SLUSCU1A May 2017 – May 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power-Up from Battery Without DC Source
- 8.3.2 Power-Up From DC Source
- 8.3.3 USB On-The-Go (OTG)
- 8.3.4 Converter Operation
- 8.3.5 Current and Power Monitor
- 8.3.6 Input Source Dynamic Power Manage
- 8.3.7 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 8.3.8 Processor Hot Indication
- 8.3.9 Device Protection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Map
- 8.6.1
Setting Charge and PROCHOT Options
- 8.6.1.1 ChargeOption0 Register (I2C address = 01/00h) [reset = E20Eh]
- 8.6.1.2 ChargeOption1 Register (I2C address = 31/30h) [reset = 211h]
- 8.6.1.3 ChargeOption2 Register (I2C address = 33/32h) [reset = 2B7]
- 8.6.1.4 ChargeOption3 Register (I2C address = 35/34h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.5 ProchotOption0 Register (I2C address = 37/36h) [reset = 04A54h]
- 8.6.1.6 ProchotOption1 Register (I2C address = 39/38h) [reset = 8120h]
- 8.6.1.7 ADCOption Register (I2C address = 3B/3Ah) [reset = 2000h]
- 8.6.2 Charge and PROCHOT Status
- 8.6.3 ChargeCurrent Register (I2C address = 03/02h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.4 MaxChargeVoltage Register (I2C address = 05/04h) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 8.6.5 MinSystemVoltage Register (I2C address = 0D/0Ch) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 8.6.6 Input Current and Input Voltage Registers for Dynamic Power Management
- 8.6.7 OTGVoltage Register (I2C address = 07/06h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.8 OTGCurrent Register (I2C address = 09/08h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.9 ADCVBUS/PSYS Register (I2C address = 27/26h)
- 8.6.10 ADCIBAT Register (I2C address = 29/28h)
- 8.6.11 ADCIINCMPIN Register (I2C address = 2B/2Ah)
- 8.6.12 ADCVSYSVBAT Register (I2C address = 2D/2Ch)
- 8.6.13 ID Registers
- 8.6.1
Setting Charge and PROCHOT Options
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Orderable Information
9.2.2.5 Power MOSFETs Selection
Four external N-channel MOSFETs are used for a synchronous switching battery charger. The gate drivers are internally integrated into the IC with 6 V of gate drive voltage. 30 V or higher voltage rating MOSFETs are preferred for 19 V - 20 V input voltage.
Figure-of-merit (FOM) is usually used for selecting proper MOSFET based on a tradeoff between the conduction loss and switching loss. For the top side MOSFET, FOM is defined as the product of a MOSFET's on-resistance, RDS(ON), and the gate-to-drain charge, QGD. For the bottom side MOSFET, FOM is defined as the product of the MOSFET's on-resistance, RDS(ON), and the total gate charge, QG.
The lower the FOM value, the lower the total power loss. Usually lower RDS(ON) has higher cost with the same package size.
The top-side MOSFET loss includes conduction loss and switching loss. It is a function of duty cycle (D=VOUT/VIN), charging current (ICHG), MOSFET's on-resistance (RDS(ON)), input voltage (VIN), switching frequency (fS), turn on time (ton) and turn off time (toff):

The first item represents the conduction loss. Usually MOSFET RDS(ON) increases by 50% with 100°C junction temperature rise. The second term represents the switching loss. The MOSFET turn-on and turn-off times are given by:
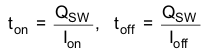
where Qsw is the switching charge, Ion is the turn-on gate driving current and Ioff is the turn-off gate driving current. If the switching charge is not given in MOSFET datasheet, it can be estimated by gate-to-drain charge (QGD) and gate-to-source charge (QGS):

Gate driving current can be estimated by REGN voltage (VREGN), MOSFET plateau voltage (Vplt), total turn-on gate resistance (Ron) and turn-off gate resistance (Roff) of the gate driver:

The conduction loss of the bottom-side MOSFET is calculated with the following equation when it operates in synchronous continuous conduction mode:
When charger operates in non-synchronous mode, the bottom-side MOSFET is off. As a result all the freewheeling current goes through the body-diode of the bottom-side MOSFET. The body diode power loss depends on its forward voltage drop (VF), non-synchronous mode charging current (INONSYNC), and duty cycle (D).
The maximum charging current in non-synchronous mode can be up to 0.25 A for a 10-mΩ charging current sensing resistor or 0.5 A if battery voltage is below 2.5 V. The minimum duty cycle happens at lowest battery voltage. Choose the bottom-side MOSFET with either an internal Schottky or body diode capable of carrying the maximum non-synchronous mode charging current.