SLUS912A August 2009 – August 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The bq24312 device is a highly integrated circuit designed to provide protection to Li-ion batteries from failures of the charging circuit. The device continuously monitors the input voltage, the input current, and the battery voltage. In case of an input overvoltage condition, the device immediately removes power from the charging circuit by turning off an internal switch. In the case of an overcurrent condition, it limits the system current at the threshold value, and if the overcurrent persists, switches the pass element OFF after a blanking period. If the battery voltage rises to an unsafe level, the device disconnects power from the charging circuit until the battery voltage returns to an acceptable value. Additionally, the device also monitors its own die temperature and switches off if it exceeds 140°C. The input overcurrent threshold is user-programmable. The device can be controlled by a processor and also provides status information about fault conditions to the host.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
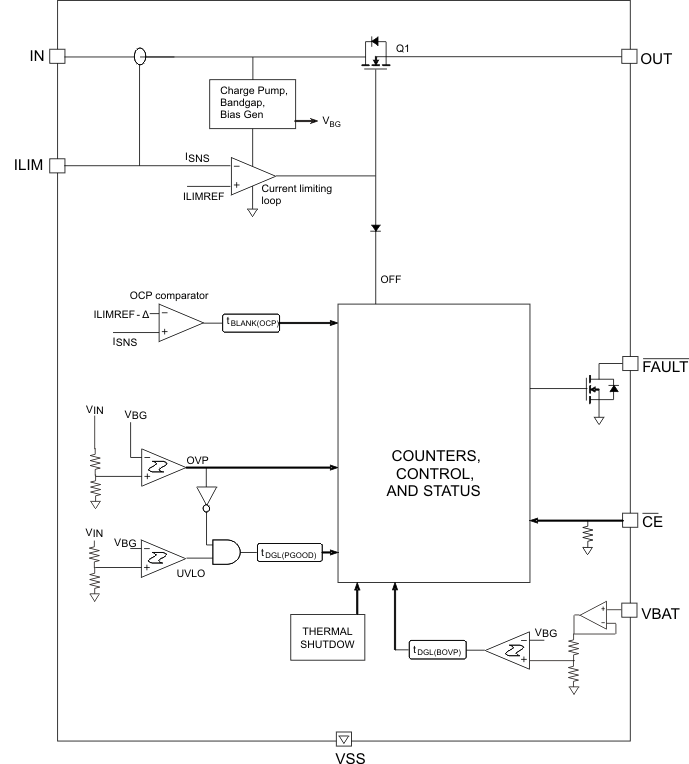
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Input Overvoltage Protection
The bq24312 device integrates an input overvoltage protection feature to protect downstream devices from faulty input sources. As long as the input voltage is less than VO(REG), the output voltage tracks the input voltage (less the drop caused by RDSON of Q1). If the input voltage is greater than VO(REG) (plus the RDSON drop) and less than VOVP, the device acts like a series linear regulator, with the output voltage regulated to VO(REG). If the input voltage rises above VOVP, the output voltage is clamped to VO(REG) for a blanking duration tBLANK(OVP). If the input voltage returns below VOVP within tBLANK(OVP), the device continues normal operation (See Figure 15). This provides protection against turning power off due to transient overvoltage spikes while still protecting the system. However, if the input voltage remains above VOVP for more than tBLANK(OVP), the internal FET is turned off, removing power from the circuit (see Figure 16). When the input voltage comes back to a safe value the device waits for tON(OVP), then switches on Q1 and goes through the soft-start routine (see Figure 17).
7.3.2 Input Overcurrent Protection
The overcurrent threshold is programmed by a resistor RILIM connected from the ILIM pin to VSS. Figure 4 shows the OCP threshold as a function of RILIM, and may be approximated by the following equation:
where
- RILIM must be between 15 kΩ and 90 kΩ
If the load current tries to exceed the IOCP threshold, the device limits the current for a blanking duration of tBLANK(OCP). If the load current returns to less than IOCP before tBLANK(OCP) times out, the device continues to operate. However, if the overcurrent situation persists for tBLANK(OCP), the FET Q1 is turned off for a duration of tREC(OCP), and the FAULT pin is driven low. The FET is then turned on again after tREC(OCP) and the current is monitored all over again. Each time an OCP fault occurs, an internal counter is incremented. If 15 OCP faults occur in one charge cycle, the FET is turned off permanently. The counter is cleared either by removing and re-applying input power, or by disabling and re-enabling the device with the CE pin. Figure 18 to Figure 20 show what happens in an overcurrent fault.
To prevent the input voltage from spiking up due to the inductance of the input cable, Q1 is turned off slowly, resulting in a soft-stop, as shown in Figure 20.
7.3.3 Battery Overvoltage Protection
The battery overvoltage threshold BVOVP is internally set to 4.35 V. If the battery voltage exceeds the BVOVP threshold, the FET Q1 is turned off, and the FAULT pin is driven low. The FET is turned back on once the battery voltage drops to BVOVP – Vhys(Bovp) (see Figure 21 and Figure 22). Each time a battery overvoltage fault occurs, an internal counter is incremented. If 15 such faults occur in one charge cycle, the FET is turned off permanently. The counter is cleared either by removing and re-applying input power, or by disabling and re-enabling the device with the CE pin. In the case of a battery overvoltage fault, Q1 is switched OFF gradually (see Figure 21).
7.3.4 Thermal Protection
If the junction temperature of the device exceeds TJ(OFF), the FET Q1 is turned off, and the FAULT pin is driven low. The FET is turned back on when the junction temperature falls below TJ(OFF) – TJ(OFF-HYS).
7.3.5 Enable Function
The device has an enable pin which can be used to enable or disable the device. When the CE pin is driven high, the internal FET is turned off. When the CE pin is low, the FET is turned on if other conditions are safe. The OCP counter and the Bat-OVP counter are both reset when the device is disabled and re-enabled. The CE pin has an internal pulldown resistor and can be left floating. Note that the FAULT pin functionality is also disabled when the CE pin is high.
7.3.6 Fault Indication
The FAULT pin is an active-low open-drain output. It is in a high-impedance state when operating conditions are safe, or when the device is disabled by setting CE high. With CE low, the FAULT pin goes low whenever any of these events occurs:
- Input overvoltage
- Input overcurrent
- Battery overvoltage
- IC overtemperature
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 OPERATION Mode
The device continuously monitors the input voltage, the input current, and the battery voltage. As long as the input voltage is less than VOVP, the output voltage tracks the input voltage (less the drop caused by RDSON of Q1). During fault conditions, the internal FET is turned off and the output is isolated from the input source.
7.4.2 POWER-DOWN Mode
The device remains in POWER-DOWN mode when the input voltage at the IN pin is below the undervoltage threshold UVLO. The FET Q1 connected between IN and OUT pins is off, and the status output, FAULT, is set to Hi-Z. See Figure 9.
7.4.3 POWER-ON RESET Mode
The device resets when the input voltage at the IN pin exceeds the UVLO threshold. All internal counters and other circuit blocks are reset. The device then waits for duration tDGL(PGOOD) for the input voltage to stabilize. If, after tDGL(PGOOD), the input voltage and battery voltage are safe, FET Q1 is turned ON. The device has a soft-start feature to control the inrush current. The soft-start minimizes the ringing at the input (the ringing occurs because the parasitic inductance of the adapter cable and the input bypass capacitor form a resonant circuit). Figure 13 shows the power-up behavior of the device. Because of the deglitch time at power-on, if the input voltage rises rapidly to beyond the OVP threshold, the device will not switch on at all, instead it will go into PROTECTION mode and indicate a fault on the FAULT pin, as shown in Figure 14.
 Figure 9. Flow Diagram
Figure 9. Flow Diagram