise the device's boundary scan functionality. Note: TRST is synchronous and must be clocked by TCK; otherwise, the boundary scan logic may not respond as expected after TRST is asserted.
RESET must be released only in order for boundary-scan JTAG to read the variant field of IDCODE correctly. Other boundary-scan instructions work correctly independent of current state of RESET. For maximum reliability, the device includes an internal pulldown on the TRST pin to ensure that TRST will always be asserted upon power up and the device's internal emulation logic will always be properly initialized.
JTAG controllers from Texas Instruments actively drive TRST high. However, some third-party JTAG controllers may not drive TRST high but expect the use of a pullup resistor on TRST. When using this type of JTAG controller, assert TRST to intialize the device after powerup and externally drive TRST high before attempting any emulation or boundary scan operations.
RTCK/GP7[14] is maintained active through a POR.
A summary of the effects of Power-On Reset is given below:
- All internal logic (including emulation logic and the PLL logic) is reset to its default state
- Internal memory is not maintained through a POR
- RESETOUT goes active
- All device pins go to a high-impedance state
- The RTC peripheral is not reset during a POR. A software sequence is required to reset the RTC.
CAUTION: A watchdog reset triggers a POR.
5.4.2 Warm Reset
A warm reset provides a limited reset to the device. Warm Reset is initiated by bringing only RESET low (TRST is maintained high through a warm reset). Warm reset sets certain portions of the device to their default state while leaving others unaltered. All pins are 3-stated with the exception of RESETOUT which remains active through the reset sequence and RTCK/GP7[14]. If an emulator is driving TCK into the device during reset, then RTCK/GP7[14] will drive out RTCK. If TCK is not being driven into the device during reset, then RTCK/GP7[14] will drive low. RESETOUT is an output for use by other controllers in the system that indicates the device is currently in reset
During emulation, the emulator will maintain TRST high and hence only warm reset (not POR) is available during emulation debug and development.
RTCK/GP7[14] is maintained active through a warm reset.
A summary of the effects of Warm Reset is given below:
- All internal logic (except for the emulation logic and the PLL logic) is reset to its default state
- Internal memory is maintained through a warm reset
- RESETOUT goes active
- All device pins go to a high-impedance state
- The RTC peripheral is not reset during a warm reset. A software sequence is required to reset the RTC.
5.4.3 Reset Electrical Data Timings
Table 5-1 assumes testing over the recommended operating conditions.
Table 5-1 Reset Timing Requirements(1)(2)
| No. | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tw(RSTL) | Pulse width, RESET/TRST low | 100 | ns | |
| 2 | tsu(BPV-RSTH) | Setup time, boot pins valid before RESET/TRST high | 20 | ns | |
| 3 | th(RSTH-BPV) | Hold time, boot pins valid after RESET/TRST high | 20 | ns | |
| 4 | td(RSTH-RESETOUTH) | RESET high to RESETOUT high; Warm reset | 4096 | cycles(3) | |
| RESET high to RESETOUT high; Power-on Reset | 6192 | ||||
 Figure 5-4 Power-On Reset (RESET and TRST active) Timing
Figure 5-4 Power-On Reset (RESET and TRST active) Timing
 Figure 5-5 Warm Reset (RESET active, TRST high) Timing
Figure 5-5 Warm Reset (RESET active, TRST high) Timing
5.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
The device includes two choices to provide an external clock input, which is fed to the on-chip PLL to generate high-frequency system clocks. These options are illustrated in Figure 5-6 and Figure 5-7. For input clock frequencies between 12 and 20 MHz, a crystal with 80 ohm max ESR is recommended. For input clock frequencies between 20 and 30 MHz, a crystal with 60 ohm max ESR is recommended. Typical load capacitance values are 10-20 pF, where the load capacitance is the series combination of C1 and C2.
The CLKMODE bit in the PLLCTL register must be 0 to use the on-chip oscillator. If CLKMODE is set to 1, the internal oscillator is disabled.
- Figure 5-6 illustrates the option that uses on-chip 1.2V oscillator with external crystal circuit.
- Figure 5-7 illustrates the option that uses an external 1.2V clock input.
 Figure 5-6 On-Chip 1.2V Oscillator
Figure 5-6 On-Chip 1.2V Oscillator
Table 5-2 Oscillator Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fosc | Oscillator frequency range (OSCIN/OSCOUT) | 12 | 30 | MHz |
 Figure 5-7 External 1.2V Clock Source
Figure 5-7 External 1.2V Clock Source
Table 5-3 OSCIN Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fOSCIN | OSCIN frequency range (OSCIN) | 12 | 50 | MHz |
| tc(OSCIN) | Cycle time, external clock driven on OSCIN | 20 | ns | |
| tw(OSCINH) | Pulse width high, external clock on OSCIN | 0.4 tc(OSCIN) | ns | |
| tw(OSCINL) | Pulse width low, external clock on OSCIN | 0.4 tc(OSCIN) | ns | |
| tt(OSCIN) | Transition time, OSCIN | 0.25P or 10 (1) | ns | |
| tj(OSCIN) | Period jitter, OSCIN | 0.02P | ns | |
5.6 Clock PLLs
The device has one PLL controller that provides clock to different parts of the system. PLL0 provides clocks (though various dividers) to most of the components of the device.
The PLL controller provides the following:
- Glitch-Free Transitions (on changing clock settings)
- Domain Clocks Alignment
- Clock Gating
- PLL power down
The various clock outputs given by the controller are as follows:
- Domain Clocks: SYSCLK [1:n]
- Auxiliary Clock from reference clock source: AUXCLK
Various dividers that can be used are as follows:
- Post-PLL Divider: POSTDIV
- SYSCLK Divider: D1, ¼, Dn
Various other controls supported are as follows:
- PLL Multiplier Control: PLLM
- Software programmable PLL Bypass: PLLEN
5.6.1 PLL Device-Specific Information
The PLL requires some external filtering components to reduce power supply noise as shown in Figure 5-8.
 Figure 5-8 PLL External Filtering Components
Figure 5-8 PLL External Filtering Components
The input to the PLL is either from the on-chip oscillator (OSCIN pin) or from an external clock on the OSCIN pin. The PLL outputs seven clocks that have programmable divider options. Figure 5-9 illustrates the PLL Topology.
The PLL is disabled by default after a device reset. It must be configured by software according to the allowable operating conditions listed in Table 5-4 before enabling the processor to run from the PLL by setting PLLEN = 1.
 Figure 5-9 PLL Topology
Figure 5-9 PLL Topology
Table 5-4 Allowed PLL Operating Conditions
| No. | PARAMETER | Default Value | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PLLRST: Assertion time during initialization | N/A | 1000 | N/A | ns |
| 2 | Lock time: The time that the application has to wait for the PLL to acquire locks before setting PLLEN, after changing PREDIV, PLLM, or OSCIN | N/A | N/A |  |
OSCIN cycles |
| 3 | PREDIV | /1 | /1 | /32 | |
| 4 | PLL input frequency ( PLLREF) |
12 | 30 (if internal oscillator is used) 50 (if external clock source is used) |
MHz | |
| 5 | PLL multiplier values (PLLM) (1) | x20 | x4 | x32 | |
| 6 | PLL output frequency. ( PLLOUT ) | N/A | 300 | 600 | MHz |
| 7 | POSTDIV | /1 | /1 | /32 |
5.6.2 Device Clock Generation
PLL0 is controlled by PLL Controller 0. The PLLC0 manages the clock ratios, alignment, and gating for the system clocks to the chip. The PLLC is responsible for controlling all modes of the PLL through software, in terms of pre-division of the clock inputs, multiply factor within the PLL, and post-division for each of the chip-level clocks from the PLL output. The PLLC also controls reset propagation through the chip, clock alignment, and test points.
5.6.3 PLL Controller 0 Registers
Table 5-5 PLL Controller 0 Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01C1 1000 | REVID | Revision Identification Register |
| 0x01C1 10E4 | RSTYPE | Reset Type Status Register |
| 0x01C1 1100 | PLLCTL | PLL Control Register |
| 0x01C1 1104 | OCSEL | OBSCLK Select Register |
| 0x01C1 1110 | PLLM | PLL Multiplier Control Register |
| 0x01C1 1114 | PREDIV | PLL Pre-Divider Control Register |
| 0x01C1 1118 | PLLDIV1 | PLL Controller Divider 1 Register |
| 0x01C1 111C | PLLDIV2 | PLL Controller Divider 2 Register |
| 0x01C1 1120 | PLLDIV3 | PLL Controller Divider 3 Register |
| 0x01C1 1124 | OSCDIV | Oscillator Divider 1 Register (OBSCLK) |
| 0x01C1 1128 | POSTDIV | PLL Post-Divider Control Register |
| 0x01C1 1138 | PLLCMD | PLL Controller Command Register |
| 0x01C1 113C | PLLSTAT | PLL Controller Status Register |
| 0x01C1 1140 | ALNCTL | PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register |
| 0x01C1 1144 | DCHANGE | PLLDIV Ratio Change Status Register |
| 0x01C1 1148 | CKEN | Clock Enable Control Register |
| 0x01C1 114C | CKSTAT | Clock Status Register |
| 0x01C1 1150 | SYSTAT | SYSCLK Status Register |
| 0x01C1 1160 | PLLDIV4 | PLL Controller Divider 4 Register |
| 0x01C1 1164 | PLLDIV5 | PLL Controller Divider 5 Register |
| 0x01C1 1168 | PLLDIV6 | PLL Controller Divider 6 Register |
| 0x01C1 116C | PLLDIV7 | PLL Controller Divider 7 Register |
5.7 Interrupts
5.7.1 ARM CPU Interrupts
The ARM9 CPU core supports 2 direct interrupts: FIQ and IRQ. The ARM Interrupt Controller extends the number of interrupts to 100, and provides features like programmable masking, priority, hardware nesting support, and interrupt vector generation.
5.7.1.1 ARM Interrupt Controller (AINTC) Interrupt Signal Hierarchy
The ARM Interrupt controller organizes interrupts into the following hierarchy:
- Peripheral Interrupt Requests
- Individual Interrupt Sources from Peripherals
- 100 System Interrupts
- One or more Peripheral Interrupt Requests are combined (fixed configuration) to generate a System Interrupt.
- After prioritization, the AINTC will provide an interrupt vector based unique to each System Interrupt
- 32 Interrupt Channels
- Each System Interrupt is mapped to one of the 32 Interrupt Channels
- Channel Number determines the first level of prioritization, Channel 0 is highest priority and 31 lowest.
- If more than one system interrupt is mapped to a channel, priority within the channel is determined by system interrupt number (0 highest priority)
- Host Interrupts (FIQ and IRQ)
- Interrupt Channels 0 and 1 generate the ARM FIQ interrupt
- Interrupt Channels 2 through 31 Generate the ARM IRQ interrupt
- Debug Interrupts
- Two Debug Interrupts are supported and can be used to trigger events in the debug subsystem
- Sources can be selected from any of the System Interrupts or Host Interrupts
5.7.1.2 AINTC Hardware Vector Generation
The AINTC also generates an interrupt vector in hardware for both IRQ and FIQ host interrupts. This may be used to accelerate interrupt dispatch. A unique vector is generated for each of the 100 system interrupts. The vector is computed in hardware as:
VECTOR = BASE + (SYSTEM INTERRUPT NUMBER × SIZE)
Where BASE and SIZE are programmable. The computed vector is a 32-bit address which may dispatched to using a single instruction of type LDR PC, [PC, #-<offset_12>] at the FIQ and IRQ vector locations (0xFFFF0018 and 0xFFFF001C respectively).
5.7.1.3 AINTC Hardware Interrupt Nesting Support
Interrupt nesting occurs when an interrupt service routine re-enables interrupts, to allow the CPU to interrupt the ISR if a higher priority event occurs. The AINTC provides hardware support to facilitate interrupt nesting. It supports both global and per host interrupt (FIQ and IRQ in this case) automatic nesting. If enabled, the AINTC will automatically update an internal nesting register that temporarily masks interrupts at and below the priority of the current interrupt channel. Then if the ISR re-enables interrupts; only higher priority channels will be able to interrupt it. The nesting level is restored by the ISR by writing to the nesting level register on completion. Support for nesting can be enabled/disabled by software, with the option of automatic nesting on a global or per host interrupt basis; or manual nesting.
5.7.1.4 AINTC System Interrupt Assignments on the device
System Interrupt assignments for the device are listed in Table 5-6
Table 5-6 AINTC System Interrupt Assignments
| System Interrupt | Interrupt Name | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | COMMTX | ARM |
| 1 | COMMRX | ARM |
| 2 | NINT | ARM |
| 3 | PRU_EVTOUT0 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 4 | PRU_EVTOUT1 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 5 | PRU_EVTOUT2 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 6 | PRU_EVTOUT3 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 7 | PRU_EVTOUT4 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 8 | PRU_EVTOUT5 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 9 | PRU_EVTOUT6 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 10 | PRU_EVTOUT7 | PRUSS Interrupt |
| 11 | EDMA3_CC0_CCINT | EDMA CC Region 0 |
| 12 | EDMA3_CC0_CCERRINT | EDMA Channel Controller |
| 13 | EDMA3_TC0_TCERRINT | EDMA Transfer Controller 0 |
| 14 | EMIFA_INT | EMIFA |
| 15 | IIC0_INT | I2C0 |
| 16 | MMCSD_INT0 | MMCSD |
| 17 | MMCSD_INT1 | MMCSD |
| 18 | PSC0_ALLINT | PSC0 |
| 19 | RTC_IRQS[1:0] | RTC |
| 20 | SPI0_INT | SPI0 |
| 21 | T64P0_TINT12 | Timer64P0 Interrupt 12 |
| 22 | T64P0_TINT34 | Timer64P0 Interrupt 34 |
| 23 | T64P1_TINT12 | Timer64P1 Interrupt 12 |
| 24 | T64P1_TINT34 | Timer64P1 Interrupt 34 |
| 25 | UART0_INT | UART0 |
| 26 | - | Reserved |
| 27 | MPU_BOOTCFG_ERR | Shared MPU and SYSCFG Address/Protection Error Interrupt |
| 28 - 31 | - | Reserved |
| 32 | EDMA3_TC1_TCERRINT | EDMA Transfer Controller 1 |
| 33 | EMAC_C0RXTHRESH | EMAC - Core 0 Receive Threshold Interrupt |
| 34 | EMAC_C0RX | EMAC - Core 0 Receive Interrupt |
| 35 | EMAC_C0TX | EMAC - Core 0 Transmit Interrupt |
| 36 | EMAC_C0MISC | EMAC - Core 0 Miscellaneous Interrupt |
| 37 | EMAC_C1RXTHRESH | EMAC - Core 1 Receive Threshold Interrupt |
| 38 | EMAC_C1RX | EMAC - Core 1 Receive Interrupt |
| 39 | EMAC_C1TX | EMAC - Core 1 Transmit Interrupt |
| 40 | EMAC_C1MISC | EMAC - Core 1 Miscellaneous Interrupt |
| 41 | EMIF_MEMERR | EMIFB |
| 42 | GPIO_B0INT | GPIO Bank 0 Interrupt |
| 43 | GPIO_B1INT | GPIO Bank 1 Interrupt |
| 44 | GPIO_B2INT | GPIO Bank 2 Interrupt |
| 45 | GPIO_B3INT | GPIO Bank 3 Interrupt |
| 46 | GPIO_B4INT | GPIO Bank 4 Interrupt |
| 47 | GPIO_B5INT | GPIO Bank 5 Interrupt |
| 48 | GPIO_B6INT | GPIO Bank 6 Interrupt |
| 49 | GPIO_B7INT | GPIO Bank 7 Interrupt |
| 50 | - | Reserved |
| 51 | IIC1_INT | I2C1 |
| 52 | LCDC_INT | LCD Controller |
| 53 | UART_INT1 | UART1 |
| 54 | MCASP_INT | McASP0, 1, 2 Combined RX / TX Interrupts |
| 55 | PSC1_ALLINT | PSC1 |
| 56 | SPI1_INT | SPI1 |
| 57 | UHPI_ARMINT | HPI ARM Interrupt |
| 58 | USB0_INT | USB0 Interrupt |
| 59 | USB1_HCINT | USB1 OHCI Host Controller Interrupt |
| 60 | USB1_RWAKEUP | USB1 Remote Wakeup Interrupt |
| 61 | UART2_INT | UART2 |
| 62 | - | Reserved |
| 63 | EHRPWM0 | HiResTimer / PWM0 Interrupt |
| 64 | EHRPWM0TZ | HiResTimer / PWM0 Trip Zone Interrupt |
| 65 | EHRPWM1 | HiResTimer / PWM1 Interrupt |
| 66 | EHRPWM1TZ | HiResTimer / PWM1 Trip Zone Interrupt |
| 67 | EHRPWM2 | HiResTimer / PWM2 Interrupt |
| 68 | EHRPWM2TZ | HiResTimer / PWM2 Trip Zone Interrupt |
| 69 | ECAP0 | ECAP0 |
| 70 | ECAP1 | ECAP1 |
| 71 | ECAP2 | ECAP2 |
| 72 | EQEP0 | EQEP0 |
| 73 | EQEP1 | EQEP1 |
| 74 | T64P0_CMPINT0 | Timer64P0 - Compare 0 |
| 75 | T64P0_CMPINT1 | Timer64P0 - Compare 1 |
| 76 | T64P0_CMPINT2 | Timer64P0 - Compare 2 |
| 77 | T64P0_CMPINT3 | Timer64P0 - Compare 3 |
| 78 | T64P0_CMPINT4 | Timer64P0 - Compare 4 |
| 79 | T64P0_CMPINT5 | Timer64P0 - Compare 5 |
| 80 | T64P0_CMPINT6 | Timer64P0 - Compare 6 |
| 81 | T64P0_CMPINT7 | Timer64P0 - Compare 7 |
| 82 | T64P1_CMPINT0 | Timer64P1 - Compare 0 |
| 83 | T64P1_CMPINT1 | Timer64P1 - Compare 1 |
| 84 | T64P1_CMPINT2 | Timer64P1 - Compare 2 |
| 85 | T64P1_CMPINT3 | Timer64P1 - Compare 3 |
| 86 | T64P1_CMPINT4 | Timer64P1 - Compare 4 |
| 87 | T64P1_CMPINT5 | Timer64P1 - Compare 5 |
| 88 | T64P1_CMPINT6 | Timer64P1 - Compare 6 |
| 89 | T64P1_CMPINT7 | Timer64P1 - Compare 7 |
| 90 | ARMCLKSTOPREQ | PSC0 |
| 91 - 100 | - | Reserved |
5.7.1.5 AINTC Memory Map
Table 5-7 AINTC Memory Map
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0xFFFE E000 | REV | Revision Register |
| 0xFFFE E004 | CR | Control Register |
| 0xFFFE E008 - 0xFFFE E00F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E010 | GER | Global Enable Register |
| 0xFFFE E014 - 0xFFFE E01B | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E01C | GNLR | Global Nesting Level Register |
| 0xFFFE E020 | SISR | System Interrupt Status Indexed Set Register |
| 0xFFFE E024 | SICR | System Interrupt Status Indexed Clear Register |
| 0xFFFE E028 | EISR | System Interrupt Enable Indexed Set Register |
| 0xFFFE E02C | EICR | System Interrupt Enable Indexed Clear Register |
| 0xFFFE E030 | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E034 | HIEISR | Host Interrupt Enable Indexed Set Register |
| 0xFFFE E038 | HIEICR | Host Interrupt Enable Indexed Clear Register |
| 0xFFFE E03C - 0xFFFE E04F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E050 | VBR | Vector Base Register |
| 0xFFFE E054 | VSR | Vector Size Register |
| 0xFFFE E058 | VNR | Vector Null Register |
| 0xFFFE E05C - 0xFFFE E07F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E080 | GPIR | Global Prioritized Index Register |
| 0xFFFE E084 | GPVR | Global Prioritized Vector Register |
| 0xFFFE E088 - 0xFFFE E1FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E200 - 0xFFFE E20B | SRSR[1] - SRSR[3] | System Interrupt Status Raw / Set Registers |
| 0xFFFE E20C- 0xFFFE E27F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E280 - 0xFFFE E28B | SECR[1] - SECR[3] | System Interrupt Status Enabled / Clear Registers |
| 0xFFFE E28C - 0xFFFE E2FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E300 - 0xFFFE E30B | ESR[1] - ESR[3] | System Interrupt Enable Set Registers |
| 0xFFFE E30C - 0xFFFE E37F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E380 - 0xFFFE E38B | ECR[1] - ECR[3] | System Interrupt Enable Clear Registers |
| 0xFFFE E38C - 0xFFFE E3FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E400 - 0xFFFE E458 | CMR[0] - CMR[22] | Channel Map Registers (Byte Wide Registers) |
| 0xFFFE E459 - 0xFFFE E7FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E800 - 0xFFFE E81F | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E820 - 0xFFFE E8FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE E900 - 0xFFFE E904 | HIPIR[1] - HIPIR[2] | Host Interrupt Prioritized Index Registers |
| 0xFFFE E908 - 0xFFFE EEFF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE EF00 - 0xFFFE EF04 | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE EF08 - 0xFFFE F0FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE F100 - 0xFFFE F104 | HINLR[1] - HINLR[2] | Host Interrupt Nesting Level Registers |
| 0xFFFE F108 - 0xFFFE F4FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE F500 | HIER | Host Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0xFFFE F504 - 0xFFFE F5FF | - | Reserved |
| 0xFFFE F600 | HIPVR[1] - HIPVR[2] | Host Interrupt Prioritized Vector Registers |
| 0xFFFE F608 - 0xFFFE FFFF | - | Reserved |
5.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
The GPIO peripheral provides general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs or outputs. When configured as an output, a write to an internal register can control the state driven on the output pin. When configured as an input, the state of the input is detectable by reading the state of an internal register. In addition, the GPIO peripheral can produce CPU interrupts and EDMA events in different interrupt/event generation modes. The GPIO peripheral provides generic connections to external devices. The GPIO pins are grouped into banks of 16 pins per bank (i.e., bank 0 consists of GPIO [0:15]).
The device GPIO peripheral supports the following:
- Up to 128 Pins on ZKB package configurable as GPIO
- External Interrupt and DMA request Capability
- Every GPIO pin may be configured to generate an interrupt request on detection of rising and/or falling edges on the pin.
- The interrupt requests within each bank are combined (logical or) to create eight unique bank level interrupt requests.
- The bank level interrupt service routine may poll the INTSTATx register for its bank to determine which pin(s) have triggered the interrupt.
- GPIO Banks 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 Interrupts assigned to ARM INTC Interrupt Requests 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, and 49 respectively
- Additionally, GPIO Banks 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 Interrupts assigned to EDMA events 6, 7, 22, 23, 28, and 29 respectively.
- Set/clear functionality: Firmware writes 1 to corresponding bit position(s) to set or to clear GPIO signal(s). This allows multiple firmware processes to toggle GPIO output signals without critical section protection (disable interrupts, program GPIO, re-enable interrupts, to prevent context switching to anther process during GPIO programming).
- Separate Input/Output registers
- Output register in addition to set/clear so that, if preferred by firmware, some GPIO output signals can be toggled by direct write to the output register(s).
- Output register, when read, reflects output drive status. This, in addition to the input register reflecting pin status and open-drain I/O cell, allows wired logic be implemented.
The memory map for the GPIO registers is shown in Table 5-8.
5.8.1 GPIO Register Description(s)
Table 5-8 GPIO Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 6000 | REV | Peripheral Revision Register |
| 0x01E2 6004 | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E2 6008 | BINTEN | GPIO Interrupt Per-Bank Enable Register |
| GPIO BANKS 0 AND 1 | ||
| 0x01E2 6010 | DIR01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Direction Register |
| 0x01E2 6014 | OUT_DATA01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Output Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6018 | SET_DATA01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Set Data Register |
| 0x01E2 601C | CLR_DATA01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Clear Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6020 | IN_DATA01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Input Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6024 | SET_RIS_TRIG01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Set Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6028 | CLR_RIS_TRIG01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Clear Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 602C | SET_FAL_TRIG01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Set Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6030 | CLR_FAL_TRIG01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Clear Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6034 | INTSTAT01 | GPIO Banks 0 and 1 Interrupt Status Register |
| GPIO BANKS 2 AND 3 | ||
| 0x01E2 6038 | DIR23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Direction Register |
| 0x01E2 603C | OUT_DATA23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Output Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6040 | SET_DATA23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Set Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6044 | CLR_DATA23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Clear Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6048 | IN_DATA23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Input Data Register |
| 0x01E2 604C | SET_RIS_TRIG23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Set Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6050 | CLR_RIS_TRIG23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Clear Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6054 | SET_FAL_TRIG23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Set Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6058 | CLR_FAL_TRIG23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Clear Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 605C | INTSTAT23 | GPIO Banks 2 and 3 Interrupt Status Register |
| GPIO BANKS 4 AND 5 | ||
| 0x01E2 6060 | DIR45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Direction Register |
| 0x01E2 6064 | OUT_DATA45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Output Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6068 | SET_DATA45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Set Data Register |
| 0x01E2 606C | CLR_DATA45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Clear Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6070 | IN_DATA45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Input Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6074 | SET_RIS_TRIG45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Set Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6078 | CLR_RIS_TRIG45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Clear Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 607C | SET_FAL_TRIG45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Set Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6080 | CLR_FAL_TRIG45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Clear Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 6084 | INTSTAT45 | GPIO Banks 4 and 5 Interrupt Status Register |
| GPIO BANKS 6 AND 7 | ||
| 0x01E2 6088 | DIR67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Direction Register |
| 0x01E2 608C | OUT_DATA67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Output Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6090 | SET_DATA67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Set Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6094 | CLR_DATA67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Clear Data Register |
| 0x01E2 6098 | IN_DATA67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Input Data Register |
| 0x01E2 609C | SET_RIS_TRIG67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Set Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 60A0 | CLR_RIS_TRIG67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Clear Rising Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 60A4 | SET_FAL_TRIG67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Set Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 60A8 | CLR_FAL_TRIG67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Clear Falling Edge Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E2 60AC | INTSTAT67 | GPIO Banks 6 and 7 Interrupt Status Register |
5.8.2 GPIO Peripheral Input/Output Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-9 Timing Requirements for GPIO Inputs(1) (see Figure 5-10)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tw(GPIH) | Pulse duration, GPn[m] as input high | 2C(1)(2) | ns | |
| 2 | tw(GPIL) | Pulse duration, GPn[m] as input low | 2C(1)(2) | ns | |
Table 5-10 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for GPIO Outputs
(see Figure 5-10)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | tw(GPOH) | Pulse duration, GPn[m] as output high | 2C(1)(2) | ns | |
| 4 | tw(GPOL) | Pulse duration, GPn[m] as output low | 2C(1)(2) | ns | |
 Figure 5-10 GPIO Port Timing
Figure 5-10 GPIO Port Timing
5.8.3 GPIO Peripheral External Interrupts Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-11 Timing Requirements for External Interrupts(1) (see Figure 5-11)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tw(ILOW) | Width of the external interrupt pulse low | 2C(1)(2) | ns | ||
| 2 | tw(IHIGH) | Width of the external interrupt pulse high | 2C (1)(2) | ns | ||
 Figure 5-11 GPIO External Interrupt Timing
Figure 5-11 GPIO External Interrupt Timing
5.9 EDMA
Table 5-12 is the list of EDMA3 Channel Contoller Registers and Table 5-13 is the list of EDMA3 Transfer Controller registers.
Table 5-12 EDMA3 Channel Controller (EDMA3CC) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01C0 0000 | PID | Peripheral Identification Register |
| 0x01C0 0004 | CCCFG | EDMA3CC Configuration Register |
| GLOBAL REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01C0 0200 | QCHMAP0 | QDMA Channel 0 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0204 | QCHMAP1 | QDMA Channel 1 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0208 | QCHMAP2 | QDMA Channel 2 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 020C | QCHMAP3 | QDMA Channel 3 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0210 | QCHMAP4 | QDMA Channel 4 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0214 | QCHMAP5 | QDMA Channel 5 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0218 | QCHMAP6 | QDMA Channel 6 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 021C | QCHMAP7 | QDMA Channel 7 Mapping Register |
| 0x01C0 0240 | DMAQNUM0 | DMA Channel Queue Number Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 0244 | DMAQNUM1 | DMA Channel Queue Number Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 0248 | DMAQNUM2 | DMA Channel Queue Number Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 024C | DMAQNUM3 | DMA Channel Queue Number Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 0260 | QDMAQNUM | QDMA Channel Queue Number Register |
| 0x01C0 0284 | QUEPRI | Queue Priority Register(1) |
| 0x01C0 0300 | EMR | Event Missed Register |
| 0x01C0 0308 | EMCR | Event Missed Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 0310 | QEMR | QDMA Event Missed Register |
| 0x01C0 0314 | QEMCR | QDMA Event Missed Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 0318 | CCERR | EDMA3CC Error Register |
| 0x01C0 031C | CCERRCLR | EDMA3CC Error Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 0320 | EEVAL | Error Evaluate Register |
| 0x01C0 0340 | DRAE0 | DMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 0 |
| 0x01C0 0348 | DRAE1 | DMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 1 |
| 0x01C0 0350 | DRAE2 | DMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 2 |
| 0x01C0 0358 | DRAE3 | DMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 3 |
| 0x01C0 0380 | QRAE0 | QDMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 0 |
| 0x01C0 0384 | QRAE1 | QDMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 1 |
| 0x01C0 0388 | QRAE2 | QDMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 2 |
| 0x01C0 038C | QRAE3 | QDMA Region Access Enable Register for Region 3 |
| 0x01C0 0400 - 0x01C0 043C | Q0E0-Q0E15 | Event Queue Entry Registers Q0E0-Q0E15 |
| 0x01C0 0440 - 0x01C0 047C | Q1E0-Q1E15 | Event Queue Entry Registers Q1E0-Q1E15 |
| 0x01C0 0600 | QSTAT0 | Queue 0 Status Register |
| 0x01C0 0604 | QSTAT1 | Queue 1 Status Register |
| 0x01C0 0620 | QWMTHRA | Queue Watermark Threshold A Register |
| 0x01C0 0640 | CCSTAT | EDMA3CC Status Register |
| GLOBAL CHANNEL REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01C0 1000 | ER | Event Register |
| 0x01C0 1008 | ECR | Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 1010 | ESR | Event Set Register |
| 0x01C0 1018 | CER | Chained Event Register |
| 0x01C0 1020 | EER | Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 1028 | EECR | Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 1030 | EESR | Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 1038 | SER | Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 1040 | SECR | Secondary Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 1050 | IER | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 1058 | IECR | Interrupt Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 1060 | IESR | Interrupt Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 1068 | IPR | Interrupt Pending Register |
| 0x01C0 1070 | ICR | Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 1078 | IEVAL | Interrupt Evaluate Register |
| 0x01C0 1080 | QER | QDMA Event Register |
| 0x01C0 1084 | QEER | QDMA Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 1088 | QEECR | QDMA Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 108C | QEESR | QDMA Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 1090 | QSER | QDMA Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 1094 | QSECR | QDMA Secondary Event Clear Register |
| SHADOW REGION 0 CHANNEL REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01C0 2000 | ER | Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2008 | ECR | Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2010 | ESR | Event Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2018 | CER | Chained Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2020 | EER | Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2028 | EECR | Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2030 | EESR | Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2038 | SER | Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2040 | SECR | Secondary Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2050 | IER | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2058 | IECR | Interrupt Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2060 | IESR | Interrupt Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2068 | IPR | Interrupt Pending Register |
| 0x01C0 2070 | ICR | Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2078 | IEVAL | Interrupt Evaluate Register |
| 0x01C0 2080 | QER | QDMA Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2084 | QEER | QDMA Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2088 | QEECR | QDMA Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 208C | QEESR | QDMA Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2090 | QSER | QDMA Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2094 | QSECR | QDMA Secondary Event Clear Register |
| SHADOW REGION 1 CHANNEL REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01C0 2200 | ER | Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2208 | ECR | Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2210 | ESR | Event Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2218 | CER | Chained Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2220 | EER | Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2228 | EECR | Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2230 | EESR | Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2238 | SER | Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2240 | SECR | Secondary Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2250 | IER | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2258 | IECR | Interrupt Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2260 | IESR | Interrupt Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2268 | IPR | Interrupt Pending Register |
| 0x01C0 2270 | ICR | Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 2278 | IEVAL | Interrupt Evaluate Register |
| 0x01C0 2280 | QER | QDMA Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2284 | QEER | QDMA Event Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 2288 | QEECR | QDMA Event Enable Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 228C | QEESR | QDMA Event Enable Set Register |
| 0x01C0 2290 | QSER | QDMA Secondary Event Register |
| 0x01C0 2294 | QSECR | QDMA Secondary Event Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 4000 - 0x01C0 4FFF | — | Parameter RAM (PaRAM) |
Table 5-13 EDMA3 Transfer Controller (EDMA3TC) Registers
| TRANSFER CONTROLLER 0 BYTE ADDRESS |
TRANSFER CONTROLLER 1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C0 8000 | 0x01C0 8400 | PID | Peripheral Identification Register |
| 0x01C0 8004 | 0x01C0 8404 | TCCFG | EDMA3TC Configuration Register |
| 0x01C0 8100 | 0x01C0 8500 | TCSTAT | EDMA3TC Channel Status Register |
| 0x01C0 8120 | 0x01C0 8520 | ERRSTAT | Error Status Register |
| 0x01C0 8124 | 0x01C0 8524 | ERREN | Error Enable Register |
| 0x01C0 8128 | 0x01C0 8528 | ERRCLR | Error Clear Register |
| 0x01C0 812C | 0x01C0 852C | ERRDET | Error Details Register |
| 0x01C0 8130 | 0x01C0 8530 | ERRCMD | Error Interrupt Command Register |
| 0x01C0 8140 | 0x01C0 8540 | RDRATE | Read Command Rate Register |
| 0x01C0 8240 | 0x01C0 8640 | SAOPT | Source Active Options Register |
| 0x01C0 8244 | 0x01C0 8644 | SASRC | Source Active Source Address Register |
| 0x01C0 8248 | 0x01C0 8648 | SACNT | Source Active Count Register |
| 0x01C0 824C | 0x01C0 864C | SADST | Source Active Destination Address Register |
| 0x01C0 8250 | 0x01C0 8650 | SABIDX | Source Active B-Index Register |
| 0x01C0 8254 | 0x01C0 8654 | SAMPPRXY | Source Active Memory Protection Proxy Register |
| 0x01C0 8258 | 0x01C0 8658 | SACNTRLD | Source Active Count Reload Register |
| 0x01C0 825C | 0x01C0 865C | SASRCBREF | Source Active Source Address B-Reference Register |
| 0x01C0 8260 | 0x01C0 8660 | SADSTBREF | Source Active Destination Address B-Reference Register |
| 0x01C0 8280 | 0x01C0 8680 | DFCNTRLD | Destination FIFO Set Count Reload Register |
| 0x01C0 8284 | 0x01C0 8684 | DFSRCBREF | Destination FIFO Set Source Address B-Reference Register |
| 0x01C0 8288 | 0x01C0 8688 | DFDSTBREF | Destination FIFO Set Destination Address B-Reference Register |
| 0x01C0 8300 | 0x01C0 8700 | DFOPT0 | Destination FIFO Options Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 8304 | 0x01C0 8704 | DFSRC0 | Destination FIFO Source Address Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 8308 | 0x01C0 8708 | DFCNT0 | Destination FIFO Count Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 830C | 0x01C0 870C | DFDST0 | Destination FIFO Destination Address Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 8310 | 0x01C0 8710 | DFBIDX0 | Destination FIFO B-Index Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 8314 | 0x01C0 8714 | DFMPPRXY0 | Destination FIFO Memory Protection Proxy Register 0 |
| 0x01C0 8340 | 0x01C0 8740 | DFOPT1 | Destination FIFO Options Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 8344 | 0x01C0 8744 | DFSRC1 | Destination FIFO Source Address Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 8348 | 0x01C0 8748 | DFCNT1 | Destination FIFO Count Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 834C | 0x01C0 874C | DFDST1 | Destination FIFO Destination Address Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 8350 | 0x01C0 8750 | DFBIDX1 | Destination FIFO B-Index Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 8354 | 0x01C0 8754 | DFMPPRXY1 | Destination FIFO Memory Protection Proxy Register 1 |
| 0x01C0 8380 | 0x01C0 8780 | DFOPT2 | Destination FIFO Options Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 8384 | 0x01C0 8784 | DFSRC2 | Destination FIFO Source Address Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 8388 | 0x01C0 8788 | DFCNT2 | Destination FIFO Count Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 838C | 0x01C0 878C | DFDST2 | Destination FIFO Destination Address Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 8390 | 0x01C0 8790 | DFBIDX2 | Destination FIFO B-Index Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 8394 | 0x01C0 8794 | DFMPPRXY2 | Destination FIFO Memory Protection Proxy Register 2 |
| 0x01C0 83C0 | 0x01C0 87C0 | DFOPT3 | Destination FIFO Options Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 83C4 | 0x01C0 87C4 | DFSRC3 | Destination FIFO Source Address Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 83C8 | 0x01C0 87C8 | DFCNT3 | Destination FIFO Count Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 83CC | 0x01C0 87CC | DFDST3 | Destination FIFO Destination Address Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 83D0 | 0x01C0 87D0 | DFBIDX3 | Destination FIFO B-Index Register 3 |
| 0x01C0 83D4 | 0x01C0 87D4 | DFMPPRXY3 | Destination FIFO Memory Protection Proxy Register 3 |
Table 5-14 shows an abbreviation of the set of registers which make up the parameter set for each of 128 EDMA events. Each of the parameter register sets consist of 8 32-bit word entries. Table 5-15 shows the parameter set entry registers with relative memory address locations within each of the parameter sets.
Table 5-14 EDMA Parameter Set RAM
| BYTE ADDRESS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| 0x01C0 4000 - 0x01C0 401F | Parameters Set 0 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 4020 - 0x01C0 403F | Parameters Set 1 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 4040 - 0x01C0 405F | Parameters Set 2 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 4060 - 0x01C0 407F | Parameters Set 3 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 4080 - 0x01C0 409F | Parameters Set 4 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 40A0 - 0x01C0 40BF | Parameters Set 5 (8 32-bit words) |
| ... | ... |
| 0x01C0 4FC0 - 0x01C0 4FDF | Parameters Set 126 (8 32-bit words) |
| 0x01C0 4FE0 - 0x01C0 4FFF | Parameters Set 127 (8 32-bit words) |
Table 5-15 Parameter Set Entries
| BYTE OFFSET ADDRESS WITHIN THE PARAMETER SET |
ACRONYM | PARAMETER ENTRY |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 | OPT | Option |
| 0x0004 | SRC | Source Address |
| 0x0008 | A_B_CNT | A Count, B Count |
| 0x000C | DST | Destination Address |
| 0x0010 | SRC_DST_BIDX | Source B Index, Destination B Index |
| 0x0014 | LINK_BCNTRLD | Link Address, B Count Reload |
| 0x0018 | SRC_DST_CIDX | Source C Index, Destination C Index |
| 0x001C | CCNT | C Count |
Table 5-16 EDMA Events
| Event | Event Name / Source | Event | Event Name / Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | McASP0 Receive | 16 | MMCSD Receive | |
| 1 | McASP0 Transmit | 17 | MMCSD Transmit | |
| 2 | McASP1 Receive | 18 | SPI1 Receive | |
| 3 | McASP1 Transmit | 19 | SPI1 Transmit | |
| 4 | McASP2 Receive | 20 | PRU_EVTOUT6 | |
| 5 | McASP2 Transmit | 21 | PRU_EVTOUT7 | |
| 6 | GPIO Bank 0 Interrupt | 22 | GPIO Bank 2 Interrupt | |
| 7 | GPIO Bank 1 Interrupt | 23 | GPIO Bank 3 Interrupt | |
| 8 | UART0 Receive | 24 | I2C0 Receive | |
| 9 | UART0 Transmit | 25 | I2C0 Transmit | |
| 10 | Timer64P0 Event Out 12 | 26 | I2C1 Receive | |
| 11 | Timer64P0 Event Out 34 | 27 | I2C1 Transmit | |
| 12 | UART1 Receive | 28 | GPIO Bank 4 Interrupt | |
| 13 | UART1 Transmit | 29 | GPIO Bank 5 Interrupt | |
| 14 | SPI0 Receive | 30 | UART2 Receive | |
| 15 | SPI0 Transmit | 31 | UART2 Transmit |
5.10 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
EMIFA is one of two external memory interfaces supported on the device. It is primarily intended to support asynchronous memory types, such as NAND and NOR flash and Asynchronous SRAM. However the EMIFA also provides a secondary interface to SDRAM.
5.10.1 EMIFA Asynchronous Memory Support
EMIFA supports asynchronous:
- SRAM memories
- NAND Flash memories
- NOR Flash memories
The EMIFA data bus width is up to 16-bits on the ZKB package.The device supports up to fifteen address lines and an external wait/interrupt input. Up to four asynchronous chip selects are supported by EMIFA (EMA_CS[5:2]) .
All four chip selects are available on the ZKB package.
Each chip select has the following individually programmable attributes:
- Data Bus Width
- Read cycle timings: setup, hold, strobe
- Write cycle timings: setup, hold, strobe
- Bus turn around time
- Extended Wait Option With Programmable Timeout
- Select Strobe Option
- NAND flash controller supports 1-bit and 4-bit ECC calculation on blocks of 512 bytes.
5.10.2 EMIFA Synchronous DRAM Memory Support
The device ZKB package supports 16-bit SDRAM in addition to the asynchronous memories listed in Section 5.10.1. It has a single SDRAM chip select (EMA_CS[0]). SDRAM configurations that are supported are:
- One, Two, and Four Bank SDRAM devices
- Devices with Eight, Nine, Ten, and Eleven Column Address
- CAS Latency of two or three clock cycles
- Sixteen Bit Data Bus Width
- 3.3V LVCMOS Interface
Additionally, the SDRAM interface of EMIFA supports placing the SDRAM in Self Refresh and Powerdown Modes. Self Refresh mode allows the SDRAM to be put into a low power state while still retaining memory contents. Powerdown mode achieves even lower power, except the processor must periodically wake the SDRAM up and issue refreshes if data retention is required.
Finally, note that the EMIFA does not support Mobile SDRAM devices. Table 5-17 below shows the supported SDRAM configurations for EMIFA.
Table 5-17 EMIFA Supported SDRAM Configurations(1)
| SDRAM Memory Data Bus Width (bits) |
Number of Memories | EMIFB Data Bus Size | Rows | Columns | Banks | Total Memory (Mbits) |
Total Memory (Mbytes) |
Memory Density (Mbits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 1 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 1 | 32 | 4 | 32 |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 2 | 64 | 8 | 64 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 128 | 16 | 128 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 1 | 64 | 8 | 64 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 128 | 16 | 128 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 4 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 128 | 16 | 128 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 512 | 64 | 512 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 512 | 64 | 512 | |
| 1 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 1024 | 128 | 1024 | |
| 8 | 2 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 1 | 32 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 2 | 64 | 8 | 32 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 128 | 16 | 64 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 1 | 64 | 8 | 32 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 128 | 16 | 64 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 9 | 4 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 128 | 16 | 64 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 512 | 64 | 256 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 512 | 64 | 256 | |
| 2 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 1024 | 128 | 512 |
5.10.3 EMIFA SDRAM Loading Limitations
EMIFA supports SDRAM up to 100 MHz with up to two SDRAM or asynchronous memory loads. Additional loads will limit the SDRAM operation to lower speeds and the maximum speed should be confirmed by board simulation using IBIS models.
5.10.4 EMIFA Connection Examples
Figure 5-12 illustrates an example of how SDRAM, NOR, and NAND flash devices might be connected to EMIFA of a AM1707 device simultaneously. The SDRAM chip select must be EMA_CS[0]. Note that the NOR flash is connected to EMA_CS[2] and the NAND flash is connected to EMA_CS[3] in this example. Note that any type of asynchronous memory may be connected to EMA_CS[5:2].
The on-chip bootloader makes some assumptions on which chip select the contains the boot image, and this depends on the boot mode. For NOR boot mode; the on-chip bootloader requires that the image be stored in NOR flash on EMA_CS[2]. For NAND boot mode, the bootloader requires that the boot image is stored in NAND flash on EMA_CS[3]. It is always possible to have the image span multiple chip selects, but this must be supported by second stage boot code stored in the external flash.
A likely use case with more than one EMIFA chip select used for NAND flash is illustrated in Figure 5-13. This figure shows how two multiplane NAND flash devices with two chip selects each would connect to the EMIFA. In this case if NAND is the boot memory, then the boot image needs to be stored in the NAND area selected by EMA_CS[3]. Part of the application image could spill over into the NAND regions selected by other EMIFA chip selects; but would rely on the code stored in the EMA_CS[3] area to bootload it.
 Figure 5-12 AM1707 Connection Diagram: SDRAM, NOR, NAND
Figure 5-12 AM1707 Connection Diagram: SDRAM, NOR, NAND
 Figure 5-13 AM1707 EMIFA Connection Diagram: Multiple NAND Flash Planes
Figure 5-13 AM1707 EMIFA Connection Diagram: Multiple NAND Flash Planes
5.10.5 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA) Registers
Table 5-18 is a list of the EMIF registers.
Table 5-18 External Memory Interface (EMIFA) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x6800 0000 | MIDR | Module ID Register |
| 0x6800 0004 | AWCC | Asynchronous Wait Cycle Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 0008 | SDCR | SDRAM Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 000C | SDRCR | SDRAM Refresh Control Register |
| 0x6800 0010 | CE2CFG | Asynchronous 1 Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 0014 | CE3CFG | Asynchronous 2 Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 0018 | CE4CFG | Asynchronous 3 Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 001C | CE5CFG | Asynchronous 4 Configuration Register |
| 0x6800 0020 | SDTIMR | SDRAM Timing Register |
| 0x6800 003C | SDSRETR | SDRAM Self Refresh Exit Timing Register |
| 0x6800 0040 | INTRAW | EMIFA Interrupt Raw Register |
| 0x6800 0044 | INTMSK | EMIFA Interrupt Mask Register |
| 0x6800 0048 | INTMSKSET | EMIFA Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x6800 004C | INTMSKCLR | EMIFA Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
| 0x6800 0060 | NANDFCR | NAND Flash Control Register |
| 0x6800 0064 | NANDFSR | NAND Flash Status Register |
| 0x6800 0070 | NANDF1ECC | NAND Flash 1 ECC Register (CS2 Space) |
| 0x6800 0074 | NANDF2ECC | NAND Flash 2 ECC Register (CS3 Space) |
| 0x6800 0078 | NANDF3ECC | NAND Flash 3 ECC Register (CS4 Space) |
| 0x6800 007C | NANDF4ECC | NAND Flash 4 ECC Register (CS5 Space) |
| 0x6800 00BC | NAND4BITECCLOAD | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Load Register |
| 0x6800 00C0 | NAND4BITECC1 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Register 1 |
| 0x6800 00C4 | NAND4BITECC2 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Register 2 |
| 0x6800 00C8 | NAND4BITECC3 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Register 3 |
| 0x6800 00CC | NAND4BITECC4 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Register 4 |
| 0x6800 00D0 | NANDERRADD1 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Error Address Register 1 |
| 0x6800 00D4 | NANDERRADD2 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Error Address Register 2 |
| 0x6800 00D8 | NANDERRVAL1 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Error Value Register 1 |
| 0x6800 00DC | NANDERRVAL2 | NAND Flash 4-Bit ECC Error Value Register 2 |
5.10.6 EMIFA Electrical Data/Timing
The following assume testing over recommended operating conditions.
Table 5-19 EMIFA SDRAM Interface Timing Requirements
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | tsu(DV-CLKH) | Input setup time, read data valid on EMA_D[15:0] before EMA_CLK rising | 1.3 | ns | ||||
| 20 | th(CLKH-DIV) | Input hold time, read data valid on EMA_D[15:0] after EMA_CLK rising | 1.5 | ns | ||||
Table 5-20 EMIFA SDRAM Interface Switching Characteristics
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(CLK) | Cycle time, EMIF clock EMA_CLK | 10 | ns | ||||
| 2 | tw(CLK) | Pulse width, EMIF clock EMA_CLK high or low | 3 | ns | ||||
| 3 | td(CLKH-CSV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_CS[0] valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 4 | toh(CLKH-CSIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_CS[0] invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 5 | td(CLKH-DQMV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_WE_DQM[1:0] valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 6 | toh(CLKH-DQMIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_WE_DQM[1:0] invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 7 | td(CLKH-AV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_A[12:0] and EMA_BA[1:0] valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 8 | toh(CLKH-AIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_A[12:0] and EMA_BA[1:0] invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 9 | td(CLKH-DV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_D[15:0] valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 10 | toh(CLKH-DIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_D[15:0] invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 11 | td(CLKH-RASV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_RAS valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 12 | toh(CLKH-RASIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_RAS invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 13 | td(CLKH-CASV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_CAS valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 14 | toh(CLKH-CASIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_CAS invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 15 | td(CLKH-WEV) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_WE valid | 7 | ns | ||||
| 16 | toh(CLKH-WEIV) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_WE invalid | 1 | ns | ||||
| 17 | tdis(CLKH-DHZ) | Delay time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_D[15:0] 3-stated | 7 | ns | ||||
| 18 | tena(CLKH-DLZ) | Output hold time, EMA_CLK rising to EMA_D[15:0] driving | 1 | ns | ||||
Table 5-21 EMIFA Asynchronous Memory Timing Requirements(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| READS and WRITES | ||||||
| E | tc(CLK) | Cycle time, EMIFA module clock | 10 | ns | ||
| 2 | tw(EM_WAIT) | Pulse duration, EM_WAIT assertion and deassertion | 2E | ns | ||
| READS | ||||||
| 12 | tsu(EMDV-EMOEH) | Setup time, EM_D[15:0] valid before EM_OE high | 3 | ns | ||
| 13 | th(EMOEH-EMDIV) | Hold time, EM_D[15:0] valid after EM_OE high | 0 | ns | ||
| 14 | tsu(EMOEL-EMWAIT) | Setup Time, EM_WAIT asserted before end of Strobe Phase(2) | 4E+3 | ns | ||
| WRITES | ||||||
| 28 | tsu(EMWEL-EMWAIT) | Setup Time, EM_WAIT asserted before end of Strobe Phase(2) | 4E+3 | ns | ||
Table 5-22 EMIFA Asynchronous Memory Switching Characteristics(1)(2)(3)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| READS and WRITES | ||||||
| 1 | td(TURNAROUND) | Turn around time | (TA)*E - 3 | (TA)*E | (TA)*E + 3 | ns |
| READS | ||||||
| 3 | tc(EMRCYCLE) | EMIF read cycle time (EW = 0) | (RS+RST+RH)*E - 3 | (RS+RST+RH)*E | (RS+RST+RH)*E + 3 | ns |
| EMIF read cycle time (EW = 1) | (RS+RST+RH+EWC)*E - 3 | (RS+RST+RH+EWC)*E | (RS+RST+RH+EWC)*E + 3 | ns | ||
| 4 | tsu(EMCEL-EMOEL) | Output setup time, EMA_CE[5:2] low to EMA_OE low (SS = 0) | (RS)*E-3 | (RS)*E | (RS)*E+3 | ns |
| Output setup time, EMA_CE[5:2] low to EMA_OE low (SS = 1) | -3 | 0 | +3 | ns | ||
| 5 | th(EMOEH-EMCEH) | Output hold time, EMA_OE high to EMA_CE[5:2] high (SS = 0) | (RH)*E - 3 | (RH)*E | (RH)*E + 3 | ns |
| Output hold time, EMA_OE high to EMA_CE[5:2] high (SS = 1) | -3 | 0 | +3 | ns | ||
| 6 | tsu(EMBAV-EMOEL) | Output setup time, EMA_BA[1:0] valid to EMA_OE low | (RS)*E-3 | (RS)*E | (RS)*E+3 | ns |
| 7 | th(EMOEH-EMBAIV) | Output hold time, EMA_OE high to EMA_BA[1:0] invalid | (RH)*E-3 | (RH)*E | (RH)*E+3 | ns |
| 8 | tsu(EMBAV-EMOEL) | Output setup time, EMA_A[13:0] valid to EMA_OE low | (RS)*E-3 | (RS)*E | (RS)*E+3 | ns |
| 9 | th(EMOEH-EMAIV) | Output hold time, EMA_OE high to EMA_A[13:0] invalid | (RH)*E-3 | (RH)*E | (RH)*E+3 | ns |
| 10 | tw(EMOEL) | EMA_OE active low width (EW = 0) | (RST)*E-3 | (RST)*E | (RST)*E+3 | ns |
| EMA_OE active low width (EW = 1) | (RST+EWC)*E-3 | (RST+EWC)*E | (RST+EWC)*E+3 | ns | ||
| 11 | td(EMWAITH-EMOEH) | Delay time from EMA_WAIT deasserted to EMA_OE high | 3E-3 | 4E | 4E+3 | ns |
| WRITES | ||||||
| 15 | tc(EMWCYCLE) | EMIF write cycle time (EW = 0) | (WS+WST+WH)*E-3 | (WS+WST+WH)*E | (WS+WST+WH)*E+3 | ns |
| EMIF write cycle time (EW = 1) | (WS+WST+WH+EWC)*E - 3 | (WS+WST+WH+EWC)*E | (WS+WST+WH+EWC)*E + 3 | ns | ||
| 16 | tsu(EMCEL-EMWEL) | Output setup time, EMA_CE[5:2] low to EMA_WE low (SS = 0) | (WS)*E - 3 | (WS)*E | (WS)*E + 3 | ns |
| Output setup time, EMA_CE[5:2] low to EMA_WE low (SS = 1) | -3 | 0 | +3 | ns | ||
| 17 | th(EMWEH-EMCEH) | Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_CE[5:2] high (SS = 0) | (WH)*E-3 | (WH)*E | (WH)*E+3 | ns |
| Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_CE[5:2] high (SS = 1) | -3 | 0 | +3 | ns | ||
| 18 | tsu(EMDQMV-EMWEL) | Output setup time, EMA_BA[1:0] valid to EMA_WE low | (WS)*E-3 | (WS)*E | (WS)*E+3 | ns |
| 19 | th(EMWEH-EMDQMIV) | Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_BA[1:0] invalid | (WH)*E-3 | (WH)*E | (WH)*E+3 | ns |
| 20 | tsu(EMBAV-EMWEL) | Output setup time, EMA_BA[1:0] valid to EMA_WE low | (WS)*E-3 | (WS)*E | (WS)*E+3 | ns |
| 21 | th(EMWEH-EMBAIV) | Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_BA[1:0] invalid | (WH)*E-3 | (WH)*E | (WH)*E+3 | ns |
| 22 | tsu(EMAV-EMWEL) | Output setup time, EMA_A[13:0] valid to EMA_WE low | (WS)*E-3 | (WS)*E | (WS)*E+3 | ns |
| 23 | th(EMWEH-EMAIV) | Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_A[13:0] invalid | (WH)*E-3 | (WH)*E | (WH)*E+3 | ns |
| 24 | tw(EMWEL) | EMA_WE active low width (EW = 0) | (WST)*E-3 | (WST)*E | (WST)*E+3 | ns |
| EMA_WE active low width (EW = 1) | (WST+EWC)*E-3 | (WST+EWC)*E | (WST+EWC)*E+3 | ns | ||
| 25 | td(EMWAITH-EMWEH) | Delay time from EMA_WAIT deasserted to EMA_WE high | 3E-3 | 4E | 4E+3 | ns |
| 26 | tsu(EMDV-EMWEL) | Output setup time, EMA_D[15:0] valid to EMA_WE low | (WS)*E-3 | (WS)*E | (WS)*E+3 | ns |
| 27 | th(EMWEH-EMDIV) | Output hold time, EMA_WE high to EMA_D[15:0] invalid | (WH)*E-3 | (WH)*E | (WH)*E+3 | ns |
 Figure 5-14 EMIFA Basic SDRAM Write Operation
Figure 5-14 EMIFA Basic SDRAM Write Operation
 Figure 5-15 EMIFA Basic SDRAM Read Operation
Figure 5-15 EMIFA Basic SDRAM Read Operation
 Figure 5-16 Asynchronous Memory Read Timing for EMIFA
Figure 5-16 Asynchronous Memory Read Timing for EMIFA
 Figure 5-17 Asynchronous Memory Write Timing for EMIFA
Figure 5-17 Asynchronous Memory Write Timing for EMIFA
 Figure 5-18 EMA_WAIT Read Timing Requirements
Figure 5-18 EMA_WAIT Read Timing Requirements
 Figure 5-19 EMA_WAIT Write Timing Requirements
Figure 5-19 EMA_WAIT Write Timing Requirements
5.11 External Memory Interface B (EMIFB)
The following EMIFB Functional Block Diagram illustrates a high-level view of the EMIFB and its connections within the device. Multiple requesters have access to EMIFB through a switched central resource (indicated as an overbar in the figure). The EMIFB implements a split transaction internal bus, allowing concurrence between reads and writes from the various requesters.
 Figure 5-20 EMIFB Functional Block Diagram
Figure 5-20 EMIFB Functional Block Diagram
EMIFB supports a 3.3V LVCMOS Interface.
5.11.1 EMIFB SDRAM Loading Limitations
EMIFB supports SDRAM up to 152 MHz with up to two SDRAM or asynchronous memory loads. Additional loads will limit the SDRAM operation to lower speeds and the maximum speed should be confirmed by board simulation using IBIS models.
5.11.2 Interfacing to SDRAM
The EMIFB supports a glueless interface to SDRAM devices with the following characteristics:
- Pre-charge bit is A[10]
- Supports 8, 9, 10 or 11 column address bits
- Supports up to 13 row address bits
- Supports 1, 2 or 4 internal banks
Table 5-23 shows the supported SDRAM configurations for EMIFB.
Table 5-23 EMIFB Supported SDRAM Configurations(1)
| SDRAM Memory Data Bus Width (bits) |
Number of Memories | EMIFB Data Bus Size | Rows | Columns | Banks | Total Memory (Mbits) |
Total Memory (Mbytes) |
Memory Density (Mbits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 1 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 1 | 64 | 8 | 64 |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 2 | 128 | 16 | 128 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 1 | 128 | 16 | 128 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 4 | 512 | 64 | 512 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 256 | 32 | 256 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 512 | 64 | 512 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 1024 | 128 | 1024 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 512 | 64 | 512 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 1024 | 128 | 1024 | |
| 1 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 2048 | 256 | 2048 | |
| 16 | 2 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 1 | 64 | 8 | 32 |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 2 | 128 | 16 | 64 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 8 | 4 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 1 | 128 | 16 | 64 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 9 | 4 | 512 | 64 | 256 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 1 | 256 | 32 | 128 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 512 | 64 | 256 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 10 | 4 | 1024 | 128 | 512 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 1 | 512 | 64 | 256 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 1024 | 128 | 512 | |
| 2 | 32 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 2048 | 256 | 1024 |
Figure 5-21 shows an interface between the EMIFB and a 2M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM device. In addition, Figure 5-22 shows an interface between the EMIFB and a 2M × 32 × 4 bank SDRAM device and Figure 5-23 shows an interface between the EMIFB and two 4M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM devices. Refer to Table 5-24 , as an example that shows additional list of commonly-supported SDRAM devices and the required connections for the address pins. Note that in Table 5-24, page size/column size (not indicated in the table) is varied to get the required addressability range.
 Figure 5-21 EMIFB to 2M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
Figure 5-21 EMIFB to 2M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
 Figure 5-22 EMIFB to 2M × 32 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
Figure 5-22 EMIFB to 2M × 32 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
 Figure 5-23 EMIFB to Dual 4M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
Figure 5-23 EMIFB to Dual 4M × 16 × 4 bank SDRAM Interface
Table 5-24 Example of 16/32-bit EMIFB Address Pin Connections
| SDRAM Size | Width | Banks | Address Pins | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64M bits | ×16 | 4 | SDRAM | A[11:0] |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[11:0] | |||
| ×32 | 4 | SDRAM | A[10:0] | |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[10:0] | |||
| 128M bits | ×16 | 4 | SDRAM | A[11:0] |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[11:0] | |||
| ×32 | 4 | SDRAM | A[11:0] | |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[11:0] | |||
| 256M bits | ×16 | 4 | SDRAM | A[12:0] |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[12:0] | |||
| ×32 | 4 | SDRAM | A[11:0] | |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[11:0] | |||
| 512M bits | ×16 | 4 | SDRAM | A[12:0] |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[12:0] | |||
| ×32 | 4 | SDRAM | A[12:0] | |
| EMIFB | EMB_A[12:0] |
5.11.3 EMIFB Registers
Table 5-25 is a list of the EMIFB registers.
Table 5-25 EMIFB Controller Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0xB000 0000 | MIDR | Module ID Register |
| 0xB000 0008 | SDCFG | SDRAM Configuration Register |
| 0xB000 000C | SDRFC | SDRAM Refresh Control Register |
| 0xB000 0010 | SDTIM1 | SDRAM Timing Register 1 |
| 0xB000 0014 | SDTIM2 | SDRAM Timing Register 2 |
| 0xB000 001C | SDCFG2 | SDRAM Configuration 2 Register |
| 0xB000 0020 | BPRIO | Peripheral Bus Burst Priority Register |
| 0xB000 0040 | PC1 | Performance Counter 1 Register |
| 0xB000 0044 | PC2 | Performance Counter 2 Register |
| 0xB000 0048 | PCC | Performance Counter Configuration Register |
| 0xB000 004C | PCMRS | Performance Counter Master Region Select Register |
| 0xB000 0050 | PCT | Performance Counter Time Register |
| 0xB000 00C0 | IRR | Interrupt Raw Register |
| 0xB000 00C4 | IMR | Interrupt Mask Register |
| 0xB000 00C8 | IMSR | Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0xB000 00CC | IMCR | Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
5.11.4 EMIFB Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-26 EMIFB SDRAM Interface Timing Requirements
| NO. | CVDD = 1.3 V(1) | CVDD = 1.2V(2) | UNIT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||||||
| 19 | t(DV-CLKH) | Input setup time, read data valid on EMB_D[31:0] before EMB_CLK rising | 0.59 | 0.8 | ns | |||||
| 20 | th(CLKH-DIV) | Input hold time, read data valid on EMB_D[31:0] after EMB_CLK rising | 1.25 | 1.5 | ns | |||||
Table 5-27 EMIFB SDRAM Interface Switching Characteristics for Commercial (Default) Temperature Range
| NO. | PARAMETER | CVDD = 1.3 V(1) | CVDD = 1.2V(2) | UNIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||||||
| 1 | tc(CLK) | Cycle time, EMIF clock EMB_CLK | 6.579 | 7.5 | ns | |||||
| 2 | tw(CLK) | Pulse width, EMIF clock EMB_CLK high or low | 2.63 | 3 | ns | |||||
| 3 | td(CLKH-CSV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CS[0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 4 | toh(CLKH-CSIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CS[0] invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 5 | td(CLKH-DQMV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE_DQM[3:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 6 | toh(CLKH-DQMIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE_DQM[3:0] invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 7 | td(CLKH-AV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_A[12:0] and EMB_BA[1:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 8 | toh(CLKH-AIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_A[12:0] and EMB_BA[1:0] invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 9 | td(CLKH-DV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 10 | toh(CLKH-DIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 11 | td(CLKH-RASV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_RAS valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 12 | toh(CLKH-RASIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_RAS invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 13 | td(CLKH-CASV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CAS valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 14 | toh(CLKH-CASIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CAS invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 15 | td(CLKH-WEV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 16 | toh(CLKH-WEIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE invalid | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
| 17 | tdis(CLKH-DHZ) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] tri-stated | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 18 | t(CLKH-DLZ) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] driving | 1.1 | 1.1 | ns | |||||
Table 5-28 EMIFB SDRAM Interface Switching Characteristics for Industrial, Extended, and Automotive Temperature Ranges
| NO. | PARAMETER | CVDD = 1.3 V(1) | CVDD = 1.2V(2) | UNIT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||||||
| 1 | tc(CLK) | Cycle time, EMIF clock EMB_CLK | 6.579 | 7.5 | ns | |||||
| 2 | tw(CLK) | Pulse width, EMIF clock EMB_CLK high or low | 2.63 | 3 | ns | |||||
| 3 | td(CLKH-CSV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CS[0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 4 | toh(CLKH-CSIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CS[0] invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 5 | td(CLKH-DQMV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE_DQM[3:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 6 | toh(CLKH-DQMIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE_DQM[3:0] invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 7 | td(CLKH-AV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_A[12:0] and EMB_BA[1:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 8 | toh(CLKH-AIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_A[12:0] and EMB_BA[1:0] invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 9 | td(CLKH-DV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 10 | toh(CLKH-DIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 11 | td(CLKH-RASV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_RAS valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 12 | toh(CLKH-RASIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_RAS invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 13 | td(CLKH-CASV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CAS valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 14 | toh(CLKH-CASIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_CAS invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 15 | td(CLKH-WEV) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE valid | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 16 | toh(CLKH-WEIV) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_WE invalid | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
| 17 | tdis(CLKH-DHZ) | Delay time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] tri-stated | 4.25 | 5.1 | ns | |||||
| 18 | t(CLKH-DLZ) | Output hold time, EMB_CLK rising to EMB_D[31:0] driving | 1.1 | 0.9 | ns | |||||
 Figure 5-24 EMIFB Basic SDRAM Write Operation
Figure 5-24 EMIFB Basic SDRAM Write Operation
 Figure 5-25 EMIFB Basic SDRAM Read Operation
Figure 5-25 EMIFB Basic SDRAM Read Operation
5.12 Memory Protection Units
The MPU performs memory protection checking. It receives requests from a bus master in the system and checks the address against the fixed and programmable regions to see if the access is allowed. If allowed, the transfer is passed unmodified to its output bus (to the targeted address). If the transfer is illegal (fails the protection check) then the MPU does not pass the transfer to the output bus but rather services the transfer internally back to the input bus (to prevent a hang) returning the fault status to the requestor as well as generating an interrupt about the fault. The following features are supported by the MPU:
- Provides memory protection for fixed and programmable address ranges
- Supports multiple programmable address region
- Supports secure and debug access privileges
- Supports read, write, and execute access privileges
- Supports privid(8) associations with ranges
- Generates an interrupt when there is a protection violation, and saves violating transfer parameters
- MMR access is also protected
Table 5-29 MPU1 Configuration Registers
| MPU1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E1 4000 | REVID | Revision ID |
| 0x01E1 4004 | CONFIG | Configuration |
| 0x01E1 4010 | IRAWSTAT | Interrupt raw status/set |
| 0x01E1 4014 | IENSTAT | Interrupt enable status/clear |
| 0x01E1 4018 | IENSET | Interrupt enable |
| 0x01E1 401C | IENCLR | Interrupt enable clear |
| 0x01E1 4020 - 0x01E1 41FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4200 | PROG1_MPSAR | Programmable range 1, start address |
| 0x01E1 4204 | PROG1_MPEAR | Programmable range 1, end address |
| 0x01E1 4208 | PROG1_MPPA | Programmable range 1, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 420C - 0x01E1 420F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4210 | PROG2_MPSAR | Programmable range 2, start address |
| 0x01E1 4214 | PROG2_MPEAR | Programmable range 2, end address |
| 0x01E1 4218 | PROG2_MPPA | Programmable range 2, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 421C - 0x01E1 421F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4220 | PROG3_MPSAR | Programmable range 3, start address |
| 0x01E1 4224 | PROG3_MPEAR | Programmable range 3, end address |
| 0x01E1 4228 | PROG3_MPPA | Programmable range 3, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 422C - 0x01E1 422F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4230 | PROG4_MPSAR | Programmable range 4, start address |
| 0x01E1 4234 | PROG4_MPEAR | Programmable range 4, end address |
| 0x01E1 4238 | PROG4_MPPA | Programmable range 4, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 423C - 0x01E1 423F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4240 | PROG5_MPSAR | Programmable range 5, start address |
| 0x01E1 4244 | PROG5_MPEAR | Programmable range 5, end address |
| 0x01E1 4248 | PROG5_MPPA | Programmable range 5, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 424C - 0x01E1 424F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 4250 | PROG6_MPSAR | Programmable range 6, start address |
| 0x01E1 4254 | PROG6_MPEAR | Programmable range 6, end address |
| 0x01E1 4258 | PROG6_MPPA | Programmable range 6, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 425C - 0x01E1 42FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E14300 | FLTADDRR | Fault address |
| 0x01E1 4304 | FLTSTAT | Fault status |
| 0x01E1 4308 | FLTCLR | Fault clear |
| 0x01E1 430C - 0x01E1 4FFF | - | Reserved |
Table 5-30 MPU2 Configuration Registers
| MPU2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E1 5000 | REVID | Revision ID |
| 0x01E1 5004 | CONFIG | Configuration |
| 0x01E1 5010 | IRAWSTAT | Interrupt raw status/set |
| 0x01E1 5014 | IENSTAT | Interrupt enable status/clear |
| 0x01E1 5018 | IENSET | Interrupt enable |
| 0x01E1 501C | IENCLR | Interrupt enable clear |
| 0x01E1 5020 - 0x01E1 50FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5100 | FXD_MPSAR | Fixed range start address |
| 0x01E1 5104 | FXD_MPEAR | Fixed range end start address |
| 0x01E1 5108 | FXD_MPPA | Fixed range memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 510C - 0x01E1 51FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5200 | PROG1_MPSAR | Programmable range 1, start address |
| 0x01E1 5204 | PROG1_MPEAR | Programmable range 1, end address |
| 0x01E1 5208 | PROG1_MPPA | Programmable range 1, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 520C - 0x01E1 520F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5210 | PROG2_MPSAR | Programmable range 2, start address |
| 0x01E1 5214 | PROG2_MPEAR | Programmable range 2, end address |
| 0x01E1 5218 | PROG2_MPPA | Programmable range 2, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 521C - 0x01E1 521F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5220 | PROG3_MPSAR | Programmable range 3, start address |
| 0x01E1 5224 | PROG3_MPEAR | Programmable range 3, end address |
| 0x01E1 5228 | PROG3_MPPA | Programmable range 3, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 522C - 0x01E1 522F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5230 | PROG4_MPSAR | Programmable range 4, start address |
| 0x01E1 5234 | PROG4_MPEAR | Programmable range 4, end address |
| 0x01E1 5238 | PROG4_MPPA | Programmable range 4, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 523C - 0x01E1 523F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5240 | PROG5_MPSAR | Programmable range 5, start address |
| 0x01E1 5244 | PROG5_MPEAR | Programmable range 5, end address |
| 0x01E1 5248 | PROG5_MPPA | Programmable range 5, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 524C - 0x01E1 524F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5250 | PROG6_MPSAR | Programmable range 6, start address |
| 0x01E1 5254 | PROG6_MPEAR | Programmable range 6, end address |
| 0x01E1 5258 | PROG6_MPPA | Programmable range 6, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 525C - 0x01E1 525F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5260 | PROG7_MPSAR | Programmable range 7, start address |
| 0x01E1 5264 | PROG7_MPEAR | Programmable range 7, end address |
| 0x01E1 5268 | PROG7_MPPA | Programmable range 7, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 526C - 0x01E1 526F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5270 | PROG8_MPSAR | Programmable range 8, start address |
| 0x01E1 5274 | PROG8_MPEAR | Programmable range 8, end address |
| 0x01E1 5278 | PROG8_MPPA | Programmable range 8, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 527C - 0x01E1 527F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5280 | PROG9_MPSAR | Programmable range 9, start address |
| 0x01E1 5284 | PROG9_MPEAR | Programmable range 9, end address |
| 0x01E1 5288 | PROG9_MPPA | Programmable range 9, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 528C - 0x01E1 528F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5290 | PROG10_MPSAR | Programmable range 10, start address |
| 0x01E1 5294 | PROG10_MPEAR | Programmable range 10, end address |
| 0x01E1 5298 | PROG10_MPPA | Programmable range 10, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 529C - 0x01E1 529F | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 52A0 | PROG11_MPSAR | Programmable range 11, start address |
| 0x01E1 52A4 | PROG11_MPEAR | Programmable range 11, end address |
| 0x01E1 52A8 | PROG11_MPPA | Programmable range 11, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 52AC - 0x01E1 52AF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 52B0 | PROG12_MPSAR | Programmable range 12, start address |
| 0x01E1 52B4 | PROG12_MPEAR | Programmable range 12, end address |
| 0x01E1 52B8 | PROG12_MPPA | Programmable range 12, memory page protection attributes |
| 0x01E1 52BC - 0x01E1 52FF | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E1 5300 | FLTADDRR | Fault address |
| 0x01E1 5304 | FLTSTAT | Fault status |
| 0x01E1 5308 | FLTCLR | Fault clear |
| 0x01E1 530C - 0x01E1 5FFF | - | Reserved |
5.13 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD)
5.13.1 MMCSD Peripheral Description
The device includes an MMCSD controller which is compliant with MMC V4.0, Secure Digital Part 1 Physical Layer Specification V1.1 and Secure Digital Input Output (SDIO) V2.0 specifications.
The MMC/SD Controller has following features:
- MultiMediaCard (MMC) support
- Secure Digital (SD) Memory Card support
- MMC/SD protocol support
- SD high capacity support
- SDIO protocol support
- Programmable clock frequency
- 512 bit Read/Write FIFO to lower system overhead
- Slave EDMA transfer capability
The device MMC/SD Controller does not support SPI mode.
5.13.2 MMCSD Peripheral Register Description(s)
Table 5-31 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD) Card Controller Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01C4 0000 | MMCCTL | MMC Control Register |
| 0x01C4 0004 | MMCCLK | MMC Memory Clock Control Register |
| 0x01C4 0008 | MMCST0 | MMC Status Register 0 |
| 0x01C4 000C | MMCST1 | MMC Status Register 1 |
| 0x01C4 0010 | MMCIM | MMC Interrupt Mask Register |
| 0x01C4 0014 | MMCTOR | MMC Response Time-Out Register |
| 0x01C4 0018 | MMCTOD | MMC Data Read Time-Out Register |
| 0x01C4 001C | MMCBLEN | MMC Block Length Register |
| 0x01C4 0020 | MMCNBLK | MMC Number of Blocks Register |
| 0x01C4 0024 | MMCNBLC | MMC Number of Blocks Counter Register |
| 0x01C4 0028 | MMCDRR | MMC Data Receive Register |
| 0x01C4 002C | MMCDXR | MMC Data Transmit Register |
| 0x01C4 0030 | MMCCMD | MMC Command Register |
| 0x01C4 0034 | MMCARGHL | MMC Argument Register |
| 0x01C4 0038 | MMCRSP01 | MMC Response Register 0 and 1 |
| 0x01C4 003C | MMCRSP23 | MMC Response Register 2 and 3 |
| 0x01C4 0040 | MMCRSP45 | MMC Response Register 4 and 5 |
| 0x01C4 0044 | MMCRSP67 | MMC Response Register 6 and 7 |
| 0x01C4 0048 | MMCDRSP | MMC Data Response Register |
| 0x01C4 0050 | MMCCIDX | MMC Command Index Register |
| 0x01C4 0064 | SDIOCTL | SDIO Control Register |
| 0x01C4 0068 | SDIOST0 | SDIO Status Register 0 |
| 0x01C4 006C | SDIOIEN | SDIO Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C4 0070 | SDIOIST | SDIO Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01C4 0074 | MMCFIFOCTLπ | MMC FIFO Control Register |
5.13.3 MMC/SD Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-32 Timing Requirements for MMC/SD Module
(see Figure 5-27 and Figure 5-29)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tsu(CMDV-CLKH) | Setup time, MMCSD_CMD valid before MMCSD_CLK high | 3.2 | ns | |
| 2 | th(CLKH-CMDV) | Hold time, MMCSD_CMD valid after MMCSD_CLK high | 1.5 | ns | |
| 3 | tsu(DATV-CLKH) | Setup time, MMCSD_DATx valid before MMCSD_CLK high | 3.2 | ns | |
| 4 | th(CLKH-DATV) | Hold time, MMCSD_DATx valid after MMCSD_CLK high | 1.5 | ns | |
Table 5-33 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for MMC/SD Module (see Figure 5-26 through Figure 5-29)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | f(CLK) | Operating frequency, MMCSD_CLK | 0 | 52 | MHz |
| 8 | f(CLK_ID) | Identification mode frequency, MMCSD_CLK | 0 | 400 | KHz |
| 9 | tW(CLKL) | Pulse width, MMCSD_CLK low | 6.5 | ns | |
| 10 | tW(CLKH) | Pulse width, MMCSD_CLK high | 6.5 | ns | |
| 11 | tr(CLK) | Rise time, MMCSD_CLK | 3 | ns | |
| 12 | tf(CLK) | Fall time, MMCSD_CLK | 3 | ns | |
| 13 | td(CLKL-CMD) | Delay time, MMCSD_CLK low to MMCSD_CMD transition | -4.5 | 2.5 | ns |
| 14 | td(CLKL-DAT) | Delay time, MMCSD_CLK low to MMCSD_DATx transition | -4.5 | 2.5 | ns |
 Figure 5-26 MMC/SD Host Command Timing
Figure 5-26 MMC/SD Host Command Timing
 Figure 5-27 MMC/SD Card Response Timing
Figure 5-27 MMC/SD Card Response Timing
 Figure 5-28 MMC/SD Host Write Timing
Figure 5-28 MMC/SD Host Write Timing
 Figure 5-29 MMC/SD Host Read and Card CRC Status Timing
Figure 5-29 MMC/SD Host Read and Card CRC Status Timing
5.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
The Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) provides an efficient interface between the device and the network. The EMAC supports both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX, or 10 Mbits/second (Mbps) and 100 Mbps in either half- or full-duplex mode, with hardware flow control and quality of service (QOS) support.
The EMAC controls the flow of packet data from the device to the PHY. The MDIO module controls PHY configuration and status monitoring.
Both the EMAC and the MDIO modules interface to the device through a custom interface that allows efficient data transmission and reception. This custom interface is referred to as the EMAC control module, and is considered integral to the EMAC/MDIO peripheral. The control module is also used to multiplex and control interrupts.
5.14.1 EMAC Peripheral Register Description(s)
Table 5-34 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 3000 | TXREV | Transmit Revision Register |
| 0x01E2 3004 | TXCONTROL | Transmit Control Register |
| 0x01E2 3008 | TXTEARDOWN | Transmit Teardown Register |
| 0x01E2 3010 | RXREV | Receive Revision Register |
| 0x01E2 3014 | RXCONTROL | Receive Control Register |
| 0x01E2 3018 | RXTEARDOWN | Receive Teardown Register |
| 0x01E2 3080 | TXINTSTATRAW | Transmit Interrupt Status (Unmasked) Register |
| 0x01E2 3084 | TXINTSTATMASKED | Transmit Interrupt Status (Masked) Register |
| 0x01E2 3088 | TXINTMASKSET | Transmit Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x01E2 308C | TXINTMASKCLEAR | Transmit Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01E2 3090 | MACINVECTOR | MAC Input Vector Register |
| 0x01E2 3094 | MACEOIVECTOR | MAC End Of Interrupt Vector Register |
| 0x01E2 30A0 | RXINTSTATRAW | Receive Interrupt Status (Unmasked) Register |
| 0x01E2 30A4 | RXINTSTATMASKED | Receive Interrupt Status (Masked) Register |
| 0x01E2 30A8 | RXINTMASKSET | Receive Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x01E2 30AC | RXINTMASKCLEAR | Receive Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
| 0x01E2 30B0 | MACINTSTATRAW | MAC Interrupt Status (Unmasked) Register |
| 0x01E2 30B4 | MACINTSTATMASKED | MAC Interrupt Status (Masked) Register |
| 0x01E2 30B8 | MACINTMASKSET | MAC Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x01E2 30BC | MACINTMASKCLEAR | MAC Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
| 0x01E2 3100 | RXMBPENABLE | Receive Multicast/Broadcast/Promiscuous Channel Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 3104 | RXUNICASTSET | Receive Unicast Enable Set Register |
| 0x01E2 3108 | RXUNICASTCLEAR | Receive Unicast Clear Register |
| 0x01E2 310C | RXMAXLEN | Receive Maximum Length Register |
| 0x01E2 3110 | RXBUFFEROFFSET | Receive Buffer Offset Register |
| 0x01E2 3114 | RXFILTERLOWTHRESH | Receive Filter Low Priority Frame Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3120 | RX0FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 0 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3124 | RX1FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 1 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3128 | RX2FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 2 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 312C | RX3FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 3 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3130 | RX4FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 4 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3134 | RX5FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 5 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3138 | RX6FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 6 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 313C | RX7FLOWTHRESH | Receive Channel 7 Flow Control Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 3140 | RX0FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 0 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3144 | RX1FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 1 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3148 | RX2FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 2 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 314C | RX3FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 3 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3150 | RX4FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 4 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3154 | RX5FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 5 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3158 | RX6FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 6 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 315C | RX7FREEBUFFER | Receive Channel 7 Free Buffer Count Register |
| 0x01E2 3160 | MACCONTROL | MAC Control Register |
| 0x01E2 3164 | MACSTATUS | MAC Status Register |
| 0x01E2 3168 | EMCONTROL | Emulation Control Register |
| 0x01E2 316C | FIFOCONTROL | FIFO Control Register |
| 0x01E2 3170 | MACCONFIG | MAC Configuration Register |
| 0x01E2 3174 | SOFTRESET | Soft Reset Register |
| 0x01E2 31D0 | MACSRCADDRLO | MAC Source Address Low Bytes Register |
| 0x01E2 31D4 | MACSRCADDRHI | MAC Source Address High Bytes Register |
| 0x01E2 31D8 | MACHASH1 | MAC Hash Address Register 1 |
| 0x01E2 31DC | MACHASH2 | MAC Hash Address Register 2 |
| 0x01E2 31E0 | BOFFTEST | Back Off Test Register |
| 0x01E2 31E4 | TPACETEST | Transmit Pacing Algorithm Test Register |
| 0x01E2 31E8 | RXPAUSE | Receive Pause Timer Register |
| 0x01E2 31EC | TXPAUSE | Transmit Pause Timer Register |
| 0x01E2 3200 - 0x01E2 32FC | (see Table 5-35) | EMAC Statistics Registers |
| 0x01E2 3500 | MACADDRLO | MAC Address Low Bytes Register, Used in Receive Address Matching |
| 0x01E2 3504 | MACADDRHI | MAC Address High Bytes Register, Used in Receive Address Matching |
| 0x01E2 3508 | MACINDEX | MAC Index Register |
| 0x01E2 3600 | TX0HDP | Transmit Channel 0 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3604 | TX1HDP | Transmit Channel 1 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3608 | TX2HDP | Transmit Channel 2 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 360C | TX3HDP | Transmit Channel 3 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3610 | TX4HDP | Transmit Channel 4 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3614 | TX5HDP | Transmit Channel 5 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3618 | TX6HDP | Transmit Channel 6 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 361C | TX7HDP | Transmit Channel 7 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3620 | RX0HDP | Receive Channel 0 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3624 | RX1HDP | Receive Channel 1 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3628 | RX2HDP | Receive Channel 2 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 362C | RX3HDP | Receive Channel 3 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3630 | RX4HDP | Receive Channel 4 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3634 | RX5HDP | Receive Channel 5 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3638 | RX6HDP | Receive Channel 6 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 363C | RX7HDP | Receive Channel 7 DMA Head Descriptor Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3640 | TX0CP | Transmit Channel 0 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3644 | TX1CP | Transmit Channel 1 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3648 | TX2CP | Transmit Channel 2 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 364C | TX3CP | Transmit Channel 3 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3650 | TX4CP | Transmit Channel 4 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3654 | TX5CP | Transmit Channel 5 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3658 | TX6CP | Transmit Channel 6 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 365C | TX7CP | Transmit Channel 7 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3660 | RX0CP | Receive Channel 0 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3664 | RX1CP | Receive Channel 1 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3668 | RX2CP | Receive Channel 2 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 366C | RX3CP | Receive Channel 3 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3670 | RX4CP | Receive Channel 4 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3674 | RX5CP | Receive Channel 5 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 3678 | RX6CP | Receive Channel 6 Completion Pointer Register |
| 0x01E2 367C | RX7CP | Receive Channel 7 Completion Pointer Register |
Table 5-35 EMAC Statistics Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 3200 | RXGOODFRAMES | Good Receive Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3204 | RXBCASTFRAMES | Broadcast Receive Frames Register (Total number of good broadcast frames received) |
| 0x01E2 3208 | RXMCASTFRAMES | Multicast Receive Frames Register (Total number of good multicast frames received) |
| 0x01E2 320C | RXPAUSEFRAMES | Pause Receive Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3210 | RXCRCERRORS | Receive CRC Errors Register (Total number of frames received with CRC errors) |
| 0x01E2 3214 | RXALIGNCODEERRORS | Receive Alignment/Code Errors Register (Total number of frames received with alignment/code errors) |
| 0x01E2 3218 | RXOVERSIZED | Receive Oversized Frames Register (Total number of oversized frames received) |
| 0x01E2 321C | RXJABBER | Receive Jabber Frames Register (Total number of jabber frames received) |
| 0x01E2 3220 | RXUNDERSIZED | Receive Undersized Frames Register (Total number of undersized frames received) |
| 0x01E2 3224 | RXFRAGMENTS | Receive Frame Fragments Register |
| 0x01E2 3228 | RXFILTERED | Filtered Receive Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 322C | RXQOSFILTERED | Received QOS Filtered Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3230 | RXOCTETS | Receive Octet Frames Register (Total number of received bytes in good frames) |
| 0x01E2 3234 | TXGOODFRAMES | Good Transmit Frames Register (Total number of good frames transmitted) |
| 0x01E2 3238 | TXBCASTFRAMES | Broadcast Transmit Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 323C | TXMCASTFRAMES | Multicast Transmit Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3240 | TXPAUSEFRAMES | Pause Transmit Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3244 | TXDEFERRED | Deferred Transmit Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3248 | TXCOLLISION | Transmit Collision Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 324C | TXSINGLECOLL | Transmit Single Collision Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3250 | TXMULTICOLL | Transmit Multiple Collision Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3254 | TXEXCESSIVECOLL | Transmit Excessive Collision Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3258 | TXLATECOLL | Transmit Late Collision Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 325C | TXUNDERRUN | Transmit Underrun Error Register |
| 0x01E2 3260 | TXCARRIERSENSE | Transmit Carrier Sense Errors Register |
| 0x01E2 3264 | TXOCTETS | Transmit Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3268 | FRAME64 | Transmit and Receive 64 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 326C | FRAME65T127 | Transmit and Receive 65 to 127 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3270 | FRAME128T255 | Transmit and Receive 128 to 255 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3274 | FRAME256T511 | Transmit and Receive 256 to 511 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3278 | FRAME512T1023 | Transmit and Receive 512 to 1023 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 327C | FRAME1024TUP | Transmit and Receive 1024 to 1518 Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3280 | NETOCTETS | Network Octet Frames Register |
| 0x01E2 3284 | RXSOFOVERRUNS | Receive FIFO or DMA Start of Frame Overruns Register |
| 0x01E2 3288 | RXMOFOVERRUNS | Receive FIFO or DMA Middle of Frame Overruns Register |
| 0x01E2 328C | RXDMAOVERRUNS | Receive DMA Start of Frame and Middle of Frame Overruns Register |
Table 5-36 EMAC Control Module Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 2000 | REV | EMAC Control Module Revision Register |
| 0x01E2 2004 | SOFTRESET | EMAC Control Module Software Reset Register |
| 0x01E2 200C | INTCONTROL | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Control Register |
| 0x01E2 2010 | C0RXTHRESHEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Receive Threshold Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2014 | C0RXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Receive Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2018 | C0TXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Transmit Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 201C | C0MISCEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Miscellaneous Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2020 | C1RXTHRESHEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Receive Threshold Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2024 | C1RXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Receive Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2028 | C1TXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Transmit Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 202C | C1MISCEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Miscellaneous Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2030 | C2RXTHRESHEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Receive Threshold Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2034 | C2RXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Receive Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2038 | C2TXEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Transmit Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 203C | C2MISCEN | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Miscellaneous Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 2040 | C0RXTHRESHSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Receive Threshold Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2044 | C0RXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Receive Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2048 | C0TXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Transmit Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 204C | C0MISCSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Miscellaneous Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2050 | C1RXTHRESHSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Receive Threshold Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2054 | C1RXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Receive Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2058 | C1TXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Transmit Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 205C | C1MISCSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Miscellaneous Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2060 | C2RXTHRESHSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Receive Threshold Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2064 | C2RXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Receive Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2068 | C2TXSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Transmit Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 206C | C2MISCSTAT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Miscellaneous Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01E2 2070 | C0RXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Receive Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
| 0x01E2 2074 | C0TXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 0 Transmit Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
| 0x01E2 2078 | C1RXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Receive Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
| 0x01E2 207C | C1TXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 1 Transmit Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
| 0x01E2 2080 | C2RXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Receive Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
| 0x01E2 2084 | C2TXIMAX | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Core 2 Transmit Interrupts Per Millisecond Register |
Table 5-37 EMAC Control Module RAM
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | |
|---|---|
| 0x01E2 0000 - 0x01E2 1FFF | EMAC Local Buffer Descriptor Memory |
Table 5-38 RMII Timing Requirements
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(REFCLK) | Cycle Time, RMII_MHZ_50_CLK(1) | 20 | ns | ||
| 2 | tw(REFCLKH) | Pulse Width, RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 7 | 13 | ns | |
| 3 | tw(REFCLKL) | Pulse Width, RMII_MHZ_50_CLK Low | 7 | 13 | ns | |
| 6 | tsu(RXD-REFCLK) | Input Setup Time, RXD Valid before RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 4 | ns | ||
| 7 | th(REFCLK-RXD) | Input Hold Time, RXD Valid after RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 2 | ns | ||
| 8 | tsu(CRSDV-REFCLK) | Input Setup Time, CRSDV Valid before RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 4 | ns | ||
| 9 | th(REFCLK-CRSDV) | Input Hold Time, CRSDV Valid after RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 2 | ns | ||
| 10 | tsu(RXER-REFCLK) | Input Setup Time, RXER Valid before RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 4 | ns | ||
| 11 | th(REFCLKR-RXER) | Input Hold Time, RXER Valid after RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High | 2 | ns | ||
Table 5-39 RMII Switching Characteristics
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | td(REFCLK-TXD) | Output Delay Time, RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High to TXD Valid | 2.5 | 13 | ns | |
| 5 | td(REFCLK-TXEN) | Output Delay Time, RMII_MHZ_50_CLK High to TXEN Valid | 2.5 | 13 | ns | |
 Figure 5-30 RMII Timing Diagram
Figure 5-30 RMII Timing Diagram
5.15 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
The Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module continuously polls all 32 MDIO addresses in order to enumerate all PHY devices in the system.
The Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module implements the 802.3 serial management interface to interrogate and control Ethernet PHY(s) using a shared two-wire bus. Host software uses the MDIO module to configure the auto-negotiation parameters of each PHY attached to the EMAC, retrieve the negotiation results, and configure required parameters in the EMAC module for correct operation. The module is designed to allow almost transparent operation of the MDIO interface, with very little maintenance from the core processor. Only one PHY may be connected at any given time.
5.15.1 MDIO Registers
For a list of supported MDIO registers see Table 5-40 [MDIO Registers].
Table 5-40 MDIO Register Memory Map
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 4000 | REV | Revision Identification Register |
| 0x01E2 4004 | CONTROL | MDIO Control Register |
| 0x01E2 4008 | ALIVE | MDIO PHY Alive Status Register |
| 0x01E2 400C | LINK | MDIO PHY Link Status Register |
| 0x01E2 4010 | LINKINTRAW | MDIO Link Status Change Interrupt (Unmasked) Register |
| 0x01E2 4014 | LINKINTMASKED | MDIO Link Status Change Interrupt (Masked) Register |
| 0x01E2 4018 | – | Reserved |
| 0x01E2 4020 | USERINTRAW | MDIO User Command Complete Interrupt (Unmasked) Register |
| 0x01E2 4024 | USERINTMASKED | MDIO User Command Complete Interrupt (Masked) Register |
| 0x01E2 4028 | USERINTMASKSET | MDIO User Command Complete Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x01E2 402C | USERINTMASKCLEAR | MDIO User Command Complete Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
| 0x01E2 4030 - 0x01E2 407C | – | Reserved |
| 0x01E2 4080 | USERACCESS0 | MDIO User Access Register 0 |
| 0x01E2 4084 | USERPHYSEL0 | MDIO User PHY Select Register 0 |
| 0x01E2 4088 | USERACCESS1 | MDIO User Access Register 1 |
| 0x01E2 408C | USERPHYSEL1 | MDIO User PHY Select Register 1 |
| 0x01E2 4090 - 0x01E2 47FF | – | Reserved |
5.15.2 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-41 Timing Requirements for MDIO Input (see Figure 5-31 and Figure 5-32)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(MDIO_CLK) | Cycle time, MDIO_CLK | 400 | ns | |
| 2 | tw(MDIO_CLK) | Pulse duration, MDIO_CLK high/low | 180 | ns | |
| 3 | tt(MDIO_CLK) | Transition time, MDIO_CLK | 5 | ns | |
| 4 | tsu(MDIO-MDIO_CLKH) | Setup time, MDIO_D data input valid before MDIO_CLK high | 10 | ns | |
| 5 | th(MDIO_CLKH-MDIO) | Hold time, MDIO_D data input valid after MDIO_CLK high | 0 | ns | |
 Figure 5-31 MDIO Input Timing
Figure 5-31 MDIO Input Timing
Table 5-42 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for MDIO Output
(see Figure 5-32)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | td(MDIO_CLKL-MDIO) | Delay time, MDIO_CLK low to MDIO_D data output valid | 0 | 100 | ns |
 Figure 5-32 MDIO Output Timing
Figure 5-32 MDIO Output Timing
5.16 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1, and McASP2)
The McASP serial port is specifically designed for multichannel audio applications. Its key features are:
- Flexible clock and frame sync generation logic and on-chip dividers
- Up to sixteen transmit or receive data pins and serializers
- Large number of serial data format options, including:
- TDM Frames with 2 to 32 time slots per frame (periodic) or 1 slot per frame (burst)
- Time slots of 8,12,16, 20, 24, 28, and 32 bits
- First bit delay 0, 1, or 2 clocks
- MSB or LSB first bit order
- Left- or right-aligned data words within time slots
- DIT Mode (optional) with 384-bit Channel Status and 384-bit User Data registers
- Extensive error checking and mute generation logic
- All unused pins GPIO-capable
- Transmit & Receive FIFO Buffers for each McASP. Allows the McASP to operate at a higher sample rate by making it more tolerant to DMA latency.
- Dynamic Adjustment of Clock Dividers
- Clock Divider Value may be changed without resetting the McASP
The McASPs on the device are configured with the following options:
Table 5-43 McASP Configurations(1)
| Module | Serializers | AFIFO | DIT | Pins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| McASP0 | 16 | 64 Word RX 64 Word TX |
N | AXR0[15:0], AHCLKR0, ACLKR0, AFSR0, AHCLKX0, ACLKX0, AFSX0, AMUTE0 |
| McASP1 | 12 | 64 Word RX 64 Word TX |
N | AXR1[11:10], AHCLKR1, ACLKR1, AFSR1, AHCLKX1, ACLKX1, AFSX1, AMUTE1 |
| McASP2 | 4 | 16 Word RX 16 Word TX |
Y | AXR2[3:0], AHCLKR2, ACLKR2, AFSR2, AHCLKX2, ACLKX2, AFSX2, AMUTE2 |
 Figure 5-33 McASP Block Diagram
Figure 5-33 McASP Block Diagram
5.16.1 McASP Peripheral Registers Description(s)
Registers for the McASP are summarized in Table 5-44. The registers are accessed through the peripheral configuration port. The receive buffer registers (RBUF) and transmit buffer registers (XBUF) can also be accessed through the DMA port, as listed in Table 5-45
Registers for the McASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO) are summarized in Table 5-46. Note that the AFIFO Write FIFO (WFIFO) and Read FIFO (RFIFO) have independent control and status registers. The AFIFO control registers are accessed through the peripheral configuration port.
Table 5-44 McASP Registers Accessed Through Peripheral Configuration Port
| McASP0 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP1 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01D0 0000 | 0x01D0 4000 | 0x01D0 8000 | REV | Revision identification register |
| 0x01D0 0010 | 0x01D0 4010 | 0x01D0 8010 | PFUNC | Pin function register |
| 0x01D0 0014 | 0x01D0 4014 | 0x01D0 8014 | PDIR | Pin direction register |
| 0x01D0 0018 | 0x01D0 4018 | 0x01D0 8018 | PDOUT | Pin data output register |
| 0x01D0 001C | 0x01D0 401C | 0x01D0 801C | PDIN | Read returns: Pin data input register |
| 0x01D0 001C | 0x01D0 401C | 0x01D0 801C | PDSET | Writes affect: Pin data set register (alternate write address: PDOUT) |
| 0x01D0 0020 | 0x01D0 4020 | 0x01D0 8020 | PDCLR | Pin data clear register (alternate write address: PDOUT) |
| 0x01D0 0044 | 0x01D0 4044 | 0x01D0 8044 | GBLCTL | Global control register |
| 0x01D0 0048 | 0x01D0 4048 | 0x01D0 8048 | AMUTE | Audio mute control register |
| 0x01D0 004C | 0x01D0 404C | 0x01D0 804C | DLBCTL | Digital loopback control register |
| 0x01D0 0050 | 0x01D0 4050 | 0x01D0 8050 | DITCTL | DIT mode control register |
| 0x01D0 0060 | 0x01D0 4060 | 0x01D0 8060 | RGBLCTL | Receiver global control register: Alias of GBLCTL, only receive bits are affected - allows receiver to be reset independently from transmitter |
| 0x01D0 0064 | 0x01D0 4064 | 0x01D0 8064 | RMASK | Receive format unit bit mask register |
| 0x01D0 0068 | 0x01D0 4068 | 0x01D0 8068 | RFMT | Receive bit stream format register |
| 0x01D0 006C | 0x01D0 406C | 0x01D0 806C | AFSRCTL | Receive frame sync control register |
| 0x01D0 0070 | 0x01D0 4070 | 0x01D0 8070 | ACLKRCTL | Receive clock control register |
| 0x01D0 0074 | 0x01D0 4074 | 0x01D0 8074 | AHCLKRCTL | Receive high-frequency clock control register |
| 0x01D0 0078 | 0x01D0 4078 | 0x01D0 8078 | RTDM | Receive TDM time slot 0-31 register |
| 0x01D0 007C | 0x01D0 407C | 0x01D0 807C | RINTCTL | Receiver interrupt control register |
| 0x01D0 0080 | 0x01D0 4080 | 0x01D0 8080 | RSTAT | Receiver status register |
| 0x01D0 0084 | 0x01D0 4084 | 0x01D0 8084 | RSLOT | Current receive TDM time slot register |
| 0x01D0 0088 | 0x01D0 4088 | 0x01D0 8088 | RCLKCHK | Receive clock check control register |
| 0x01D0 008C | 0x01D0 408C | 0x01D0 808C | REVTCTL | Receiver DMA event control register |
| 0x01D0 00A0 | 0x01D0 40A0 | 0x01D0 80A0 | XGBLCTL | Transmitter global control register. Alias of GBLCTL, only transmit bits are affected - allows transmitter to be reset independently from receiver |
| 0x01D0 00A4 | 0x01D0 40A4 | 0x01D0 80A4 | XMASK | Transmit format unit bit mask register |
| 0x01D0 00A8 | 0x01D0 40A8 | 0x01D0 80A8 | XFMT | Transmit bit stream format register |
| 0x01D0 00AC | 0x01D0 40AC | 0x01D0 80AC | AFSXCTL | Transmit frame sync control register |
| 0x01D0 00B0 | 0x01D0 40B0 | 0x01D0 80B0 | ACLKXCTL | Transmit clock control register |
| 0x01D0 00B4 | 0x01D0 40B4 | 0x01D0 80B4 | AHCLKXCTL | Transmit high-frequency clock control register |
| 0x01D0 00B8 | 0x01D0 40B8 | 0x01D0 80B8 | XTDM | Transmit TDM time slot 0-31 register |
| 0x01D0 00BC | 0x01D0 40BC | 0x01D0 80BC | XINTCTL | Transmitter interrupt control register |
| 0x01D0 00C0 | 0x01D0 40C0 | 0x01D0 80C0 | XSTAT | Transmitter status register |
| 0x01D0 00C4 | 0x01D0 40C4 | 0x01D0 80C4 | XSLOT | Current transmit TDM time slot register |
| 0x01D0 00C8 | 0x01D0 40C8 | 0x01D0 80C8 | XCLKCHK | Transmit clock check control register |
| 0x01D0 00CC | 0x01D0 40CC | 0x01D0 80CC | XEVTCTL | Transmitter DMA event control register |
| 0x01D0 0100 | 0x01D0 4100 | 0x01D0 8100 | DITCSRA0 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 0 |
| 0x01D0 0104 | 0x01D0 4104 | 0x01D0 8104 | DITCSRA1 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 1 |
| 0x01D0 0108 | 0x01D0 4108 | 0x01D0 8108 | DITCSRA2 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 2 |
| 0x01D0 010C | 0x01D0 410C | 0x01D0 810C | DITCSRA3 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 3 |
| 0x01D0 0110 | 0x01D0 4110 | 0x01D0 8110 | DITCSRA4 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 4 |
| 0x01D0 0114 | 0x01D0 4114 | 0x01D0 8114 | DITCSRA5 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 5 |
| 0x01D0 0118 | 0x01D0 4118 | 0x01D0 8118 | DITCSRB0 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 0 |
| 0x01D0 011C | 0x01D0 411C | 0x01D0 811C | DITCSRB1 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 1 |
| 0x01D0 0120 | 0x01D0 4120 | 0x01D0 8120 | DITCSRB2 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 2 |
| 0x01D0 0124 | 0x01D0 4124 | 0x01D0 8124 | DITCSRB3 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 3 |
| 0x01D0 0128 | 0x01D0 4128 | 0x01D0 8128 | DITCSRB4 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 4 |
| 0x01D0 012C | 0x01D0 412C | 0x01D0 812C | DITCSRB5 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel status register (DIT mode) 5 |
| 0x01D0 0130 | 0x01D0 4130 | 0x01D0 8130 | DITUDRA0 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 0 |
| 0x01D0 0134 | 0x01D0 4134 | 0x01D0 8134 | DITUDRA1 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 1 |
| 0x01D0 0138 | 0x01D0 4138 | 0x01D0 8138 | DITUDRA2 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 2 |
| 0x01D0 013C | 0x01D0 413C | 0x01D0 813C | DITUDRA3 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 3 |
| 0x01D0 0140 | 0x01D0 4140 | 0x01D0 8140 | DITUDRA4 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 4 |
| 0x01D0 0144 | 0x01D0 4144 | 0x01D0 8144 | DITUDRA5 | Left (even TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 5 |
| 0x01D0 0148 | 0x01D0 4148 | 0x01D0 8148 | DITUDRB0 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 0 |
| 0x01D0 014C | 0x01D0 414C | 0x01D0 814C | DITUDRB1 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 1 |
| 0x01D0 0150 | 0x01D0 4150 | 0x01D0 8150 | DITUDRB2 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 2 |
| 0x01D0 0154 | 0x01D0 4154 | 0x01D0 8154 | DITUDRB3 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 3 |
| 0x01D0 0158 | 0x01D0 4158 | 0x01D0 8158 | DITUDRB4 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 4 |
| 0x01D0 015C | 0x01D0 415C | 0x01D0 815C | DITUDRB5 | Right (odd TDM time slot) channel user data register (DIT mode) 5 |
| 0x01D0 0180 | 0x01D0 4180 | 0x01D0 8180 | SRCTL0 | Serializer control register 0 |
| 0x01D0 0184 | 0x01D0 4184 | 0x01D0 8184 | SRCTL1 | Serializer control register 1 |
| 0x01D0 0188 | 0x01D0 4188 | 0x01D0 8188 | SRCTL2 | Serializer control register 2 |
| 0x01D0 018C | 0x01D0 418C | 0x01D0 818C | SRCTL3 | Serializer control register 3 |
| 0x01D0 0190 | 0x01D0 4190 | 0x01D0 8190 | SRCTL4 | Serializer control register 4 |
| 0x01D0 0194 | 0x01D0 4194 | 0x01D0 8194 | SRCTL5 | Serializer control register 5 |
| 0x01D0 0198 | 0x01D0 4198 | 0x01D0 8198 | SRCTL6 | Serializer control register 6 |
| 0x01D0 019C | 0x01D0 419C | 0x01D0 819C | SRCTL7 | Serializer control register 7 |
| 0x01D0 01A0 | 0x01D0 41A0 | 0x01D0 81A0 | SRCTL8 | Serializer control register 8 |
| 0x01D0 01A4 | 0x01D0 41A4 | 0x01D0 81A4 | SRCTL9 | Serializer control register 9 |
| 0x01D0 01A8 | 0x01D0 41A8 | 0x01D0 81A8 | SRCTL10 | Serializer control register 10 |
| 0x01D0 01AC | 0x01D0 41AC | 0x01D0 81AC | SRCTL11 | Serializer control register 11 |
| 0x01D0 01B0 | 0x01D0 41B0 | 0x01D0 81B0 | SRCTL12 | Serializer control register 12 |
| 0x01D0 01B4 | 0x01D0 41B4 | 0x01D0 81B4 | SRCTL13 | Serializer control register 13 |
| 0x01D0 01B8 | 0x01D0 41B8 | 0x01D0 81B8 | SRCTL14 | Serializer control register 14 |
| 0x01D0 01BC | 0x01D0 41BC | 0x01D0 81BC | SRCTL15 | Serializer control register 15 |
| 0x01D0 0200 | 0x01D0 4200 | 0x01D0 8200 | XBUF0(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 0 |
| 0x01D0 0204 | 0x01D0 4204 | 0x01D0 8204 | XBUF1(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 1 |
| 0x01D0 0208 | 0x01D0 4208 | 0x01D0 8208 | XBUF2(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 2 |
| 0x01D0 020C | 0x01D0 420C | 0x01D0 820C | XBUF3(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 3 |
| 0x01D0 0210 | 0x01D0 4210 | 0x01D0 8210 | XBUF4(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 4 |
| 0x01D0 0214 | 0x01D0 4214 | 0x01D0 8214 | XBUF5(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 5 |
| 0x01D0 0218 | 0x01D0 4218 | 0x01D0 8218 | XBUF6(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 6 |
| 0x01D0 021C | 0x01D0 421C | 0x01D0 821C | XBUF7(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 7 |
| 0x01D0 0220 | 0x01D0 4220 | 0x01D0 8220 | XBUF8(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 8 |
| 0x01D0 0224 | 0x01D0 4224 | 0x01D0 8224 | XBUF9(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 9 |
| 0x01D0 0228 | 0x01D0 4228 | 0x01D0 8228 | XBUF10(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 10 |
| 0x01D0 022C | 0x01D0 422C | 0x01D0 822C | XBUF11(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 11 |
| 0x01D0 0230 | 0x01D0 4230 | 0x01D0 8230 | XBUF12(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 12 |
| 0x01D0 0234 | 0x01D0 4234 | 0x01D0 8234 | XBUF13(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 13 |
| 0x01D0 0238 | 0x01D0 4238 | 0x01D0 8238 | XBUF14(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 14 |
| 0x01D0 023C | 0x01D0 423C | 0x01D0 823C | XBUF15(1) | Transmit buffer register for serializer 15 |
| 0x01D0 0280 | 0x01D0 4280 | 0x01D0 8280 | RBUF0(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 0 |
| 0x01D0 0284 | 0x01D0 4284 | 0x01D0 8284 | RBUF1(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 1 |
| 0x01D0 0288 | 0x01D0 4288 | 0x01D0 8288 | RBUF2(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 2 |
| 0x01D0 028C | 0x01D0 428C | 0x01D0 828C | RBUF3(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 3 |
| 0x01D0 0290 | 0x01D0 4290 | 0x01D0 8290 | RBUF4(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 4 |
| 0x01D0 0294 | 0x01D0 4294 | 0x01D0 8294 | RBUF5(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 5 |
| 0x01D0 0298 | 0x01D0 4298 | 0x01D0 8298 | RBUF6(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 6 |
| 0x01D0 029C | 0x01D0 429C | 0x01D0 829C | RBUF7(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 7 |
| 0x01D0 02A0 | 0x01D0 42A0 | 0x01D0 82A0 | RBUF8(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 8 |
| 0x01D0 02A4 | 0x01D0 42A4 | 0x01D0 82A4 | RBUF9(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 9 |
| 0x01D0 02A8 | 0x01D0 42A8 | 0x01D0 82A8 | RBUF10(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 10 |
| 0x01D0 02AC | 0x01D0 42AC | 0x01D0 82AC | RBUF11(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 11 |
| 0x01D0 02B0 | 0x01D0 42B0 | 0x01D0 82B0 | RBUF12(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 12 |
| 0x01D0 02B4 | 0x01D0 42B4 | 0x01D0 82B4 | RBUF13(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 13 |
| 0x01D0 02B8 | 0x01D0 42B8 | 0x01D0 82BB | RBUF14(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 14 |
| 0x01D0 02BC | 0x01D0 42BC | 0x01D0 82BC | RBUF15(2) | Receive buffer register for serializer 15 |
Table 5-45 McASP Registers Accessed Through DMA Port
| McASP0 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP1 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read Accesses |
01D0 2000 | 01D0 6000 | 01D0 A000 | RBUF | Receive buffer DMA port address. Cycles through receive serializers, skipping over transmit serializers and inactive serializers. Starts at the lowest serializer at the beginning of each time slot. Reads from DMA port only if RBUSEL = 0 in RFMT. |
| Write Accesses |
01D0 2000 | 01D0 6000 | 01D0 A000 | XBUF | Transmit buffer DMA port address. Cycles through transmit serializers, skipping over receive and inactive serializers. Starts at the lowest serializer at the beginning of each time slot. Writes to DMA port only if XBUSEL = 0 in XFMT. |
Table 5-46 McASP AFIFO Registers Accessed Through Peripheral Configuration Port
| McASP0 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP1 BYTE ADDRESS |
McASP2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01D0 1000 | 0x01D0 5000 | 0x01D0 9000 | AFIFOREV | AFIFO revision identification register |
| 0x01D0 1010 | 0x01D0 5010 | 0x01D0 9010 | WFIFOCTL | Write FIFO control register |
| 0x01D0 1014 | 0x01D0 5014 | 0x01D0 9014 | WFIFOSTS | Write FIFO status register |
| 0x01D0 1018 | 0x01D0 5018 | 0x01D0 9018 | RFIFOCTL | Read FIFO control register |
| 0x01D0 101C | 0x01D0 501C | 0x01D0 901C | RFIFOSTS | Read FIFO status register |
5.16.2 McASP Electrical Data/Timing
5.16.2.1 Multichannel Audio Serial Port 0 (McASP0) Timing
Table 5-47 and Table 5-48 assume testing over recommended operating conditions (see Figure 5-34 and Figure 5-35).
Table 5-47 McASP0 Timing Requirements(1)(4)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR0 external, AHCLKR0 input | 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKX0 external, AHCLKX0 input | 25 | ||||
| 2 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR0 external, AHCLKR0 input | 12.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX0 external, AHCLKX0 input | 12.5 | ||||
| 3 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR0 external, ACLKR0 input | greater of 2P or 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKX0 external, ACLKX0 input | greater of 2P or 25 | ||||
| 4 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR0 external, ACLKR0 input | 12.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKX0 external, ACLKX0 input | 12.5 | ||||
| 5 | tsu(AFSRX-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AFSR0 input to ACLKR0 internal(2) | 9.4 | ns | |
| Setup time, AFSX0 input to ACLKX0 internal | 9.4 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR0 input to ACLKR0 external input(2) | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX0 input to ACLKX0 external input | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR0 input to ACLKR0 external output(2) | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX0 input to ACLKX0 external output | 2.9 | ||||
| 6 | th(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Hold time, AFSR0 input after ACLKR0 internal(2) | -1.2 | ns | |
| Hold time, AFSX0 input after ACLKX0 internal | -1.2 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR0 input after ACLKR0 external input(2) | 0.9 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX0 input after ACLKX0 external input | 0.9 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR0 input after ACLKR0 external output(2) | 0.9 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX0 input after ACLKX0 external output | 0.9 | ||||
| 7 | tsu(AXR-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKR0 internal(2) | 9.4 | ns | |
| Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKX0 internal(3) | 9.4 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKR0 external input(2) | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKX0 external input(3) | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKR0 external output(2) | 2.9 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR0[n] input to ACLKX0 external output(3) | 2.9 | ||||
| 8 | th(ACLKRX-AXR) | Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKR0 internal(2) | -1.3 | ns | |
| Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKX0 internal(3) | -1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKR0 external input(2) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKX0 external input(3) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKR0 external output(2) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR0[n] input after ACLKX0 external output(3) | 0.5 | ||||
ACLKX0 external input – McASP0 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
ACLKX0 external output – McASP0 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
ACLKR0 internal – McASP0 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
ACLKR0 external input – McASP0 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
ACLKR0 external output – McASP0 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1
Table 5-48 McASP0 Switching Characteristics(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR0 internal, AHCLKR0 output | 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKR0 external, AHCLKR0 output | 25 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX0 internal, AHCLKX0 output | 25 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX0 external, AHCLKX0 output | 25 | ||||
| 10 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR0 internal, AHCLKR0 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKR0 external, AHCLKR0 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX0 internal, AHCLKX0 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX0 external, AHCLKX0 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| 11 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR0 internal, ACLKR0 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKR0 external, ACLKR0 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX0 internal, ACLKX0 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX0 external, ACLKX0 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| 12 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR0 internal, ACLKR0 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKR0 external, ACLKR0 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX0 internal, ACLKX0 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX0 external, ACLKX0 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| 13 | td(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Delay time, ACLKR0 internal, AFSR output(7) | 0 | 5.8 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX0 internal, AFSX output | 0 | 5.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR0 external input, AFSR output(7) | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX0 external input, AFSX output | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR0 external output, AFSR output(7) | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX0 external output, AFSX output | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| 14 | td(ACLKX-AXRV) | Delay time, ACLKX0 internal, AXR0[n] output | 0 | 5.8 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX0 external input, AXR0[n] output | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX0 external output, AXR0[n] output | 2.5 | 11.6 | |||
| 15 | tdis(ACLKX-AXRHZ) | Disable time, ACLKX0 internal, AXR0[n] output | 0 | 5.8 | ns |
| Disable time, ACLKX0 external input, AXR0[n] output | 3 | 11.6 | |||
| Disable time, ACLKX0 external output, AXR0[n] output | 3 | 11.6 | |||
ACLKX0 external input – McASP0 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
ACLKX0 external output – McASP0ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
ACLKR0 internal – McASP0 ACLKR0CTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
ACLKR0 external input – McASP0 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
ACLKR0 external output – McASP0 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1
5.16.2.2 Multichannel Audio Serial Port 1 (McASP1) Timing
Table 5-49 and Table 5-50 assume testing over recommended operating conditions (see Figure 5-34 and Figure 5-35).
Table 5-49 McASP1 Timing Requirements(1)(4)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR1 external, AHCLKR1 input | 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKX1 external, AHCLKX1 input | 25 | ||||
| 2 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR1 external, AHCLKR1 input | 12.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX1 external, AHCLKX1 input | 12.5 | ||||
| 3 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR1 external, ACLKR1 input | greater of 2P or 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKX1 external, ACLKX1 input | greater of 2P or 25 | ||||
| 4 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR1 external, ACLKR1 input | 12.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKX1 external, ACLKX1 input | 12.5 | ||||
| 5 | tsu(AFSRX-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AFSR1 input to ACLKR1 internal(2) | 10.4 | ns | |
| Setup time, AFSX1 input to ACLKX1 internal | 10.4 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR1 input to ACLKR1 external input(2) | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX1 input to ACLKX1 external input | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR1 input to ACLKR1 external output(2) | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX1 input to ACLKX1 external output | 2.6 | ||||
| 6 | th(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Hold time, AFSR1 input after ACLKR1 internal(2) | -1.9 | ns | |
| Hold time, AFSX1 input after ACLKX1 internal | -1.9 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR1 input after ACLKR1 external input(2) | 0.7 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX1 input after ACLKX1 external input | 0.7 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR1 input after ACLKR1 external output(2) | 0.7 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX1 input after ACLKX1 external output | 0.7 | ||||
| 7 | tsu(AXR-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKR1 internal(2) | 10.4 | ns | |
| Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKX1 internal(3) | 10.4 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKR1 external input(2) | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKX1 external input(3) | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKR1 external output(2) | 2.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR1[n] input to ACLKX1 external output(3) | 2.6 | ||||
| 8 | th(ACLKRX-AXR) | Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKR1 internal(2) | -1.8 | ns | |
| Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKX1 internal(3) | -1.8 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKR1 external input(2) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKX1 external input(3) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKR1 external output(2) | 0.5 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR1[n] input after ACLKX1 external output(3) | 0.5 | ||||
ACLKX1 external input – McASP1 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
ACLKX1 external output – McASP1 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
ACLKR1 internal – McASP1 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
ACLKR1 external input – McASP1 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
ACLKR1 external output – McASP1 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1
Table 5-50 McASP1 Switching Characteristics(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR1 internal, AHCLKR1 output | 25 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKR1 external, AHCLKR1 output | 25 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX1 internal, AHCLKX1 output | 25 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX1 external, AHCLKX1 output | 25 | ||||
| 10 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR1 internal, AHCLKR1 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKR1 external, AHCLKR1 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX1 internal, AHCLKX1 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX1 external, AHCLKX1 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| 11 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR1 internal, ACLKR1 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKR1 external, ACLKR1 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX1 internal, ACLKX1 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX1 external, ACLKX1 output | greater of 2P or 25 ns(4) | ||||
| 12 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR1 internal, ACLKR1 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKR1 external, ACLKR1 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX1 internal, ACLKX1 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX1 external, ACLKX1 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| 13 | td(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Delay time, ACLKR1 internal, AFSR output(7) | 0.5 | 6.7 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX1 internal, AFSX output | 0.5 | 6.7 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR1 external input, AFSR output(7) | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX1 external input, AFSX output | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR1 external output, AFSR output(7) | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX1 external output, AFSX output | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| 14 | td(ACLKX-AXRV) | Delay time, ACLKX1 internal, AXR1[n] output | 0.5 | 6.7 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX1 external input, AXR1[n] output | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX1 external output, AXR1[n] output | 3.4 | 13.8 | |||
| 15 | tdis(ACLKX-AXRHZ) | Disable time, ACLKX1 internal, AXR1[n] output | 0.5 | 6.7 | ns |
| Disable time, ACLKX1 external input, AXR1[n] output | 3.9 | 13.8 | |||
| Disable time, ACLKX1 external output, AXR1[n] output | 3.9 | 13.8 | |||
McASP1 ACLKX1 external input – ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
McASP1 ACLKX1 external output – ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
McASP1 ACLKR1 internal – ACLKR1CTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
McASP1 ACLKR1 external input – ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
McASP1 ACLKR1 external output – ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1


5.16.2.3 Multichannel Audio Serial Port 2 (McASP2) Timing
Table 5-51 and Table 5-52 assume testing over recommended operating conditions (see Figure 5-34 and Figure 5-35).
Table 5-51 McASP2 Timing Requirements(1)(4)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR2 external, AHCLKR2 input | 15 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKX2 external, AHCLKX2 input | 15 | ||||
| 2 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR2 external, AHCLKR2 input | 7.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX2 external, AHCLKX2 input | 7.5 | ||||
| 3 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR2 external, ACLKR2 input | greater of 2P or 15 | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKX2 external, ACLKX2 input | greater of 2P or 15 | ||||
| 4 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR2 external, ACLKR2 input | 7.5 | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKX2 external, ACLKX2 input | 7.5 | ||||
| 5 | tsu(AFSRX-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AFSR2 input to ACLKR2 internal(2) | 10 | ns | |
| Setup time, AFSX2 input to ACLKX2 internal | 10 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR2 input to ACLKR2 external input(2) | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX2 input to ACLKX2 external input | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSR2 input to ACLKR2 external output(2) | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AFSX2 input to ACLKX2 external output | 1.6 | ||||
| 6 | th(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Hold time, AFSR2 input after ACLKR2 internal(2) | -1.7 | ns | |
| Hold time, AFSX2 input after ACLKX2 internal | -1.7 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR2 input after ACLKR2 external input(2) | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX2 input after ACLKX2 external input | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSR2 input after ACLKR2 external output(2) | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AFSX2 input after ACLKX2 external output | 1.3 | ||||
| 7 | tsu(AXR-ACLKRX) | Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKR2 internal(2) | 10 | ns | |
| Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKX2 internal(3) | 10 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKR2 external input(2) | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKX2 external input(3) | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKR2 external output(2) | 1.6 | ||||
| Setup time, AXR2[n] input to ACLKX2 external output(3) | 1.6 | ||||
| 8 | th(ACLKRX-AXR) | Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKR2 internal(2) | -1.7 | ns | |
| Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKX2 internal(3) | -1.7 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKR2 external input(2) | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKX2 external input(3) | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKR2 external output(2) | 1.3 | ||||
| Hold time, AXR2[n] input after ACLKX2 external output(3) | 1.3 | ||||
ACLKX2 external input – McASP2 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
ACLKX2 external output – McASP2 ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
ACLKR2 internal – McASP2 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
ACLKR2 external input – McASP2 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
ACLKR2 external output – McASP2 ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1
Table 5-52 McASP2 Switching Characteristics(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | tc(AHCLKRX) | Cycle time, AHCLKR2 internal, AHCLKR2 output | 15 | ns | |
| Cycle time, AHCLKR2 external, AHCLKR2 output | 15 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX2 internal, AHCLKX2 output | 15 | ||||
| Cycle time, AHCLKX2 external, AHCLKX2 output | 15 | ||||
| 10 | tw(AHCLKRX) | Pulse duration, AHCLKR2 internal, AHCLKR2 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, AHCLKR2 external, AHCLKR2 output | (AHR/2) – 2.5(2) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX2 internal, AHCLKX2 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| Pulse duration, AHCLKX2 external, AHCLKX2 output | (AHX/2) – 2.5(3) | ||||
| 11 | tc(ACLKRX) | Cycle time, ACLKR2 internal, ACLKR2 output | greater of 2P or 15 ns(4) | ns | |
| Cycle time, ACLKR2 external, ACLKR2 output | greater of 2P or 15 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX2 internal, ACLKX2 output | greater of 2P or 15 ns(4) | ||||
| Cycle time, ACLKX2 external, ACLKX2 output | greater of 2P or 15 ns(4) | ||||
| 12 | tw(ACLKRX) | Pulse duration, ACLKR2 internal, ACLKR2 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ns | |
| Pulse duration, ACLKR2 external, ACLKR2 output | (AR/2) – 2.5(5) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX2 internal, ACLKX2 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| Pulse duration, ACLKX2 external, ACLKX2 output | (AX/2) – 2.5(6) | ||||
| 13 | td(ACLKRX-AFSRX) | Delay time, ACLKR2 internal, AFSR output(7) | -1.4 | 2.8 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX2 internal, AFSX output | -1.4 | 2.8 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR2 external input, AFSR output(7) | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX2 external input, AFSX output | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKR2 external output, AFSR output(7) | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX2 external output, AFSX output | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| 14 | td(ACLKX-AXRV) | Delay time, ACLKX2 internal, AXR2[n] output | -1.4 | 2.8 | ns |
| Delay time, ACLKX2 external input, AXR2[n] output | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| Delay time, ACLKX2 external output, AXR2[n] output | 2.1 | 10 | |||
| 15 | tdis(ACLKX-AXRHZ) | Disable time, ACLKX2 internal, AXR2[n] output | -1.4 | 2.8 | ns |
| Disable time, ACLKX2 external input, AXR2[n] output | 2.9 | 10 | |||
| Disable time, ACLKX2 external output, AXR2[n] output | 2.9 | 10 | |||
McASP2 ACLKX2 external input – ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 0
McASP2 ACLKX2 external output – ACLKXCTL.CLKXM = 0, PDIR.ACLKX = 1
McASP2 ACLKR2 internal – ACLKR2CTL.CLKRM = 1, PDIR.ACLKR =1
McASP2 ACLKR2 external input – ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 0
McASP2 ACLKR2 external output – ACLKRCTL.CLKRM = 0, PDIR.ACLKR = 1
5.17 Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
Figure 5-36 is a block diagram of the SPI module, which is a simple shift register and buffer plus control logic. Data is written to the shift register before transmission occurs and is read from the buffer at the end of transmission. The SPI can operate either as a master, in which case, it initiates a transfer and drives the SPIx_CLK pin, or as a slave. Four clock phase and polarity options are supported as well as many data formatting options.
 Figure 5-36 Block Diagram of SPI Module
Figure 5-36 Block Diagram of SPI Module
The SPI supports 3-, 4-, and 5-pin operation with three basic pins (SPIx_CLK, SPIx_SIMO, and SPIx_SOMI) and two optional pins (SPIx_SCS, SPIx_ENA).
The optional SPIx_SCS (Slave Chip Select) pin is most useful to enable in slave mode when there are other slave devices on the same SPI port. The device will only shift data and drive the SPIx_SOMI pin when SPIx_SCS is held low.
In slave mode, SPIx_ENA is an optional output. The SPIx_ENA output provides the status of the internal transmit buffer (SPIDAT0/1 registers). In four-pin mode with the enable option, SPIx_ENA is asserted only when the transmit buffer is full, indicating that the slave is ready to begin another transfer. In five-pin mode, the SPIx_ENA is additionally qualified by SPIx_SCS being asserted. This allows a single handshake line to be shared by multiple slaves on the same SPI bus.
In master mode, the SPIx_ENA pin is an optional input and the master can be configured to delay the start of the next transfer until the slave asserts SPIx_ENA. The addition of this handshake signal simplifies SPI communications and, on average, increases SPI bus throughput since the master does not need to delay each transfer long enough to allow for the worst-case latency of the slave device. Instead, each transfer can begin as soon as both the master and slave have actually serviced the previous SPI transfer.
Although the SPI module supports two interrupt outputs, SPIx_INT1 is the only interrupt connected on this device.
 Figure 5-37 Illustration of SPI Master-to-SPI Slave Connection
Figure 5-37 Illustration of SPI Master-to-SPI Slave Connection
5.17.1 SPI Peripheral Registers Description(s)
Table 5-53 is a list of the SPI registers.
Table 5-53 SPIx Configuration Registers
| SPI0 BYTE ADDRESS |
SPI1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C4 1000 | 0x01E1 2000 | SPIGCR0 | Global Control Register 0 |
| 0x01C4 1004 | 0x01E1 2004 | SPIGCR1 | Global Control Register 1 |
| 0x01C4 1008 | 0x01E1 2008 | SPIINT0 | Interrupt Register |
| 0x01C4 100C | 0x01E1 200C | SPILVL | Interrupt Level Register |
| 0x01C4 1010 | 0x01E1 2010 | SPIFLG | Flag Register |
| 0x01C4 1014 | 0x01E1 2014 | SPIPC0 | Pin Control Register 0 (Pin Function) |
| 0x01C4 1018 | 0x01E1 2018 | SPIPC1 | Pin Control Register 1 (Pin Direction) |
| 0x01C4 101C | 0x01E1 201C | SPIPC2 | Pin Control Register 2 (Pin Data In) |
| 0x01C4 1020 | 0x01E1 2020 | SPIPC3 | Pin Control Register 3 (Pin Data Out) |
| 0x01C4 1024 | 0x01E1 2024 | SPIPC4 | Pin Control Register 4 (Pin Data Set) |
| 0x01C4 1028 | 0x01E1 2028 | SPIPC5 | Pin Control Register 5 (Pin Data Clear) |
| 0x01C4 102C | 0x01E1 202C | Reserved | Reserved - Do not write to this register |
| 0x01C4 1030 | 0x01E1 2030 | Reserved | Reserved - Do not write to this register |
| 0x01C4 1034 | 0x01E1 2034 | Reserved | Reserved - Do not write to this register |
| 0x01C4 1038 | 0x01E1 2038 | SPIDAT0 | Shift Register 0 (without format select) |
| 0x01C4 103C | 0x01E1 203C | SPIDAT1 | Shift Register 1 (with format select) |
| 0x01C4 1040 | 0x01E1 2040 | SPIBUF | Buffer Register |
| 0x01C4 1044 | 0x01E1 2044 | SPIEMU | Emulation Register |
| 0x01C4 1048 | 0x01E1 2048 | SPIDELAY | Delay Register |
| 0x01C4 104C | 0x01E1 204C | SPIDEF | Default Chip Select Register |
| 0x01C4 1050 | 0x01E1 2050 | SPIFMT0 | Format Register 0 |
| 0x01C4 1054 | 0x01E1 2054 | SPIFMT1 | Format Register 1 |
| 0x01C4 1058 | 0x01E1 2058 | SPIFMT2 | Format Register 2 |
| 0x01C4 105C | 0x01E1 205C | SPIFMT3 | Format Register 3 |
| 0x01C4 1060 | 0x01E1 2060 | Reserved | Reserved - Do not write to this register |
| 0x01C4 1064 | 0x01E1 2064 | INTVEC1 | Interrupt Vector for SPI INT1 |
5.17.2 SPI Electrical Data/Timing
5.17.2.1 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
Table 5-54 through Table 5-69 assume testing over recommended operating conditions (see Figure 5-38 through Figure 5-41).
Table 5-54 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Master Modes(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(SPC)M | Cycle Time, SPI0_CLK, All Master Modes | greater of 3P or 20 | 256P | ns | |
| 2 | tw(SPCH)M | Pulse Width High, SPI0_CLK, All Master Modes | 0.5tc(SPC)M - 1 | ns | ||
| 3 | tw(SPCL)M | Pulse Width Low, SPI0_CLK, All Master Modes | 0.5tc(SPC)M - 1 | ns | ||
| 4 | td(SIMO_SPC)M | Delay, initial data bit valid on SPI0_SIMO after initial edge on SPI0_CLK(2) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
- 0.5tc(SPC)M + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
- 0.5tc(SPC)M + 5 | |||||
| 5 | td(SPC_SIMO)M | Delay, subsequent bits valid on SPI0_SIMO after transmit edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| 6 | toh(SPC_SIMO)M | Output hold time, SPI0_SIMO valid afterreceive edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| 7 | tsu(SOMI_SPC)M | Input Setup Time, SPI0_SOMI valid beforereceive edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0 | |||||
| 8 | tih(SPC_SOMI)M | Input Hold Time, SPI0_SOMI valid after receive edge of SPI0_CLK |
Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
Table 5-55 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Slave Modes(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | tc(SPC)S | Cycle Time, SPI0_CLK, All Slave Modes | greater of 3P or 40 | ns | ||
| 10 | tw(SPCH)S | Pulse Width High, SPI0_CLK, All Slave Modes | 18 | ns | ||
| 11 | tw(SPCL)S | Pulse Width Low, SPI0_CLK, All Slave Modes | 18 | ns | ||
| 12 | tsu(SOMI_SPC)S | Setup time, transmit data written to SPI before initial clock edge from master.(2)(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
2P | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
2P | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
2P | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
2P | |||||
| 13 | td(SPC_SOMI)S | Delay, subsequent bits valid on SPI0_SOMI after transmit edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
18.5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
18.5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
18.5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
18.5 | |||||
| 14 | toh(SPC_SOMI)S | Output hold time, SPI0_SOMI valid afte receive edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| 15 | tsu(SIMO_SPC)S | Input Setup Time, SPI0_SIMO valid before receive edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0 | |||||
| 16 | tih(SPC_SIMO)S | Input Hold Time, SPI0_SIMO valid after receive edge of SPI0_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
Table 5-56 Additional(5) SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | td(ENA_SPC)M | Delay from slave assertion of SPI0_ENA active to first SPI0_CLK from master.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
3P + 3.6 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3.6 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
3P + 3.6 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3.6 | |||||
| 18 | td(SPC_ENA)M | Max delay for slave to deassert SPI0_ENA after final SPI0_CLK edge to ensure master does not begin the next transfer.(4) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
Table 5-57 Additional(7) SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | td(SCS_SPC)M | Delay from SPI0_SCS active to first SPI0_CLK(3)(4) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
2P - 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| 20 | td(SPC_SCS)M | Delay from final SPI0_CLK edge to master deasserting SPI0_SCS(5)(6) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P - 3 | |||||
Table 5-58 Additional(10) SPI0 Master Timings, 5-Pin Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | td(SPC_ENA)M | Max delay for slave to deassert SPI0_ENA after final SPI0_CLK edge to ensure master does not begin the next transfer.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 20 | td(SPC_SCS)M | Delay from final SPI0_CLK edge to master deasserting SPI0_SCS(4)(5) |
Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P - 3 | |||||
| 21 | td(SCSL_ENAL)M | Max delay for slave SPI to drive SPI0_ENA valid after master asserts SPI0_SCS to delay the master from beginning the next transfer, |
C2TDELAY + P | ns | ||
| 22 | td(SCS_SPC)M | Delay from SPI0_SCS active to first SPI0_CLK(6)(7)(8) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
2P - 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| 23 | td(ENA_SPC)M | Delay from assertion of SPI0_ENA low to first SPI0_CLK edge.(9) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK rising |
3P + 3.6 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3.6 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI0_CLK falling |
3P + 3.6 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3.6 | |||||
Table 5-59 Additional(3) SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | td(SPC_ENAH)S | Delay from final SPI0_CLK edge to slave deasserting SPI0_ENA. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
1.5 P - 3 | 2.5 P + 18.5 | ns |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
– 0.5tc(SPC)M + 1.5 P - 3 | – 0.5tc(SPC)M + 2.5 P + 18.5 | ||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
1.5 P - 3 | 2.5 P + 18.5 | ||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
– 0.5tc(SPC)M + 1.5 P - 3 | – 0.5tc(SPC)M + 2.5 P + 18.5 | ||||
Table 5-60 Additional(3) SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | td(SCSL_SPC)S | Required delay from SPI0_SCS asserted at slave to first SPI0_CLK edge at slave. | 2P | ns | ||
| 26 | td(SPC_SCSH)S | Required delay from final SPI0_CLK edge before SPI0_SCS is deasserted. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 27 | tena(SCSL_SOMI)S | Delay from master asserting SPI0_SCS to slave driving SPI0_SOMI valid | P + 18.5 | ns | ||
| 28 | tdis(SCSH_SOMI)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI0_SCS to slave 3-stating SPI0_SOMI | P + 18.5 | ns | ||
Table 5-61 Additional(4) SPI0 Slave Timings, 5-Pin Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | td(SCSL_SPC)S | Required delay from SPI0_SCS asserted at slave to first SPI0_CLK edge at slave. | 2P | ns | ||
| 26 | td(SPC_SCSH)S | Required delay from final SPI0_CLK edge before SPI0_SCS is deasserted. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 27 | tena(SCSL_SOMI)S | Delay from master asserting SPI0_SCS to slave driving SPI0_SOMI valid | P + 18.5 | ns | ||
| 28 | tdis(SCSH_SOMI)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI0_SCS to slave 3-stating SPI0_SOMI | P + 18.5 | ns | ||
| 29 | tena(SCSL_ENA)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI0_SCS to slave driving SPI0_ENA valid | 18.5 | ns | ||
| 30 | tdis(SPC_ENA)S | Delay from final clock receive edge on SPI0_CLK to slave 3-stating or driving high SPI0_ENA.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK falling |
2.5 P + 18.5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK rising |
2.5 P + 18.5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI0_CLK rising |
2.5 P + 18.5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI0_CLK falling |
2.5 P + 18.5 | |||||
Table 5-62 General Timing Requirements for SPI1 Master Modes(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(SPC)M | Cycle Time, SPI1_CLK, All Master Modes | greater of 3P or 20 | 256P | ns | |
| 2 | tw(SPCH)M | Pulse Width High, SPI1_CLK, All Master Modes | 0.5tc(SPC)M - 1 | ns | ||
| 3 | tw(SPCL)M | Pulse Width Low, SPI1_CLK, All Master Modes | 0.5tc(SPC)M - 1 | ns | ||
| 4 | td(SIMO_SPC)M | Delay, initial data bit valid on SPI1_SIMO to initial edge on SPI1_CLK(2) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
- 0.5tc(SPC)M + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
- 0.5tc(SPC)M + 5 | |||||
| 5 | td(SPC_SIMO)M | Delay, subsequent bits valid on SPI1_SIMO after transmit edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| 6 | toh(SPC_SIMO)M | Output hold time, SPI1_SIMO valid after receive edge of SPI1_CLK |
Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M - 3 | |||||
| 7 | tsu(SOMI_SPC)M | Input Setup Time, SPI1_SOMI valid before receive edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0 | |||||
| 8 | tih(SPC_SOMI)M | Input Hold Time, SPI1_SOMI valid after receive edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
Table 5-63 General Timing Requirements for SPI1 Slave Modes(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | tc(SPC)S | Cycle Time, SPI1_CLK, All Slave Modes | greater of 3P or 40 | ns | ||
| 10 | tw(SPCH)S | Pulse Width High, SPI1_CLK, All Slave Modes | 18 | ns | ||
| 11 | tw(SPCL)S | Pulse Width Low, SPI1_CLK, All Slave Modes | 18 | ns | ||
| 12 | tsu(SOMI_SPC)S | Setup time, transmit data written to SPI before initial clock edge from master.(2)(3) |
Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
2P | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
2P | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
2P | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
2P | |||||
| 13 | td(SPC_SOMI)S | Delay, subsequent bits valid on SPI1_SOMI after transmit edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
19 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
19 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
19 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
19 | |||||
| 14 | toh(SPC_SOMI)S | Output hold time, SPI1_SOMI valid after receive edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)S - 3 | |||||
| 15 | tsu(SIMO_SPC)S | Input Setup Time, SPI1_SIMO valid before receive edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0 | |||||
| 16 | tih(SPC_SIMO)S | Input Hold Time, SPI1_SIMO valid after receive edge of SPI1_CLK | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
5 | |||||
Table 5-64 Additional(5) SPI1 Master Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | td(EN A_SPC)M | Delay from slave assertion of SPI1_ENA active to first SPI1_CLK from master.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
3P + 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
3P + 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3 | |||||
| 18 | td(SPC_ENA)M | Max delay for slave to deassert SPI1_ENA after final SPI1_CLK edge to ensure master does not begin the next transfer.(4) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
Table 5-65 Additional(7) SPI1 Master Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | td(SCS_SPC)M | Delay from SPI1_SCS active to first SPI1_CLK(3)(4) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
2P - 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| 20 | td(SPC_SCS)M | Delay from final SPI1_CLK edge to master deasserting SPI1_SCS(5)(6) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P -3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P - 3 | |||||
Table 5-66 Additional(10) SPI1 Master Timings, 5-Pin Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | td(SPC_ENA)M | Max delay for slave to deassert SPI1_ENA after final SPI1_CLK edge to ensure master does not begin the next transfer.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 20 | td(SPC_SCS)M | Delay from final SPI1_CLK edge to master deasserting SPI1_SCS(4)(5) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P - 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P - 3 | |||||
| 21 | td(SCSL_ENAL)M | Max delay for slave SPI to drive SPI1_ENA valid after master asserts SPI1_SCS to delay the master from beginning the next transfer. | C2TDELAY + P | ns | ||
| 22 | td(SCS_SPC)M | Delay from SPI1_SCS active to first SPI1_CLK(6)(7)(8) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
2P - 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
2P - 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 2P - 5 | |||||
| 23 | td(ENA_SPC)M | Delay from assertion of SPI1_ENA low to first SPI1_CLK edge.(9) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK rising |
3P + 3 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, to SPI1_CLK falling |
3P + 3 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, to SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + 3P + 3 | |||||
Table 5-67 Additional(3) SPI1 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | td(SPC_ENAH)S | Delay from final SPI1_CLK edge to slave deasserting SPI1_ENA. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
1.5 P - 3 | 2.5 P + 19 | ns |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
– 0.5tc(SPC)M + 1.5 P - 3 | – 0.5tc(SPC)M + 2.5 P + 19 | ||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
1.5 P - 3 | 2.5 P + 19 | ||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
– 0.5tc(SPC)M + 1.5 P - 3 | – 0.5tc(SPC)M + 2.5 P + 19 | ||||
Table 5-68 Additional(3) SPI1 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | td(SCSL_SPC)S | Required delay from SPI1_SCS asserted at slave to first SPI1_CLK edge at slave. | 2P | ns | ||
| 26 | td(SPC_SCSH)S | Required delay from final SPI1_CLK edge before SPI1_SCS is deasserted. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 27 | tena(SCSL_SOMI)S | Delay from master asserting SPI1_SCS to slave driving SPI1_SOMI valid | P + 19 | ns | ||
| 28 | tdis(SCSH_SOMI)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI1_SCS to slave 3-stating SPI1_SOMI | P + 19 | ns | ||
Table 5-69 Additional(4) SPI1 Slave Timings, 5-Pin Option(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | td(SCSL_SPC)S | Required delay from SPI1_SCS asserted at slave to first SPI1_CLK edge at slave. | 2P | ns | ||
| 26 | td(SPC_SCSH)S | Required delay from final SPI1_CLK edge before SPI1_SCS is deasserted. | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
0.5tc(SPC)M + P + 5 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
P + 5 | |||||
| 27 | tena(SCSL_SOMI)S | Delay from master asserting SPI1_SCS to slave driving SPI1_SOMI valid | P + 19 | ns | ||
| 28 | tdis(SCSH_SOMI)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI1_SCS to slave 3-stating SPI1_SOMI | P + 19 | ns | ||
| 29 | tena(SCSL_ENA)S | Delay from master deasserting SPI1_SCS to slave driving SPI1_ENA valid | 19 | ns | ||
| 30 | tdis(SPC_ENA)S | Delay from final clock receive edge on SPI1_CLK to slave 3-stating or driving high SPI1_ENA.(3) | Polarity = 0, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK falling |
2.5 P + 19 | ns | |
| Polarity = 0, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK rising |
2.5 P + 19 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 0, from SPI1_CLK rising |
2.5 P + 19 | |||||
| Polarity = 1, Phase = 1, from SPI1_CLK falling |
2.5 P + 19 | |||||
 Figure 5-38 SPI Timings—Master Mode
Figure 5-38 SPI Timings—Master Mode
 Figure 5-39 SPI Timings—Slave Mode
Figure 5-39 SPI Timings—Slave Mode
 Figure 5-40 SPI Timings—Master Mode (4-Pin and 5-Pin)
Figure 5-40 SPI Timings—Master Mode (4-Pin and 5-Pin)
 Figure 5-41 SPI Timings—Slave Mode (4-Pin and 5-Pin)
Figure 5-41 SPI Timings—Slave Mode (4-Pin and 5-Pin)
5.18 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
The device contains up to three enhanced capture (eCAP) modules. Figure 5-42 shows a functional block diagram of a module.
Uses for ECAP include:
- Speed measurements of rotating machinery (e.g. toothed sprockets sensed via Hall sensors)
- Elapsed time measurements between position sensor triggers
- Period and duty cycle measurements of Pulse train signals
- Decoding current or voltage amplitude derived from cuty cycle encoded current/voltage sensors
The ECAP module described in this specification includes the following features:
- 32 bit time base
- 4 event time-stamp registers (each 32 bits)
- Edge polarity selection for up to 4 sequenced time-stamp capture events
- Interrupt on either of the 4 events
- Single shot capture of up to 4 event time-stamps
- Continuous mode capture of time-stamps in a 4 deep circular buffer
- Absolute time-stamp capture
- Difference mode time-stamp capture
- All the above resources are dedicated to a single input pin
The eCAP modules are clocked at the SYSCLK2 rate.
 Figure 5-42 eCAP Functional Block Diagram
Figure 5-42 eCAP Functional Block Diagram
Table 5-70 is the list of the ECAP registers.
Table 5-70 ECAPx Configuration Registers
| ECAP0 BYTE ADDRESS |
ECAP1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ECAP2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01F0 6000 | 0x01F0 7000 | 0x01F0 8000 | TSCTR | Time-Stamp Counter |
| 0x01F0 6004 | 0x01F0 7004 | 0x01F0 8004 | CTRPHS | Counter Phase Offset Value Register |
| 0x01F0 6008 | 0x01F0 7008 | 0x01F0 8008 | CAP1 | Capture 1 Register |
| 0x01F0 600C | 0x01F0 700C | 0x01F0 800C | CAP2 | Capture 2 Register |
| 0x01F0 6010 | 0x01F0 7010 | 0x01F0 8010 | CAP3 | Capture 3 Register |
| 0x01F0 6014 | 0x01F0 7014 | 0x01F0 8014 | CAP4 | Capture 4 Register |
| 0x01F0 6028 | 0x01F0 7028 | 0x01F0 8028 | ECCTL1 | Capture Control Register 1 |
| 0x01F0 602A | 0x01F0 702A | 0x01F0 802A | ECCTL2 | Capture Control Register 2 |
| 0x01F0 602C | 0x01F0 702C | 0x01F0 802C | ECEINT | Capture Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01F0 602E | 0x01F0 702E | 0x01F0 802E | ECFLG | Capture Interrupt Flag Register |
| 0x01F0 6030 | 0x01F0 7030 | 0x01F0 8030 | ECCLR | Capture Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01F0 6032 | 0x01F0 7032 | 0x01F0 8032 | ECFRC | Capture Interrupt Force Register |
| 0x01F0 605C | 0x01F0 705C | 0x01F0 805C | REVID | Revision ID |
Table 5-71 shows the eCAP timing requirement and Table 5-72 shows the eCAP switching characteristics.
Table 5-71 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Timing Requirement
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(CAP) | Capture input pulse width | Asynchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| Synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |||
Table 5-72 eCAP Switching Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(APWM) | Pulse duration, APWMx output high/low | 20 | ns | |
5.19 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP) Peripheral
The device contains up to two enhanced quadrature encoder (eQEP) modules.
 Figure 5-43 eQEP Functional Block Diagram
Figure 5-43 eQEP Functional Block Diagram
Table 5-73 is the list of the EQEP registers.
Table 5-74 shows the eQEP timing requirement and Table 5-75 shows the eQEP switching characteristics.
Table 5-73 EQEP Registers
| EQEP0 BYTE ADDRESS |
EQEP1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01F0 9000 | 0x01F0 A000 | QPOSCNT | eQEP Position Counter |
| 0x01F0 9004 | 0x01F0 A004 | QPOSINIT | eQEP Initialization Position Count |
| 0x01F0 9008 | 0x01F0 A008 | QPOSMAX | eQEP Maximum Position Count |
| 0x01F0 900C | 0x01F0 A00C | QPOSCMP | eQEP Position-compare |
| 0x01F0 9010 | 0x01F0 A010 | QPOSILAT | eQEP Index Position Latch |
| 0x01F0 9014 | 0x01F0 A014 | QPOSSLAT | eQEP Strobe Position Latch |
| 0x01F0 9018 | 0x01F0 A018 | QPOSLAT | eQEP Position Latch |
| 0x01F0 901C | 0x01F0 A01C | QUTMR | eQEP Unit Timer |
| 0x01F0 9020 | 0x01F0 A020 | QUPRD | eQEP Unit Period Register |
| 0x01F0 9024 | 0x01F0 A024 | QWDTMR | eQEP Watchdog Timer |
| 0x01F0 9026 | 0x01F0 A026 | QWDPRD | eQEP Watchdog Period Register |
| 0x01F0 9028 | 0x01F0 A028 | QDECCTL | eQEP Decoder Control Register |
| 0x01F0 902A | 0x01F0 A02A | QEPCTL | eQEP Control Register |
| 0x01F0 902C | 0x01F0 A02C | QCAPCTL | eQEP Capture Control Register |
| 0x01F0 902E | 0x01F0 A02E | QPOSCTL | eQEP Position-compare Control Register |
| 0x01F0 9030 | 0x01F0 A030 | QEINT | eQEP Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01F0 9032 | 0x01F0 A032 | QFLG | eQEP Interrupt Flag Register |
| 0x01F0 9034 | 0x01F0 A034 | QCLR | eQEP Interrupt Clear Register |
| 0x01F0 9036 | 0x01F0 A036 | QFRC | eQEP Interrupt Force Register |
| 0x01F0 9038 | 0x01F0 A038 | QEPSTS | eQEP Status Register |
| 0x01F0 903A | 0x01F0 A03A | QCTMR | eQEP Capture Timer |
| 0x01F0 903C | 0x01F0 A03C | QCPRD | eQEP Capture Period Register |
| 0x01F0 903E | 0x01F0 A03E | QCTMRLAT | eQEP Capture Timer Latch |
| 0x01F0 9040 | 0x01F0 A040 | QCPRDLAT | eQEP Capture Period Latch |
| 0x01F0 905C | 0x01F0 A05C | REVID | eQEP Revision ID |
Table 5-74 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(QEPP) | QEP input period | Asynchronous/synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| tw(INDEXH) | QEP Index Input High time | Asynchronous/synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| tw(INDEXL) | QEP Index Input Low time | Asynchronous/synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| tw(STROBH) | QEP Strobe High time | Asynchronous/synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| tw(STROBL) | QEP Strobe Input Low time | Asynchronous/synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
Table 5-75 eQEP Switching Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| td(CNTR)xin | Delay time, external clock to counter increment | 4tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| td(PCS-OUT)QEP | Delay time, QEP input edge to position compare sync output | 6tc(SCO) | cycles | |
5.20 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
The device contains up to three enhanced PWM Modules (eHRPWM). Figure 5-44 shows a block diagram of multiple eHRPWM modules. Figure 4-4 shows the signal interconnections with the eHRPWM.
 Figure 5-44 Multiple PWM Modules in the System
Figure 5-44 Multiple PWM Modules in the System
 Figure 5-45 eHRPWM Sub-Modules Showing Critical Internal Signal Interconnections
Figure 5-45 eHRPWM Sub-Modules Showing Critical Internal Signal Interconnections
Table 5-76 eHRPWM Module Control and Status Registers Grouped by Submodule
| eHRPWM0 BYTE ADDRESS |
eHRPWM1 BYTE ADDRESS |
eHRPWM2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | SIZE (×16) |
SHADOW | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIME-BASE SUBMODULE REGISTERS | ||||||
| 0x01F0 0000 | 0x01F0 2000 | 0x01F0 4000 | TBCTL | 1 | No | Time-Base Control Register |
| 0x01F0 0002 | 0x01F0 2002 | 0x01F0 4002 | TBSTS | 1 | No | Time-Base Status Register |
| 0x01F0 0004 | 0x01F0 2004 | 0x01F0 4004 | TBPHSHR | 1 | No | Extension for HRPWM Phase Register (1) |
| 0x01F0 0006 | 0x01F0 2006 | 0x01F0 4006 | TBPHS | 1 | No | Time-Base Phase Register |
| 0x01F0 0008 | 0x01F0 2008 | 0x01F0 4008 | TBCNT | 1 | No | Time-Base Counter Register |
| 0x01F0 000A | 0x01F0 200A | 0x01F0 400A | TBPRD | 1 | Yes | Time-Base Period Register |
| COUNTER-COMPARE SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 000E | 0x01F0 200E | 0x01F0 400E | CMPCTL | 1 | No | Counter-Compare Control Register |
| 0x01F0 0010 | 0x01F0 2010 | 0x01F0 4010 | CMPAHR | 1 | No | Extension for HRPWM Counter-Compare A Register (1) |
| 0x01F0 0012 | 0x01F0 2012 | 0x01F0 4012 | CMPA | 1 | Yes | Counter-Compare A Register |
| 0x01F0 0014 | 0x01F0 2014 | 0x01F0 4014 | CMPB | 1 | Yes | Counter-Compare B Register |
| ACTION-QUALIFIER SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 0016 | 0x01F0 2016 | 0x01F0 4016 | AQCTLA | 1 | No | Action-Qualifier Control Register for Output A (eHRPWMxA) |
| 0x01F0 0018 | 0x01F0 2018 | 0x01F0 4018 | AQCTLB | 1 | No | Action-Qualifier Control Register for Output B (eHRPWMxB) |
| 0x01F0 001A | 0x01F0 201A | 0x01F0 401A | AQSFRC | 1 | No | Action-Qualifier Software Force Register |
| 0x01F0 001C | 0x01F0 201C | 0x01F0 401C | AQCSFRC | 1 | Yes | Action-Qualifier Continuous S/W Force Register Set |
| DEAD-BAND GENERATOR SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 001E | 0x01F0 201E | 0x01F0 401E | DBCTL | 1 | No | Dead-Band Generator Control Register |
| 0x01F0 0020 | 0x01F0 2020 | 0x01F0 4020 | DBRED | 1 | No | Dead-Band Generator Rising Edge Delay Count Register |
| 0x01F0 0022 | 0x01F0 2022 | 0x01F0 4022 | DBFED | 1 | No | Dead-Band Generator Falling Edge Delay Count Register |
| PWM-CHOPPER SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 003C | 0x01F0 203C | 0x01F0 403C | PCCTL | 1 | No | PWM-Chopper Control Register |
| TRIP-ZONE SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 0024 | 0x01F0 2024 | 0x01F0 4024 | TZSEL | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Select Register |
| 0x01F0 0028 | 0x01F0 2028 | 0x01F0 4028 | TZCTL | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Control Register |
| 0x01F0 002A | 0x01F0 202A | 0x01F0 402A | TZEINT | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Enable Interrupt Register |
| 0x01F0 002C | 0x01F0 202C | 0x01F0 402C | TZFLG | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Flag Register |
| 0x01F0 002E | 0x01F0 202E | 0x01F0 402E | TZCLR | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Clear Register |
| 0x01F0 0030 | 0x01F0 2030 | 0x01F0 4030 | TZFRC | 1 | No | Trip-Zone Force Register |
| EVENT-TRIGGER SUBMODULE REGISTER | ||||||
| 0x01F0 0032 | 0x01F0 2032 | 0x01F0 4032 | ETSEL | 1 | No | Event-Trigger Selection Register |
| 0x01F0 0034 | 0x01F0 2034 | 0x01F0 4034 | ETPS | 1 | No | Event-Trigger Pre-Scale Register |
| 0x01F0 0036 | 0x01F0 2036 | 0x01F0 4036 | ETFLG | 1 | No | Event-Trigger Flag Register |
| 0x01F0 0038 | 0x01F0 2038 | 0x01F0 4038 | ETCLR | 1 | No | Event-Trigger Clear Register |
| 0x01F0 003A | 0x01F0 203A | 0x01F0 403A | ETFRC | 1 | No | Event-Trigger Force Register |
| HIGH-RESOLUTION PWM (HRPWM) SUBMODULE | ||||||
| 0x01F0 1040 | 0x01F0 3040 | 0x01F0 5040 | HRCNFG | 1 | No | HRPWM Configuration Register (1) |
5.20.1 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (eHRPWM) Timing
PWM refers to PWM outputs on eHRPWM1-6. Table 5-77 shows the PWM timing requirements and Table 5-78, switching characteristics.
Table 5-77 eHRPWM Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(SYNCIN) | Sync input pulse width | Asynchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| Synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |||
Table 5-78 eHRPWM Switching Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(PWM) | Pulse duration, PWMx output high/low | 20 | ns | ||
| tw(SYNCOUT) | Sync output pulse width | 8tc(SCO) | cycles | ||
| td(PWM)TZA | Delay time, trip input active to PWM forced high Delay time, trip input active to PWM forced low |
no pin load; no additional programmable delay |
25 | ns | |
| td(TZ-PWM)HZ | Delay time, trip input active to PWM Hi-Z | no additional programmable delay | 20 | ns | |
5.20.2 Trip-Zone Input Timing

Table 5-79 Trip-Zone input Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw(TZ) | Pulse duration, TZx input low | Asynchronous | 1tc(SCO) | cycles | |
| Synchronous | 2tc(SCO) | cycles | |||
Table 5-80 shows the high-resolution PWM switching characteristics.
Table 5-80 High Resolution PWM Characteristics at SYSCLKOUT = (60 - 100 MHz)
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Edge Positioning (MEP) step size(1) | 200 | ps |
5.21 LCD Controller
The LCD controller consists of two independent controllers, the Raster Controller and the LCD Interface Display Driver (LIDD) controller. Each controller operates independently from the other and only one of them is active at any given time.
- The Raster Controller handles the synchronous LCD interface. It provides timing and data for constant graphics refresh to a passive display. It supports a wide variety of monochrome and full-color display types and sizes by use of programmable timing controls, a built-in palette, and a gray-scale/serializer. Graphics data is processed and stored in frame buffers. A frame buffer is a contiguous memory block in the system. A built-in DMA engine supplies the graphics data to the Raster engine which, in turn, outputs to the external LCD device.
- The LIDD Controller supports the asynchronous LCD interface. It provides full-timing programmability of control signals (CS, WE, OE, ALE) and output data.
The maximum resolution for the LCD controller is 1024 x 1024 pixels. The maximum frame rate is determined by the image size in combination with the pixel clock rate. OMAP-L1x/C674x/AM1x SOC Architecture and Throughput Overview (SPRAB93).
Table 5-81 lists the LCD Controller registers.
Table 5-81 LCD Controller (LCDC) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E1 3000 | REVID | LCD Revision Identification Register |
| 0x01E1 3004 | LCD_CTRL | LCD Control Register |
| 0x01E1 3008 | LCD_STAT | LCD Status Register |
| 0x01E1 300C | LIDD_CTRL | LCD LIDD Control Register |
| 0x01E1 3010 | LIDD_CS0_CONF | LCD LIDD CS0 Configuration Register |
| 0x01E1 3014 | LIDD_CS0_ADDR | LCD LIDD CS0 Address Read/Write Register |
| 0x01E1 3018 | LIDD_CS0_DATA | LCD LIDD CS0 Data Read/Write Register |
| 0x01E1 301C | LIDD_CS1_CONF | LCD LIDD CS1 Configuration Register |
| 0x01E1 3020 | LIDD_CS1_ADDR | LCD LIDD CS1 Address Read/Write Register |
| 0x01E1 3024 | LIDD_CS1_DATA | LCD LIDD CS1 Data Read/Write Register |
| 0x01E1 3028 | RASTER_CTRL | LCD Raster Control Register |
| 0x01E1 302C | RASTER_TIMING_0 | LCD Raster Timing 0 Register |
| 0x01E1 3030 | RASTER_TIMING_1 | LCD Raster Timing 1 Register |
| 0x01E1 3034 | RASTER_TIMING_2 | LCD Raster Timing 2 Register |
| 0x01E1 3038 | RASTER_SUBPANEL | LCD Raster Subpanel Display Register |
| 0x01E1 3040 | LCDDMA_CTRL | LCD DMA Control Register |
| 0x01E1 3044 | LCDDMA_FB0_BASE | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E1 3048 | LCDDMA_FB0_CEILING | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Ceiling Address Register |
| 0x01E1 304C | LCDDMA_FB1_BASE | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E1 3050 | LCDDMA_FB1_CEILING | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Ceiling Address Register |
5.21.1 LCD Interface Display Driver (LIDD Mode)
Table 5-82 LCD LIDD Mode Timing Requirements
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | tsu(LCD_D) | Setup time, LCD_D[15:0] valid before LCD_MCLK high | 7 | ns | |
| 17 | th(LCD_D) | Hold time, LCD_D[15:0] valid after LCD_MCLK high | 0.5 | ns | |
Table 5-83 LCD LIDD Mode Timing Characteristics
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | td(LCD_D_V) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] valid (write) | -0.5 | 10 | ns |
| 5 | td(LCD_D_I) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] invalid (write) | -0.5 | 10 | ns |
| 6 | td(LCD_E_A) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_AC_ENB_CS low | -0.5 | 7 | ns |
| 7 | td(LCD_E_I) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_AC_ENB_CS high | -0.5 | 7 | ns |
| 8 | td(LCD_A_A) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_VSYNC low | -0.5 | 8 | ns |
| 9 | td(LCD_A_I) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_VSYNC high | -0.5 | 8 | ns |
| 10 | td(LCD_W_A) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_HSYNC low | -0.5 | 8 | ns |
| 11 | td(LCD_W_I) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_HSYNC high | -0.5 | 8 | ns |
| 12 | td(LCD_STRB_A) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_PCLK active | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 13 | td(LCD_STRB_I) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_PCLK inactive | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 14 | td(LCD_D_Z) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] in 3-state | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 15 | td(Z_LCD_D) | Delay time, LCD_MCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] (valid from 3-state) | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
 Figure 5-47 Character Display HD44780 Write
Figure 5-47 Character Display HD44780 Write
 Figure 5-48 Character Display HD44780 Read
Figure 5-48 Character Display HD44780 Read
 Figure 5-49 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Write
Figure 5-49 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Write
 Figure 5-50 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Read
Figure 5-50 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Read
 Figure 5-51 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Status
Figure 5-51 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 6800 Status
 Figure 5-52 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Write
Figure 5-52 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Write
 Figure 5-53 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Read
Figure 5-53 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Read
 Figure 5-54 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Status
Figure 5-54 Micro-Interface Graphic Display 8080 Status
5.21.2 LCD Raster Mode
Table 5-84 LCD Raster Mode Timing
See Figure 5-55 through Figure 5-59| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(PIXEL_CLK) | Cycle time, pixel clock | 26.6 | ns | |
| 2 | tw(PIXEL_CLK_H) | Pulse duration, pixel clock high | 10 | ns | |
| 3 | tw(PIXEL_CLK_L) | Pulse duration, pixel clock low | 10 | ns | |
| 4 | td(LCD_D_V) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] valid (write) | -0.5 | 9 | ns |
| 5 | td(LCD_D_IV) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK high to LCD_D[15:0] invalid (write) | -0.5 | 9 | ns |
| 6 | td(LCD_AC_ENB_CS_A) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK low to LCD_AC_ENB_CS high | S2 - 0.5(2) | S2 + 9(2) | ns |
| 7 | td(LCD_AC_ENB_CS_I) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK low to LCD_AC_ENB_CS low | S2 - 0.5(2) | S2 + 9(2) | ns |
| 8 | td(LCD_VSYNC_A) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK low to LCD_VSYNC high(1) | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 9 | td(LCD_VSYNC_I) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK low to LCD_VSYNC low(1) | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 10 | td(LCD_HSYNC_A) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK high to LCD_HSYNC high(1) | --0.5 | 12 | ns |
| 11 | td(LCD_HSYNC_I) | Delay time, LCD_PCLK high to LCD_HSYNC low(1) | -0.5 | 12 | ns |
Frame-to-frame timing is derived through the following parameters in the LCD (RASTER_TIMING_1) register:
- Vertical front porch (VFP)
- Vertical sync pulse width (VSW)
- Vertical back porch (VBP)
- Lines per panel (LPP)
Line-to-line timing is derived through the following parameters in the LCD (RASTER_TIMING_0) register:
- Horizontal front porch (HFP)
- Horizontal sync pulse width (HSW)
- Horizontal back porch (HBP)
- Pixels per panel (PPL)
LCD_AC_ENB_CS timing is derived through the following parameter in the LCD (RASTER_TIMING_2) register:
- AC bias frequency (ACB)
The display format produced in raster mode is shown in Figure 5-55. An entire frame is delivered one line at a time. The first line delivered starts at data pixel (1, 1) and ends at data pixel (P, 1). The last line delivered starts at data pixel (1, L) and ends at data pixel (P, L). The beginning of each new frame is denoted by the activation of I/O signal LCD_VSYNC. The beginning of each new line is denoted by the activation of I/O signal LCD_HSYNC.
 Figure 5-55 LCD Raster-Mode Display Format
Figure 5-55 LCD Raster-Mode Display Format
 Figure 5-56 LCD Raster-Mode Active
Figure 5-56 LCD Raster-Mode Active
 Figure 5-57 LCD Raster-Mode Passive
Figure 5-57 LCD Raster-Mode Passive
 Figure 5-58 LCD Raster-Mode Control Signal Activation
Figure 5-58 LCD Raster-Mode Control Signal Activation
 Figure 5-59 LCD Raster-Mode Control Signal Deactivation
Figure 5-59 LCD Raster-Mode Control Signal Deactivation
5.22 Timers
The timers support the following features:
- Configurable as single 64-bit timer or two 32-bit timers
- Period timeouts generate interrupts, DMA events or external pin events
- 8 32-bit compare registers
- Compare matches generate interrupt events
- Capture capability
- 64-bit Watchdog capability (Timer64P1 only)
Table 5-85 Timer Registers
| Timer64P 0 | Timer64P 1 | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C2 0000 | 0x01C2 1000 | REV | Revision Register |
| 0x01C2 0004 | 0x01C2 1004 | EMUMGT | Emulation Management Register |
| 0x01C2 0008 | 0x01C2 1008 | GPINTGPEN | GPIO Interrupt and GPIO Enable Register |
| 0x01C2 000C | 0x01C2 100C | GPDATGPDIR | GPIO Data and GPIO Direction Register |
| 0x01C2 0010 | 0x01C2 1010 | TIM12 | Timer Counter Register 12 |
| 0x01C2 0014 | 0x01C2 1014 | TIM34 | Timer Counter Register 34 |
| 0x01C2 0018 | 0x01C2 1018 | PRD12 | Timer Period Register 12 |
| 0x01C2 001C | 0x01C2 101C | PRD34 | Timer Period Register 34 |
| 0x01C2 0020 | 0x01C2 1020 | TCR | Timer Control Register |
| 0x01C2 0024 | 0x01C2 1024 | TGCR | Timer Global Control Register |
| 0x01C2 0028 | 0x01C2 1028 | WDTCR | Watchdog Timer Control Register |
| 0x01C2 0034 | 0x01C2 1034 | REL12 | Timer Reload Register 12 |
| 0x01C2 0038 | 0x01C2 1038 | REL34 | Timer Reload Register 34 |
| 0x01C2 003C | 0x01C2 103C | CAP12 | Timer Capture Register 12 |
| 0x01C2 0040 | 0x01C2 1040 | CAP34 | Timer Capture Register 34 |
| 0x01C2 0044 | 0x01C2 1044 | INTCTLSTAT | Timer Interrupt Control and Status Register |
| 0x01C2 0060 | 0x01C2 1060 | CMP0 | Compare Register 0 |
| 0x01C2 0064 | 0x01C2 1064 | CMP1 | Compare Register 1 |
| 0x01C2 0068 | 0x01C2 1068 | CMP2 | Compare Register 2 |
| 0x01C2 006C | 0x01C2 106C | CMP3 | Compare Register 3 |
| 0x01C2 0070 | 0x01C2 1070 | CMP4 | Compare Register 4 |
| 0x01C2 0074 | 0x01C2 1074 | CMP5 | Compare Register 5 |
| 0x01C2 0078 | 0x01C2 1078 | CMP6 | Compare Register 6 |
| 0x01C2 007C | 0x01C2 107C | CMP7 | Compare Register 7 |
5.22.1 Timer Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-86 Timing Requirements for Timer Input(1)(2) (see Figure 5-60)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(TM64Px_IN12) | Cycle time, TM64Px_IN12 | 4P | ns | |
| 2 | tw(TINPH) | Pulse duration, TM64Px_IN12 high | 0.45C | 0.55C | ns |
| 3 | tw(TINPL) | Pulse duration, TM64Px_IN12 low | 0.45C | 0.55C | ns |
| 4 | tt(TM64Px_IN12) | Transition time, TM64Px_IN12 | 0.25P or 10(3) | ns | |
 Figure 5-60 Timer Timing
Figure 5-60 Timer Timing
Table 5-87 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for Timer Output (1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | tw(TOUTH) | Pulse duration, TM64P0_OUT12 high | 4P | ns | |
| 6 | tw(TOUTL) | Pulse duration, TM64P0_OUT12 low | 4P | ns | |
 Figure 5-61 Timer Timing
Figure 5-61 Timer Timing
5.23 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C0, I2C1)
5.23.1 I2C Device-Specific Information
Having two I2C modules on the device simplifies system architecture. Figure 5-62 is block diagram of the I2C Module.
Each I2C port supports:
- Compatible with Philips® I2C Specification Revision 2.1 (January 2000)
- Fast Mode up to 400 Kbps (no fail-safe I/O buffers)
- Noise Filter to Remove Noise 50 ns or less
- Seven- and Ten-Bit Device Addressing Modes
- Master (Transmit/Receive) and Slave (Transmit/Receive) Functionality
- Events: DMA, Interrupt, or Polling
- General-Purpose I/O Capability if not used as I2C
 Figure 5-62 I2C Module Block Diagram
Figure 5-62 I2C Module Block Diagram
5.23.2 I2C Peripheral Registers Description(s)
Table 5-88 is the list of the I2C registers.
Table 5-88 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Registers
| I2C0 BYTE ADDRESS |
I2C1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C2 2000 | 0x01E2 8000 | ICOAR | I2C Own Address Register |
| 0x01C2 2004 | 0x01E2 8004 | ICIMR | I2C Interrupt Mask Register |
| 0x01C2 2008 | 0x01E2 8008 | ICSTR | I2C Interrupt Status Register |
| 0x01C2 200C | 0x01E2 800C | ICCLKL | I2C Clock Low-Time Divider Register |
| 0x01C2 2010 | 0x01E2 8010 | ICCLKH | I2C Clock High-Time Divider Register |
| 0x01C2 2014 | 0x01E2 8014 | ICCNT | I2C Data Count Register |
| 0x01C2 2018 | 0x01E2 8018 | ICDRR | I2C Data Receive Register |
| 0x01C2 201C | 0x01E2 801C | ICSAR | I2C Slave Address Register |
| 0x01C2 2020 | 0x01E2 8020 | ICDXR | I2C Data Transmit Register |
| 0x01C2 2024 | 0x01E2 8024 | ICMDR | I2C Mode Register |
| 0x01C2 2028 | 0x01E2 8028 | ICIVR | I2C Interrupt Vector Register |
| 0x01C2 202C | 0x01E2 802C | ICEMDR | I2C Extended Mode Register |
| 0x01C2 2030 | 0x01E2 8030 | ICPSC | I2C Prescaler Register |
| 0x01C2 2034 | 0x01E2 8034 | REVID1 | I2C Revision Identification Register 1 |
| 0x01C2 2038 | 0x01E2 8038 | REVID2 | I2C Revision Identification Register 2 |
| 0x01C2 2048 | 0x01E2 8048 | ICPFUNC | I2C Pin Function Register |
| 0x01C2 204C | 0x01E2 804C | ICPDIR | I2C Pin Direction Register |
| 0x01C2 2050 | 0x01E2 8050 | ICPDIN | I2C Pin Data In Register |
| 0x01C2 2054 | 0x01E2 8054 | ICPDOUT | I2C Pin Data Out Register |
| 0x01C2 2058 | 0x01E2 8058 | ICPDSET | I2C Pin Data Set Register |
| 0x01C2 205C | 0x01E2 805C | ICPDCLR | I2C Pin Data Clear Register |
5.23.3 I2C Electrical Data/Timing
5.23.3.1 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Timing
Table 5-89 and Table 5-90 assume testing over recommended operating conditions (see Figure 5-63 and Figure 5-64).
Table 5-89 I2C Input Timing Requirements
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(SCL) | Cycle time, I2Cx_SCL | Standard Mode | 10 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 2.5 | |||||
| 2 | tsu(SCLH-SDAL) | Setup time, I2Cx_SCL high before I2Cx_SDA low | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 3 | th(SCLL-SDAL) | Hold time, I2Cx_SCL low after I2Cx_SDA low | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 4 | tw(SCLL) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SCL low | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 1.3 | |||||
| 5 | tw(SCLH) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SCL high | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 6 | tsu(SDA-SCLH) | Setup time, I2Cx_SDA before I2Cx_SCL high | Standard Mode | 250 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 100 | |||||
| 7 | th(SDA-SCLL) | Hold time, I2Cx_SDA after I2Cx_SCL low | Standard Mode | 0 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0 | 0.9 | ||||
| 8 | tw(SDAH) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SDA high | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 1.3 | |||||
| 9 | tr(SDA) | Rise time, I2Cx_SDA | Standard Mode | 1000 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 20 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ||||
| 10 | tr(SCL) | Rise time, I2Cx_SCL | Standard Mode | 1000 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 20 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ||||
| 11 | tf(SDA) | Fall time, I2Cx_SDA | Standard Mode | 300 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 20 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ||||
| 12 | tf(SCL) | Fall time, I2Cx_SCL | Standard Mode | 300 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 20 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ||||
| 13 | tsu(SCLH-SDAH) | Setup time, I2Cx_SCL high before I2Cx_SDA high | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 14 | tw(SP) | Pulse duration, spike (must be suppressed) | Standard Mode | N/A | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 0 | 50 | ||||
| 15 | Cb | Capacitive load for each bus line | Standard Mode | 400 | pF | |
| Fast Mode | 400 | |||||
Table 5-90 I2C Switching Characteristics(1)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | tc(SCL) | Cycle time, I2Cx_SCL | Standard Mode | 10 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 2.5 | |||||
| 17 | tsu(SCLH-SDAL) | Setup time, I2Cx_SCL high before I2Cx_SDA low | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 18 | th(SDAL-SCLL) | Hold time, I2Cx_SCL low after I2Cx_SDA low | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 19 | tw(SCLL) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SCL low | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 1.3 | |||||
| 20 | tw(SCLH) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SCL high | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
| 21 | tsu(SDAV-SCLH) | Setup time, I2Cx_SDA valid before I2Cx_SCL high | Standard Mode | 250 | ns | |
| Fast Mode | 100 | |||||
| 22 | th(SCLL-SDAV) | Hold time, I2Cx_SDA valid after I2Cx_SCL low | Standard Mode | 0 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0 | 0.9 | ||||
| 23 | tw(SDAH) | Pulse duration, I2Cx_SDA high | Standard Mode | 4.7 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 1.3 | |||||
| 28 | tsu(SCLH-SDAH) | Setup time, I2Cx_SCL high before I2Cx_SDA high | Standard Mode | 4 | μs | |
| Fast Mode | 0.6 | |||||
 Figure 5-63 I2C Receive Timings
Figure 5-63 I2C Receive Timings
 Figure 5-64 I2C Transmit Timings
Figure 5-64 I2C Transmit Timings
5.24 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
The device has 3 UART peripherals. Each UART has the following features:
- 16-byte storage space for both the transmitter and receiver FIFOs
- 1, 4, 8, or 14 byte selectable receiver FIFO trigger level for autoflow control and DMA
- Autoflow control signals (CTS, RTS) on UART0 only
- DMA signaling capability for both received and transmitted data
- Programmable auto-rts and auto-cts for autoflow control
- Programmable Baud Rate up to 3MBaud
- Programmable Oversampling Options of x13 and x16
- Frequency pre-scale values from 1 to 65,535 to generate appropriate baud rates
- Prioritized interrupts
- Programmable serial data formats
- 5, 6, 7, or 8-bit characters
- Even, odd, or no parity bit generation and detection
- 1, 1.5, or 2 stop bit generation
- False start bit detection
- Line break generation and detection
- Internal diagnostic capabilities
- Loopback controls for communications link fault isolation
- Break, parity, overrun, and framing error simulation
The UART registers are listed in Section 5.24.1
5.24.1 UART Peripheral Registers Description(s)
Table 5-91 is the list of UART registers.
Table 5-91 UART Registers
| UART0 BYTE ADDRESS |
UART1 BYTE ADDRESS |
UART2 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C4 2000 | 0x01D0 C000 | 0x01D0 D000 | RBR | Receiver Buffer Register (read only) |
| 0x01C4 2000 | 0x01D0 C000 | 0x01D0 D000 | THR | Transmitter Holding Register (write only) |
| 0x01C4 2004 | 0x01D0 C004 | 0x01D0 D004 | IER | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C4 2008 | 0x01D0 C008 | 0x01D0 D008 | IIR | Interrupt Identification Register (read only) |
| 0x01C4 2008 | 0x01D0 C008 | 0x01D0 D008 | FCR | FIFO Control Register (write only) |
| 0x01C4 200C | 0x01D0 C00C | 0x01D0 D00C | LCR | Line Control Register |
| 0x01C4 2010 | 0x01D0 C010 | 0x01D0 D010 | MCR | Modem Control Register |
| 0x01C4 2014 | 0x01D0 C014 | 0x01D0 D014 | LSR | Line Status Register |
| 0x01C4 2018 | 0x01D0 C018 | 0x01D0 D018 | MSR | Modem Status Register |
| 0x01C4 201C | 0x01D0 C01C | 0x01D0 D01C | SCR | Scratchpad Register |
| 0x01C4 2020 | 0x01D0 C020 | 0x01D0 D020 | DLL | Divisor LSB Latch |
| 0x01C4 2024 | 0x01D0 C024 | 0x01D0 D024 | DLH | Divisor MSB Latch |
| 0x01C4 2028 | 0x01D0 C028 | 0x01D0 D028 | REVID1 | Revision Identification Register 1 |
| 0x01C4 2030 | 0x01D0 C030 | 0x01D0 D030 | PWREMU_MGMT | Power and Emulation Management Register |
| 0x01C4 2034 | 0x01D0 C034 | 0x01D0 D034 | MDR | Mode Definition Register |
5.24.2 UART Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-92 Timing Requirements for UARTx Receive(1) (see Figure 5-65)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | tw(URXDB) | Pulse duration, receive data bit (RXDn) | 0.96U | 1.05U | ns |
| 5 | tw(URXSB) | Pulse duration, receive start bit | 0.96U | 1.05U | ns |
Table 5-93 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for UARTx Transmit(1)
(see Figure 5-65)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | f(baud) | Maximum programmable baud rate | D/E (2)(3) | MBaud(4) | |
| 2 | tw(UTXDB) | Pulse duration, transmit data bit (TXDn) | U - 2 | U + 2 | ns |
| 3 | tw(UTXSB) | Pulse duration, transmit start bit | U - 2 | U + 2 | ns |
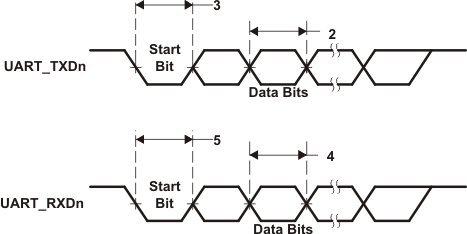 Figure 5-65 UART Transmit/Receive Timing
Figure 5-65 UART Transmit/Receive Timing
5.25 USB1 Host Controller Registers (USB1.1 OHCI)
All the device USB interfaces are compliant with Universal Serial Bus Specification, Revision 1.1.
Table 5-94 is the list of USB1 Host Controller registers.
Table 5-94 USB1 Host Controller Registers
| USB 1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E2 5000 | HCREVISION | OHCI Revision Number Register |
| 0x01E2 5004 | HCCONTROL | HC Operating Mode Register |
| 0x01E2 5008 | HCCOMMANDSTATUS | HC Command and Status Register |
| 0x01E2 500C | HCINTERRUPTSTATUS | HC Interrupt and Status Register |
| 0x01E2 5010 | HCINTERRUPTENABLE | HC Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01E2 5014 | HCINTERRUPTDISABLE | HC Interrupt Disable Register |
| 0x01E2 5018 | HCHCCA | HC HCAA Address Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 501C | HCPERIODCURRENTED | HC Current Periodic Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 5020 | HCCONTROLHEADED | HC Head Control Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 5024 | HCCONTROLCURRENTED | HC Current Control Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 5028 | HCBULKHEADED | HC Head Bulk Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 502C | HCBULKCURRENTED | HC Current Bulk Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 5030 | HCDONEHEAD | HC Head Done Register(1) |
| 0x01E2 5034 | HCFMINTERVAL | HC Frame Interval Register |
| 0x01E2 5038 | HCFMREMAINING | HC Frame Remaining Register |
| 0x01E2 503C | HCFMNUMBER | HC Frame Number Register |
| 0x01E2 5040 | HCPERIODICSTART | HC Periodic Start Register |
| 0x01E2 5044 | HCLSTHRESHOLD | HC Low-Speed Threshold Register |
| 0x01E2 5048 | HCRHDESCRIPTORA | HC Root Hub A Register |
| 0x01E2 504C | HCRHDESCRIPTORB | HC Root Hub B Register |
| 0x01E2 5050 | HCRHSTATUS | HC Root Hub Status Register |
| 0x01E2 5054 | HCRHPORTSTATUS1 | HC Port 1 Status and Control Register(2) |
| 0x01E2 5058 | HCRHPORTSTATUS2 | HC Port 2 Status and Control Register(3) |
Table 5-95 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for USB1
| No. | PARAMETER | LOW SPEED | FULL SPEED | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MAX | MAX | ||||
| U1 | tr | Rise time, USB1_DP and USB1_DM signals(1) | 75(1) | 300(1) | 4(1) | 20(1) | ns |
| U2 | tf | Fall time, USB1_DP and USB1_DM signals(1) | 75(1) | 300(1) | 4(1) | 20(1) | ns |
| U3 | tRFM | Rise/Fall time matching(2) | 80(2) | 120(2) | 90(2) | 110(2) | % |
| U4 | VCRS | Output signal cross-over voltage(1) | 1.3(1) | 2(1) | 1.3(1) | 2(1) | V |
| U5 | tj | Differential propagation jitter(3) | -25(3) | 25(3) | -2(3) | 2(3) | ns |
| U6 | fop | Operating frequency(4) | 1.5 | 12 | MHz | ||
5.25.1 USB1 Unused Signal Configuration
If USB1 is unused, then the USB1 signals should be configured as shown in Section 3.6.22.
5.26 USB0 OTG (USB2.0 OTG)
The device USB2.0 peripheral supports the following features:
- USB 2.0 peripheral at high-speed (HS: 480 Mb/s) and full-speed (FS: 12 Mb/s)
- USB 2.0 host at speeds HS, FS, and low speed (LS: 1.5 Mb/s)
- All transfer modes (control, bulk, interrupt, and isochronous)
- 4 Transmit (TX) and 4 Receive (RX) endpoints in addition to endpoint 0
- FIFO RAM
- 4K endpoint
- Programmable size
- Integrated USB 2.0 High Speed PHY
- Connects to a standard Charge Pump for VBUS 5 V generation
- RNDIS mode for accelerating RNDIS type protocols using short packet termination over USB
Important Notice: On the original device pinout (marked "A" in the lower right corner of the package), pins USB0_VSSA33 (H4) and USB0_VSSA (F3) were connected to ground outside the package. For more robust ESD performance, the USB0 ground references are now connected inside the package on packages marked "B" and the package pins are unconnected. This change will require that any external filter circuits previously referenced to ground at these pins will need to reference the board ground instead.
Important Notice: The USB0 controller module clock (PLL0_SYSCLK2) must be greater than 30 MHz for proper operation of the USB controller. A clock rate of 60 MHz or greater is recommended to avoid da`ta throughput reduction.
Table 5-96 is the list of USB OTG registers.
Table 5-96 Universal Serial Bus OTG (USB0) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01E0 0000 | REVID | Revision Register |
| 0x01E0 0004 | CTRLR | Control Register |
| 0x01E0 0008 | STATR | Status Register |
| 0x01E0 000C | EMUR | Emulation Register |
| 0x01E0 0010 | MODE | Mode Register |
| 0x01E0 0014 | AUTOREQ | Autorequest Register |
| 0x01E0 0018 | SRPFIXTIME | SRP Fix Time Register |
| 0x01E0 001C | TEARDOWN | Teardown Register |
| 0x01E0 0020 | INTSRCR | USB Interrupt Source Register |
| 0x01E0 0024 | INTSETR | USB Interrupt Source Set Register |
| 0x01E0 0028 | INTCLRR | USB Interrupt Source Clear Register |
| 0x01E0 002C | INTMSKR | USB Interrupt Mask Register |
| 0x01E0 0030 | INTMSKSETR | USB Interrupt Mask Set Register |
| 0x01E0 0034 | INTMSKCLRR | USB Interrupt Mask Clear Register |
| 0x01E0 0038 | INTMASKEDR | USB Interrupt Source Masked Register |
| 0x01E0 003C | EOIR | USB End of Interrupt Register |
| 0x01E0 0040 | - | Reserved |
| 0x01E0 0050 | GENRNDISSZ1 | Generic RNDIS Size EP1 |
| 0x01E0 0054 | GENRNDISSZ2 | Generic RNDIS Size EP2 |
| 0x01E0 0058 | GENRNDISSZ3 | Generic RNDIS Size EP3 |
| 0x01E0 005C | GENRNDISSZ4 | Generic RNDIS Size EP4 |
| 0x01E0 0400 | FADDR | Function Address Register |
| 0x01E0 0401 | POWER | Power Management Register |
| 0x01E0 0402 | INTRTX | Interrupt Register for Endpoint 0 plus Transmit Endpoints 1 to 4 |
| 0x01E0 0404 | INTRRX | Interrupt Register for Receive Endpoints 1 to 4 |
| 0x01E0 0406 | INTRTXE | Interrupt Enable Register for INTRTX |
| 0x01E0 0408 | INTRRXE | Interrupt Enable Register for INTRRX |
| 0x01E0 040A | INTRUSB | Interrupt Register for Common USB Interrupts |
| 0x01E0 040B | INTRUSBE | Interrupt Enable Register for INTRUSB |
| 0x01E0 040C | FRAME | Frame Number Register |
| 0x01E0 040E | INDEX | Index Register for Selecting the Endpoint Status and Control Registers |
| 0x01E0 040F | TESTMODE | Register to Enable the USB 2.0 Test Modes |
| INDEXED REGISTERS
These registers operate on the endpoint selected by the INDEX register |
||
| 0x01E0 0410 | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Transmit Endpoint (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 0412 | PERI_CSR0 | Control Status Register for Endpoint 0 in Peripheral Mode. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| HOST_CSR0 | Control Status Register for Endpoint 0 in Host Mode. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
|
| PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
|
| HOST_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Transmit Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
|
| 0x01E0 0414 | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Receive Endpoint (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 0416 | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| HOST_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Receive Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
|
| 0x01E0 0418 | COUNT0 | Number of Received Bytes in Endpoint 0 FIFO. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive Endpoint FIFO. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1- 4) |
|
| 0x01E0 041A | HOST_TYPE0 | Defines the speed of Endpoint 0 |
| HOST_TXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Transmit endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
|
| 0x01E0 041B | HOST_NAKLIMIT0 | Sets the NAK response timeout on Endpoint 0. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| HOST_TXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Transmit endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) | |
| 0x01E0 041C | HOST_RXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Receive endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 041D | HOST_RXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Receive endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 041F | CONFIGDATA | Returns details of core configuration. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| FIFO | ||
| 0x01E0 0420 | FIFO0 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register for Endpoint 0 |
| 0x01E0 0424 | FIFO1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register for Endpoint 1 |
| 0x01E0 0428 | FIFO2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register for Endpoint 2 |
| 0x01E0 042C | FIFO3 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register for Endpoint 3 |
| 0x01E0 0430 | FIFO4 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register for Endpoint 4 |
| OTG DEVICE CONTROL | ||
| 0x01E0 0460 | DEVCTL | Device Control Register |
| DYNAMIC FIFO CONTROL | ||
| 0x01E0 0462 | TXFIFOSZ | Transmit Endpoint FIFO Size (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 0463 | RXFIFOSZ | Receive Endpoint FIFO Size (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 0464 | TXFIFOADDR | Transmit Endpoint FIFO Address (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 0466 | RXFIFOADDR | Receive Endpoint FIFO Address (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4 only) |
| 0x01E0 046C | HWVERS | Hardware Version Register |
| TARGET ENDPOINT 0 CONTROL REGISTERS, VALID ONLY IN HOST MODE | ||
| 0x01E0 0480 | TXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 0482 | TXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0483 | TXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0484 | RXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 0486 | RXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0487 | RXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| TARGET ENDPOINT 1 CONTROL REGISTERS, VALID ONLY IN HOST MODE | ||
| 0x01E0 0488 | TXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 048A | TXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 048B | TXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 048C | RXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 048E | RXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 048F | RXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| TARGET ENDPOINT 2 CONTROL REGISTERS, VALID ONLY IN HOST MODE | ||
| 0x01E0 0490 | TXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 0492 | TXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0493 | TXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0494 | RXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 0496 | RXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 0497 | RXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| TARGET ENDPOINT 3 CONTROL REGISTERS, VALID ONLY IN HOST MODE | ||
| 0x01E0 0498 | TXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 049A | TXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 049B | TXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 049C | RXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 049E | RXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 049F | RXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| TARGET ENDPOINT 4 CONTROL REGISTERS, VALID ONLY IN HOST MODE | ||
| 0x01E0 04A0 | TXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 04A2 | TXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 04A3 | TXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Transmit Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 04A4 | RXFUNCADDR | Address of the target function that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 04A6 | RXHUBADDR | Address of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| 0x01E0 04A7 | RXHUBPORT | Port of the hub that has to be accessed through the associated Receive Endpoint. This is used only when full speed or low speed device is connected via a USB2.0 high-speed hub. |
| CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTER FOR ENDPOINT 0 | ||
| 0x01E0 0502 | PERI_CSR0 | Control Status Register for Endpoint 0 in Peripheral Mode |
| HOST_CSR0 | Control Status Register for Endpoint 0 in Host Mode | |
| 0x01E0 0508 | COUNT0 | Number of Received Bytes in Endpoint 0 FIFO |
| 0x01E0 050A | HOST_TYPE0 | Defines the Speed of Endpoint 0 |
| 0x01E0 050B | HOST_NAKLIMIT0 | Sets the NAK Response Timeout on Endpoint 0 |
| 0x01E0 050F | CONFIGDATA | Returns details of core configuration. |
| CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTER FOR ENDPOINT 1 | ||
| 0x01E0 0510 | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0512 | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Transmit Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0514 | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Receive Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0516 | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Receive Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0518 | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 0x01E0 051A | HOST_TXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 051B | HOST_TXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 051C | HOST_RXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Receive endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 051D | HOST_RXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Receive endpoint. |
| CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTER FOR ENDPOINT 2 | ||
| 0x01E0 0520 | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0522 | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Transmit Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0524 | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Receive Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0526 | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Receive Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0528 | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 0x01E0 052A | HOST_TXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 052B | HOST_TXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 052C | HOST_RXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Receive endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 052D | HOST_RXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Receive endpoint. |
| CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTER FOR ENDPOINT 3 | ||
| 0x01E0 0530 | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0532 | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Transmit Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0534 | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Receive Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0536 | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Receive Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0538 | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 0x01E0 053A | HOST_TXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 053B | HOST_TXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 053C | HOST_RXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Receive endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 053D | HOST_RXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Receive endpoint. |
| CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTER FOR ENDPOINT 4 | ||
| 0x01E0 0540 | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0542 | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Transmit Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0544 | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral/Host Receive Endpoint |
| 0x01E0 0546 | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| HOST_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Host Receive Endpoint (host mode) |
|
| 0x01E0 0548 | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 0x01E0 054A | HOST_TXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 054B | HOST_TXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Transmit endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 054C | HOST_RXTYPE | Sets the operating speed, transaction protocol and peripheral endpoint number for the host Receive endpoint. |
| 0x01E0 054D | HOST_RXINTERVAL | Sets the polling interval for Interrupt/ISOC transactions or the NAK response timeout on Bulk transactions for host Receive endpoint. |
| DMA REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01E0 1000 | DMAREVID | DMA Revision Register |
| 0x01E0 1004 | TDFDQ | DMA Teardown Free Descriptor Queue Control Register |
| 0x01E0 1008 | DMAEMU | DMA Emulation Control Register |
| 0x01E0 1800 | TXGCR[0] | Transmit Channel 0 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 1808 | RXGCR[0] | Receive Channel 0 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 180C | RXHPCRA[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register A |
| 0x01E0 1810 | RXHPCRB[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register B |
| 0x01E0 1820 | TXGCR[1] | Transmit Channel 1 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 1828 | RXGCR[1] | Receive Channel 1 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 182C | RXHPCRA[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register A |
| 0x01E0 1830 | RXHPCRB[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register B |
| 0x01E0 1840 | TXGCR[2] | Transmit Channel 2 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 1848 | RXGCR[2] | Receive Channel 2 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 184C | RXHPCRA[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register A |
| 0x01E0 1850 | RXHPCRB[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register B |
| 0x01E0 1860 | TXGCR[3] | Transmit Channel 3 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 1868 | RXGCR[3] | Receive Channel 3 Global Configuration Register |
| 0x01E0 186C | RXHPCRA[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register A |
| 0x01E0 1870 | RXHPCRB[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register B |
| 0x01E0 2000 | DMA_SCHED_CTRL | DMA Scheduler Control Register |
| 0x01E0 2800 | WORD[0] | DMA Scheduler Table Word 0 |
| 0x01E0 2804 | WORD[1] | DMA Scheduler Table Word 1 |
| . . . | . . . | . . . |
| 0x01E0 28FC | WORD[63] | DMA Scheduler Table Word 63 |
| QUEUE MANAGER REGISTERS | ||
| 0x01E0 4000 | QMGRREVID | Queue Manager Revision Register |
| 0x01E0 4008 | DIVERSION | Queue Diversion Register |
| 0x01E0 4020 | FDBSC0 | Free Descriptor/Buffer Starvation Count Register 0 |
| 0x01E0 4024 | FDBSC1 | Free Descriptor/Buffer Starvation Count Register 1 |
| 0x01E0 4028 | FDBSC2 | Free Descriptor/Buffer Starvation Count Register 2 |
| 0x01E0 402C | FDBSC3 | Free Descriptor/Buffer Starvation Count Register 3 |
| 0x01E0 4080 | LRAM0BASE | Linking RAM Region 0 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E0 4084 | LRAM0SIZE | Linking RAM Region 0 Size Register |
| 0x01E0 4088 | LRAM1BASE | Linking RAM Region 1 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E0 4090 | PEND0 | Queue Pending Register 0 |
| 0x01E0 4094 | PEND1 | Queue Pending Register 1 |
| 0x01E0 5000 | QMEMRBASE[0] | Memory Region 0 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E0 5004 | QMEMRCTRL[0] | Memory Region 0 Control Register |
| 0x01E0 5010 | QMEMRBASE[1] | Memory Region 1 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E0 5014 | QMEMRCTRL[1] | Memory Region 1 Control Register |
| . . . | . . . | . . . |
| 0x01E0 50F0 | QMEMRBASE[15] | Memory Region 15 Base Address Register |
| 0x01E0 50F4 | QMEMRCTRL[15] | Memory Region 15 Control Register |
| 0x01E0 600C | CTRLD[0] | Queue Manager Queue 0 Control Register D |
| 0x01E0 601C | CTRLD[1] | Queue Manager Queue 1 Control Register D |
| . . . | . . . | . . . |
| 0x01E0 63FC | CTRLD[63] | Queue Manager Queue 63 Status Register D |
| 0x01E0 6800 | QSTATA[0] | Queue Manager Queue 0 Status Register A |
| 0x01E0 6804 | QSTATB[0] | Queue Manager Queue 0 Status Register B |
| 0x01E0 6808 | QSTATC[0] | Queue Manager Queue 0 Status Register C |
| 0x01E0 6810 | QSTATA[1] | Queue Manager Queue 1 Status Register A |
| 0x01E0 6814 | QSTATB[1] | Queue Manager Queue 1 Status Register B |
| 0x01E0 6818 | QSTATC[1] | Queue Manager Queue 1 Status Register C |
| . . . | . . . | . . . |
| 0x01E0 6BF0 | QSTATA[63] | Queue Manager Queue 63 Status Register A |
| 0x01E0 6BF4 | QSTATB[63] | Queue Manager Queue 63 Status Register B |
| 0x01E0 6BF8 | QSTATC[63] | Queue Manager Queue 63 Status Register C |
5.26.1 USB2.0 (USB0) Electrical Data/Timing
The USB PHY PLL can support input clock of the following frequencies: 12.0 MHz, 13.0 MHz, 19.2 MHz, 20.0 MHz, 24.0 MHz, 26.0 MHz, 38.4 MHz, 40.0 MHz or 48.0 MHz. USB_REFCLKIN jitter tolerance is 50 ppm maximum.
Table 5-97 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for USB2.0 [USB0] (see Figure 5-66)
| No. | PARAMETER | LOW SPEED 1.5 Mbps |
FULL SPEED 12 Mbps |
HIGH SPEED 480 Mbps |
UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | ||||
| 1 | tr(D) | Rise time, USB0_DP and USB0_DM signals(1) | 75 | 300 | 4 | 20 | 0.5 | ns | |
| 2 | tf(D) | Fall time, USB0_DP and USB0_DM signals(1) | 75 | 300 | 4 | 20 | 0.5 | ns | |
| 3 | trfM | Rise/Fall time, matching(2) | 80 | 120 | 90 | 111 | – | – | % |
| 4 | VCRS | Output signal cross-over voltage(1) | 1.3 | 2 | 1.3 | 2 | – | – | V |
| 5 | tjr(source)NT | Source (Host) Driver jitter, next transition | 2 | 2 | (4) | ns | |||
| tjr(FUNC)NT | Function Driver jitter, next transition | 25 | 2 | (4) | ns | ||||
| 6 | tjr(source)PT | Source (Host) Driver jitter, paired transition(3) | 1 | 1 | (4) | ns | |||
| tjr(FUNC)PT | Function Driver jitter, paired transition | 10 | 1 | (4) | ns | ||||
| 7 | tw(EOPT) | Pulse duration, EOP transmitter (5) | 1250 | 1500 | 160 | 175 | – | – | ns |
| 8 | tw(EOPR) | Pulse duration, EOP receiver (5) | 670 | 82 | – | ns | |||
| 9 | t(DRATE) | Data Rate | 1.5 | 12 | 480 | Mb/s | |||
| 10 | ZDRV | Driver Output Resistance | – | – | 40.5 | 49.5 | 40.5 | 49.5 | Ω |
| 11 | ZINP | Receiver Input Impedance | 100k | 100k | - | - | Ω | ||
 Figure 5-66 USB0 Integrated Transceiver Interface Timing
Figure 5-66 USB0 Integrated Transceiver Interface Timing
5.26.2 USB0 Unused Signal Configuration
If USB0 is unused, then the USB0 signals should be configured as shown in Section 3.6.22.
5.27 Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
5.27.1 HPI Device-Specific Information
The device includes a user-configurable 16-bit Host-port interface (HPI16).
5.27.2 HPI Peripheral Register Description(s)
Table 5-98 HPI Control Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01E1 0000 | PID | Peripheral Identification Register | |
| 0x01E1 0004 | PWREMU_MGMT | HPI power and emulation management register | The CPU has read/write access to the PWREMU_MGMT register. |
| 0x01E1 0008 | - | Reserved | |
| 0x01E1 000C | GPIO_EN | General Purpose IO Enable Register | |
| 0x01E1 0010 | GPIO_DIR1 | General Purpose IO Direction Register 1 | |
| 0x01E1 0014 | GPIO_DAT1 | General Purpose IO Data Register 1 | |
| 0x01E1 0018 | GPIO_DIR2 | General Purpose IO Direction Register 2 | |
| 0x01E1 001C | GPIO_DAT2 | General Purpose IO Data Register 2 | |
| 0x01E1 0020 | GPIO_DIR3 | General Purpose IO Direction Register 3 | |
| 0x01E1 0024 | GPIO_DAT3 | General Purpose IO Data Register 3 | |
| 0x01E1 0028 | - | Reserved | |
| 0x01E1 002C | - | Reserved | |
| 0x01E1 0030 | HPIC | HPI control register | The Host and the CPU both have read/write access to the HPIC register. |
| 0x01E1 0034 | HPIA (HPIAW)(1) |
HPI address register (Write) |
The Host has read/write access to the HPIA registers. The CPU has only read access to the HPIA registers. |
| 0x01E1 0038 | HPIA (HPIAR)(1) |
HPI address register (Read) |
|
| 0x01E1 000C- 0x01E1 07FF |
- | Reserved |
5.27.3 HPI Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-99 Timing Requirements for Host-Port Interface Cycles(1)(2)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tsu(SELV-HSTBL) | Setup time, select signals(3) valid before UHPI_HSTROBE low | 5 | ns | |
| 2 | th(HSTBL-SELV) | Hold time, select signals(3) valid after UHPI_HSTROBE low | 2 | ns | |
| 3 | tw(HSTBL) | Pulse duration, UHPI_HSTROBE active low | 15 | ns | |
| 4 | tw(HSTBH) | Pulse duration, UHPI_HSTROBE inactive high between consecutive accesses | 2M | ns | |
| 9 | tsu(SELV-HASL) | Setup time, selects signals valid before UHPI_HAS low | 5 | ns | |
| 10 | th(HASL-SELV) | Hold time, select signals valid after UHPI_HAS low | 2 | ns | |
| 11 | tsu(HDV-HSTBH) | Setup time, host data valid before UHPI_HSTROBE high | 5 | ns | |
| 12 | th(HSTBH-HDV) | Hold time, host data valid after UHPI_HSTROBE high | 2 | ns | |
| 13 | th(HRDYL-HSTBH) | Hold time, UHPI_HSTROBE high after UHPI_HRDY low. UHPI_HSTROBE should not be inactivated until UHPI_HRDY is active (low); otherwise, HPI writes will not complete properly. | 2 | ns | |
| 16 | tsu(HASL-HSTBL) | Setup time, UHPI_HAS low before UHPI_HSTROBE low | 2 | ns | |
| 17 | th(HSTBL-HASH) | Hold time, UHPI_HAS low after UHPI_HSTROBE low | 2 | ns | |
Table 5-100 Switching Characteristics for Host-Port Interface Cycles(1)(2)(3)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | td(HSTBL-HRDYV) | Delay time, UHPI_HSTROBE low to UHPI_HRDY valid |
For HPI Write, UHPI_HRDY can go high (not ready) for these HPI Write conditions; otherwise, UHPI_HRDY stays low (ready): Case 1: Back-to-back HPIA writes (can be either first or second half-word) Case 2: HPIA write following a PREFETCH command (can be either first or second half-word) Case 3: HPID write when FIFO is full or flushing (can be either first or second half-word) Case 4: HPIA write and Write FIFO not empty For HPI Read, UHPI_HRDY can go high (not ready) for these HPI Read conditions: Case 1: HPID read (with auto-increment) and data not in Read FIFO (can only happen to first half-word of HPID access) Case 2: First half-word access of HPID Read without auto-increment For HPI Read, UHPI_HRDY stays low (ready) for these HPI Read conditions: Case 1: HPID read with auto-increment and data is already in Read FIFO (applies to either half-word of HPID access) Case 2: HPID read without auto-increment and data is already in Read FIFO (always applies to second half-word of HPID access) Case 3: HPIC or HPIA read (applies to either half-word access) |
12 | ns | |
| 5a | td(HASL-HRDYV) | Delay time, UHPI_HAS low to UHPI_HRDY valid | 13 | |||
| 6 | ten(HSTBL-HDLZ) | Enable time, HD driven from UHPI_HSTROBE low | 2 | ns | ||
| 7 | td(HRDYL-HDV) | Delay time, UHPI_HRDY low to HD valid | 0 | ns | ||
| 8 | toh(HSTBH-HDV) | Output hold time, HD valid after UHPI_HSTROBE high | 1.5 | ns | ||
| 14 | tdis(HSTBH-HDHZ) | Disable time, HD high-impedance from UHPI_ HSTROBE high | 12 | ns | ||
| 15 | td(HSTBL-HDV) | Delay time, UHPI_HSTROBE low to HD valid |
For HPI Read. Applies to conditions where data is already residing in HPID/FIFO: Case 1: HPIC or HPIA read Case 2: First half-word of HPID read with auto-increment and data is already in Read FIFO Case 3: Second half-word of HPID read with or without auto-increment |
15 | ns | |
| 18 | td(HSTBH-HRDYV) | Delay time, UHPI_HSTROBE high to UHPI_HRDY valid |
For HPI Write, UHPI_HRDY can go high (not ready) for these HPI Write conditions; otherwise, UHPI_HRDY stays low (ready): Case 1: HPID write when Write FIFO is full (can happen to either half-word) Case 2: HPIA write (can happen to either half-word) Case 3: HPID write without auto-increment (only happens to second half-word) |
12 | ns | |




5.28 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
The Power and Sleep Controllers (PSC) are responsible for managing transitions of system power on/off, clock on/off, resets (device level and module level). It is used primarily to provide granular power control for on chip modules (peripherals and CPU). A PSC module consists of a Global PSC (GPSC) and a set of Local PSCs (LPSCs). The GPSC contains memory mapped registers, PSC interrupts, a state machine for each peripheral/module it controls. An LPSC is associated with every module that is controlled by the PSC and provides clock and reset control.
The PSC includes the following features:
- Provides a software interface to:
- Control module clock enable/disable
- Control module reset
- Control CPU local reset
- Supports ICEPick TAP Router power, clock and reset features. For details on ICEPick features see http://tiexpressdsp.com/wiki/index.php?title=ICEPick.
Table 5-101 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC) Registers
| PSC0 BYTE ADDRESS |
PSC1 BYTE ADDRESS |
ACRONYM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C1 0000 | 0x01E2 7000 | REVID | Peripheral Revision and Class Information Register |
| 0x01C1 0018 | 0x01E2 7018 | INTEVAL | Interrupt Evaluation Register |
| 0x01C1 0040 | 0x01E2 7040 | MERRPR0 | Module Error Pending Register 0 (module 0-15) (PSC0) |
| Module Error Pending Register 0 (module 0-31) (PSC1) | |||
| 0x01C1 0050 | 0x01E2 7050 | MERRCR0 | Module Error Clear Register 0 (module 0-15) (PSC0) |
| Module Error Clear Register 0 (module 0-31) (PSC1) | |||
| 0x01C1 0060 | 0x01E2 7060 | PERRPR | Power Error Pending Register |
| 0x01C1 0068 | 0x01E2 7068 | PERRCR | Power Error Clear Register |
| 0x01C1 0120 | 0x01E2 7120 | PTCMD | Power Domain Transition Command Register |
| 0x01C1 0128 | 0x01E2 7128 | PTSTAT | Power Domain Transition Status Register |
| 0x01C1 0200 | 0x01E2 7200 | PDSTAT0 | Power Domain 0 Status Register |
| 0x01C1 0204 | 0x01E2 7204 | PDSTAT1 | Power Domain 1 Status Register |
| 0x01C1 0300 | 0x01E2 7300 | PDCTL0 | Power Domain 0 Control Register |
| 0x01C1 0304 | 0x01E2 7304 | PDCTL1 | Power Domain 1 Control Register |
| 0x01C1 0400 | 0x01E2 7400 | PDCFG0 | Power Domain 0 Configuration Register |
| 0x01C1 0404 | 0x01E2 7404 | PDCFG1 | Power Domain 1 Configuration Register |
| 0x01C1 0800- 0x01C1 083C |
0x01E2 7800- 0x01E2 787C |
MDSTAT0-MDSTAT15 | Module Status n Register (modules 0-15) (PSC0) |
| MDSTAT0-MDSTAT31 | Module Status n Register (modules 0-31) (PSC1) | ||
| 0x01C1 0A00- 0x01C1 0A3C |
0x01E2 7A00- 0x01E2 7A7C |
MDCTL0-MDCTL15 | Module Control n Register (modules 0-15) (PSC0) |
| MDCTL0-MDCTL31 | Module Control n Register (modules 0-31) (PSC1) |
5.28.1 Power Domain and Module Topology
The device includes two PSC modules.
Each PSC module controls clock states for several of the on chip modules, controllers and interconnect components. Table 5-102 and Table 5-103 lists the set of peripherals/modules that are controlled by the PSC, the power domain they are associated with, the LPSC assignment and the default (power-on reset) module states. See the device-specific data manual for the peripherals available on a given device. The module states and terminology are defined in Section 5.28.1.2.
Table 5-102 PSC0 Default Module Configuration
| LPSC Number | Module Name | Power Domain | Default Module State | Auto Sleep/Wake Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | EDMA3 Channel Controller | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 1 | EDMA3 Transfer Controller 0 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 2 | EDMA3 Transfer Controller 1 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 3 | EMIFA (BR7) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 4 | SPI 0 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 5 | MMC/SD 0 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 6 | ARM Interrupt Controller | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 7 | ARM RAM/ROM | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 8 | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | UART 0 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 10 | SCR0 (Br 0, Br 1, Br 2, Br 8) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 11 | SCR1 (Br 4) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 12 | SCR2 (Br 3, Br 5, Br 6) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 13 | PRUSS | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 14 | ARM | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 15 | - | - | - | — |
Table 5-103 PSC1 Default Module Configuration
| LPSC Number | Module Name | Power Domain | Default Module State | Auto Sleep/Wake Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Not Used | — | — | — |
| 1 | USB0 (USB2.0) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 2 | USB1 (USB1.1) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 3 | GPIO | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 4 | UHPI | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 5 | EMAC | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 6 | EMIFB (Br 20) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 7 | McASP0 ( + McASP0 FIFO) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 8 | McASP1 ( + McASP1 FIFO) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 9 | McASP2( + McASP2 FIFO) | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 10 | SPI 1 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 11 | I2C 1 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 12 | UART 1 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 13 | UART 2 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 14-15 | Not Used | — | — | — |
| 16 | LCDC | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 17 | eHRPWM0/1/2 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 18-19 | Not Used | — | — | — |
| 20 | ECAP0/1/2 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 21 | EQEP0/1 | AlwaysON (PD0) | SwRstDisable | — |
| 22-23 | Not Used | — | — | — |
| 24 | SCR8 (Br 15) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 25 | SCR7 (Br 12) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 26 | SCR12 (Br 18) | AlwaysON (PD0) | Enable | Yes |
| 27-30 | Not Used | — | — | — |
| 31 | On-chip RAM (Br 13) | PD_SHRAM | Enable | Yes |
5.28.1.1 Power Domain States
A power domain can only be in one of the two states: ON or OFF, defined as follows:
- ON: power to the domain is on
- OFF: power to the domain is off
In the device, for both PSC0 and PSC1, the Always ON domain, or PD0 power domain, is always in the ON state when the chip is powered-on. This domain is not programmable to OFF state.
- On PSC1 PD1/PD_SHRAM Domain: Controls the sleep state for the 128K Shared RAM
5.28.1.2 Module States
The PSC defines several possible states for a module. This states are essentially a combination of the module reset asserted or de-asserted and module clock on/enabled or off/disabled. The module states are defined in Table 5-104.
Table 5-104 Module States
| Module State | Module Reset | Module Clock | Module State Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable | De-asserted | On | A module in the enable state has its module reset de-asserted and it has its clock on. This is the normal operational state for a given module |
| Disable | De-asserted | Off | A module in the disabled state has its module reset de-asserted and it has its module clock off. This state is typically used for disabling a module clock to save power. The device is designed in full static CMOS, so when you stop a module clock, it retains the module’s state. When the clock is restarted, the module resumes operating from the stopping point. |
| SyncReset | Asserted | On | A module state in the SyncReset state has its module reset asserted and it has its clock on. Generally, software is not expected to initiate this state |
| SwRstDisable | Asserted | Off | A module in the SwResetDisable state has its module reset asserted and it has its clock disabled. After initial power-on, several modules come up in the SwRstDisable state. Generally, software is not expected to initiate this state |
| Auto Sleep | De-asserted | Off | A module in the Auto Sleep state also has its module reset de-asserted and its module clock disabled, similar to the Disable state. However this is a special state, once a module is configured in this state by software, it can “automatically” transition to “Enable” state whenever there is an internal read/write request made to it, and after servicing the request it will “automatically” transition into the sleep state (with module reset re de-asserted and module clock disabled), without any software intervention. The transition from sleep to enabled and back to sleep state has some cycle latency associated with it. It is not envisioned to use this mode when peripherals are fully operational and moving data. |
| Auto Wake | De-asserted | Off | A module in the Auto Wake state also has its module reset de-asserted and its module clock disabled, similar to the Disable state. However this is a special state, once a module is configured in this state by software, it will “automatically” transition to “Enable” state whenever there is an internal read/write request made to it, and will remain in the “Enabled” state from then on (with module reset re de-asserted and module clock on), without any software intervention. The transition from sleep to enabled state has some cycle latency associated with it. It is not envisioned to use this mode when peripherals are fully operational and moving data. |
5.29 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
The Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) consists of
- Two Programmable Real-Time Units (PRU0 and PRU1) and their associated memories
- An Interrupt Controller (INTC) for handling system interrupt events. The INTC also supports posting events back to the device level host CPU.
- A Switched Central Resource (SCR) for connecting the various internal and external masters to the resources inside the PRUSS.
The two PRUs can operate completely independently or in coordination with each other. The PRUs can also work in coordination with the device level host CPU. This is determined by the nature of the program which is loaded into the PRUs instruction memory. Several different signaling mechanisms are available between the two PRUs and the device level host CPU.
The PRUs are optimized for performing embedded tasks that require manipulation of packed memory mapped data structures, handling of system events that have tight realtime constraints and interfacing with systems external to the device.
The PRUSS comprises various distinct addressable regions. Externally the subsystem presents a single 64Kbyte range of addresses. The internal interconnect bus (also called switched central resource, or SCR) of the PRUSS decodes accesses for each of the individual regions. The PRUSS memory map is documented in Table 5-105 and in Table 5-106. Note that these two memory maps are implemented inside the PRUSS and are local to the components of the PRUSS.
Table 5-105 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) Local Instruction Space Memory Map
| BYTE ADDRESS | PRU0 | PRU1 |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 0000 - 0x0000 0FFF | PRU0 Instruction RAM | PRU1 Instruction RAM |
Table 5-106 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) Local Data Space Memory Map
| BYTE ADDRESS | PRU0 | PRU1 |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0000 0000 - 0x0000 01FF | Data RAM 0 (1) | Data RAM 1 (1) |
| 0x0000 0200 - 0x0000 1FFF | Reserved | Reserved |
| 0x0000 2000 - 0x0000 21FF | Data RAM 1 (1) | Data RAM 0 (1) |
| 0x0000 2200 - 0x0000 3FFF | Reserved | Reserved |
| 0x0000 4000 - 0x0000 6FFF | INTC Registers | INTC Registers |
| 0x0000 7000 - 0x0000 73FF | PRU0 Control Registers | PRU0 Control Registers |
| 0x0000 7400 - 0x0000 77FF | Reserved | Reserved |
| 0x0000 7800 - 0x0000 7BFF | PRU1 Control Registers | PRU1 Control Registers |
| 0x0000 7C00 - 0xFFFF FFFF | Reserved | Reserved |
The global view of the PRUSS internal memories and control ports is documented in Table 5-107. The offset addresses of each region are implemented inside the PRUSS but the global device memory mapping places the PRUSS slave port in the address range 0x01C3 0000-0x01C3 FFFF. The PRU0 and PRU1 can use either the local or global addresses to access their internal memories, but using the local addresses will provide access time several cycles faster than using the global addresses. This is because when accessing via the global address the access needs to be routed through the switch fabric outside PRUSS and back in through the PRUSS slave port.
Table 5-107 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) Global Memory Map
| BYTE ADDRESS | REGION |
|---|---|
| 0x01C3 0000 - 0x01C3 01FF | Data RAM 0 |
| 0x01C3 0200 - 0x01C3 1FFF | Reserved |
| 0x01C3 2000 - 0x01C3 21FF | Data RAM 1 |
| 0x01C3 2200 - 0x01C3 3FFF | Reserved |
| 0x01C3 4000 - 0x01C3 6FFF | INTC Registers |
| 0x01C3 7000 - 0x01C3 73FF | PRU0 Control Registers |
| 0x01C3 7400 - 0x01C3 77FF | PRU0 Debug Registers |
| 0x01C3 7800 - 0x01C3 7BFF | PRU1 Control Registers |
| 0x01C3 7C00 - 0x01C3 7FFF | PRU1 Debug Registers |
| 0x01C3 8000 - 0x01C3 8FFF | PRU0 Instruction RAM |
| 0x01C3 9000 - 0x01C3 BFFF | Reserved |
| 0x01C3 C000 - 0x01C3 CFFF | PRU1 Instruction RAM |
| 0x01C3 D000 - 0x01C3 FFFF | Reserved |
Each of the PRUs can access the rest of the device memory (including memory mapped peripheral and configuration registers) using the global memory space addresses.
5.29.1 PRUSS Register Descriptions
Table 5-108 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) Control / Status Registers
| PRU0 BYTE ADDRESS | PRU1 BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C3 7000 | 0x01C3 7800 | CONTROL | PRU Control Register |
| 0x01C3 7004 | 0x01C3 7804 | STATUS | PRU Status Register |
| 0x01C3 7008 | 0x01C3 7808 | WAKEUP | PRU Wakeup Enable Register |
| 0x01C3 700C | 0x01C3 780C | CYCLCNT | PRU Cycle Count |
| 0x01C3 7010 | 0x01C3 7810 | STALLCNT | PRU Stall Count |
| 0x01C3 7020 | 0x01C3 7820 | CONTABBLKIDX0 | PRU Constant Table Block Index Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 7028 | 0x01C3 7828 | CONTABPROPTR0 | PRU Constant Table Programmable Pointer Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 702C | 0x01C3 782C | CONTABPROPTR1 | PRU Constant Table Programmable Pointer Register 1 |
| 0x01C37400 - 0x01C3747C | 0x01C3 7C00 - 0x01C3 7C7C | INTGPR0 – INTGPR31 | PRU Internal General Purpose Registers (for Debug) |
| 0x01C37480 - 0x01C374FC | 0x01C3 7C80 - 0x01C3 7CFC | INTCTER0 – INTCTER31 | PRU Internal Constants Table Registers (for Debug) |
Table 5-109 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem Interrupt Controller (PRUSS INTC) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01C3 4000 | REVID | Revision ID Register |
| 0x01C3 4004 | CONTROL | Control Register |
| 0x01C3 4010 | GLBLEN | Global Enable Register |
| 0x01C3 401C | GLBLNSTLVL | Global Nesting Level Register |
| 0x01C3 4020 | STATIDXSET | System Interrupt Status Indexed Set Register |
| 0x01C3 4024 | STATIDXCLR | System Interrupt Status Indexed Clear Register |
| 0x01C3 4028 | ENIDXSET | System Interrupt Enable Indexed Set Register |
| 0x01C3 402C | ENIDXCLR | System Interrupt Enable Indexed Clear Register |
| 0x01C3 4034 | HSTINTENIDXSET | Host Interrupt Enable Indexed Set Register |
| 0x01C3 4038 | HSTINTENIDXCLR | Host Interrupt Enable Indexed Clear Register |
| 0x01C3 4080 | GLBLPRIIDX | Global Prioritized Index Register |
| 0x01C3 4200 | STATSETINT0 | System Interrupt Status Raw/Set Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4204 | STATSETINT1 | System Interrupt Status Raw/Set Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 4280 | STATCLRINT0 | System Interrupt Status Enabled/Clear Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4284 | STATCLRINT1 | System Interrupt Status Enabled/Clear Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 4300 | ENABLESET0 | System Interrupt Enable Set Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4304 | ENABLESET1 | System Interrupt Enable Set Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 4380 | ENABLECLR0 | System Interrupt Enable Clear Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4384 | ENABLECLR1 | System Interrupt Enable Clear Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 4400 - 0x01C3 4440 | CHANMAP0 - CHANMAP15 | Channel Map Registers 0-15 |
| 0x01C3 4800 - 0x01C3 4808 | HOSTMAP0 - HOSTMAP2 | Host Map Register 0-2 |
| 0x01C3 4900 - 0x01C3 4928 | HOSTINTPRIIDX0 - HOSTINTPRIIDX9 | Host Interrupt Prioritized Index Registers 0-9 |
| 0x01C3 4D00 | POLARITY0 | System Interrupt Polarity Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4D04 | POLARITY1 | System Interrupt Polarity Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 4D80 | TYPE0 | System Interrupt Type Register 0 |
| 0x01C3 4D84 | TYPE1 | System Interrupt Type Register 1 |
| 0x01C3 5100 - 0x01C3 5128 | HOSTINTNSTLVL0-HOSTINTNSTLVL9 | Host Interrupt Nesting Level Registers 0-9 |
| 0x01C3 5500 | HOSTINTEN | Host Interrupt Enable Register |
5.30 Emulation Logic
This section describes the steps to use a third party debugger. The debug capabilities and features for ARM are as shown below.
For TI’s latest debug and emulation information see :
http://tiexpressdsp.com/wiki/index.php?title=Category:Emulation
ARM:
- Basic Debug
- Execution Control
- System Visibility
- Advanced Debug
- Global Start
- Global Stop
- Advanced System Control
- Subsystem reset via debug
- Peripheral notification of debug events
- Cache-coherent debug accesses
- Program Trace
- Program flow corruption
- Code coverage
- Path coverage
- Thread/interrupt synchronization problems
- Data Trace
- Memory corruption
- Timing Trace
- Profiling
- Analysis Actions
- Stop program execution
- Control trace streams
- Generate debug interrupt
- Benchmarking with counters
- External trigger generation
- Debug state machine state transition
- Combinational and Sequential event generation
- Analysis Events
- Program event detection
- Data event detection
- External trigger Detection
- System event detection (i.e. cache miss)
- Debug state machine state detection
- Analysis Configuration
- Application access
- Debugger access
Table 5-110 ARM Debug Features
| Category | Hardware Feature | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Debug | Software breakpoint | Unlimited |
| Hardware breakpoint | Up to 14 HWBPs, including: | |
| 2 precise(1) HWBP inside ARM core which are shared with watch points. | ||
| 8 imprecise(1) HWBPs from ETM’s address comparators, which are shared with trace function, and can be used as watch point too. | ||
| 4 imprecise(1) HWBPs from ICECrusher. | ||
| Analysis | Watch point | Up to 6 watch points, including: |
| 2 from ARM core which is shared with HWBPs and can be associated with a data. | ||
| 8 from ETM’s address comparators, which are shared with trace function, and HWBPs. | ||
| Watch point with Data | 2 from ARM core which is shared with HWBPs. | |
| 8 watch points from ETM can be associated with a data comparator, and ETM has total 4 data comparators. | ||
| Counters/timers | 3x32-bit (1 cycle ; 2 event) | |
| External Event Trigger In | 1 | |
| External Event Trigger Out | 1 | |
| Trace Control | Address range for trace | 4 |
| Data qualification for trace | 2 | |
| System events for trace control | 20 | |
| Counters/Timers for trace control | 2x16-bit | |
| State Machines/Sequencers | 1x3-State State Machine | |
| Context/Thread ID Comparator | 1 | |
| Independent trigger control units | 12 | |
| On-chip Trace Capture | Capture depth PC | 4k bytes ETB |
| Capture depth PC + Timing | 4k bytes ETB | |
| Application accessible | Y |
5.30.1 JTAG Port Description
The device target debug interface uses the five standard IEEE 1149.1(JTAG) signals (TRST, TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO), a return clock (RTCK) due to the clocking requirements of the ARM926EJ-S and EMU0 .
TRST holds the debug and boundary scan logic in reset when pulled low (its default state). Since TRST has an internal pull-down resistor, this ensures that at power up the device functions in its normal (non-test) operation mode if TRST is not connected. Otherwise, TRST should be driven inactive by the emulator or boundary scan controller. Boundary scan test cannot be performed while the TRST pin is pulled low.
Table 5-111 JTAG Port Description
| PIN | TYPE | NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRST | I | Test Logic Reset | When asserted (active low) causes all test and debug logic in the device to be reset along with the IEEE 1149.1 interface |
| TCK | I | Test Clock | This is the test clock used to drive an IEEE 1149.1 TAP state machine and logic. Depending on the emulator attached to , this is a free running clock or a gated clock depending on RTCK monitoring. |
| RTCK | O | Returned Test Clock | Synchronized TCK. Depending on the emulator attached to, the JTAG signals are clocked from RTCK or RTCK is monitored by the emulator to gate TCK. |
| TMS | I | Test Mode Select | Directs the next state of the IEEE 1149.1 test access port state machine |
| TDI | I | Test Data Input | Scan data input to the device |
| TDO | O | Test Data Output | Scan data output of the device |
| EMU0 | I/O | Emulation 0 | Channel 0 trigger + HSRTDX |
5.30.2 Scan Chain Configuration Parameters
Table 5-112 shows the TAP configuration details required to configure the router/emulator for this device.
Table 5-112 JTAG Port Description
| Router Port ID | Default TAP | TAP Name | Tap IR Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | No | Reserved | 38 |
| 18 | No | ARM926 | 4 |
| 19 | No | ETB | 4 |
The router is ICEPick revision C and has a 6-bit IR length.
5.30.3 Initial Scan Chain Configuration
The first level of debug interface that sees the scan controller is the TAP router module. The debugger can configure the TAP router for serially linking up to 16 TAP controllers or individually scanning one of the TAP controllers without disrupting the IR state of the other TAPs.
5.30.3.1 Adding TAPS to the Scan Chain
The TAP router must be programmed to add additional TAPs to the scan chain. The following JTAG scans must be completed to add the ARM926EJ-S to the scan chain.
A Power-On Reset (POR) or the JTAG Test-Logic Reset state configures the TAP router to contain only the router’s TAP.
 Figure 5-71 Adding ARM926EJ-S to the scan chain
Figure 5-71 Adding ARM926EJ-S to the scan chain
Pre-amble: The device whose data reaches the emulator first is listed first in the board configuration file. This device is a pre-amble for all the other devices. This device has the lowest device ID.
Post-amble: The device whose data reaches the emulator last is listed last in the board configuration file. This device is a post-amble for all the other devices. This device has the highest device ID.
- Function : Update the JTAG preamble and post-amble counts.
- Parameter : The IR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The IR post-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The DR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The DR post-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The IR main count is '6'.
- Parameter : The DR main count is '1'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-ir'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000007'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-dr'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-dr'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '8'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000089'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-ir'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000002'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Embed the port address in next command.
- Parameter : The port address field is '0x0f000000'.
- Parameter : The port address value is '3'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-dr'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-dr'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '32'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0xa2002108'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only all-ones JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'run-test/idle'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is 'all-ones'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Wait for a minimum number of TCLK pulses.
- Parameter : The count of TCLK pulses is '10'.
- Function : Update the JTAG preamble and post-amble counts.
- Parameter : The IR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The IR post-amble count is '6'.
- Parameter : The DR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The DR post-amble count is '1'.
- Parameter : The IR main count is '4'.
- Parameter : The DR main count is '1'.
The initial scan chain contains only the TAP router module. The following steps must be completed in order to add ETB TAP to the scan chain.
 Figure 5-72 Adding ETB to the scan chain
Figure 5-72 Adding ETB to the scan chain
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-ir'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000007'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-dr'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-dr'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '8'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000089'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-ir'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0x00000002'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Embed the port address in next command.
- Parameter : The port address field is '0x0f000000'.
- Parameter : The port address value is '3'.
- Function : Do a send-only JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The route to JTAG shift state is 'shortest transition'.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-dr'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'pause-dr'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '32'.
- Parameter : The send data value is '0xa3302108'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Do a send-only all-ones JTAG IR/DR scan.
- Parameter : The JTAG shift state is 'shift-ir'.
- Parameter : The JTAG destination state is 'run-test/idle'.
- Parameter : The bit length of the command is '6'.
- Parameter : The send data value is 'all-ones'.
- Parameter : The actual receive data is 'discarded'.
- Function : Wait for a minimum number of TCLK pulses.
- Parameter : The count of TCLK pulses is '10'.
- Function : Update the JTAG preamble and post-amble counts.
- Parameter : The IR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The IR post-amble count is '6 + 4'.
- Parameter : The DR pre-amble count is '0'.
- Parameter : The DR post-amble count is '1 + 1'.
- Parameter : The IR main count is '4'.
- Parameter : The DR main count is '1'.
5.30.4 JTAG 1149.1 Boundary Scan Considerations
To use boundary scan, the following sequence should be followed:
- Execute a valid reset sequence and exit reset
- Wait at least 6000 OSCIN clock cycles
- Enter boundary scan mode using the JTAG pins
No specific value is required on the EMU0 pin for boundary scan testing. If TRST is not driven by the boundary scan tool or tester, TRST should be externally pulled high during boundary scan testing.
5.31 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
The JTAG
The device requires that both TRST and RESET be asserted upon power up to be properly initialized. While RESET initializes the device, TRST initializes the device's emulation logic. Both resets are required for proper operation.
While both TRST and RESET need to be asserted upon power up, only RESET needs to be released for the device to boot properly. TRST may be asserted indefinitely for normal operation, keeping the JTAG port interface and device's emulation logic in the reset state.
TRST only needs to be released when it is necessary to use a JTAG controller to debug the device or exercise the device's boundary scan functionality. Note: TRST is synchronous and must be clocked by TCK; otherwise, the boundary scan logic may not respond as expected after TRST is asserted.
RESET must be released only in order for boundary-scan JTAG to read the variant field of IDCODE correctly. Other boundary-scan instructions work correctly independent of current state of RESET.
For maximum reliability, the device includes an internal pulldown (IPD) on the TRST pin to ensure that TRST will always be asserted upon power up and the device's internal emulation logic will always be properly initialized.
JTAG controllers from Texas Instruments actively drive TRST high. However, some third-party JTAG controllers may not drive TRST high but expect the use of a pullup resistor on TRST.
When using this type of JTAG controller, assert TRST to initialize the device after powerup and externally drive TRST high before attempting any emulation or boundary scan operations.
5.31.1 JTAG Peripheral Register Description(s) – JTAG ID Register (DEVIDR0)
Table 5-113 DEVIDR0 Register
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x01C1 4018 | DEVIDR0 | JTAG Identification Register | Read-only. Provides 32-bit JTAG ID of the device. |
The JTAG ID register is a read-only register that identifies to the customer the JTAG/Device ID. For the device, the JTAG ID register resides at address location 0x01C1 4018. The register hex value for each silicon revision is:
- 0x8B7D F02F for silicon revision 1.1
- 0x9B7D F02F for silicon revisions 3.0, 2.1, and 2.0
| 31 | 28 | 27 | 12 | 11 | 1 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VARIANT (4-bit) |
PART NUMBER (16-bit) | MANUFACTURER (11-bit) | LSB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R-xxxx | R-1011 0111 1101 1111 | R-0000 0010 111 | R-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LEGEND: R = Read, W = Write, n = value at reset |
Table 5-114 JTAG ID Register Selection Bit Descriptions
| BIT | NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 31:28 | VARIANT | Variant (4-Bit) value |
| 27:12 | PART NUMBER | Part Number (16-Bit) value |
| 11-1 | MANUFACTURER | Manufacturer (11-Bit) value |
| 0 | LSB | LSB. This bit is read as a "1". |
5.31.2 JTAG Test-Port Electrical Data/Timing
Table 5-115 Timing Requirements for JTAG Test Port (see Figure 5-74)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(TCK) | Cycle time, TCK | 40 | ns | |
| 2 | tw(TCKH) | Pulse duration, TCK high | 16 | ns | |
| 3 | tw(TCKL) | Pulse duration, TCK low | 16 | ns | |
| 4 | tc(RTCK) | Cycle time, RTCK | 40 | ns | |
| 5 | tw(RTCKH) | Pulse duration, RTCK high | 16 | ns | |
| 6 | tw(RTCKL) | Pulse duration, RTCK low | 16 | ns | |
| 7 | tsu(TDIV-RTCKH) | Setup time, TDI/TMS/TRST valid before RTCK high | 4 | ns | |
| 8 | th(RTCKH-TDIV) | Hold time, TDI/TMS/TRST valid after RTCK high | 4 | ns | |
Table 5-116 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for JTAG Test Port
(see Figure 5-74)
| No. | PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | td(RTCKL-TDOV) | Delay time, RTCK low to TDO valid | 15 | ns | |
 Figure 5-74 JTAG Test-Port Timing
Figure 5-74 JTAG Test-Port Timing
5.32 Real Time Clock (RTC)
The RTC provides a time reference to an application running on the device. The current date and time is tracked in a set of counter registers that update once per second. The time can be represented in 12-hour or 24-hour mode. The calendar and time registers are buffered during reads and writes so that updates do not interfere with the accuracy of the time and date.
Alarms are available to interrupt the CPU at a particular time, or at periodic time intervals, such as once per minute or once per day. In addition, the RTC can interrupt the CPU every time the calendar and time registers are updated, or at programmable periodic intervals.
The real-time clock (RTC) provides the following features:
- 100-year calendar (xx00 to xx99)
- Counts seconds, minutes, hours, day of the week, date, month, and year with leap year compensation
- Binary-coded-decimal (BCD) representation of time, calendar, and alarm
- 12-hour clock mode (with AM and PM) or 24-hour clock mode
- Alarm interrupt
- Periodic interrupt
- Single interrupt to the CPU
- Supports external 32.768-kHz crystal or external clock source of the same frequency
- Separate isolated power supply
Figure 5-75 shows a block diagram of the RTC.
 Figure 5-75 Real-Time Clock Block Diagram
Figure 5-75 Real-Time Clock Block Diagram
5.32.1 Clock Source
The clock reference for the RTC is an external 32.768-kHz crystal or an external clock source of the same frequency. The RTC also has a separate power supply that is isolated from the rest of the system. When the CPU and other peripherals are without power, the RTC can remain powered to preserve the current time and calendar information.
The source for the RTC reference clock may be provided by a crystal or by an external clock source. The RTC has an internal oscillator buffer to support direct operation with a crystal. The crystal is connected between pins RTC_XI and RTC_XO. RTC_XI is the input to the on-chip oscillator and RTC_XO is the output from the oscillator back to the crystal. A crystal with 70k-ohm max ESR is recommended. Typical load capacitance values are 10-20 pF, where the load capacitance is the series combination of C1 and C2.
An external 32.768-kHz clock source may be used instead of a crystal. In such a case, the clock source is connected to RTC_XI, and RTC_XO is left unconnected.
If the RTC is not used, the RTC_XI pin should be static held high or low and RTC_XO should be left unconnected.
 Figure 5-76 Clock Source
Figure 5-76 Clock Source
5.32.2 Registers
Table 5-117 lists the memory-mapped registers for the RTC.
Table 5-117 Real-Time Clock (RTC) Registers
| BYTE ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0x01C2 3000 | SECOND | Seconds Register |
| 0x01C2 3004 | MINUTE | Minutes Register |
| 0x01C2 3008 | HOUR | Hours Register |
| 0x01C2 300C | DAY | Day of the Month Register |
| 0x01C2 3010 | MONTH | Month Register |
| 0x01C2 3014 | YEAR | Year Register |
| 0x01C2 3018 | DOTW | Day of the Week Register |
| 0x01C2 3020 | ALARMSECOND | Alarm Seconds Register |
| 0x01C2 3024 | ALARMMINUTE | Alarm Minutes Register |
| 0x01C2 3028 | ALARMHOUR | Alarm Hours Register |
| 0x01C2 302C | ALARMDAY | Alarm Days Register |
| 0x01C2 3030 | ALARMMONTH | Alarm Months Register |
| 0x01C2 3034 | ALARMYEAR | Alarm Years Register |
| 0x01C2 3040 | CTRL | Control Register |
| 0x01C2 3044 | STATUS | Status Register |
| 0x01C2 3048 | INTERRUPT | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 0x01C2 304C | COMPLSB | Compensation (LSB) Register |
| 0x01C2 3050 | COMPMSB | Compensation (MSB) Register |
| 0x01C2 3054 | OSC | Oscillator Register |
| 0x01C2 3060 | SCRATCH0 | Scratch 0 (General-Purpose) Register |
| 0x01C2 3064 | SCRATCH1 | Scratch 1 (General-Purpose) Register |
| 0x01C2 3068 | SCRATCH2 | Scratch 2 (General-Purpose) Register |
| 0x01C2 306C | KICK0 | Kick 0 (Write Protect) Register |
| 0x01C2 3070 | KICK1 | Kick 1 (Write Protect) Register |