SBOS571C August 2011 – August 2018 BUF20800-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DCP|38
Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, VS = 18 V, VSD = 5 V, VREFH = 17 V, VREFL = 1 V, RL = 1.5 kΩ connected to ground, and CL = 200 pF, unless otherwise noted.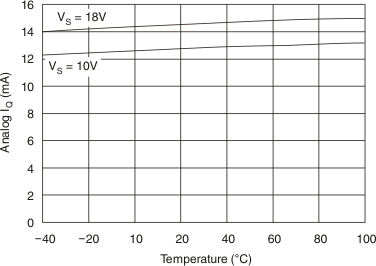
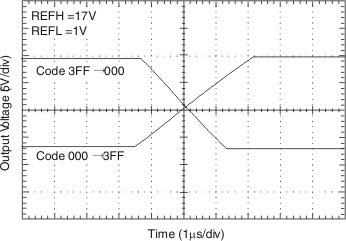 Figure 3. Full−scale Output Swing
Figure 3. Full−scale Output Swing 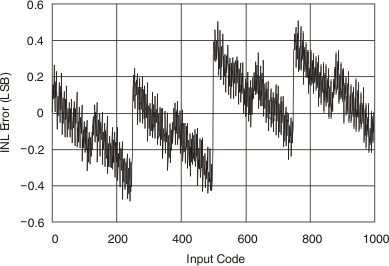 Figure 5. Integral Nonlinearity Error vs Input Code
Figure 5. Integral Nonlinearity Error vs Input Code 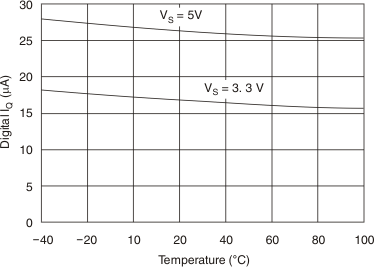 Figure 2. Digital Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 2. Digital Supply Current vs Temperature 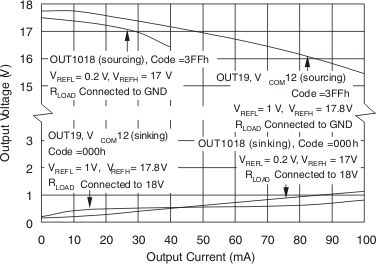 Figure 4. Output Voltage vs Output Current
Figure 4. Output Voltage vs Output Current 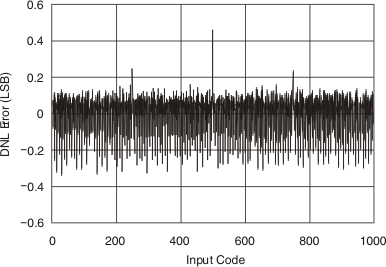 Figure 6. Differential Nonlinearity Error vs Input Code
Figure 6. Differential Nonlinearity Error vs Input Code