SLUSEE3 July 2021 BQ51013B-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Details of a Qi Wireless Power System and BQ51013B-Q1 Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 9.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 9.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 9.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 9.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 9.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1/EN2 Control
- 9.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 9.3.8 Status Outputs
- 9.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 9.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 9.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 9.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 9.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 9.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations for the TS/CTRL Pin
- 9.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 9.3.16 WPC v1.2 Compliance – Foreign Object Detection
- 9.3.17 Receiver Coil Load-Line Analysis
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
BQ51013B-Q1 Wireless Power Receiver Used as a Power
Supply
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.2.1 Using The BQ51013B-Q1 as a Wireless Power Supply: (See Figure 1-1 )
- 10.2.1.2.2 Series and Parallel Resonant Capacitor Selection
- 10.2.1.2.3 Recommended RX Coils
- 10.2.1.2.4 COMM, CLAMP, and BOOT Capacitors
- 10.2.1.2.5 Control Pins and CHG
- 10.2.1.2.6 Current Limit and FOD
- 10.2.1.2.7 RECT and OUT Capacitance
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 10.2.2 Dual Power Path: Wireless Power and DC Input
- 10.2.3 Wireless and Direct Charging of a Li-Ion Battery at 800 mA
- 10.2.1
BQ51013B-Q1 Wireless Power Receiver Used as a Power
Supply
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|20
Orderable Information
8.6 Typical Characteristics
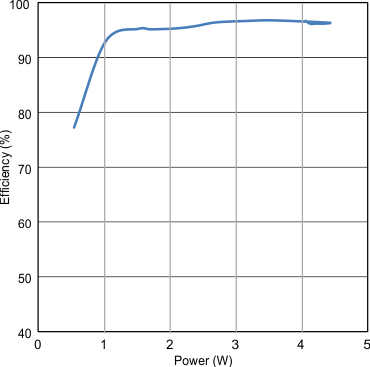
| Input: RX AC power | Output: RX RECT power | |
| Efficiency: Output Power / Input Power | ||
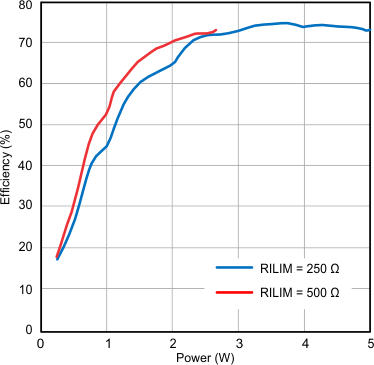
| Input: TX DC power | Output: RX RECT power | |
| Plot: Output Power / Input Power | ||
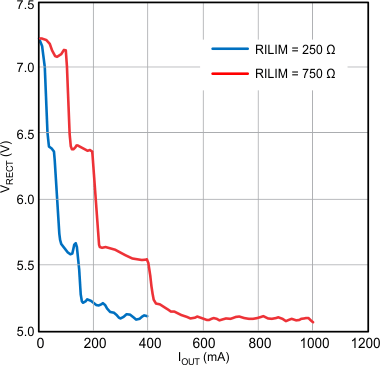
| RILIM = 250 Ω and 750 Ω |
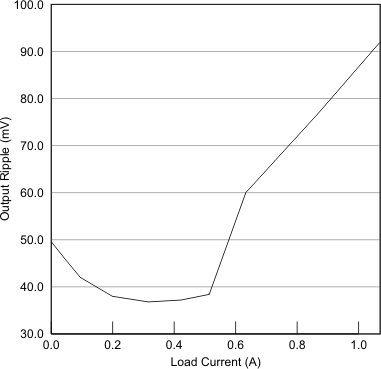
| COUT = 1 µf | Without Communication | |
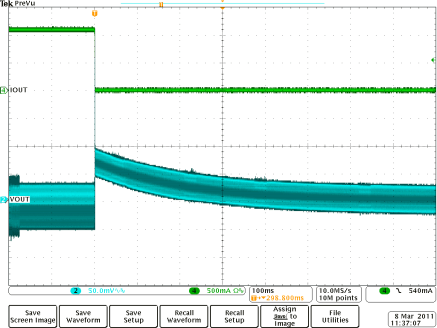 Figure 8-9 1-A
Instantaneous Load Dump (2)
Figure 8-9 1-A
Instantaneous Load Dump (2)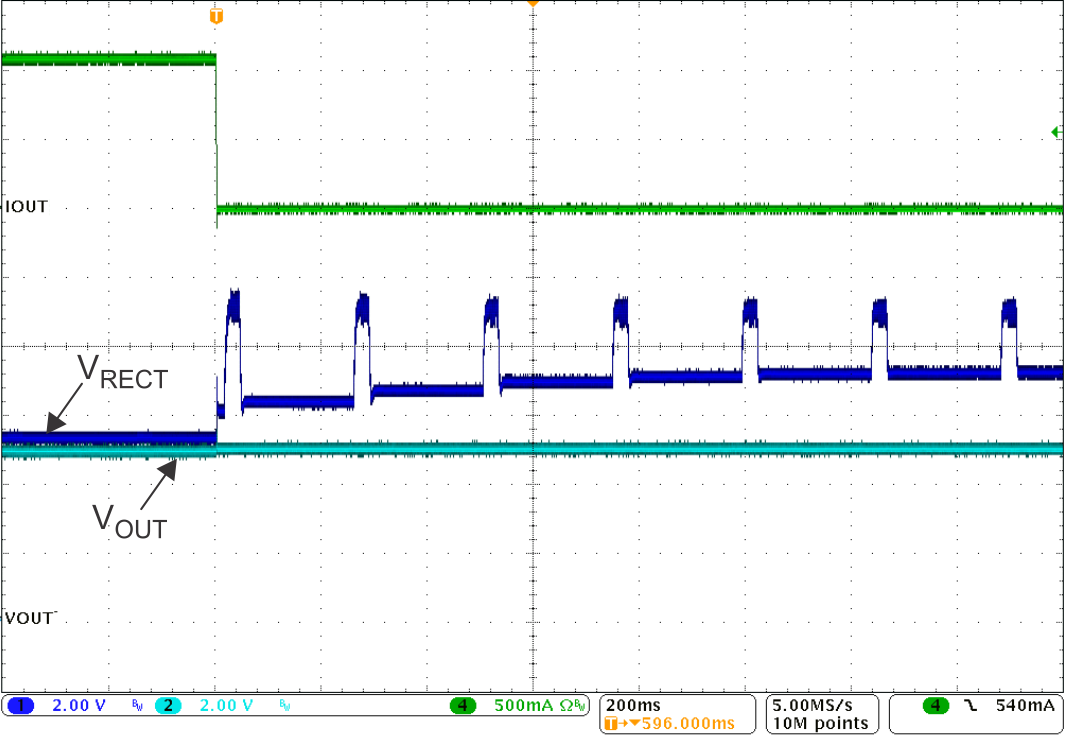 Figure 8-11 1-A
Load Dump Full System Response
Figure 8-11 1-A
Load Dump Full System Response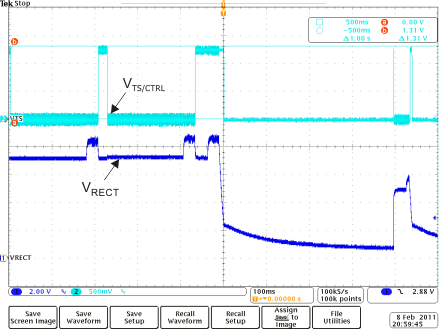 Figure 8-13 TS
Fault
Figure 8-13 TS
Fault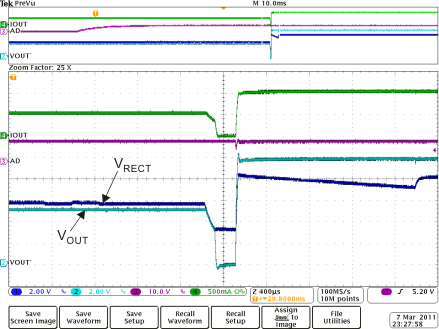 Figure 8-15 Adapter Insertion (VAD = 10 V) Illustrating Break-Before-Make
Operation
Figure 8-15 Adapter Insertion (VAD = 10 V) Illustrating Break-Before-Make
Operation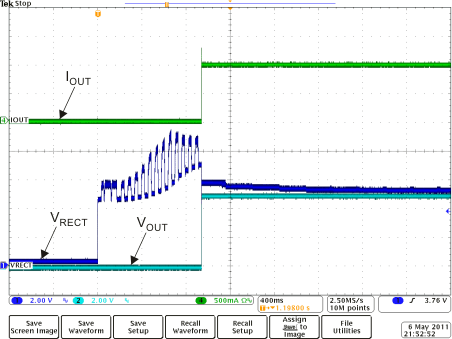 Figure 8-17 BQ51013B-Q1 Typical Start-Up With a 1-A System Load
Figure 8-17 BQ51013B-Q1 Typical Start-Up With a 1-A System Load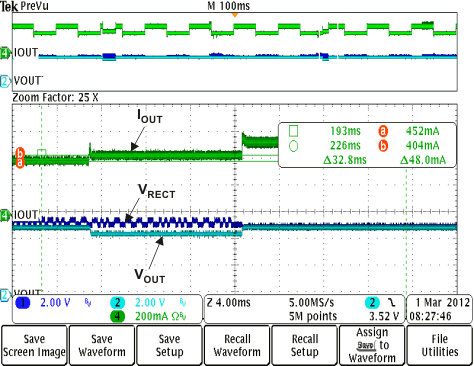 Figure 8-19 Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the Current Limit is
IOUT + 50 mA (IOUT-DC > 300 mA)
Figure 8-19 Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the Current Limit is
IOUT + 50 mA (IOUT-DC > 300 mA)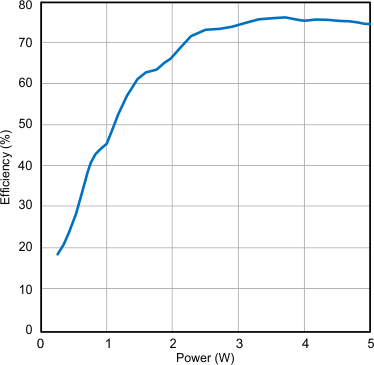
| Input: TX DC power | Output: RX RECT power | |
| Efficiency: Output Power / Input Power | ||
| RILIM = 250 Ω | ||
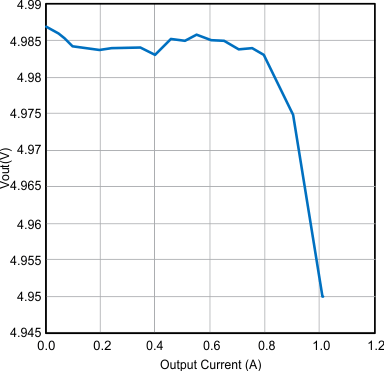
| Maximum Current = 1 A |
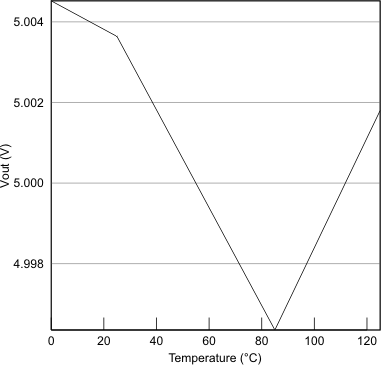 Figure 8-8 VOUT vs Temperature
Figure 8-8 VOUT vs Temperature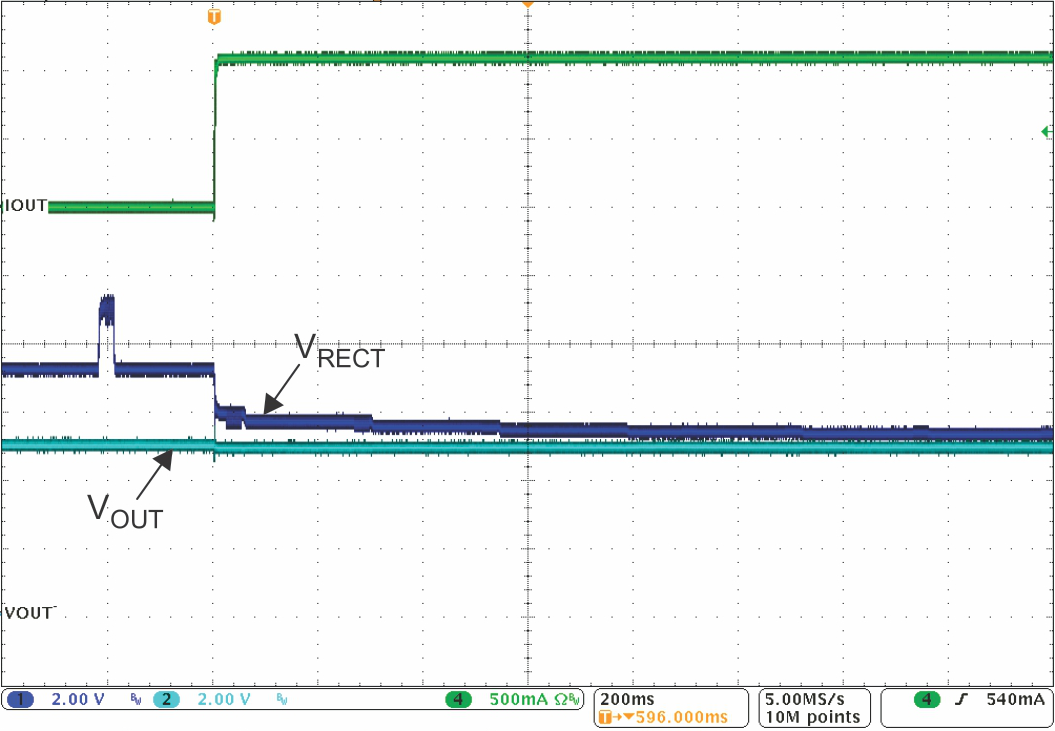 Figure 8-10 1-A
Load Step Full System Response
Figure 8-10 1-A
Load Step Full System Response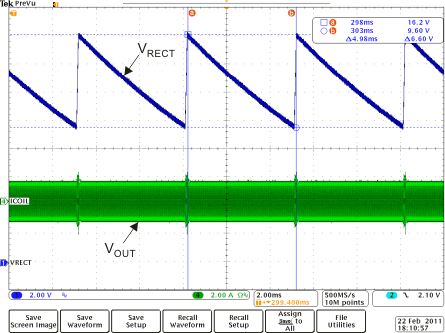 Figure 8-12 Rectifier Overvoltage Clamp (fop = 110 kHz)
Figure 8-12 Rectifier Overvoltage Clamp (fop = 110 kHz)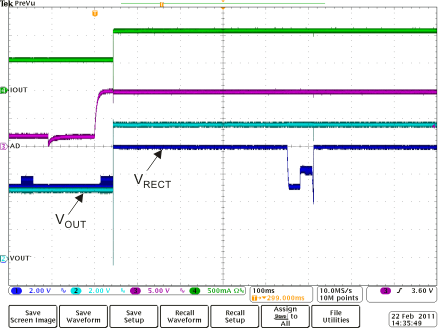 Figure 8-14 Adapter Insertion (VAD = 10 V)
Figure 8-14 Adapter Insertion (VAD = 10 V)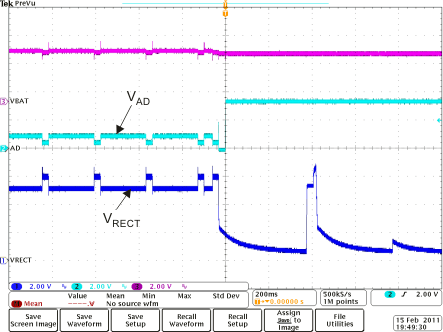 Figure 8-16 On-the-Go Enabled (VOTG = 3.5 V) (3)
Figure 8-16 On-the-Go Enabled (VOTG = 3.5 V) (3)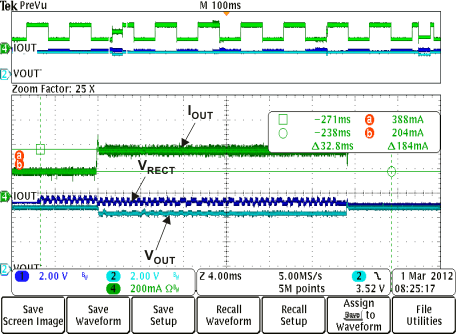 Figure 8-18 Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the 400-mA Current Limit is
Enabled (IOUT-DC < 300 mA)
Figure 8-18 Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the 400-mA Current Limit is
Enabled (IOUT-DC < 300 mA)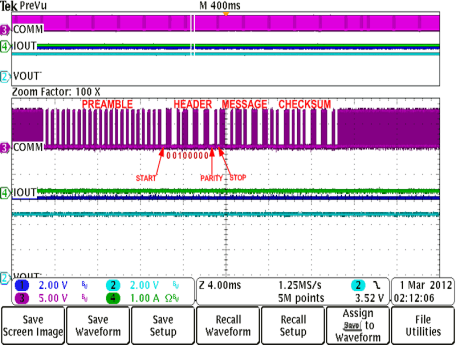 Figure 8-20 RX
Communication Packet Structure
Figure 8-20 RX
Communication Packet Structure- Efficiency measured from DC input to the transmitter to DC output of the receiver. The BQ500210EVM-689 TX was used for these measurements. Measurement subject to change if an alternate TX is used.
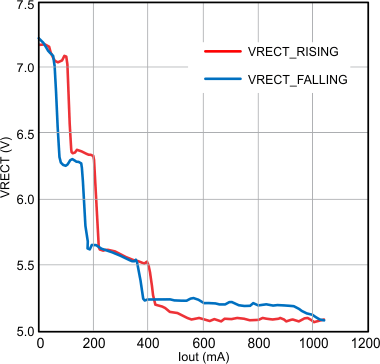
- Total droop experienced at the output is dependent on receiver coil design. The output impedance must be low enough at that particular operating frequency in order to not collapse the rectifier below 5 V.
- On-the-go mode is enabled by driving EN1 high. In this test, the external PMOS is connected between the output of the BQ51013B-Q1 device and the AD pin; therefore, any voltage source on the output is supplied to the AD pin.