SLUSE64 May 2021 BQ25723
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power-Up Sequence
- 9.3.2 Vmin Active Protection (VAP) with Battery only
- 9.3.3 Two-Level Battery Discharge Current Limit
- 9.3.4 Fast Role Swap Feature
- 9.3.5 CHRG_OK Indicator
- 9.3.6 Input and Charge Current Sensing
- 9.3.7 Input Voltage and Current Limit Setup
- 9.3.8 Battery Cell Configuration
- 9.3.9 Device HIZ State
- 9.3.10 USB On-The-Go (OTG)
- 9.3.11 Converter Operation
- 9.3.12 Inductance Detection Through IADPT Pin
- 9.3.13 Converter Compensation
- 9.3.14 Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
- 9.3.15 Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM)
- 9.3.16 Switching Frequency and Dithering Feature
- 9.3.17 Current and Power Monitor
- 9.3.18 Input Source Dynamic Power Management
- 9.3.19 Input Current Optimizer (ICO)
- 9.3.20 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 9.3.21 Processor Hot Indication
- 9.3.22
Device Protection
- 9.3.22.1 Watchdog Timer
- 9.3.22.2 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 9.3.22.3 Input Overcurrent Protection (ACOC)
- 9.3.22.4 System Overvoltage Protection (SYSOVP)
- 9.3.22.5 Battery Overvoltage Protection (BATOVP)
- 9.3.22.6 Battery Discharge Overcurrent Protection (BATOC)
- 9.3.22.7 Battery Short Protection (BATSP)
- 9.3.22.8 System Undervoltage Lockout (VSYS_UVP) and Hiccup Mode
- 9.3.22.9 Thermal Shutdown (TSHUT)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 ChargeOption0 Register (I2C address = 01/00h) [reset = E70Eh]
- 9.6.2 ChargeCurrent Register (I2C address = 03/02h) [reset = 0000h]
- 9.6.3 ChargeVoltage Register (I2C address = 05/04h) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 9.6.4 ChargerStatus Register (I2C address = 21/20h) [reset = 0000h]
- 9.6.5 ProchotStatus Register (I2C address = 23/22h) [reset = B800h]
- 9.6.6 IIN_DPM Register (I2C address = 25/24h) [reset = 4100h]
- 9.6.7 ADCVBUS/PSYS Register (I2C address = 27/26h)
- 9.6.8 ADCIBAT Register (I2C address = 29/28h)
- 9.6.9 ADCIIN/CMPIN Register (I2C address = 2B/2Ah)
- 9.6.10 ADCVSYS/VBAT Register (I2C address = 2D/2Ch)
- 9.6.11 ChargeOption1 Register (I2C address = 31/30h) [reset = 3300h]
- 9.6.12 ChargeOption2 Register (I2C address = 33/32h) [reset = 00B7]
- 9.6.13 ChargeOption3 Register (I2C address = 35/34h) [reset = 0434h]
- 9.6.14 ProchotOption0 Register (I2C address = 37/36h) [reset = 4A81h(2S~4s) 4A09(1S)]
- 9.6.15 ProchotOption1 Register (I2C address = 39/38h) [reset = 41A0h]
- 9.6.16 ADCOption Register (I2C address = 3B/3Ah) [reset = 2000h]
- 9.6.17 ChargeOption4 Register (I2C address = 3D/3Ch) [reset = 0048h]
- 9.6.18 Vmin Active Protection Register (I2C address = 3F/3Eh) [reset = 006Ch(2s~4s)/0004h(1S)]
- 9.6.19 OTGVoltage Register (I2C address = 07/06h) [reset = 09C4h]
- 9.6.20 OTGCurrent Register (I2C address = 09/08h) [reset = 3C00h]
- 9.6.21 InputVoltage(VINDPM) Register (I2C address = 0B/0Ah) [reset =VBUS-1.28V]
- 9.6.22 VSYS_MIN Register (I2C address = 0D/0Ch) [reset value based on CELL_BATPRESZ pin setting]
- 9.6.23 IIN_HOST Register (I2C address = 0F/0Eh) [reset = 4100h]
- 9.6.24 ID Registers
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Orderable Information
7 Pin Configuration and Functions
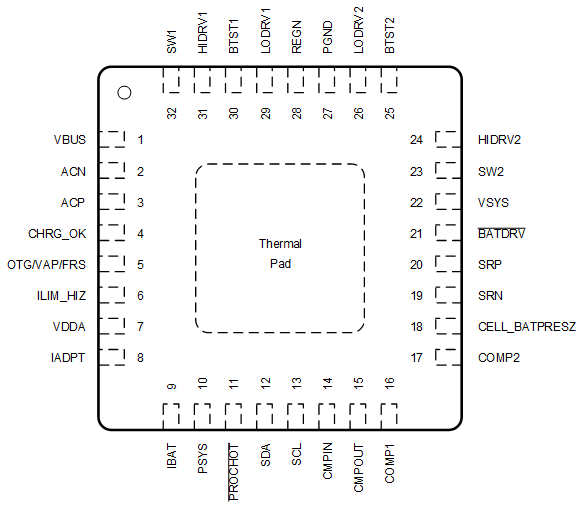 Figure 7-1 RSN Package32-Pin WQFNTop View
Figure 7-1 RSN Package32-Pin WQFNTop ViewTable 7-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NUMBER | ||
| ACN | 2 | PWR | Input current sense amplifier negative input. The leakage on ACP and ACN are matched. A RC low-pass filter is required to be placed between the sense resistor and the ACN pin to suppress the high frequency noise in the input current signal. Refer to Section 10.2.2.1 for ACP/ACN filter design. |
| ACP | 3 | PWR | Input current sense amplifier positive input. The leakage on ACP and ACN are matched. A RC low-pass filter is required to be placed between the sense resistor and the ACP pin to suppress the high frequency noise in the input current signal. Refer to Section 10.2.2.1 for ACP/ACN filter design. |
| BATDRV | 21 | O | P-channel battery FET (BATFET) gate driver output. It is shorted to VSYS to turn off the BATFET. It goes 10 V below VSYS to fully turn on BATFET. BATFET is in linear mode to regulate VSYS at minimum system voltage when battery is depleted. BATFET is fully on during fast charge and works as an ideal-diode in supplement mode. |
| BTST1 | 30 | PWR | Buck mode high-side power MOSFET driver power supply. Connect a 0.047-µF capacitor between SW1 and BTST1. The bootstrap diode between REGN and BTST1 is integrated. |
| BTST2 | 25 | PWR | Boost mode high-side power MOSFET driver power supply. Connect a 0.047-μF capacitor between SW2 and BTST2. The bootstrap diode between REGN and BTST2 is integrated. |
| CELL_BATPRESZ | 18 | I | Battery cell selection pin for 1- to 4- cell battery setting. CELL_BATPRESZ pin is biased from VDDA through a resistor divider. CELL_BATPRESZ pin also sets SYSOVP thresholds to 5 V for 1-cell, 12 V for 2-cell and 19.5 V for 3-cell/4-cell. CELL_BATPRESZ pin is pulled below VCELL_BATPRESZ_FALL to indicate battery removal. After battery is removed the charge voltage register REG0x05/04h() goes back to default. No external cap is allowed at CELL_BATPRESZ pin. The device exits LEARN mode and disables charge when CELL_BATPRESZ pin is pulled low (upon battery removal). |
| CHRG_OK | 4 | O | Open drain active high indicator to inform the system good power source is connected to the charger input. Connect to the pullup rail via 10-kΩ resistor. When VBUS rises above 3.5 V and falls below 25.8 V, CHRG_OK is HIGH after 50-ms deglitch time. When VBUS falls below 3.2 V or rises above 26.8 V, CHRG_OK is LOW. When one of SYSOVP, SYSUVP, ACOC, TSHUT, BATOVP, BATOC or force converter off faults occurs, CHRG_OK is asserted LOW. |
| CMPIN | 14 | I | Input of independent comparator. The independent comparator compares the voltage sensed on CMPIN pin with internal reference, and its output is on CMPOUT pin. Internal reference, output polarity and deglitch time is selectable by the host. With polarity HIGH (CMP_POL = 1b), place a resistor between CMPIN and CMPOUT to program hysteresis. With polarity LOW (CMP_POL = 0b), the internal hysteresis is 100 mV. If the independent comparator is not in use, tie CMPIN to ground. |
| CMPOUT | 15 | O | Open-drain output of independent comparator. Place a pullup resistor from CMPOUT to pullup supply rail. Internal reference, output polarity and deglitch time are selectable by the host. If the independent comparator is not in use, float CMPOUT pin. |
| COMP2 | 17 | I | Buck boost converter compensation pin 2. Refer to Section 9.3.13 for COMP2 pin RC network. |
| COMP1 | 16 | I | Buck boost converter compensation pin 1. Refer to Section 9.3.13 for COMP1 pin RC network. |
| OTG/VAP/FRS | 5 | I | Active HIGH to enable OTG, VAP or FRS modes. 1) When OTG_VAP_MODE=1b and EN_OTG=1b, pulling high this pin can enable OTG mode. 2) When OTG_VAP_MODE=1b and EN_FRS=1b, pulling high this pin can enable FRS mode in forward operation. 3) When OTG_VAP_MODE=0b, pulling high OTG/VAP/FRS pin is to enable VAP mode. |
| HIDRV1 | 31 | O | Buck mode high-side power MOSFET (Q1) driver. Connect to high-side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| HIDRV2 | 24 | O | Boost mode high-side power MOSFET(Q4) driver. Connect to high-side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| IADPT | 8 | O | The adapter current monitoring output pin. VIADPT = 20 or 40 × (VACP – VACN) with ratio selectable through IADPT_GAIN bit. This pin is also used to program the inductance used in the application. Refer to Section 9.3.12 for selecting resistor from the IADPT pin to ground . For a 2.2-µH inductance, the resistor is 137 kΩ. Place a 100-pF or less ceramic decoupling capacitor from IADPT pin to ground. IADPT output voltage is clamped below 3.3 V. |
| IBAT | 9 | O | The battery current monitoring output pin. VIBAT = 8 or 16 × (VSRP – VSRN) for charge current, or VIBAT = 8 or 16 × (VSRN – VSRP) for discharge current, with ratio selectable through IBAT_GAIN bit. Place a 100-pF or less ceramic decoupling capacitor from IBAT pin to ground. This pin can be floating if not in use. Its output voltage is clamped below 3.3 V. |
| ILIM_HIZ | 6 | I | Input current limit setting pin. Program ILIM_HIZ voltage by
connecting a resistor divider from VDDA rail to ground. The pin
voltage is calculated as: V(ILIM_HIZ) = 1 V + 40 × IDPM ×
Rac, in which IDPM is the target input current limit. When EN_EXTILIM = 1b the input current limit used by the charger is the lower setting of ILIM_HIZ pin and IIN_HOST register. When EN_EXTILIM = 0b input current limit is only determined by IIN_HOST register. When the pin voltage is below 0.4 V, the device enters high impedance (HIZ) mode with low quiescent current. When the pin voltage is above 0.8 V, the device is out of HIZ mode. The ILIM_HIZ pin voltage is continuous read and used for updating current limit setting (If EN_EXTILIM=1b ), this allows dynamic change input current limit setting by adjusting this pin voltage. |
| LODRV1 | 29 | O | Buck mode low side power MOSFET (Q2) driver. Connect to low side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| LODRV2 | 26 | O | Boost mode low side power MOSFET (Q3) driver. Connect to low side n-channel MOSFET gate. |
| PGND | 27 | GND | Device power ground. |
| PROCHOT | 11 | O | Active low open drain output indicator. It monitors adapter input current, battery discharge current, and system voltage. After any event in the PROCHOT profile is triggered, a pulse is asserted. The minimum pulse width is adjustable through PROCHOT_WIDTH bits. |
| PSYS | 10 | O | Current mode system power monitor. The output current is proportional to the total power from the adapter and the battery. The gain is selectable through . Place a resistor from PSYS to ground to generate output voltage. This pin can be floating if not in use. Its output voltage is clamped at 3.3 V. Place a capacitor in parallel with the resistor for filtering. |
| REGN | 28 | PWR | 6-V linear regulator output supplied from VBUS or VSYS. The LDO is active when VBUS above VVBUS_CONVEN. Connect a 2.2- or 3.3-μF ceramic capacitor from REGN to power ground. REGN pin output is for power stage gate drive. |
| SCL | 13 | I | clock input. Connect to clock line from the host controller or smart battery. Connect a 10-kΩ pullup resistor according to specifications. |
| SDA | 12 | I/O | open-drain data I/O. Connect to data line from the host controller or smart battery. Connect a 10-kΩ pullup resistor according to specifications. |
| SRN | 19 | PWR | Charge current sense amplifier negative input. SRN pin is for battery voltage sensing as well. Connect a 0.1-μF filter cap cross battery charging sensing resistor and use 10-Ω contact resistor between SRN pin and battery charging sensing resistor. The leakage current on SRP and SRN are matched. |
| SRP | 20 | PWR | Charge current sense amplifier positive input. Connect a 0.1-μF filter cap cross battery charging sensing resistor and use 10-Ω contact resistor between SRP pin and battery charging sensing resistor. The leakage current on SRP and SRN are matched. |
| SW1 | 32 | PWR | Buck mode switching node. Connect to the source of the buck half bridge high side n-channel MOSFET. |
| SW2 | 23 | PWR | Boost mode switching node. Connect to the source of the boost half bridge high side n-channel MOSFET. |
| VBUS | 1 | PWR | Charger input voltage. An input low pass filter of 1 Ω and 0.47 µF (minimum) is recommended. |
| VDDA | 7 | PWR | Internal reference bias pin. Connect a 10-Ω resistor from REGN to VDDA and a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VDDA to power ground. |
| VSYS | 22 | PWR | Charger system voltage sensing. The system voltage regulation maximum limit is programmed in ChargeVoltage register plus 150 mV and regulation minimum limit is programmed in VSYS_MIN register. |
| Thermal pad | – | – | Exposed pad beneath the IC. Always solder thermal pad to the board, and have vias on the thermal pad plane connecting to power ground planes. It serves as a thermal pad to dissipate the heat. |