SLUSDF8E June 2019 – July 2024 BQ25618 , BQ25619
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 7.3.2 Device Power Up From Battery Without Input Source
- 7.3.3 Power Up From Input Source
- 7.3.4 Boost Mode Operation From Battery
- 7.3.5 Power Path Management
- 7.3.6 Battery Charging Management
- 7.3.7 Ship Mode and QON Pin
- 7.3.8 Status Outputs (STAT, INT , PMID_GOOD)
- 7.3.9 Protections
- 7.3.10 Serial Interface
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Input Capacitor and Resistor
Design the input capacitance to provide enough ripple current rating to absorb the input switching ripple current. Worst case RMS ripple current is half of the charging current when the duty cycle is 0.5. If the converter does not operate at 50% duty cycle, then the worst case capacitor RMS current ICIN occurs where the duty cycle is closest to 50% and can be estimated using Equation 5.
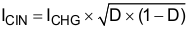
A low ESR ceramic capacitor such as X7R or X5R is preferred for the input decoupling capacitor and should be placed as close as possible to the drain of the high-side MOSFET and source of the low-side MOSFET. The voltage rating of the capacitor must be higher than the normal input voltage level. A 25-V or higher rated capacitor is preferred for a 12-V input voltage. Minimum capacitance of 10 μF is suggested for typical of 1.5-A charging current.
During high current output over 700 mA in boost mode, a 10-kΩ pull-down resistor on VBUS is recommended to keep VBUS low in case Q1 RBFET leakage gets high.