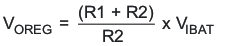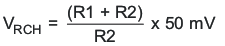-
bq241xx Synchronous Switched-Mode, Li-Ion and Li-Polymer Charge-Management IC With Integrated Power FETs (bqSWITCHER™)
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 PWM Controller
- 8.3.2 Temperature Qualification
- 8.3.3 Battery Preconditioning (Precharge)
- 8.3.4 Battery Charge Current
- 8.3.5 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.6 Charge Termination and Recharge
- 8.3.7 Sleep Mode
- 8.3.8 Charge Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 PG Output
- 8.3.10 CE Input (Charge Enable)
- 8.3.11 Timer Fault Recovery
- 8.3.12 Output Overvoltage Protection (Applies to All Versions)
- 8.3.13 Functional Description For System-Controlled Version (bq2411x)
- 8.3.14 Precharge and Fast-Charge Control
- 8.3.15 Charge Termination and Safety Timers
- 8.3.16 Battery Detection
- 8.3.17 Current Sense Amplifier
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Orderable Information
bq241xx Synchronous Switched-Mode, Li-Ion and Li-Polymer Charge-Management IC With Integrated Power FETs (bqSWITCHER™)
1 Features
- Ideal For Highly Efficient Charger Designs For Single-, Two-, or Three-Cell Li-Ion and Li-Polymer Battery Packs
- bq24105 Also for LiFePO4 Battery (see Using bq24105 to Charge the LiFePO4 Battery)
- Integrated Synchronous Fixed-Frequency PWM Controller Operating at 1.1 MHz With 0% to 100% Duty Cycle
- Integrated Power FETs for Up To 2-A Charge Rate
- High-Accuracy Voltage and Current Regulation
- Available in Both Stand-Alone (Built-In Charge Management and Control) and System-Controlled (Under System Command) Versions
- Status Outputs for LED or Host Processor Interface Indicates Charge-In-Progress, Charge Completion, Fault, and AC-Adapter Present Conditions
- 20-V Maximum Voltage Rating on IN and OUT Pins
- High-Side Battery Current Sensing
- Battery Temperature Monitoring
- Automatic Sleep Mode for Low Power Consumption
- System-Controlled Version Can Be Used in NiMH and NiCd Applications
- Reverse Leakage Protection Prevents Battery Drainage
- Thermal Shutdown and Protection
- Built-In Battery Detection
- Available in 20-Pin, 3.50 mm × 4.50 mm VQFN Package
2 Applications
- Handheld Products
- Portable Media Players
- Industrial and Medical Equipment
- Portable Equipment
3 Description
The bqSWITCHER™ series are highly integrated Li-ion and Li-polymer switch-mode charge management devices targeted at a wide range of portable applications. The bqSWITCHER™ series offers integrated synchronous PWM controller and power FETs, high-accuracy current and voltage regulation, charge preconditioning, charge status, and charge termination, in a small, thermally enhanced VQFN package. The system-controlled version provides additional inputs for full charge management under system control.
The bqSWITCHER™ charges the battery in three phases: conditioning, constant current, and constant voltage. Charge is terminated based on user- selectable minimum current level. A programmable charge timer provides a safety backup for charge termination. The bqSWITCHER™ automatically restarts the charge cycle if the battery voltage falls below an internal threshold. The bqSWITCHER™ automatically enters sleep mode when VCC supply is removed.
Device Information (1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| bq241xx | VQFN (20) | 3.50 mm × 4.50 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
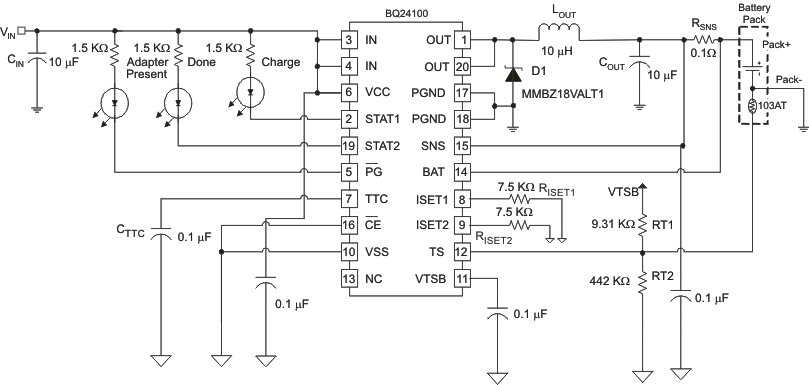
Typical 1-Cell Application
4 Revision History
Changes from O Revision (March 2010) to P Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information sectionGo
Changes from M Revision (August 2008) to N Revision
- Added part number bq24104.Go
- Added part number bq24104 to the Ordering InformationGo
- Deleted Product Preview from bq24104RHLRGo
- Deleted Product Preview from bq24104RHLTGo
- Added bq24104 to the Terminal Functions table.Go
- Added part number bq24104 to the Deglitch timeGo
- Added bq24104 to Table 2.Go
- Added part number bq24104 to Figure 16 Go
Changes from L Revision (December 2007) to M Revision
- Changed specifications and symbols for (cold, hot, and cutoff) temperature thresholdsGo
- Changed equation definitionsGo
- Changed equation definitionsGo
Changes from K Revision (November 2007) to L Revision
- Changed Added figure almost identical to Figure 3. Changed RISET2 to 20 kohms.Go
- Added Changed resistor bridge values 301 to 143, 100 to 200 KohmsGo
Changes from J Revision (October 2007) to K Revision
- Changed From: CIU To: CDYGo
- Added bq24109 to VOREG Go
- Added part number bq24109 to VLOWV Go
- Changed Deglitch time for temperature fault, TS, bq24109 typical value From: 1000 To: 500Go
- Changed From: Single-cell or two-cell To: one-, two-, or three-cell applications. Deleted text.Go
Changes from I Revision (August 2007) to J Revision
- Added part number bq24109 Go
- Added part number bq24109 to the Ordering InformationGo
- Added bq24109 to the Terminal Functions table.Go
- Added part number bq24109 to the Deglitch timeGo
- Added bq24109 to Table 2.Go
Changes from H Revision (July 2007) to I Revision
- Added part number bq24103A Go
- Changed device size From: 5,5 mm x 3.5 mm To: 4,5 mm x 3.5 mmGo
- Added part number bq24103A to the Ordering InformationGo
- Added bq24103A to the Terminal Functions table.Go
- Added part numbers bq24103Ana d bq24113A to VOREG Go
- Added part number bq24103A to VLOWV Go
- Added part number bq24103A to Figure 16 Go
Changes from G Revision (June 2007) to H Revision
- Changed Figure 1 Go
- Changed Figure 2 Go
- Added D1 to diode MMBZ18VALT1 in Figure 13.Go
- Added D1 to diode MMBZ18VALT1 in Figure 16 Go
- Added D1 to diode MMBZ18VALT1 in Figure 17 Go
- Added D1 to diode MMBZ18VALT1 and Note A to Figure 18.Go
Changes from F Revision (January 2007) to G Revision
5 Device Options
| CHARGE REGULATION VOLTAGE (V) | INTENDED APPLICATION | PART NUMBER (1) (2) (3) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.2 V | Stand-alone | bq24100 |
| 1 or 2 cells selectable (CELLS pin, 4.2 V or 8.4 V) | Stand-alone | bq24103 |
| 1 or 2 cells selectable (CELLS pin, 4.2 V or 8.4 V) | Stand-alone | bq24103A |
| 1 or 2 cells selectable (CELLS pin, 4.2 V or 8.4 V) (Blinking status pins) |
Stand-alone | bq24104 |
| Externally programmable (2.1 V to 15.5 V) | Stand-alone | bq24105 |
| 4.2 V (Blinking status pins) | Stand-alone | bq24108 |
| bq24109 | ||
| 1 or 2 cells selectable (CELLS pin, 4.2 V or 8.4 V) | System-controlled | bq24113 |
| 1 or 2 cells selectable (CELLS pin, 4.2 V or 8.4 V) | System-controlled | bq24113A |
| Externally programmable (2.1 V to 15.5 V) | System-controlled | bq24115 |
T – taped and reeled in quantities of 250 devices per reel
R – taped and reeled in quantities of 3000 devices per reel
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
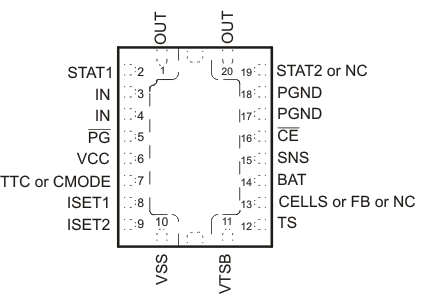
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | bq24100, bq24108, bq24109 |
bq24103, bq24103A bq24104 |
bq24105 | bq24113, bq24113A | bq24115 | ||
| BAT | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | I | Battery voltage sense input. Bypass it with a 0.1 μF capacitor to PGND if there are long inductive leads to battery. |
| CE | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | I | Charger enable input. This active low input, if set high, suspends charge and places the device in the low-power sleep mode. Do not pull up this input to VTSB. |
| CELLS | 13 | 13 | I | Available on parts with fixed output voltage. Ground or float for single-cell operation (4.2 V). For two-cell operation (8.4 V) pull up this pin with a resistor to VCC. | |||
| CMODE | 7 | 7 | I | Charge mode selection: low for precharge as set by ISET2 pin and high (pull up to VTSB or <7 V) for fast charge as set by ISET1. | |||
| FB | 13 | 13 | I | Output voltage analog feedback adjustment. Connect the output of a resistive voltage divider powered from the battery terminals to this node to adjust the output battery voltage regulation. | |||
| IN | 3, 4 | 3, 4 | 3, 4 | 3, 4 | 3, 4 | I | Charger input voltage. |
| ISET1 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | I/O | Charger current set point 1 (fast charge). Use a resistor to ground to set this value. |
| ISET2 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | I/O | Charge current set point 2 (precharge and termination), set by a resistor connected to ground. A low-level CMODE signal selects the ISET2 charge rate, but if the battery voltage reaches the regulation set point, bqSWITCHER™ changes to voltage regulation regardless of CMODE input. |
| N/C | 13 | 19 | 19 | - | No connection. This pin must be left floating in the application. | ||
| OUT | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | O | Charge current output inductor connection. Connect a zener TVS diode between OUT pin and PGND pin to clamp the voltage spike to protect the power MOSFETs during abnormal conditions. |
| 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | O | ||
| PG | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | O | Power-good status output (open drain). The transistor turns on when a valid VCC is detected. It is turned off in the sleep mode. PG can be used to drive a LED or communicate with a host processor. |
| PGND | 17,18 | 17,18 | 17,18 | 17,18 | 17, 18 | Power ground input | |
| SNS | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | I | Charge current-sense input. Battery current is sensed via the voltage drop developed on this pin by an external sense resistor in series with the battery pack. A 0.1-μF capacitor to PGND is required. |
| STAT1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | O | Charge status 1 (open-drain output). When the transistor turns on indicates charge in process. When it is off and with the condition of STAT2 indicates various charger conditions (See Table 1) |
| STAT2 | 19 | 19 | 19 | O | Charge status 2 (open-drain output). When the transistor turns on indicates charge is done. When it is off and with the condition of STAT1 indicates various charger conditions (See Table 1) | ||
| TS | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | I | Temperature sense input. This input monitors its voltage against an internal threshold to determine if charging is allowed. Use an NTC thermistor and a voltage divider powered from VTSB to develop this voltage. (See Figure 4) |
| TTC | 7 | 7 | 7 | I | Timer and termination control. Connect a capacitor from this node to GND to set the bqSWITCHER™ timer. When this input is low, the timer and termination detection are disabled. | ||
| VCC | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | I | Analog device input. A 0.1 μF capacitor to VSS is required. |
| VSS | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | Analog ground input | |
| VTSB | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | O | TS internal bias regulator voltage. Connect capacitor (with a value between a 0.1-μF and 1-μF) between this output and VSS. |
| Exposed Thermal Pad |
Pad | Pad | Pad | Pad | Pad | There is an internal electrical connection between the exposed thermal pad and VSS. The exposed thermal pad must be connected to the same potential as the VSS pin on the printed circuit board. The power pad can be used as a star ground connection between VSS and PGND. A common ground plane may be used. VSS pin must be connected to ground at all times. | |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings (1)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (with respect to VSS) | IN, VCC | 20 | V | |
| Input voltage (with respect to VSS and PGND) | STAT1, STAT2, PG, CE, CELLS, SNS, BAT | –0.3 | 20 | V |
| OUT | –0.7 | 20 | V | |
| CMODE, TS, TTC | 7 | V | ||
| VTSB | 3.6 | V | ||
| ISET1, ISET2 | 3.3 | V | ||
| Voltage difference between SNS and BAT inputs (VSNS – VBAT) | ±1 | V | ||
| Output sink | STAT1, STAT2, PG | 10 | mA | |
| Output current (average) | OUT | 2.2 | A | |
| Operating free-air temperature, TA | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| Junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Lead temperature 1.6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds | 300 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 (1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101 (2) | ±500 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VCC and IN (Tie together) | 4.35 (1) | 16 (2) | V | |
| Operating junction temperature range, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC (1) | bq241xx | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHL (VQFN) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 39.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 39.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 15.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 15.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 3.6 | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = 0°C to 125°C and recommended supply voltage range (unless otherwise stated)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CURRENTS | ||||||
| I(VCC) | VCC supply current | VCC > VCC(min), PWM switching | 10 | mA | ||
| VCC > VCC(min), PWM NOT switching | 5 | |||||
| VCC > VCC(min), CE = HIGH | 315 | μA | ||||
| I(SLP) | Battery discharge sleep current, (SNS, BAT, OUT, FB pins) | 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 4.2 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
3.5 | μA | ||
| 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 8.4 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
5.5 | |||||
| 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 12.6 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
7.7 | |||||
| VOLTAGE REGULATION | ||||||
| VOREG | Output voltage, bq24103/03A/04/13/13A | CELLS = Low, in voltage regulation | 4.2 | V | ||
| CELLS = High, in voltage regulation | 8.4 | |||||
| Output voltage, bq24100/08/09 | Operating in voltage regulation | 4.2 | ||||
| VIBAT | Feedback regulation REF for bq24105/15 only (W/FB) | IIBAT = 25 nA typical into pin | 2.1 | V | ||
| Voltage regulation accuracy | TA = 25°C | –0.5% | 0.5% | |||
| –1% | 1% | |||||
| CURRENT REGULATION - FAST CHARGE | ||||||
| IOCHARGE | Output current range of converter | VLOWV ≤ VI(BAT) < VOREG, V(VCC) - VI(BAT) > V(DO-MAX) |
150 | 2000 | mA | |
| VIREG | Voltage regulated across R(SNS) Accuracy | 100 mV ≤ VIREG≤ 200 mV, | –10% | 10% | ||
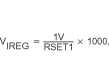 |
||||||
| Programmed Where 5 kΩ ≤ RSET1 ≤ 10 kΩ, Select RSET1 to program VIREG, VIREG(measured) = IOCHARGE + RSNS (–10% to 10% excludes errors due to RSET1 and R(SNS) tolerances) |
||||||
| V(ISET1) | Output current set voltage | V(LOWV) ≤ VI(BAT) ≤ VO(REG), V(VCC) ≤ VI(BAT) × V(DO-MAX) |
1 | V | ||
| K(ISET1) | Output current set factor | VLOWV ≤ VI(BAT) < VO(REG) , V(VCC) ≤ VI(BAT) + V(DO-MAX) |
1000 | V/A | ||
| PRECHARGE AND SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT REGULATION | ||||||
| VLOWV | Precharge to fast-charge transition voltage threshold, BAT, bq24100/03/03A/04/05/08/09 ICs only |
68 | 71.4 | 75 | %VO(REG) | |
| t | Deglitch time for precharge to fast charge transition, | Rising voltage; tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns, 2-mV overdrive |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| IOPRECHG | Precharge range | VI(BAT) < VLOWV, t < tPRECHG | 15 | 200 | mA | |
| V(ISET2) | Precharge set voltage, ISET2 | VI(BAT) < VLOWV, t < tPRECHG | 100 | mV | ||
| K(ISET2) | Precharge current set factor | 1000 | V/A | |||
| VIREG-PRE | Voltage regulated across RSNS-Accuracy | 100 mV ≤ VIREG-PRE ≤ 100 mV, | –20% | 20% | ||
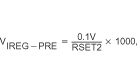 |
||||||
| (PGM) Where 1.2 kΩ ≤ RSET2 ≤ 10 kΩ, Select RSET1 to program VIREG-PRE, VIREG-PRE (Measured) = IOPRE-CHG × RSNS (–20% to 20% excludes errors due to RSET1 and RSNS tolerances) |
||||||
| CHARGE TERMINATION (CURRENT TAPER) DETECTION | ||||||
| ITERM | Charge current termination detection range | VI(BAT) > VRCH | 15 | 200 | mA | |
| VTERM | Charge termination detection set voltage, ISET2 | VI(BAT) > VRCH | 100 | mV | ||
| K(ISET2) | Termination current set factor | 1000 | V/A | |||
| Charger termination accuracy | VI(BAT) > VRCH | –20% | 20% | |||
| tdg-TERM | Deglitch time for charge termination | Both rising and falling, 2-mV overdrive tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| TEMPERATURE COMPARATOR AND VTSB BIAS REGULATOR | ||||||
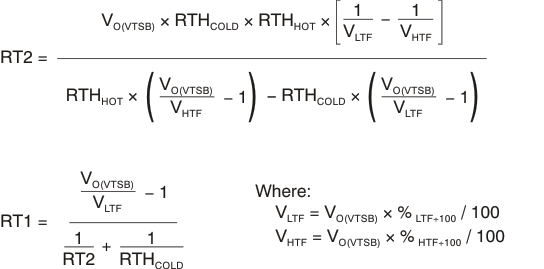
| %LTF | Cold temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VLTF = VO(VTSB) × % LTF/100 | 72.8% | 73.5% | 74.2% | |
| %HTF | Hot temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VHTF = VO(VTSB) × % HTF/100 | 33.7% | 34.4% | 35.1% | |
| %TCO | Cutoff temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VTCO = VO(VTSB) × % TCO/100 | 28.7% | 29.3% | 29.9% | |
| LTF hysteresis | 0.5% | 1% | 1.5% | |||
| tdg-TS | Deglitch time for temperature fault, TS | Both rising and falling, 2-mV overdrive tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| Deglitch time for temperature fault, TS, bq24109, bq24104 | 500 | |||||
| VO(VTSB) | TS bias output voltage | VCC > VIN(min), I(VTSB) = 10 mA 0.1 μF ≤ CO(VTSB) ≤ 1 μF |
3.15 | V | ||
| VO(VTSB) | TS bias voltage regulation accuracy | VCC > IN(min), I(VTSB) = 10 mA 0.1 μF ≤ CO(VTSB) ≤ 1 μF |
–10% | 10% | ||
| BATTERY RECHARGE THRESHOLD | ||||||
| VRCH | Recharge threshold voltage | Below VOREG | 75 | 100 | 125 | mV/cell |
| tdg-RCH | Deglitch time | VI(BAT) < decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns 10-mV overdrive |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| STAT1, STAT2, AND PG OUTPUTS | ||||||
| VOL(STATx) | Low-level output saturation voltage, STATx | IO = 5 mA | 0.5 | V | ||
| VOL(PG) | Low-level output saturation voltage, PG | IO = 10 mA | 0.1 | |||
| CE CMODE, CELLS INPUTS | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | IIL = 5 μA | 0 | 0.4 | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage | IIH = 20 μA | 1.3 | VCC | ||
| TTC INPUT | ||||||
| tPRECHG | Precharge timer | 1440 | 1800 | 2160 | s | |
| tCHARGE | Programmable charge timer range | t(CHG) = C(TTC) × K(TTC) | 25 | 572 | minutes | |
| Charge timer accuracy | 0.01 μF ≤ C(TTC) ≤ 0.18 μF | -10% | 10% | |||
| KTTC | Timer multiplier | 2.6 | min/nF | |||
| CTTC | Charge time capacitor range | 0.01 | 0.22 | μF | ||
| VTTC_EN | TTC enable threshold voltage | V(TTC) rising | 200 | mV | ||
| SLEEP COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VSLP-ENT | Sleep-mode entry threshold | 2.3 V ≤ VI(OUT) ≤ VOREG, for 1 or 2 cells | VCC ≤ VIBAT +5 mV | VCC ≤ VIBAT +75 mV | V | |
| VI(OUT) = 12.6 V, RIN = 1 kΩ bq24105/15 (1) |
VCC ≤ VIBAT -4 mV | VCC ≤ VIBAT +73 mV | ||||
| VSLP-EXIT | Sleep-mode exit hysteresis, | 2.3 V ≤ VI(OUT)≤ VOREG | 40 | 160 | mV | |
| tdg-SLP | Deglitch time for sleep mode | VCC decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive, PMOS turns off |
5 | μs | ||
| VCC decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive, STATx pins turn off |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms | ||
| UVLO | ||||||
| VUVLO-ON | IC active threshold voltage | VCC rising | 3.15 | 3.30 | 3.50 | V |
| IC active hysteresis | VCC falling | 120 | 150 | mV | ||
| PWM | ||||||
| Internal P-channel MOSFET on-resistance | 7 V ≤ VCC ≤ VCC(max) | 400 | mΩ | |||
| 4.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 7 V | 500 | |||||
| Internal N-channel MOSFET on-resistance | 7 V ≤ VCC ≤ VCC(max) | 130 | ||||
| 4.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 7 V | 150 | |||||
| fOSC | Oscillator frequency | 1.1 | MHz | |||
| Frequency accuracy | –9% | 9% | ||||
| DMAX | Maximum duty cycle | 100% | ||||
| DMIN | Minimum duty cycle | 0% | ||||
| tTOD | Switching delay time (turn on) | 20 | ns | |||
| tsyncmin | Minimum synchronous FET on time | 60 | ns | |||
| Synchronous FET minimum current-off threshold (2) | 50 | 400 | mA | |||
| BATTERY DETECTION | ||||||
| IDETECT | Battery detection current during time-out fault | VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 2 | mA | ||
| IDISCHRG1 | Discharge current | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 400 | μA | ||
| tDISCHRG1 | Discharge time | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 1 | s | ||
| IWAKE | Wake current | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 2 | mA | ||
| tWAKE | Wake time | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 0.5 | s | ||
| IDISCHRG2 | Termination discharge current | Begins after termination detected, VI(BAT) ≤ VOREG |
400 | μA | ||
| tDISCHRG2 | Termination time | 262 | ms | |||
| OUTPUT CAPACITOR | ||||||
| COUT | Required output ceramic capacitor range from SNS to PGND, between inductor and RSNS | 4.7 | 10 | 47 | μF | |
| CSNS | Required SNS capacitor (ceramic) at SNS pin | 0.1 | μF | |||
| PROTECTION | ||||||
| VOVP | OVP threshold voltage | Threshold over VOREG to turn off P-channel MOSFET, STAT1, and STAT2 during charge or termination states | 110 | 117 | 121 | %VO(REG) |
| ILIMIT | Cycle-by-cycle current limit | 2.6 | 3.6 | 4.5 | A | |
| VSHORT | Short-circuit voltage threshold, BAT | VI(BAT) falling | 1.95 | 2 | 2.05 | V/cell |
| ISHORT | Short-circuit current | VI(BAT) ≤ VSHORT | 35 | 65 | mA | |
| TSHTDWN | Thermal trip | 165 | °C | |||
| Thermal hysteresis | 10 | °C | ||||
7.6 Dissipation Ratings
| PACKAGE | θJA | θJC | TA < 40°C POWER RATING |
DERATING FACTOR ABOVE TA = 40°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHL (1) | 46.87°C/W | 2.5°C/W | 1.81 W | 0.021 W/°C |
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
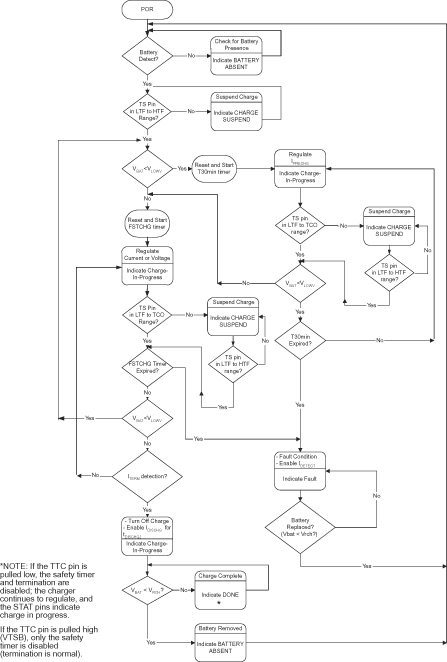
The bqSWITCHER™ supports a precision Li-ion or Li-polymer charging system for single cell or two cell applications. The device has a battery detect scheme that allows it to automatically detect the presence and absence of a battery. When the battery is detected, charging begins in one of three phases (depending upon battery voltage): precharge, constant current (fast-charge current regulation), and constant voltage (fast-charge voltage regulation). The device will terminate charging when the termination current threshold has been reached and will begin a recharge cycle when the battery voltage has dropped below the recharge threshold (VRCG). Precharge, constant current, and termination current can be configured through the ISET1 and ISET2 pins, allowing for flexibility in battery charging profile. During charging, the integrated fault monitors of the device, such as battery short detection (VSHORT), thermal shutdown (internal TSHTDWN and TS pin), and safety timer expiration (TTC pin), ensure battery safety.
bqSWITCHER™ has three status pins (STAT1, STAT2, and PG) to indicate the charging status and input voltage (AC adapter) status. These pins can be used to drive LEDs or communicate with a host processor.
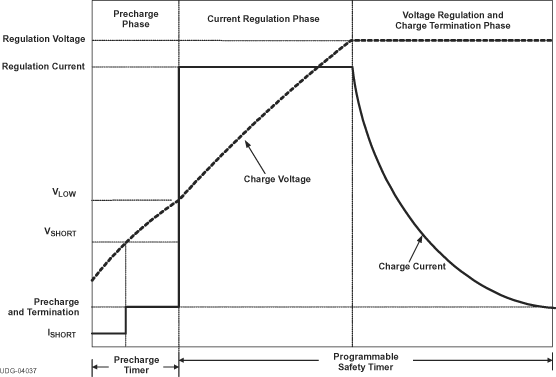 Figure 3. Typical Charging Profile
Figure 3. Typical Charging Profile
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
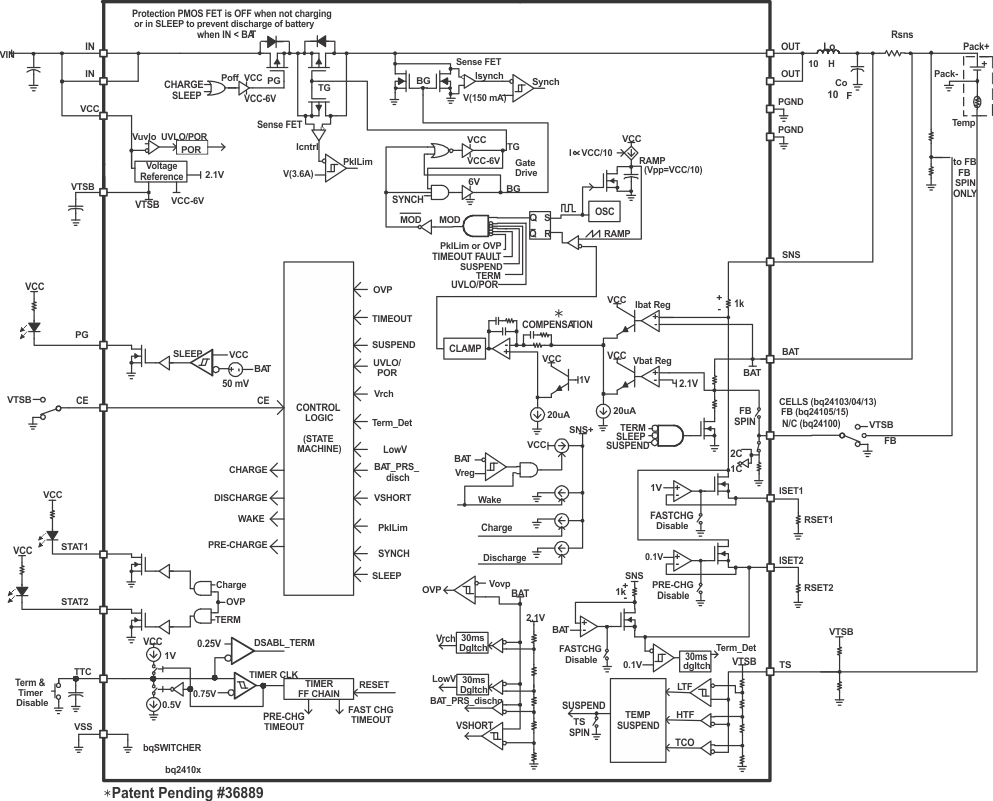
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 PWM Controller
The bq241xx provides an integrated fixed 1-MHz frequency voltage-mode controller with Feed-Forward function to regulate charge current or voltage. This type of controller is used to help improve line transient response, thereby simplifying the compensation network used for both continuous and discontinuous current conduction operation. The voltage and current loops are internally compensated using a Type-III compensation scheme that provides enough phase boost for stable operation, allowing the use of small ceramic capacitors with very low ESR. There is a 0.5 V offset on the bottom of the PWM ramp to allow the device to operate between 0% to 100% duty cycle.
The internal PWM gate drive can directly control the internal PMOS and NMOS power MOSFETs. The high-side gate voltage swings from VCC (when off), to VCC-6 (when on and VCC is greater than 6 V) to help reduce the conduction losses of the converter by enhancing the gate an extra volt beyond the standard 5 V. The low-side gate voltage swings from 6 V, to turn on the NMOS, down to PGND to turn it off. The bq241xx has two back to back common-drain P-MOSFETs on the high side. An input P-MOSFET prevents battery discharge when IN is lower than BAT. The second P-MOSFET behaves as the switching control FET, eliminating the need of a bootstrap capacitor.
Cycle-by-cycle current limit is sensed through the internal high-side sense FET. The threshold is set to a nominal 3.6 A peak current. The low-side FET also has a current limit that decides if the PWM Controller will operate in synchronous or non-synchronous mode. This threshold is set to 100 mA and it turns off the low-side NMOS before the current reverses, preventing the battery from discharging. Synchronous operation is used when the current of the low-side FET is greater than 100 mA to minimize power losses.
8.3.2 Temperature Qualification
The bqSWITCHER™ continuously monitors battery temperature by measuring the voltage between the TS pin and VSS pin. A negative temperature coefficient thermistor (NTC) and an external voltage divider typically develop this voltage. The bqSWITCHER™ compares this voltage against its internal thresholds to determine if charging is allowed. To initiate a charge cycle, the battery temperature must be within the V(LTF)-to-V(HTF) thresholds. If battery temperature is outside of this range, the bqSWITCHER™ suspends charge and waits until the battery temperature is within the V(LTF)-to-V(HTF) range. During the charge cycle (both precharge and fast charge), the battery temperature must be within the V(LTF)-to-V(TCO) thresholds. If battery temperature is outside of this range, the bqSWITCHER™ suspends charge and waits until the battery temperature is within the V(LTF)-to-V(HTF) range. The bqSWITCHER™ suspends charge by turning off the PWM and holding the timer value (that is, timers are not reset during a suspend condition). Note that the bias for the external resistor divider is provided from the VTSB output. Applying a constant voltage between the V(LTF)-to-V(HTF) thresholds to the TS pin disables the temperature-sensing feature.
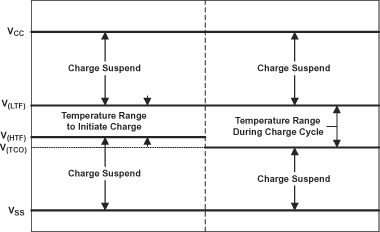 Figure 4. TS Pin Thresholds
Figure 4. TS Pin Thresholds
8.3.3 Battery Preconditioning (Precharge)
On power up, if the battery voltage is below the VLOWV threshold, the bqSWITCHER™ applies a precharge current, IPRECHG, to the battery. This feature revives deeply discharged cells. The bqSWITCHER™ activates a safety timer, tPRECHG, during the conditioning phase. If the VLOWV threshold is not reached within the timer period, the bqSWITCHER™ turns off the charger and enunciates FAULT on the STATx pins. In the case of a FAULT condition, the bqSWITCHER™ reduces the current to IDETECT. IDETECT is used to detect a battery replacement condition. Fault condition is cleared by POR or battery replacement.
The magnitude of the precharge current, IO(PRECHG), is determined by the value of programming resistor, R(ISET2), connected to the ISET2 pin.
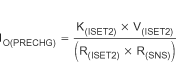
where
- RSNS is the external current-sense resistor
- V(ISET2) is the output voltage of the ISET2 pin
- K(ISET2) is the V/A gain factor
- V(ISET2) and K(ISET2) are specified in the Electrical Characteristics table.
8.3.4 Battery Charge Current
The battery charge current, IO(CHARGE), is established by setting the external sense resistor, R(SNS), and the resistor, R(ISET1), connected to the ISET1 pin.
In order to set the current, first choose R(SNS) based on the regulation threshold VIREG across this resistor. The best accuracy is achieved when the VIREG is between 100mV and 200mV.
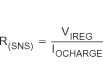
If the results is not a standard sense resistor value, choose the next larger value. Using the selected standard value, solve for VIREG. Once the sense resistor is selected, the ISET1 resistor can be calculated using the following equation:
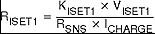
8.3.5 Battery Voltage Regulation
The voltage regulation feedback occurs through the BAT pin. This input is tied directly to the positive side of the battery pack. The bqSWITCHER™ monitors the battery-pack voltage between the BAT and VSS pins. The bqSWITCHER™ is offered in a fixed single-cell voltage version (4.2 V) and as a one-cell or two-cell version selected by the CELLS input. A low or floating input on the CELLS selects single-cell mode (4.2 V) while a high-input through a resistor selects two-cell mode (8.4 V).
For the bq24105 and bq24115, the output regulation voltage is specified as:
where R1 and R2 are resistor divider from BAT to FB and FB to VSS, respectively.
The bq24105 and bq24115 recharge threshold voltage is specified as:
8.3.6 Charge Termination and Recharge
The bqSWITCHER™ monitors the charging current during the voltage regulation phase. Once the termination threshold, ITERM, is detected, the bqSWITCHER™ terminates charge. The termination current level is selected by the value of programming resistor, R(ISET2), connected to the ISET2 pin.
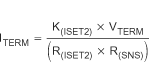
where
- R(SNS) is the external current-sense resistor
- VTERM is the output of the ISET2 pin
- K(ISET2) is the A/V gain factor
- VTERM and K(ISET2) are specified in the Electrical Characteristics table
As a safety backup, the bqSWITCHER™ also provides a programmable charge timer. The charge time is programmed by the value of a capacitor connected between the TTC pin and GND by the following formula:
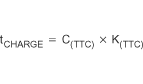
where
- C(TTC) is the capacitor connected to the TTC pin
- K(TTC) is the multiplier
A new charge cycle is initiated when one of the following conditions is detected:
- The battery voltage falls below the VRCH threshold.
- Power-on reset (POR), if battery voltage is below the VRCH threshold
- CE toggle
- TTC pin, described as follows.
To disable the charge termination and safety timer, the user can pull the TTC input below the VTTC_EN threshold. Going above this threshold enables the termination and safety timer features and also resets the timer. Tying TTC high disables the safety timer only.
8.3.7 Sleep Mode
The bqSWITCHER™ enters the low-power sleep mode if the VCC pin is removed from the circuit. This feature prevents draining the battery during the absence of VCC.
8.3.8 Charge Status Outputs
The open-drain STAT1 and STAT2 outputs indicate various charger operations as shown in Table 1. These status pins can be used to drive LEDs or communicate to the host processor. Note that OFF indicates that the open-drain transistor is turned off.
Table 1. Status Pins Summary
| Charge State | STAT1 | STAT2 |
|---|---|---|
| Charge-in-progress | ON | OFF |
| Charge complete | OFF | ON |
| Charge suspend, timer fault, overvoltage, sleep mode, battery absent | OFF | OFF |
Table 2. Status Pins Summary (bq24104, bq24108 and bq24109 Only)
| Charge State | STAT1 | STAT2 |
|---|---|---|
| Battery absent | OFF | OFF |
| Charge-in-progress | ON | OFF |
| Charge complete | OFF | ON |
| Battery over discharge, VI(BAT) < V(SC) | ON/OFF (0.5 Hz) | OFF |
| Charge suspend (due to TS pin and internal thermal protection) | ON/OFF (0.5 Hz) | OFF |
| Precharge timer fault | ON/OFF (0.5 Hz) | OFF |
| Fast charge timer fault | ON/OFF (0.5 Hz) | OFF |
| Sleep mode | OFF | OFF |
8.3.9 PG Output
The open-drain PG (power good) indicates when the AC-to-DC adapter (that is, VCC) is present. The output turns on when sleep-mode exit threshold, VSLP-EXIT, is detected. This output is turned off in the sleep mode. The PG pin can be used to drive an LED or communicate to the host processor.
8.3.10 CE Input (Charge Enable)
The CE digital input is used to disable or enable the charge process. A low-level signal on this pin enables the charge and a high-level VCC signal disables the charge. A high-to-low transition on this pin also resets all timers and fault conditions. Note that the CE pin cannot be pulled up to VTSB voltage. This may create power-up issues.
8.3.11 Timer Fault Recovery
As shown in Figure 4, bqSWITCHER™ provides a recovery method to deal with timer fault conditions. The following summarizes this method.
Condition 1 VI(BAT) above recharge threshold (VOREG - VRCH) and timeout fault occurs.
Recovery method: bqSWITCHER™ waits for the battery voltage to fall below the recharge threshold. This could happen as a result of a load on the battery, self-discharge or battery removal. Once the battery falls below the recharge threshold, the bqSWITCHER™ clears the fault and enters the battery absent detection routine. A POR or CE toggle also clears the fault.
Condition 2 Charge voltage below recharge threshold (VOREG – VRCH) and timeout fault occurs
Recovery method: In this scenario, the bqSWITCHER™ applies the IDETECT current. This small current is used to detect a battery removal condition and remains on as long as the battery voltage stays below the recharge threshold. If the battery voltage goes above the recharge threshold, then the bqSWITCHER™ disables the IDETECT current and executes the recovery method described in Condition 1. Once the battery falls below the recharge threshold, the bqSWITCHER™ clears the fault and enters the battery absent detection routine. A POR or CE toggle also clears the fault.
8.3.12 Output Overvoltage Protection (Applies to All Versions)
The bqSWITCHER™ provides a built-in overvoltage protection to protect the device and other components against damages if the battery voltage gets too high, as when the battery is suddenly removed. When an overvoltage condition is detected, this feature turns off the PWM and STATx pins. The fault is cleared once VIBAT drops to the recharge threshold (VOREG – VRCH).
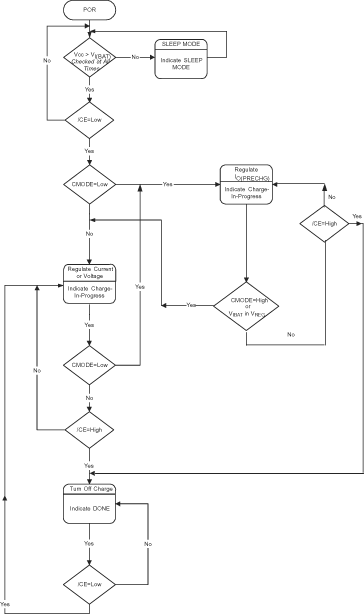
8.3.13 Functional Description For System-Controlled Version (bq2411x)
For applications requiring charge management under the host system control, the bqSWITCHER™ (bq2411x) offers a number of control functions. The following section describes these functions.
8.3.14 Precharge and Fast-Charge Control
A low-level signal on the CMODE pin forces the bqSWITCHER™ to charge at the precharge rate set on the ISET2 pin. A high-level signal forces charge at fast-charge rate as set by the ISET1 pin. If the battery reaches the voltage regulation level, VOREG, the bqSWITCHER™ transitions to voltage regulation phase regardless of the status of the CMODE input.
8.3.15 Charge Termination and Safety Timers
The charge timers and termination are disabled in the system-controlled versions of the bqSWITCHER™. The host system can use the CE input to enable or disable charge. When an overvoltage condition is detected, the charger process stops, and all power FETs are turned off.
8.3.16 Battery Detection
For applications with removable battery packs, bqSWITCHER™ provides a battery absent detection scheme to reliably detect insertion and/or removal of battery packs.
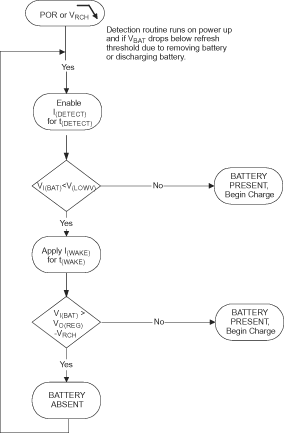 Figure 5. Battery Absent Detection for bq2410x ICs only
Figure 5. Battery Absent Detection for bq2410x ICs only
The voltage at the BAT pin is held above the battery recharge threshold, VOREG – VRCH, by the charged battery following fast charging. When the voltage at the BAT pin falls to the recharge threshold, either by a load on the battery or due to battery removal, the bqSWITCHER™ begins a battery absent detection test. This test involves enabling a detection current, IDISCHARGE1, for a period of tDISCHARGE1 and checking to see if the battery voltage is below the short circuit threshold, VSHORT. Following this, the wake current, IWAKE is applied for a period of tWAKE and the battery voltage is checked again to ensure that it is above the recharge threshold. The purpose of this current is to attempt to close an open battery pack protector, if one is connected to the bqSWITCHER™.
Passing both of the discharge and charge tests indicates a battery absent fault at the STAT pins. Failure of either test starts a new charge cycle. For the absent battery condition, typically the voltage on the BAT pin rises and falls between 0V and VOVPthresholds indefinitely.
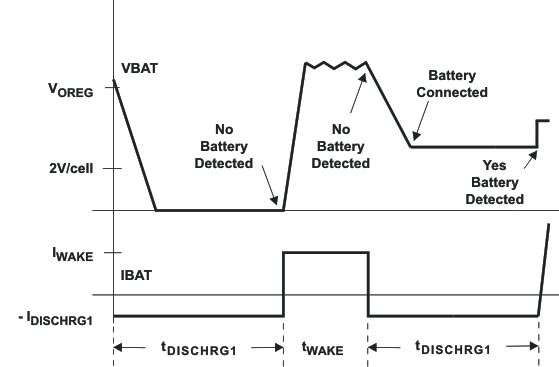 Figure 6. Battery Detect Timing Diagram
Figure 6. Battery Detect Timing Diagram
8.3.16.1 Battery Detection Example
In order to detect a no battery condition during the discharge and wake tests, the maximum output capacitance should not exceed the following:
- Discharge (IDISCHRG1 = 400 μA, tDISCHRG1 = 1s, VSHORT = 2V)
- Wake (IWAKE = 2 mA, tWAKE = 0.5 s, VOREG – VRCH = 4.1V)

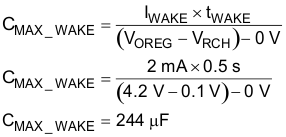
Based on these calculations the recommended maximum output capacitance to ensure proper operation of the battery detection scheme is 100 μF which will allow for process and temperature variations.
Figure 7 shows the battery detection scheme when a battery is inserted. Channel 3 is the output signal and Channel 4 is the output current. The output signal switches between VOREG and GND until a battery is inserted. Once the battery is detected, the output current increases from 0 A to 1.3 A, which is the programmed charge current for this application.
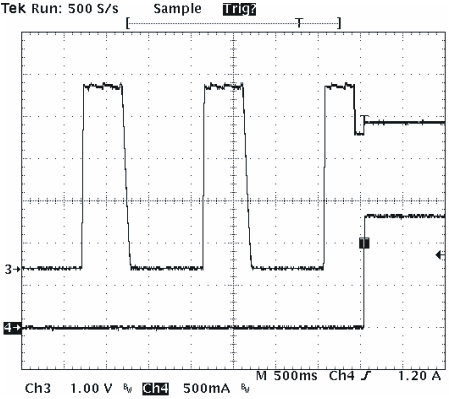 Figure 7. Battery Detection Waveform When a Battery is Inserted
Figure 7. Battery Detection Waveform When a Battery is Inserted
Figure 8 shows the battery detection scheme when a battery is removed. Channel 3 is the output signal and Channel 4 is the output current. When the battery is removed, the output signal goes up due to the stored energy in the inductor and it crosses the VOREG – VRCH threshold. At this point the output current goes to 0 A and the IC terminates the charge process and turns on the IDISCHG2 for tDISCHG2. This causes the output voltage to fall down below the VOREG – VRCHG threshold triggering a Battery Absent condition and starting the battery detection scheme.
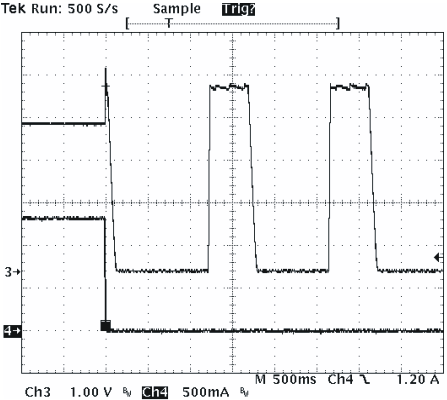 Figure 8. Battery Detection Waveform When a Battery is Removed
Figure 8. Battery Detection Waveform When a Battery is Removed
8.3.17 Current Sense Amplifier
BQ241xx family offers a current sense amplifier feature that translates the charge current into a DC voltage. Figure 9 is a block diagram of this feature.
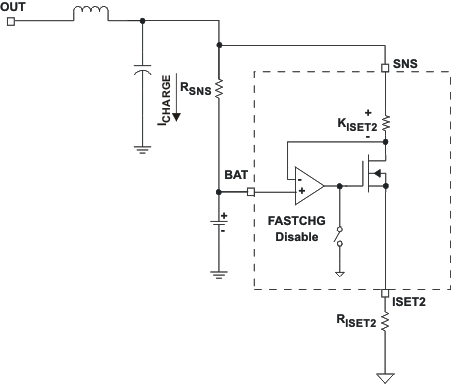 Figure 9. Current Sense Amplifier
Figure 9. Current Sense Amplifier
The voltage on the ISET2 pin can be used to calculate the charge current. Equation 11 shows the relationship between the ISET2 voltage and the charge current:

This feature can be used to monitor the charge current (see Figure 10) during the current regulation phase (Fastcharge only) and the voltage regulation phase. The schematic for the application circuit for this waveform is shown in Figure 13.
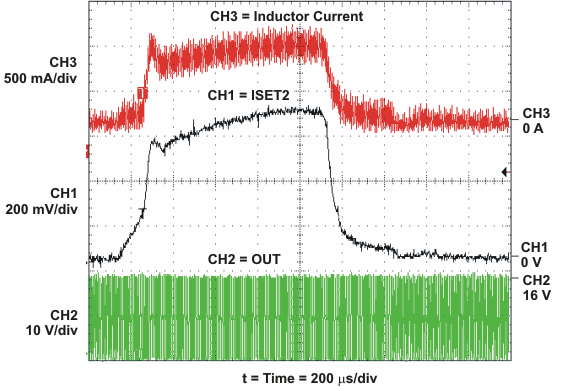 Figure 10. Current Sense Amplifier Charge Current Waveform
Figure 10. Current Sense Amplifier Charge Current Waveform