SPRSP65G April 2021 – May 2024 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagram
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 17
- 5.3.1 AM243x_ALX Package - Unsupported Interfaces and Signals
- 5.3.2 ADC
- 5.3.3 CPSW
- 5.3.4 CPTS
- 5.3.5 DDRSS
- 5.3.6 ECAP
- 5.3.7 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.8 EPWM
- 5.3.9 EQEP
- 5.3.10 FSI
- 5.3.11 GPIO
- 5.3.12 GPMC
- 5.3.13 I2C
- 5.3.14 MCAN
- 5.3.15 SPI (MCSPI)
- 5.3.16 MMC
- 5.3.17 OSPI
- 5.3.18 Power Supply
- 5.3.19 PRU_ICSSG
- 5.3.20 Reserved
- 5.3.21 SERDES
- 5.3.22 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.23 TIMER
- 5.3.24 UART
- 5.3.25 USB
- 5.4 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Operating Performance Points
- 6.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 6.7
Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.1 I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS RESET) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.3 High-Frequency Oscillator (HFOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.4 eMMCPHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.6 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.7 ADC12B Electrical Characteristics (ALV package)
- 6.7.8 ADC10B Electrical Characteristics (ALX package)
- 6.7.9 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.10 SerDes PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.11 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.10
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.10.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.10.2 Power Supply Requirements
- 6.10.3 System Timing
- 6.10.4 Clock Specifications
- 6.10.5
Peripherals
- 6.10.5.1 CPSW3G
- 6.10.5.2 DDRSS
- 6.10.5.3 ECAP
- 6.10.5.4 EPWM
- 6.10.5.5 EQEP
- 6.10.5.6 FSI
- 6.10.5.7 GPIO
- 6.10.5.8 GPMC
- 6.10.5.9 I2C
- 6.10.5.10 MCAN
- 6.10.5.11 MCSPI
- 6.10.5.12 MMCSD
- 6.10.5.13 CPTS
- 6.10.5.14 OSPI
- 6.10.5.15 PCIe
- 6.10.5.16
PRU_ICSSG
- 6.10.5.16.1 PRU_ICSSG Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU)
- 6.10.5.16.2 PRU_ICSSG Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- 6.10.5.16.3 PRU_ICSSG Industrial Ethernet Peripheral (IEP)
- 6.10.5.16.4 PRU_ICSSG Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 6.10.5.16.5 PRU_ICSSG Enhanced Capture Peripheral (ECAP)
- 6.10.5.16.6 PRU_ICSSG RGMII, MII_RT, and Switch
- 6.10.5.17 Timers
- 6.10.5.18 UART
- 6.10.5.19 USB
- 6.10.6 Emulation and Debug
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Processor Subsystems
- 7.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 7.4
Other Subsystems
- 7.4.1 PDMA Controller
- 7.4.2
Peripherals
- 7.4.2.1 ADC
- 7.4.2.2 DCC
- 7.4.2.3 Dual Date Rate (DDR) External Memory Interface (DDRSS)
- 7.4.2.4 ECAP
- 7.4.2.5 EPWM
- 7.4.2.6 ELM
- 7.4.2.7 ESM
- 7.4.2.8 GPIO
- 7.4.2.9 EQEP
- 7.4.2.10 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.4.2.11 I2C
- 7.4.2.12 MCAN
- 7.4.2.13 MCRC Controller
- 7.4.2.14 MCSPI
- 7.4.2.15 MMCSD
- 7.4.2.16 OSPI
- 7.4.2.17 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.4.2.18 Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) PHY
- 7.4.2.19 Real Time Interrupt (RTI/WWDT)
- 7.4.2.20 Dual Mode Timer (DMTIMER)
- 7.4.2.21 UART
- 7.4.2.22 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
-
8 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.2
Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.2.1 General Routing Guidelines
- 8.2.2 DDR Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.3 OSPI/QSPI/SPI Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.4 USB VBUS Design Guidelines
- 8.2.5 System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines
- 8.2.6 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.2.7 Thermal Solution Guidance
- 8.3 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ALV|441
- ALX|293
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1 General Routing Guidelines
The following paragraphs detail the routing guidelines that must be observed when routing the various functional LVCMOS interfaces.
- Line spacing:
- For a line width equal to W, the spacing between two lines must be 2W, at least. This minimizes the crosstalk between switching signals between the different lines. On the PCB, this is not achievable everywhere (for example, when breaking signals out from the device package), but it is recommended to follow this rule as much as possible. When violating this guideline, minimize the length of the traces running parallel to each other (see Figure 8-1).
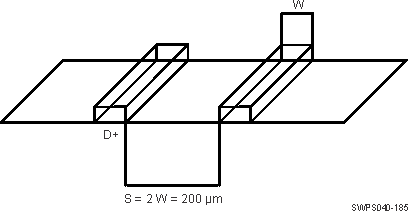 Figure 8-1 Ground Guard Illustration
Figure 8-1 Ground Guard Illustration
- For a line width equal to W, the spacing between two lines must be 2W, at least. This minimizes the crosstalk between switching signals between the different lines. On the PCB, this is not achievable everywhere (for example, when breaking signals out from the device package), but it is recommended to follow this rule as much as possible. When violating this guideline, minimize the length of the traces running parallel to each other (see Figure 8-1).
- Length matching (unless otherwise specified):
- For bus or traces at frequencies less than 10MHz, the trace length matching (maximum length difference between the longest and the shortest lines) must be less than 25mm.
- For bus or traces at frequencies greater than 10MHz, the trace length matching (maximum length difference between the longest and the shortest lines) must be less than 2.5mm.
- Characteristic impedance
- Unless otherwise specified, the characteristic impedance for single-ended interfaces is recommended to be between 35-Ω and 65-Ω.
- Multiple peripheral support
- For interfaces where multiple peripherals have to be supported in the star topology, the length of each branch has to be balanced. Before closing the PCB design, it is highly recommended to verify signal integrity based on simulations including actual PCB extraction.