SLUSB97A October 2012 – December 2014
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Device Power Up
- 8.3.2 Power Path Management
- 8.3.3 Battery Charging Management
- 8.3.4 Status Outputs (STAT and INT)
- 8.3.5 Protections
- 8.3.6 Serial Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Map
- 8.5.1
I2C Registers
- 8.5.1.1 Input Source Control Register REG00 (reset = 00110000, or 30)
- 8.5.1.2 Power-On Configuration Register REG01 (reset = 00011011, or 1B)
- 8.5.1.3 Charge Current Control Register REG02 (reset = 01100000, or 60)
- 8.5.1.4 Pre-Charge/Termination Current Control Register REG03 (reset = 00010001, or 11)
- 8.5.1.5 Charge Voltage Control Register REG04 (reset = 10110010, or B2)
- 8.5.1.6 Charge Termination/Timer Control Register REG05 (reset = 10011010, or 9A)
- 8.5.1.7 Thermal Regulation Control Register REG06 (reset = 00000011, or 03)
- 8.5.1.8 Misc Operation Control Register REG07 (reset = 01001011, or 4B)
- 8.5.1.9 System Status Register REG08
- 8.5.1.10 Fault Register REG09
- 8.5.1.11 Vender / Part / Revision Status Register REG0A (reset = 00100011, or 23)
- 8.5.1
I2C Registers
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage range (with respect to GND) | VBUS | –2 | 22 | V |
| PMID | –0.3 | 22 | V | |
| STAT, | –0.3 | 20 | V | |
| BTST | –0.3 | 26 | V | |
| SW | –2 | 20 | V | |
| BAT, SYS (converter not switching) | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| SDA, SCL, INT, OTG, ILIM, REGN, TS1, TS2, CE, D+, D– | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| BTST TO SW | –0.3 | –7 | V | |
| PGND to GND | –0.3 | –0.3 | V | |
| Output sink current | INT, STAT | 6 | mA | |
| Junction temperature | –40°C | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. All voltage values are with respect to the network ground terminal unless otherwise noted.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | 1000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | 250 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 3.9 | 17(1) | V |
| IIN | Input current | 3 | A | |
| ISYS | Output current (SYS) | 4.5 (bq24195) 2.5 (bq24195L) |
A | |
| VBAT | Battery voltage | 4.4 | V | |
| IBAT | Fast charging current | 4.5 (bq24195) 2.5 (bq24195L) |
A | |
| Discharging current with internal MOSFET | 6 continuous 9 peak (up to 1 sec duration) |
A | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature range | –40 | 85 | °C |
(1) The inherent switching noise voltage spikes should not exceed the absolute maximum rating on either the BTST or SW pins. A tight layout minimizes switching noise.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | bq24195 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGE (24 PIN) | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 32.2 | °C/W |
| RθJCtop | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 29.8 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 9.1 | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.3 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 9.1 | |
| RθJCbot | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.2 | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
VVBUS_UVLOZ < VVBUS < VACOV and VVBUS > VBAT + VSLEEP, TJ = –40°C to 125°C and TJ = 25°C for typical values unless other noted.7.6 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. Table of Figures
| FIGURE NO. | |
|---|---|
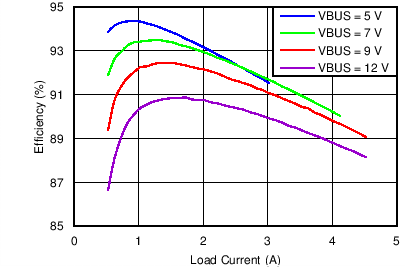
| Charging Efficiency vs Charging Current | Figure 1 |
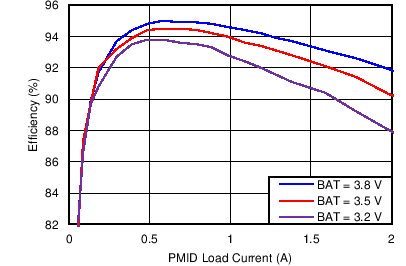
| Boost Mode Efficiency vs PMID Load Current | Figure 2 |
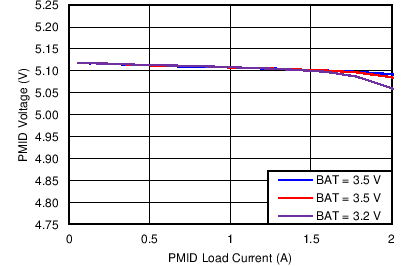
| Boost Mode PMID Voltage Regulation vs PMID Load Current | Figure 3 |
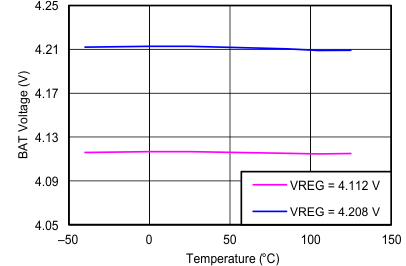
| BAT Voltage vs Temperature | Figure 4 |
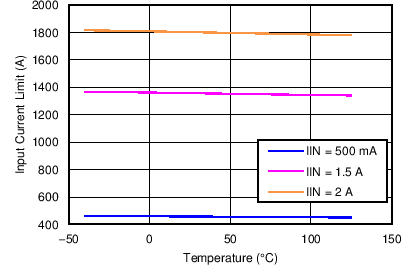
| Input Current Limit vs Temperature | Figure 5 |
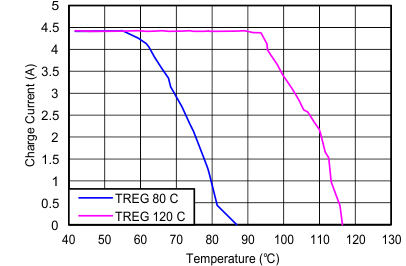
| Charge Current vs Temperature | Figure 6 |