SLUSCB6B May 2015 – June 2017
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Battery Preconditioning
- 7.3.2 Battery Fast-Charge Constant Current
- 7.3.3 Charge-Current Monitor
- 7.3.4 Battery Fast-Charge Voltage Regulation
- 7.3.5 Charge Termination Detection and Recharge
- 7.3.6 Charge Status Outputs
- 7.3.7 PG Output (bq24080-Q1)
- 7.3.8 Charge-Enabled (CE) Input (bq24080-Q1)
- 7.3.9 Timer Enabled (TE) Input (bq24081-Q1)
- 7.3.10 Temperature Qualification (bq24081-Q1)
- 7.3.11 Timer Fault and Recovery
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
It is important to pay special attention to the PCB layout. The following provides some guidelines:
- To obtain optimal performance, the decoupling capacitor from VCC to V(IN) and the output filter capacitors from OUT to VSS should be placed as close as possible to the device, with short trace runs to both signal and VSS pins. The VSS pin should have short trace runs to the GND pin.
- All low-current VSS connections should be kept separate from the high-current charge or discharge paths from the battery. Use a single-point ground technique incorporating both the small-signal ground path and the power ground path.
- The high-current charge paths into IN and from the OUT pins must be sized appropriately for the maximum charge current in order to avoid voltage drops in these traces.
- The device is packaged in a thermally enhanced MLP package. The package includes a thermal pad to provide an effective thermal contact between the device and the printed circuit board (PCB). Full PCB design guidelines for this package are provided in the application report entitled, QFN/SON PCB Attachment
(TI Literature Number SLUA271).
10.2 Layout Example
 Figure 13. Board Layout
Figure 13. Board Layout
10.3 Thermal Considerations
The bq24080-Q1 and bq24081-Q1 are packaged in a thermally enhanced MLP package. The package includes a thermal pad to provide an effective thermal contact between the device and the printed-circuit board (PCB). Full PCB design guidelines for this package are provided in the application report entitled, QFN/SON PCB Attachment (TI Literature Number SLUA271).
The most common measure of package thermal performance is thermal impedance (RθJA) measured (or modeled) from the device junction to the air surrounding the package surface (ambient). The mathematical expression for RθJA is:
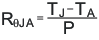
Where:
- TJ = device junction temperature
- TA = ambient temperature
- P = device power dissipation
Factors that can greatly influence the measurement and calculation of RθJA include:
- Orientation of the device (horizontal or vertical)
- Volume of the ambient air surrounding the device under test and airflow
- Whether other surfaces are in close proximity to the device being tested
- Use multiple 10–13 mil vias in the PowerPAD™ to copper ground plane.
- Avoid cutting the ground plane with a signal trace near the power IC.
- The PCB must be sized to have adequate surface area for heat dissipation.
- FR4 (figerglass) thickness should be minimized.
The device power dissipation, P, is a function of the charge rate and the voltage drop across the internal Power FET. It can be calculated from the following equation:

Due to the charge profile of Li-xx batteries, the maximum power dissipation is typically seen at the beginning of the charge cycle when the battery voltage is at its lowest. See Figure 6.