SBASB00 August 2024 AMC3306M25-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Power Ratings
- 5.6 Insulation Specifications
- 5.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 5.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 5.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 Switching Characteristics
- 5.11 Timing Diagrams
- 5.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 5.13 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DWE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
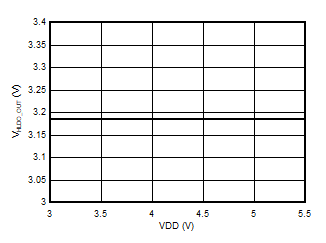
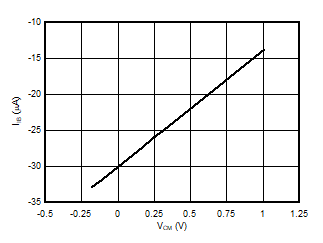
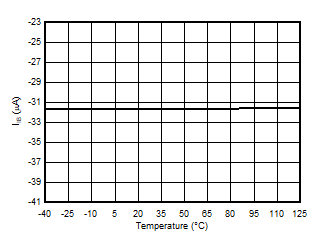
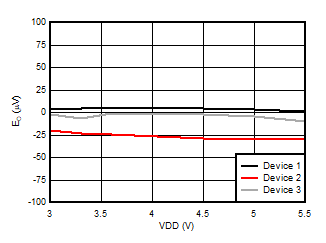
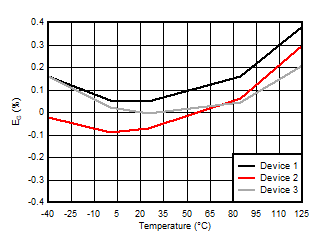
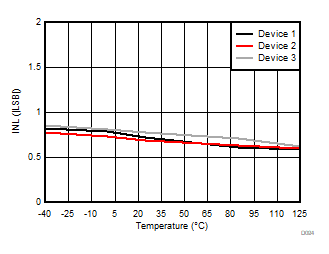
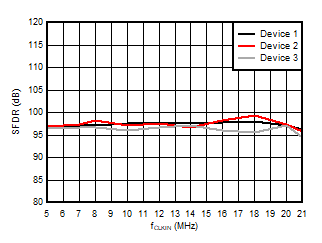
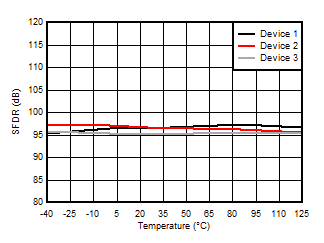
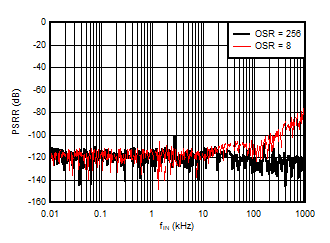
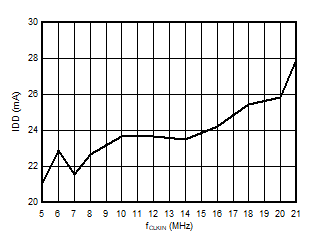
5.13 Typical Characteristics
at VDD = 3.3V, INP = –250mV to +250mV, INN = HGND, fCLKIN = 20MHz, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256, and 16-bit resolution (unless otherwise noted)
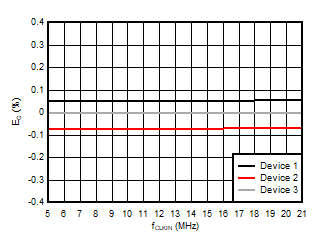
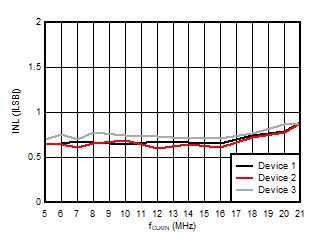
Input Clock Frequency
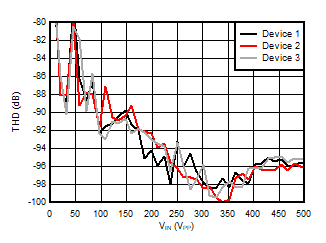
Input Signal Amplitude
Input Clock Frequency
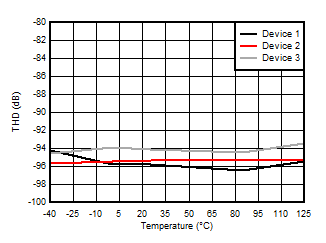
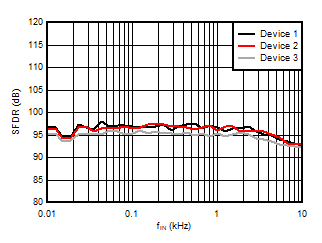
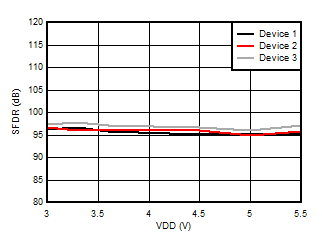
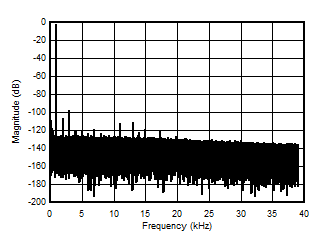
1kHz Input Signal
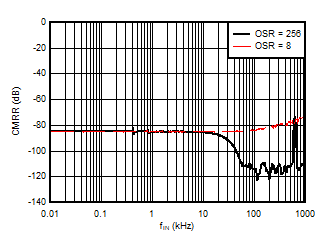
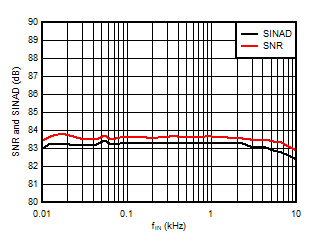
Input Signal Frequency
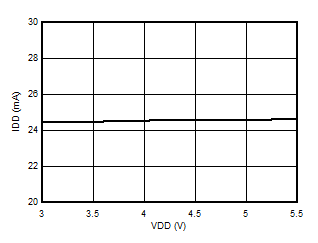
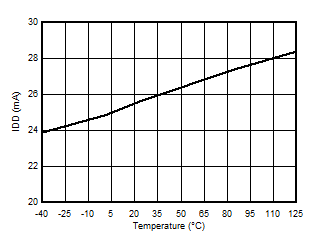
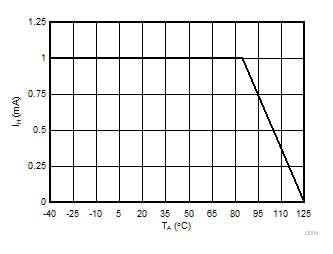
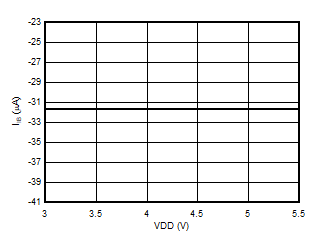
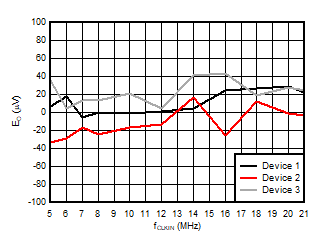
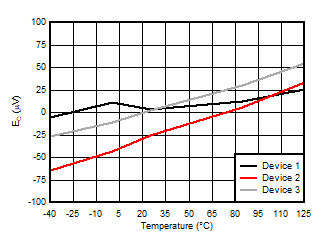
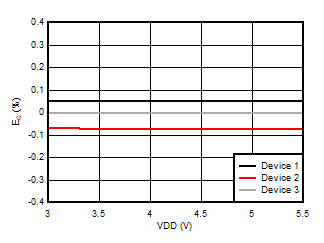
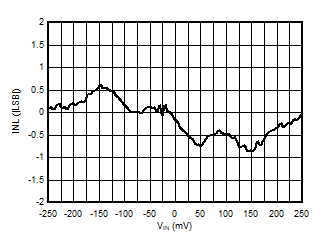
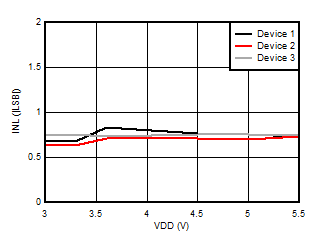
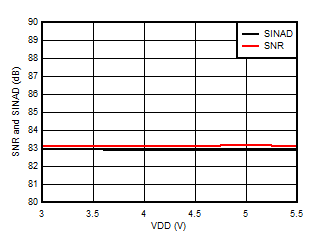
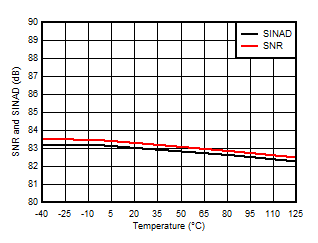
Supply Voltage
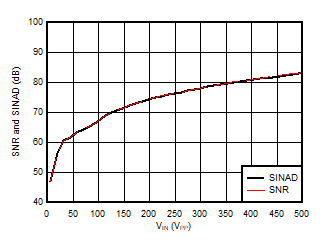
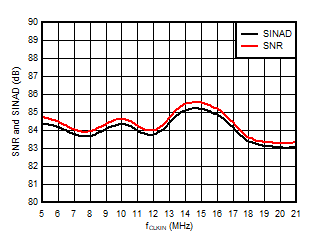
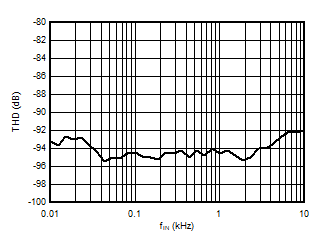
Input Signal Frequency
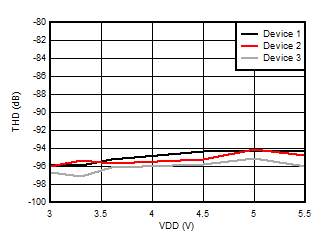
Supply Voltage
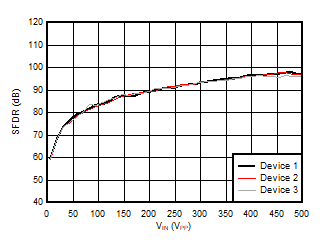
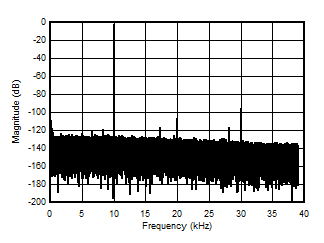
10kHz Input Signal
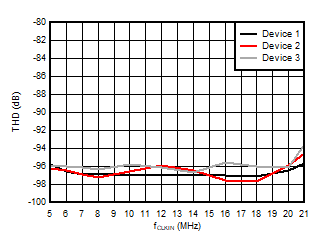
Input Clock Frequency