SWRS225E February 2019 – December 2024 CC3135MOD
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Functional Block Diagrams
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Current Consumption Summary: 2.4GHz RF Band
- 7.5 Current Consumption Summary: 5GHz RF Band
- 7.6 TX Power Control for 2.4 GHz Band
- 7.7 TX Power Control for 5GHz Band
- 7.8 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics for DIO Pins
- 7.10 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 7.11 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 7.12 BLE and WLAN Coexistence Requirements
- 7.13 Reset Requirement
- 7.14 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for MOB Package
- 7.15 Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.16 External Interfaces
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Environmental Requirements and SMT Specifications
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- MOB|63
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
10.6 Soldering and Reflow Condition
- Heating method: Conventional convection or IR convection
- Temperature measurement: Thermocouple d = 0.1mm to 0.2mm CA (K) or CC (T) at soldering portion or equivalent method
- Solder paste composition: SAC305
- Allowable reflow soldering times: 2 times based on the reflow soldering profile (see Figure 10-1)
- Temperature profile: Reflow soldering will be done according to the temperature profile (see
Figure 10-1) - Peak temp: 260°C
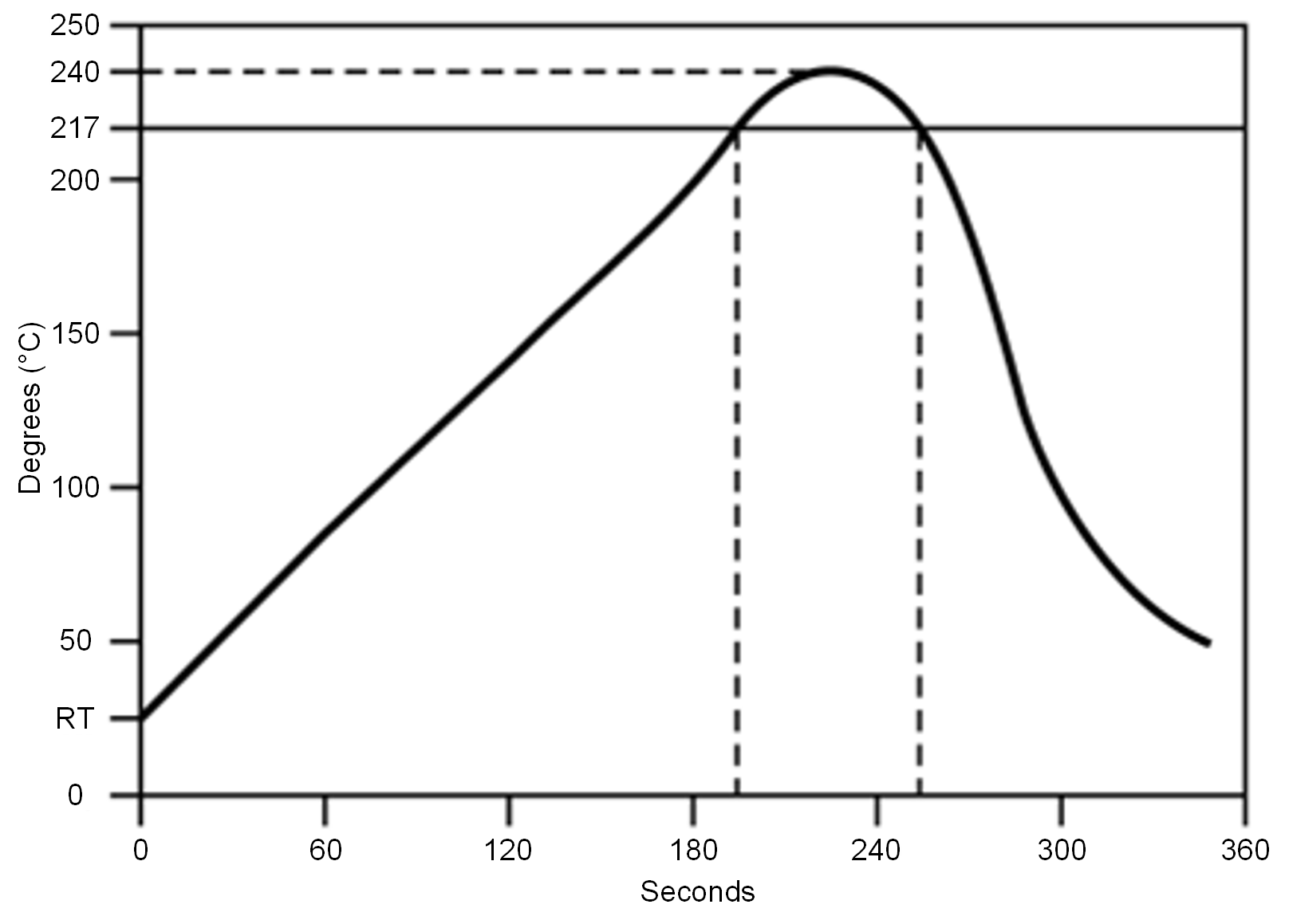 Figure 10-1 Temperature Profile for Evaluation of Solder Heat Resistance of a Component (at Solder Joint)
Figure 10-1 Temperature Profile for Evaluation of Solder Heat Resistance of a Component (at Solder Joint)Table 10-1 Temperature Profile
| Profile Elements | Convection or IR(1) |
|---|---|
| Peak temperature range | 235 to 240°C typical (260°C maximum) |
| Pre-heat / soaking (150 to 200°C) | 60 to 120 seconds |
| Time above melting point | 60 to 90 seconds |
| Time with 5°C to peak | 30 seconds maximum |
| Ramp up | < 3°C / second |
| Ramp down | < -6°C / second |
(1) For details, refer to the solder paste manufacturer's recommendation.
Note:
TI does not recommend using conformal coating or similar material on the SimpleLink™ module. This coating can lead to localized stress on the WCSP solder connections inside the module and impact the device's reliability. Use caution during the module assembly process to the final PCB to avoid the presence of foreign material inside the module.