SLVSDU6D July 2017 – November 2019 ATL431LI , ATL432LI
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
- 11Applications and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DQN|4
Orderable Information
8 Typical Characteristics
Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the recommended operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices.
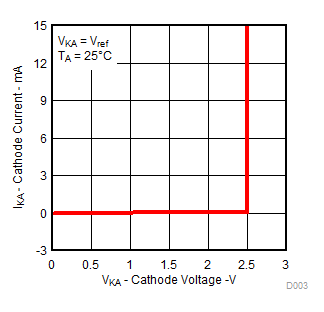 Figure 3. Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage
Figure 3. Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage 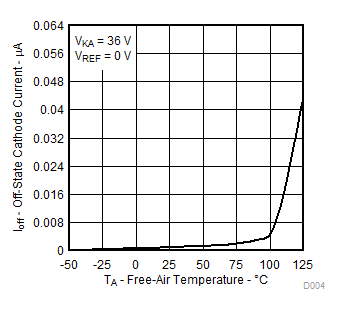 Figure 5. Off-State Cathode Current
Figure 5. Off-State Cathode Current
vs Free-Air Temperature
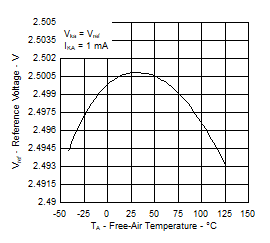
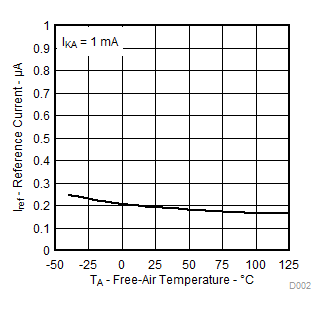 Figure 2. Reference Current vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 2. Reference Current vs Free-Air Temperature 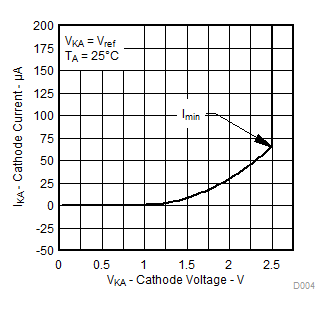 Figure 4. Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage
Figure 4. Cathode Current vs Cathode Voltage 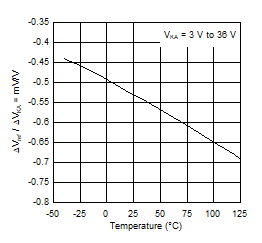 Figure 6. Ratio of Delta Reference Voltage to Delta Cathode Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature
Figure 6. Ratio of Delta Reference Voltage to Delta Cathode Voltage vs Free-Air Temperature 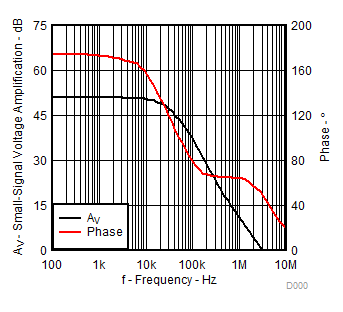
vs Frequency
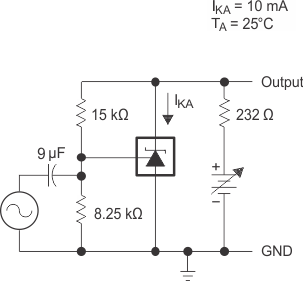
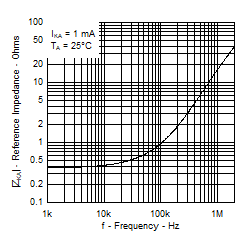 Figure 9. Reference Impedance vs Frequency
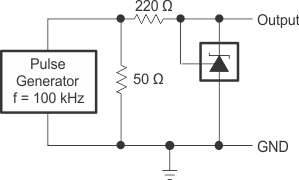
Figure 9. Reference Impedance vs Frequency 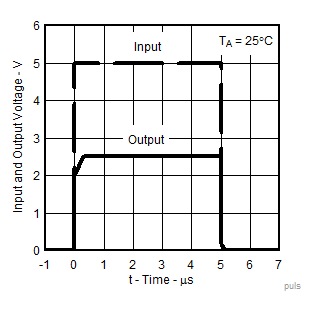 Figure 11. Pulse Response
Figure 11. Pulse Response 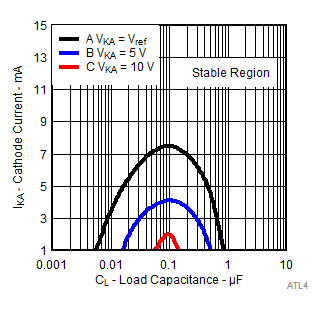
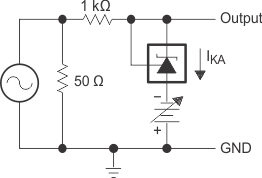
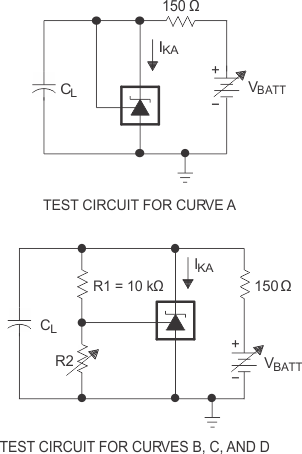
The areas under the curves represent conditions that may cause the device to oscillate. For curves B and C, R2 and V+ are adjusted to establish the initial VKA and IKA conditions, with CL = 0. VBATT and CL then are adjusted to determine the ranges of stability.
Figure 13. Stability Boundary Conditions for All ATL431LI, ATL432LI Devices Above 1 mA 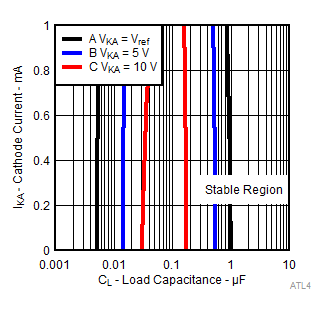
A. The areas in-between the curves represent conditions that may cause the device to oscillate. For curves B, and C, R2 and V+ are adjusted to establish the initial VKA and IKA conditions, with CL = 0. VBATT and CL then are adjusted to determine the ranges of stability.
Figure 15. Stability Boundary Conditions for All ATL431LI, ATL432LI Devices Below 1 mA