SLUSF21 june 2023 BQ79616
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Power Supplies
- 8.3.2 Measurement System
- 8.3.3 Cell Balancing
- 8.3.4 Integrated Hardware Protectors
- 8.3.5 GPIO Configuration
- 8.3.6
Communication, OTP, Diagnostic Control
- 8.3.6.1
Communication
- 8.3.6.1.1 Serial Interface
- 8.3.6.1.2 Daisy Chain Interface
- 8.3.6.1.3 Start Communication
- 8.3.6.1.4 Communication Timeout
- 8.3.6.1.5 Communication Debug Mode
- 8.3.6.1.6 Multidrop Configuration
- 8.3.6.1.7 SPI Controller
- 8.3.6.1.8 SPI Loopback
- 8.3.6.2 Fault Handling
- 8.3.6.3 Nonvolatile Memory
- 8.3.6.4 Diagnostic Control/Status
- 8.3.6.1
Communication
- 8.3.7 Bus Bar Support
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 OTP Shadow Register Summary
- 8.5.2 Read/Write Register Summary
- 8.5.3 Read-Only Register Summary
- 8.5.4
Register Field Descriptions
- 8.5.4.1 Device Addressing Setup
- 8.5.4.2 Device ID and Scratch Pad
- 8.5.4.3
General Configuration and Control
- 8.5.4.3.1 DEV_CONF
- 8.5.4.3.2 ACTIVE_CELL
- 8.5.4.3.3 BBVC_POSN1
- 8.5.4.3.4 BBVC_POSN2
- 8.5.4.3.5 PWR_TRANSIT_CONF
- 8.5.4.3.6 COMM_TIMEOUT_CONF
- 8.5.4.3.7 TX_HOLD_OFF
- 8.5.4.3.8 STACK_RESPONSE
- 8.5.4.3.9 BBP_LOC
- 8.5.4.3.10 COMM_CTRL
- 8.5.4.3.11 CONTROL1
- 8.5.4.3.12 CONTROL2
- 8.5.4.3.13 CUST_CRC_HI
- 8.5.4.3.14 CUST_CRC_LO
- 8.5.4.3.15 CUST_CRC_RSLT_HI
- 8.5.4.3.16 CUST_CRC_RSLT_LO
- 8.5.4.4 Operation Status
- 8.5.4.5 ADC Configuration and Control
- 8.5.4.6
ADC Measurement Results
- 8.5.4.6.1 VCELL16_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.2 VCELL15_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.3 VCELL14_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.4 VCELL13_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.5 VCELL12_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.6 VCELL11_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.7 VCELL10_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.8 VCELL9_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.9 VCELL8_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.10 VCELL7_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.11 VCELL6_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.12 VCELL5_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.13 VCELL4_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.14 VCELL3_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.15 VCELL2_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.16 VCELL1_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.17 BUSBAR_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.18 TSREF_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.19 GPIO1_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.20 GPIO2_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.21 GPIO3_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.22 GPIO4_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.23 GPIO5_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.24 GPIO6_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.25 GPIO7_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.26 GPIO8_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.27 DIETEMP1_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.28 DIETEMP2_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.29 AUX_CELL_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.30 AUX_GPIO_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.31 AUX_BAT_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.32 AUX_REFL_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.33 AUX_VBG2_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.34 AUX_AVAO_REF_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.35 AUX_AVDD_REF_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.36 AUX_OV_DAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.37 AUX_UV_DAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.38 AUX_OT_OTCB_DAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.39 AUX_UT_DAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.40 AUX_VCBDONE_DAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.41 AUX_VCM_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.42 REFOVDAC_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.43 DIAG_MAIN_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.6.44 DIAG_AUX_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.7 Balancing Configuration, Control and Status
- 8.5.4.8 Protector Configuration and Control
- 8.5.4.9 GPIO Configuration
- 8.5.4.10 SPI Controller
- 8.5.4.11 Diagnostic Control
- 8.5.4.12 Fault Configuration and Reset
- 8.5.4.13
Fault Status
- 8.5.4.13.1 FAULT_SUMMARY
- 8.5.4.13.2 FAULT_COMM1
- 8.5.4.13.3 FAULT_COMM2
- 8.5.4.13.4 FAULT_COMM3
- 8.5.4.13.5 FAULT_OTP
- 8.5.4.13.6 FAULT_SYS
- 8.5.4.13.7 FAULT_PROT1
- 8.5.4.13.8 FAULT_PROT2
- 8.5.4.13.9 FAULT_OV1
- 8.5.4.13.10 FAULT_OV2
- 8.5.4.13.11 FAULT_UV1
- 8.5.4.13.12 FAULT_UV2
- 8.5.4.13.13 FAULT_OT
- 8.5.4.13.14 FAULT_UT
- 8.5.4.13.15 FAULT_COMP_GPIO
- 8.5.4.13.16 FAULT_COMP_VCCB1
- 8.5.4.13.17 FAULT_COMP_VCCB2
- 8.5.4.13.18 FAULT_COMP_VCOW1
- 8.5.4.13.19 FAULT_COMP_VCOW2
- 8.5.4.13.20 FAULT_COMP_CBOW1
- 8.5.4.13.21 FAULT_COMP_CBOW2
- 8.5.4.13.22 FAULT_COMP_CBFET1
- 8.5.4.13.23 FAULT_COMP_CBFET2
- 8.5.4.13.24 FAULT_COMP_MISC
- 8.5.4.13.25 FAULT_PWR1
- 8.5.4.13.26 FAULT_PWR2
- 8.5.4.13.27 FAULT_PWR3
- 8.5.4.14
Debug Control and Status
- 8.5.4.14.1 DEBUG_CTRL_UNLOCK
- 8.5.4.14.2 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL1
- 8.5.4.14.3 DEBUG_COMM_CTRL2
- 8.5.4.14.4 DEBUG_COMM_STAT
- 8.5.4.14.5 DEBUG_UART_RC
- 8.5.4.14.6 DEBUG_UART_RR_TR
- 8.5.4.14.7 DEBUG_COMH_BIT
- 8.5.4.14.8 DEBUG_COMH_RC
- 8.5.4.14.9 DEBUG_COMH_RR_TR
- 8.5.4.14.10 DEBUG_COML_BIT
- 8.5.4.14.11 DEBUG_COML_RC
- 8.5.4.14.12 DEBUG_COML_RR_TR
- 8.5.4.14.13 DEBUG_UART_DISCARD
- 8.5.4.14.14 DEBUG_COMH_DISCARD
- 8.5.4.14.15 DEBUG_COML_DISCARD
- 8.5.4.14.16 DEBUG_UART_VALID_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.14.17 DEBUG_COMH_VALID_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.14.18 DEBUG_COML_VALID_HI/LO
- 8.5.4.14.19 DEBUG_OTP_SEC_BLK
- 8.5.4.14.20 DEBUG_OTP_DED_BLK
- 8.5.4.15
OTP Programming Control and Status
- 8.5.4.15.1 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK1D
- 8.5.4.15.2 OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2A through OTP_PROG_UNLOCK2D
- 8.5.4.15.3 OTP_PROG_CTRL
- 8.5.4.15.4 OTP_ECC_TEST
- 8.5.4.15.5 OTP_ECC_DATAIN1 through OTP_ECC_DATAIN9
- 8.5.4.15.6 OTP_ECC_DATAOUT1 through OTP_ECC_DATAOUT9
- 8.5.4.15.7 OTP_PROG_STAT
- 8.5.4.15.8 OTP_CUST1_STAT
- 8.5.4.15.9 OTP_CUST2_STAT
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Base Device Application Circuit
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curve
- 9.2.2 Daisy Device Application Circuit
- 9.2.1
Base Device Application Circuit
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PAP|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PAP|64
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.2 BAT and External NPN
| Related Pins | Components | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAT | Filter resistor | 30 Ω | Single-ended RC filter, recommended values must be used for hot-plug performance. |
| Filter capacitor | 10 nF/100 V Can use lower voltage rating based on module size | ||
| NPNB | NPN (Q1) | Collector–emitter breakdown voltage 80 V to 100 V, but can use
lower rating based on module size Power rating ≥ 1 W Gain > 80 at the expected load current Current handling >100 mA | The external NPN is used to form a
preregulation
circuit to provide a 6-V (typical) input to the LDOIN pin. The voltage rating of the NPN can be optimized by the following equation: NPN voltage rating = Max VModule – Min VLDOIN + Margin Where: Max VModule = maximum module voltage with fully charged cells Min VLDOIN = the minimum spec of the VLDOIN parameter Margin = system transient voltage + design margin per application requirement |
| Resistor on external NPN collector (RNPN) | Various based on module voltage | The resistor has a couple purposes: (a) For an RC filter for the NPN preregulation circuit (b) Share the thermal dissipation with the NPN | |
| Capacitor on external NPN collector | 0.22 μF/100 V Can use lower voltage rating based on module size | The capacitor forms the RC filter for the NPN
preregulation
circuit The capacitor rating is based on peak voltage spike seen on the module. For smaller module size, < 100-V rated capacitor can be used. System designer selects the optimized voltage-rated capacitor per their system tolerance and requirements. |
To reduce the power rating needed for the external NPN (Q1), system designers can put power resistors on the NPN collector to create an IR drop from the module voltage (VModule). Figure 9-3 shows the current paths to power the BQ79616 device.
Typical ISTARTUP current, that is, inrush startup current when the device enters from SHUTDOWN to ACTIVE, is 20 mA for TI recommended components. This current is the sum of IBAT + ILDOIN, and is dependent on PCB board components and layout. Designers must characterize this on their end.
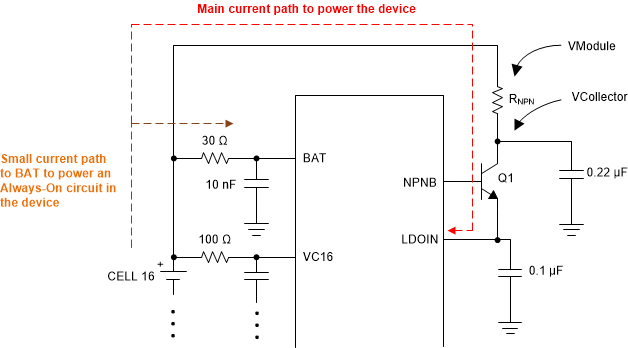 Figure 9-3 Power Consumption
Paths
Figure 9-3 Power Consumption
PathsTo ensure there is sufficient headroom to maintain 6 V (typical) regulated voltage on LDOIN pin, system designer ensures VCollector has ≥ 8 V at any time with the assumption of about 2-V drop across the NPN.
Therefore, maximum allowable RNPN value = ((Min VModule) – (VCollector)) / (Max peak current)
Where:
Min VModule: based on module size and minimum cell voltage per application
VCollector: 8 V with the assumption of about 2-V drop across NPN
Max peak current: highest operation current, which is the active current with all functions turned on. Note that different communication isolation components (for example, capacitor isolation versus transformer, or the type of transformer) contribute different loading to the total power consumption.
Powering the device separately from the top of the battery stack:
The device is designed to be powered by the battery stack. If there is a need to power the device from a separate source such as in Figure 9-4, the following relationship between the voltage on the BAT pin and the highest VC pin voltage (with respected to ground) is BAT voltage ≥ (0.5 × highest VC voltage) + 2.
For example, if the device is connected to a 14S module with max cell voltage of 4.2 V/cell, the highest VC pin is VC14, and the highest VC14 voltage is (4.2 V × 14) = 58.8 V. If the BAT pin is powered separately, BAT voltage must be ≥ 31.4 V.
Similarly, if BBP/N channel is connected above the highest cell stack, the BBP pin will has the highest voltage (with respected to ground) than the VC pins. In this scenario, VBAT ≥ [(VBBP-2.5) × 0.84] + 4.5. The requirement applies when BAT is power separately and it is to ensure proper operation of the internal level shifter. Fail to maintain the voltage relationship will increase the ADC measurement error on the VC and BB channels.
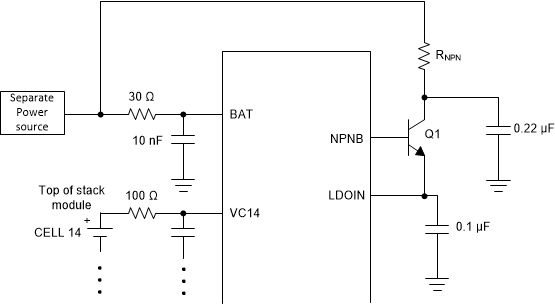 Figure 9-4 Separate Power Source to
BAT
Figure 9-4 Separate Power Source to
BAT