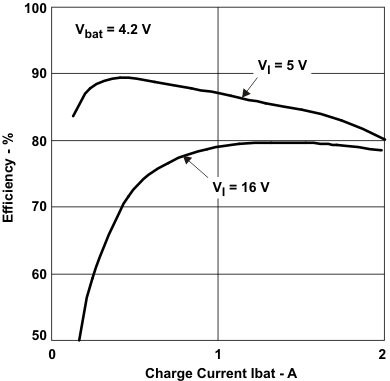
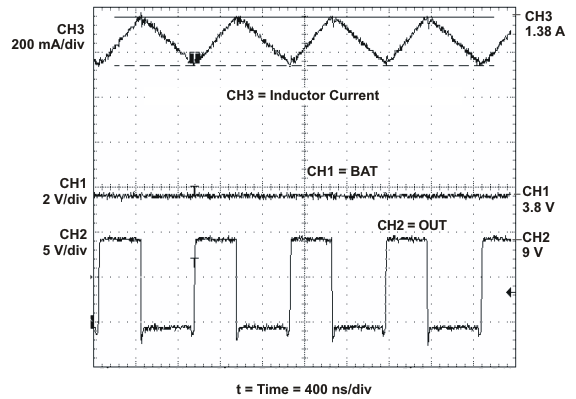
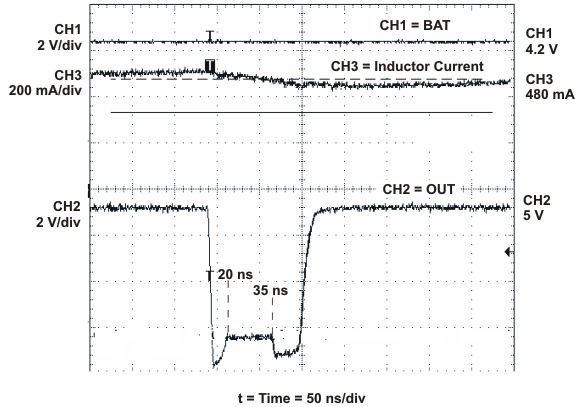
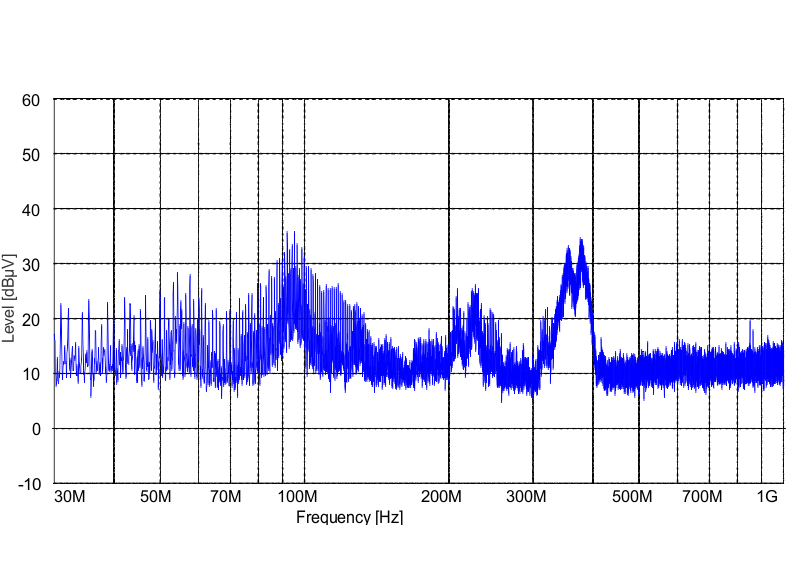
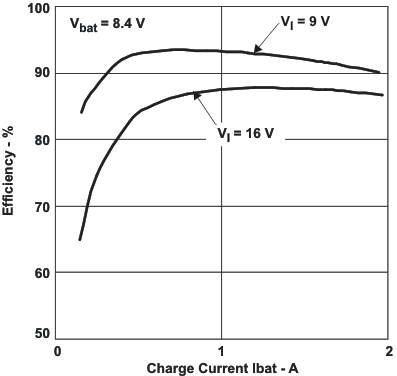
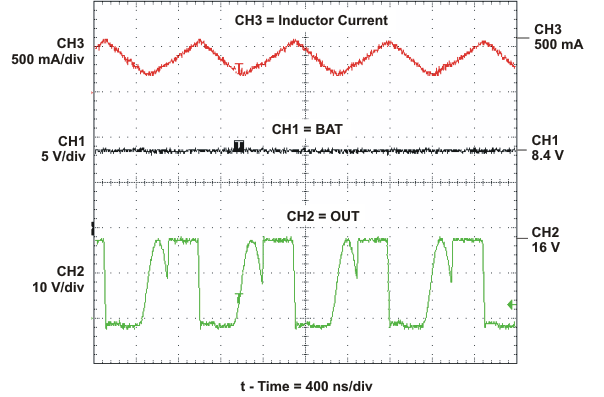
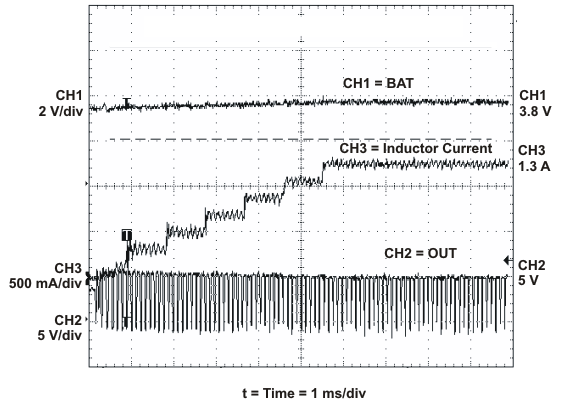
SLUS688H March 2006 – November 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 PWM Controller
- 8.3.2 Temperature Qualification
- 8.3.3 Battery Preconditioning (Precharge)
- 8.3.4 Battery Charge Current
- 8.3.5 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.6 Charge Termination And Recharge
- 8.3.7 Sleep Mode
- 8.3.8 Charge Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 PG Output
- 8.3.10 CE Input (Charge Enable)
- 8.3.11 Timer Fault Recovery
- 8.3.12 Output Overvoltage Protection (Applies to All Versions)
- 8.3.13 Battery Detection
- 8.3.14 Current Sense Amplifier
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings (1)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (with respect to VSS) | IN, VCC | 20 | V | ||
| Input voltage (with respect to VSS and PGND) | STAT1, STAT2, PG, CE, CELLS, SNS, BAT | –0.3 | 20 | V | |
| OUT | –0.7 | 20 | V | ||
| TS, TTC | 7 | V | |||
| VTSB | 3.6 | V | |||
| ISET1, ISET2 | 3.3 | V | |||
| Voltage difference between SNS and BAT inputs (VSNS - VBAT) | ±1 | V | |||
| Output sink | STAT1, STAT2, PG | 10 | mA | ||
| Output current (average) | OUT | 2.2 | A | ||
| Lead temperature 1.6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds | 300 | °C | |||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 (1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101 (2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VCC and IN (Tie together) | 4.35 (1) | 16.0 (2) | V | |
| Operating junction temperature range, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C |
(1) The IC continues to operate below Vmin, to 3.5 V, but these conditions are not tested, and are not specified.
(2) The inherent switching noise voltage spikes should not exceed the absolute maximum rating on either the IN or OUT pins. A tight layout minimizes switching noise.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC (1) | bq2412x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHL (VQFN) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 39.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 39.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 15.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 15.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 3.6 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = 0°C to 125°C and recommended supply voltage range (unless otherwise stated)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CURRENTS | ||||||
| IVCC(VCC) | VCC supply current | VCC > VCC(min), PWM switching | 10 | mA | ||
| VCC > VCC(min), PWM NOT switching | 5 | |||||
| VCC > VCC(min), CE = HIGH | 315 | μA | ||||
| I(SLP) | Battery discharge sleep current, (SNS, BAT, OUT pins) | 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 4.2 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
3.5 | μA | ||
| 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 8.4 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
5.5 | |||||
| 0°C ≤ TJ ≤ 65°C, VI(BAT) = 12.6 V, VCC < V(SLP) or VCC > V(SLP) but not in charge |
7.7 | |||||
| VOLTAGE REGULATION | ||||||
| VOREG | Output voltage, bq24123 | CELLS = Low, in voltage regulation | 4.2 | V | ||
| CELLS = High, in voltage regulation | 8.4 | |||||
| Output voltage, bq24120 | Operating in voltage regulation | 4.2 | ||||
| VIBAT | Feedback regulation REF for bq24125 only (W/FB) | IIBAT = 25 nA typical into pin | 2.1 | |||
| Voltage regulation accuracy | TA = 25°C | –0.5% | 0.5% | |||
| –1% | 1% | |||||
| CURRENT REGULATION - FAST CHARGE | ||||||
| IOCHARGE | Output current range of converter | VLOWV ≤ VI(BAT) < VOREG, V(VCC) - VI(BAT) > V(DO-MAX) |
150 | 2000 | mA | |
| VIREG | Voltage regulated across R(SNS) Accuracy | 100 mV ≤ VIREG≤ 200 mV, (1) | –10% | 10% | ||
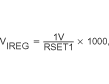 |
||||||
| Programmed Where 5 kΩ ≤ RSET1 ≤ 10 kΩ, Select RSET1 to program VIREG, VIREG(measured) = IOCHARGE ×RSNS (–10% to 10% excludes errors due to RSET1 and R(SNS) tolerances) |
||||||
| V(ISET1) | Output current set voltage | V(LOWV) ≤ VI(BAT) ≤ VO(REG), V(VCC) ≥ VI(BAT) + V (DO-MAX) |
1 | V | ||
| K(ISET1) | Output current set factor | VLOWV ≤ VI(BAT) < VO(REG) , V(VCC) ≥ VI(BAT) + V(DO-MAX) |
1000 | V/A | ||
| PRECHARGE AND SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT REGULATION | ||||||
| VLOWV | Precharge to fast-charge transition voltage threshold, BAT | 68 | 71.4 | 75 | %VO(REG) | |
| t | Deglitch time for precharge to fast charge transition | Rising voltage; tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns, 2-mV overdrive |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| IOPRECHG | Precharge range | VI(BAT) < VLOWV, t < tPRECHG | 15 | 200 | mA | |
| V(ISET2) | Precharge set voltage, ISET2 | VI(BAT) < VLOWV, t < tPRECHG | 100 | mV | ||
| K(ISET2) | Precharge current set factor | 1000 | V/A | |||
| VIREG-PRE | Voltage regulated across RSNS-Accuracy | 10 mV ≤ VIREG-PRE ≤ 100 mV, (1) | –20% | 20% | ||
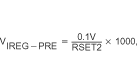 |
||||||
| Where 1.0 kΩ ≤ RSET2 ≤ 10 kΩ, Select RSET2 to program VIREG-PRE, VIREG-PRE (Measured) = IOPRE-CHG × RSNS (–20% to 20% excludes errors due to RSET2 and RSNS tolerances) |
||||||
| CHARGE TERMINATION (CURRENT TAPER) DETECTION | ||||||
| ITERM | Charge current termination detection range | VI(BAT) > VOREG- VRCH | 15 | 200 | mA | |
| VTERM | Charge termination detection set voltage, ISET2 | VI(BAT) > VOREG- VRCH | 100 | mV | ||
| K(ISET2) | Termination current set factor | 1000 | V/A | |||
| Charger termination accuracy | VI(BAT) > VOREG- VRCH | –20% | 20% | |||
| tdg-TERM | Deglitch time for charge termination | Both rising and falling, 2-mV overdrive tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| TEMPERATURE COMPARATOR AND VTSB BIAS REGULATOR | ||||||
| %LTF | Cold temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VLTF = VO(VTSB) × % LTF/100 | 72.8% | 73.5% | 74.2% | |
| %HTF | Hot temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VHTF = VO(VTSB) × % HTF/100 | 33.7% | 34.4% | 35.1% | |
| %TCO | Cutoff temperature threshold, TS, % of bias | VTCO = VO(VTSB) × % TCO/100 | 28.7% | 29.3% | 29.9% | |
| LTF hysteresis | 0.5% | 1.0% | 1.5% | |||
| tdg-TS | Deglitch time for temperature fault, TS | Both rising and falling, 2-mV overdrive tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| VO(VTSB) | TS bias output voltage | VCC > VIN(min), I(VTSB) = 10 mA 0.1 μF ≤ CO(VTSB) ≤ 1 μF |
3.15 | V | ||
| VO(VTSB) | TS bias voltage regulation accuracy | VCC > IN(min), I(VTSB) = 10 mA 0.1 μF ≤ CO(VTSB) ≤ 1 μF |
–10% | 10% | ||
| BATTERY RECHARGE THRESHOLD | ||||||
| VRCH | Recharge threshold voltage | Below VOREG | 75 | 100 | 125 | mV/cell |
| tdg-RCH | Deglitch time | VI(BAT) < decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns 10-mV overdrive |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms |
| STAT1, STAT2, AND PG OUTPUTS | ||||||
| VOL(STATx) | Low-level output saturation voltage, STATx | IO = 5 mA | 0.5 | V | ||
| VOL(PG) | Low-level output saturation voltage, PG | IO = 10 mA | 0.1 | |||
| CE , CELLS INPUTS | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | IIL = 5 μA | 0 | 0.4 | V | |
| VIH | High-level input voltage | IIH = 20 μA | 1.3 | VCC | ||
| TTC INPUT | ||||||
| tPRECHG | Precharge timer | 1440 | 1800 | 2160 | s | |
| tCHARGE | Programmable charge timer range | t(CHG) = C(TTC) × K(TTC) | 25 | 572 | minutes | |
| Charge timer accuracy | 0.01 μF ≤ C(TTC) ≤ 0.18 μF | -10% | 10% | |||
| KTTC | Timer multiplier | 2.6 | min/nF | |||
| CTTC | Charge time capacitor range | 0.01 | 0.22 | μF | ||
| VTTC_EN | TTC enable threshold voltage | V(TTC) rising | 200 | mV | ||
| SLEEP COMPARATOR | ||||||
| VSLP-ENT | Sleep-mode entry threshold | 2.3 V ≤ VI(OUT) ≤ VOREG, for 1 or 2 cells | VCC ≤ VIBAT +5 mV | VCC ≤ VIBAT +75 mV | V | |
| VI(OUT) = 12.6 V, RIN = 1kΩ, bq24125 (2) |
VCC ≤ VIBAT –4 mV | VCC ≤ VIBAT +73 mV | ||||
| VSLP-EXIT | Sleep-mode exit hysteresis, | 2.3 V ≤ VI(OUT)≤ VOREG | 40 | 160 | mV | |
| tdg-SLP | Deglitch time for sleep mode | VCC decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive, PMOS turns off |
5 | μs | ||
| VCC decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive, STATx pins turn off |
20 | 30 | 40 | ms | ||
| UVLO | ||||||
| VUVLO-ON | IC active threshold voltage | VCC rising | 3.15 | 3.30 | 3.50 | V |
| IC active hysteresis | VCC falling | 120 | 150 | mV | ||
| PWM | ||||||
| Internal P-channel MOSFET on-resistance | 7 V ≤ VCC ≤ VCC(max) | 400 | mΩ | |||
| 4.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 7 V | 500 | |||||
| Internal N-channel MOSFET on-resistance | 7 V ≤ VCC ≤ VCC(max) | 130 | ||||
| 4.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 7 V | 150 | |||||
| fOSC | Oscillator frequency | 1.1 | MHz | |||
| Frequency accuracy | –9% | 9% | ||||
| DMAX | Maximum duty cycle | 100% | ||||
| DMIN | Minimum duty cycle | 0% | ||||
| tTOD | Switching delay time (dead time) | 20 | ns | |||
| tsyncmin | Minimum synchronous FET on time | 60 | ns | |||
| Synchronous FET minimum current-off threshold (3) | 50 | 400 | mA | |||
| BATTERY DETECTION | ||||||
| IDETECT | Battery detection current during time-out fault | VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 2 | mA | ||
| IDISCHRG1 | Discharge current | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 400 | μA | ||
| tDISCHRG1 | Discharge time | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 1 | s | ||
| IWAKE | Wake current | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 2 | mA | ||
| tWAKE | Wake time | VSHORT < VI(BAT) < VOREG – VRCH | 0.5 | s | ||
| IDISCHRG2 | Termination discharge current | Begins after termination detected, VI(BAT) ≤ VOREG |
400 | μA | ||
| tDISCHRG2 | Termination time | 262 | ms | |||
| OUTPUT CAPACITOR | ||||||
| COUT | Required output ceramic capacitor range from SNS to PGND, between inductor and RSNS | 4.7 | 10 | 47 | μF | |
| CSNS | Required SNS capacitor (ceramic) at SNS pin | 0.1 | μF | |||
| PROTECTION | ||||||
| VOVP | OVP threshold voltage | Threshold over VOREG to turn off P-channel MOSFET, STAT1, and STAT2 during charge or termination states | 110 | 117 | 121 | %VO(REG) |
| ILIMIT | Cycle-by-cycle current limit | 2.6 | 3.6 | 4.5 | A | |
| VSHORT | Short-circuit voltage threshold, BAT | VI(BAT) falling | 1.95 | 2 | 2.05 | V/cell |
| ISHORT | Short-circuit current | VI(BAT) ≤ VSHORT | 35 | 65 | mA | |
| TSHTDWN | Thermal trip | 165 | °C | |||
| Thermal hysteresis | 10 | |||||
(1) Inductor peak current should be less than 2.6 A. Use equations 12, 13, 15, 18, and 19 to make sure the peak inductor current is less than 2.6 A.
(2) For bq24125 only. RIN is connected between IN and PGND pins and needed to ensure sleep entry.
(3) N-channel always turns on for approximately 60 ns and then turns off if current is too low.
7.6 Dissipation Ratings
| PACKAGE | ΘJA | ΘJC | TA < 40°C POWER RATING |
DERATING FACTOR ABOVE TA = 40°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHL (1) | 46.87°C/W | 2.15°C/W | 1.81 W | 0.021 W/°C |
(1) This data is based on using the JEDEC High-K board, and the exposed die pad is connected to a copper pad on the board. This is connected to the ground plane by a 2x3 via matrix.