SWRS314B January 2024 – December 2024 AWR2544
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Related Products
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 7.6 Power Supply Specifications
- 7.7 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.8 RF Specifications
- 7.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.10 Power Supply Sequencing and Reset Timing
- 7.11 Input Clocks and Oscillators
- 7.12
Peripheral Information
- 7.12.1
QSPI Flash Memory Peripheral
- 7.12.1.1 QSPI Timing Conditions
- 7.12.1.2 QSPI Timing Requirements #GUID-C38B9713-DC57-4B3B-8AFF-A79AF70E5A5A/GUID-97D19708-D87E-443B-9ADF-1760CFEF6F4C #GUID-C38B9713-DC57-4B3B-8AFF-A79AF70E5A5A/GUID-0A61EEC9-2B95-4C27-B219-18D27C8F9430
- 7.12.1.3 QSPI Switching Characteristics #GUID-D1480E86-4079-4A44-A68A-26C2D9F4506B/T4362547-64 #GUID-D1480E86-4079-4A44-A68A-26C2D9F4506B/T4362547-65
- 7.12.2
Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI)
- 7.12.2.1 MibSPI Peripheral Description
- 7.12.2.2
MibSPI Transmit and Receive RAM Organization
- 7.12.2.2.1 SPI Timing Conditions
- 7.12.2.2.2 SPI Controller Mode Switching Parameters (CLOCK PHASE = 0, SPICLK = output, SPISIMO = output, and SPISOMI = input) #GUID-3DD8619F-41DB-47CF-9AF7-5916CFF97E61/T4362547-236 #GUID-3DD8619F-41DB-47CF-9AF7-5916CFF97E61/T4362547-237 #GUID-3DD8619F-41DB-47CF-9AF7-5916CFF97E61/T4362547-238
- 7.12.2.2.3 SPI Controller Mode Switching Parameters (CLOCK PHASE = 1, SPICLK = output, SPISIMO = output, and SPISOMI = input) #GUID-220CE6B8-D17E-48AF-BF69-AAEC97D55C95/T4362547-244 #GUID-220CE6B8-D17E-48AF-BF69-AAEC97D55C95/T4362547-245 #GUID-220CE6B8-D17E-48AF-BF69-AAEC97D55C95/T4362547-246
- 7.12.2.3 SPI Peripheral Mode I/O Timings
- 7.12.3
Ethernet Switch (RGMII/RMII/MII)
Peripheral
- 7.12.3.1 RGMII/RMII/MII Timing Conditions
- 7.12.3.2 RGMII Transmit Clock Switching Characteristics
- 7.12.3.3 RGMII Transmit Data and Control Switching Characteristics
- 7.12.3.4 RGMII Receive Clock Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.5 RGMII RX and TX Timing Diagrams
- 7.12.3.6 RGMII Receive Data and Control Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.7 RMII Transmit Clock Switching Characteristics
- 7.12.3.8 RMII Transmit Data and Control Switching Characteristics
- 7.12.3.9 RMII Receive Clock Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.10 RMII Receive Data and Control Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.11 MII Transmit Switching Characteristics
- 7.12.3.12 MII Receive Clock Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.13 MII Receive Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.14 MII Transmit Clock Timing Requirements
- 7.12.3.15 MDIO Interface Timings
- 7.12.4 LVDS Instrumentation and Measurement Peripheral
- 7.12.5 UART Peripheral
- 7.12.6 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 7.12.7 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.12.8 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 7.12.1
QSPI Flash Memory Peripheral
- 7.13 Emulation and Debug
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Monitoring and Diagnostics
- 10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- AMQ|248
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.12.6.1 I2C Timing Requirements(1)
PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION | STANDARD MODE | FAST MODE | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | MIN | MAX | |||
fSCL | SCL clock frequency | 0 | 100 | 0 | 400 | kHz |
| tsu(SCLH-SDAL) | Setup time, SCL high before SDA low (for a repeated START condition) | 4.7 | 0.6 | μs | ||
| th(SCLL-SDAL) | Hold time, SCL low after SDA low (for a START and a repeated START condition) | 4 | 0.6 | μs | ||
| tw(SCLL) | Pulse duration, SCL low | 4.7 | 1.3 | μs | ||
| tw(SCLH) | Pulse duration, SCL high | 4 | 0.6 | μs | ||
| tsu(SDA-SCLH) | Setup time, SDA valid before SCL high | 250 | 100 | μs | ||
| th(SCLL-SDA)(1) | Hold time, SDA valid after SCL low | 0 | 3.45 | 0 | 0.9 | μs |
| tw(SDAH) | Pulse duration, SDA high between STOP and START conditions | 4.7 | 1.3 | μs | ||
| tsu(SCLH-SDAH) | Setup time, SCL high before SDA high (for STOP condition) | 4 | 0.6 | μs | ||
| tw(SP) | Pulse duration, spike (must be suppressed) | 0 | 50 | ns | ||
| Cb(2)(3) | Capacitive load for each bus line | 400 | 400 | pF | ||
(1) The I2C pins SDA and SCL do not feature fail-safe I/O buffers. These pins could potentially draw current when the device is powered down.
(2) The maximum th(SDA-SCLL) for I2C bus devices has only to be met if the device does not stretch the low period (tw(SCLL)) of the SCL signal.
(3) Cb = total capacitance of one bus line in pF. If mixed with fast-mode devices, faster fall-times are allowed.
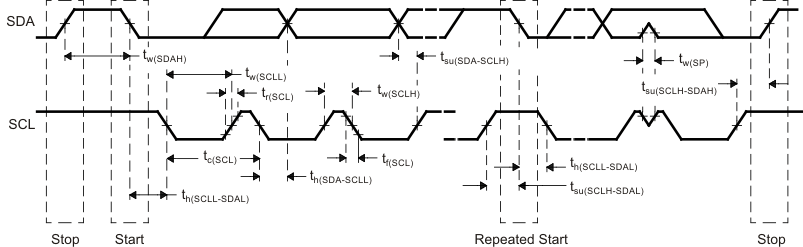 Figure 7-25 I2C Timing Diagram
Figure 7-25 I2C Timing DiagramNote:
- A device must internally provide a hold time of at least 300 ns for the SDA signal (referred to the VIHmin of the SCL signal) to bridge the undefined region of the falling edge of SCL.
- The maximum th(SDA-SCLL) has only to be met if the device does not stretch the LOW period (tw(SCLL)) of the SCL signal. E.A Fast-mode I2C-bus device can be used in a Standard-mode I2C-bus system, but the requirement tsu(SDA-SCLH) ≥ 250 ns must then be met. This will automatically be the case if the device does not stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal. If such a device does stretch the LOW period of the SCL signal, it must output the next data bit to the SDA line tr max + tsu(SDA-SCLH).