SLUSBY5G June 2014 – December 2015
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 High Impedance Mode
- 7.4.2 Battery Only Connected
- 7.4.3 Input Connected
- 7.4.4 Battery Charging Process
- 7.4.5 Charge Time Optimizer
- 7.4.6 Battery Detection
- 7.4.7 Battery Overvoltage Protection (BOVP)
- 7.4.8 Dynamic Power Path Management
- 7.4.9 Battery Discharge FET (BGATE)
- 7.4.10 IUSB1, IUSB2, and IUSB3 Input
- 7.4.11 Safety Timer in Charge Mode
- 7.4.12 LDO Output (DRV)
- 7.4.13 External NTC Monitoring (TS)
- 7.4.14 Thermal Regulation and Protection
- 7.4.15 Status Outputs (CHG, PG)
- 7.4.16 Boost Mode Operation
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
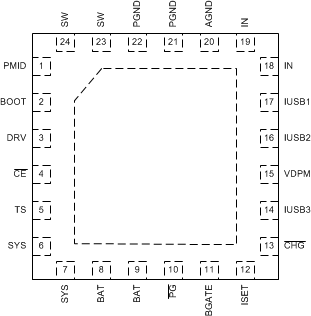
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN NAME |
PIN NUMBER |
I/O | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| AGND | 20 | – | Analog Ground. Connect to the thermal pad (for QFN only) and the ground plane of the circuit. |
| BAT | 8, 9 | I/O | Battery Connection. Connect to the positive pin of the battery. Bypass BAT to GND with at least 1μF of ceramic capacitance. See Application section for additional details. |
| BGATE | 11 | O | External Discharge MOSFET Gate Connection. BGATE drives an external P-Channel MOSFET to provide a very low resistance discharge path. Connect BGATE to the gate of the external MOSFET. BGATE is low during high impedance mode or when no input is connected. If no external FET is required, leave BGATE disconnected. Do not connect BGATE to GND. |
| BOOT | 2 | I | High Side MOSFET Gate Driver Supply. Connect 0.033µF of ceramic capacitance (voltage rating > 10V) from BOOT to SW to supply the gate drive for the high side MOSFET. |
| CE | 4 | I | IC Charge Enable Input. Drive CE high to place the part to disable charge. Drive CE low for normal operation. CE is pulled low internally with 100kΩ. |
| CHG | 13 | O | Charge Status Open Drain Output. CHG is pulled low when a charge cycle starts and remains low while charging. CHG is high impedance when the charging terminates and when when no supply exists. |
| DRV | 3 | O | Gate Drive Supply. DRV is the bias supply for the gate drive of the internal MOSFETs. Bypass DRV to PGND with at least a 2.2µF, 10V, X5R or better capacitor. DRV may be used to drive external loads up to 10mA. DRV is active whenever the input is connected and VIN > VUVLO and VIN > (VBAT + VSLP). |
| IN | 18, 19 | I | DC Input Power Supply. IN is connected to the external DC supply (AC adapter or USB port). Bypass IN to PGND with at least a 4.7μF of ceramic capacitance. |
| ISET | 12 | I | Charge Current Programming Input. Connect a resistor from ISET to GND to program the fast charge current. The charge current is programmable from 500mA to 3A. |
| IUSB1 | 17 | I | USB Input Current Limit Programming Inputs. IUSB1, IUSB2 and IUSB3 program the input current limit for the USB input. USB2.0 and USB3.0 current limits are available for easy implementation of these standards. Table 1 shows the settings for these inputs. |
| IUSB2 | 16 | I | |
| IUSB3 | 14 | I | |
| PG | 10 | O | Power Good Open Drain output. PG is pulled low wehn a valid supply is connected. A valud supply is between VBAT+VSLP and VOVP. The output is high impedance if the supply is not in this range. |
| PGND | 21,22 | – | Ground pin. Connect to the thermal pad (for QFN only) and the ground plane of the circuit. |
| PMID | 1 | I | High Side Bypass Connection. Connect at least 1µF of ceramic capacitance from PMID to PGND as close to the PMID and PGND pins as possible. |
| SW | 23, 24 | O | Inductor Connection. Connect to the switched side of the external inductor. The inductance must be between 1.5µH and 2.2µH. |
| SYS | 6, 7 | I | System Voltage Sense and Charger FET Connection. Connect SYS to the system output at the output bulk capacitors. Bypass SYS locally with at least 10μF of ceramic capacitance. The SYS rail must have at least 20µF of total capacitance for stable operation. See Application section for additional details. |
| TS | 5 | I | Battery Pack NTC Monitor. Connect TS to the center tap of a resistor divider from DRV to GND. The NTC is connected from TS to GND. The TS function provides 4 thresholds for JEITA compatibility. Pull TS high to VDRV to disable the TS function if unused. See the NTC Monitor section for more details on operation and selecting the resistor values. |
| VDPM | 15 | I | Input DPM Programming Input. Connect a resistor divider from IN to GND with VDPM connected to the center tap to program the Input Voltage based Dynamic Power Management (VIN_DPM) threshold. The input current is reduced to maintain the supply voltage at VIN_DPM. See the Input Voltage based Dynamid Power Management section for a detailed explanation. |
| Thermal PAD | – | – | There is an internal electrical connection between the exposed thermal pad and the PGND pin of the device. The thermal pad must be connected to the same potential as the PGND pin on the printed circuit board. Do not use the thermal pad as the primary ground input for the device. PGND pin must be connected to ground at all times. |