SWRS215E April 2019 – December 2024 CC3235S , CC3235SF
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Functional Block Diagrams
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Current Consumption Summary (CC3235S)
- 7.6 Current Consumption Summary (CC3235SF)
- 7.7 TX Power Control for 2.4 GHz Band
- 7.8 TX Power Control for 5 GHz
- 7.9 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics for GPIO Pins
- 7.11 Electrical Characteristics for Pin Internal Pullup and Pulldown
- 7.12 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 7.13 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 7.14 WLAN Transmitter Out-of-Band Emissions
- 7.15 BLE/2.4 GHz Radio Coexistence and WLAN Coexistence Requirements
- 7.16 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for RGK Package
- 7.17
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.17.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 7.17.2 Device Reset
- 7.17.3 Reset Timing
- 7.17.4 Wakeup From HIBERNATE Mode
- 7.17.5 Clock Specifications
- 7.17.6 Peripherals Timing
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGK|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGK|64
Orderable Information
9.1.1 BLE/2.4GHz Radio Coexistence
The CC3235x device is designed to support BLE/2.4GHz radio coexistence. Because WLAN is inherently more tolerant to time-domain disturbances, the coexistence mechanism gives priority to the Bluetooth® low energy entity over the WLAN. Bluetooth® low energy operates in the 2.4GHz band, therefore the coexistence mechanism does not affect the 5GHz band. The CC3235x device can operate normally on the 5GHz band, while the Bluetooth® low energy works on the 2.4GHz band without mutual interference.
The following coexistence modes can be configured by the user:
- Off mode or intrinsic mode
- No BLE/2.4GHz radio coexistence, or no synchronization between WLAN and Bluetooth® low energy—in case Bluetooth® low energy exists in this mode, collisions can randomly occur.
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM, Single Antenna)
- 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band (see Figure 9-1)
In this mode, the two entities share the antenna through an RF switch using two GPIOs (one input and one output from the WLAN perspective).
- 5GHz Wi-Fi band (see Figure 9-2)
In this mode, the WLAN operates on the 5GHz band and Bluetooth® low energy operates on the 2.4GHz band. A 2.4- or 5GHz diplexer is required for sharing the single antenna.
- 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band (see Figure 9-1)
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM, Dual Antenna)
- 2.4GHz Wi-Fi Band (see Figure 9-3)
In this mode, the two entities have separate antennas. No RF switch is required and only a single GPIO (one input from the WLAN perspective).
- 5GHz Wi-Fi band (see Figure 9-4)
In this mode, the WLAN operates on the 5GHz band and Bluetooth® low energy operates on the 2.4GHz band. No diplexer is required for the dual-antenna solution.
- 2.4GHz Wi-Fi Band (see Figure 9-3)
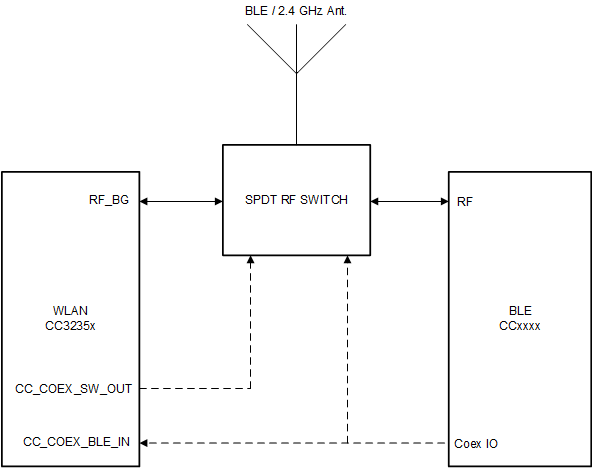 Figure 9-1 2.4GHz, Single-Antenna Coexistence Mode Block Diagram
Figure 9-1 2.4GHz, Single-Antenna Coexistence Mode Block Diagram
Figure 9-2 shows the single antenna implementation of a complete Bluetooth® low energy and WLAN coexistence network with the WLAN operating on either a 2.4- or a 5GHz band. The SOP lines control the 5GHz switch. The Coex switch is controlled by a GPIO signal from the BLE device and a GPIO signal from the CC3235x device.
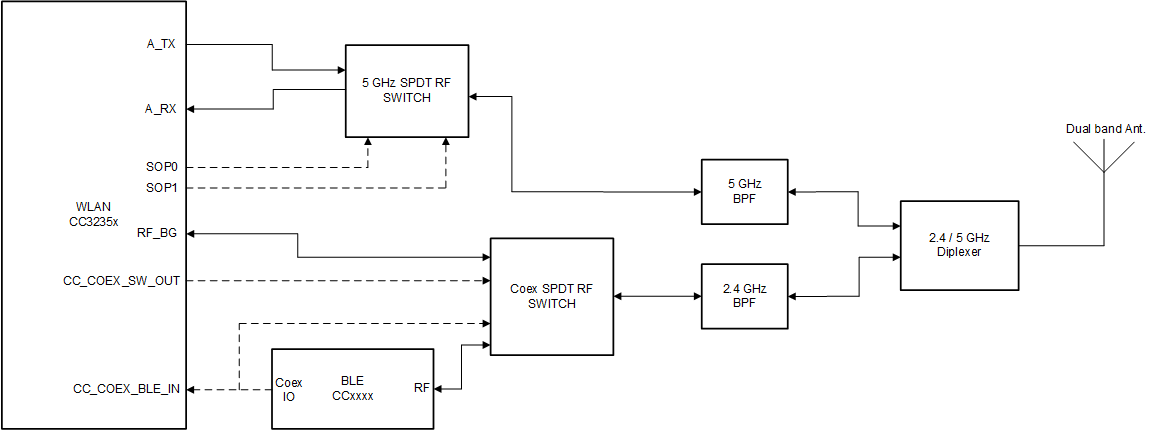 Figure 9-2 Single Antenna Coexistence Solution with 5GHz Wi-Fi
Figure 9-2 Single Antenna Coexistence Solution with 5GHz Wi-FiFigure 9-3 shows the dual antenna implementation of a complete Bluetooth® low energy and WLAN coexistence network with the WLAN operating on either a 2.4- or a 5GHz band. Note in this implementation no Coex switch is required and only a single GPIO from the BLE device to the CC3235x device is required.
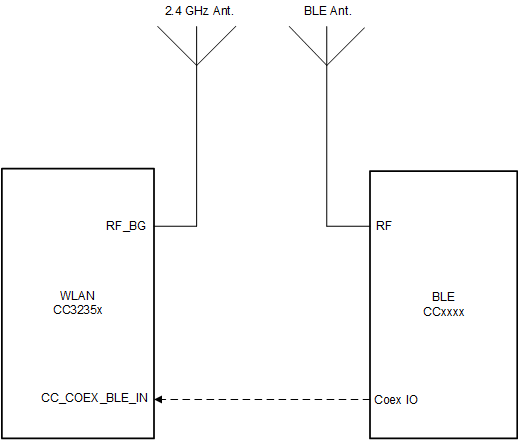 Figure 9-3 Dual-Antenna Coexistence Mode Block Diagram
Figure 9-3 Dual-Antenna Coexistence Mode Block DiagramFigure 9-4 shows the dual antenna implementation of a complete Bluetooth® low energy and WLAN coexistence network with the WLAN operating on either a 2.4- or a 5GHz band. In this case, the 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi share an antenna and the BLE has its own dedicated antenna. The SOP lines control the 5GHz switch. Note that in this implementation, no Coex switch is required and only a single GPIO from the BLE device to the CC3235x device is required.
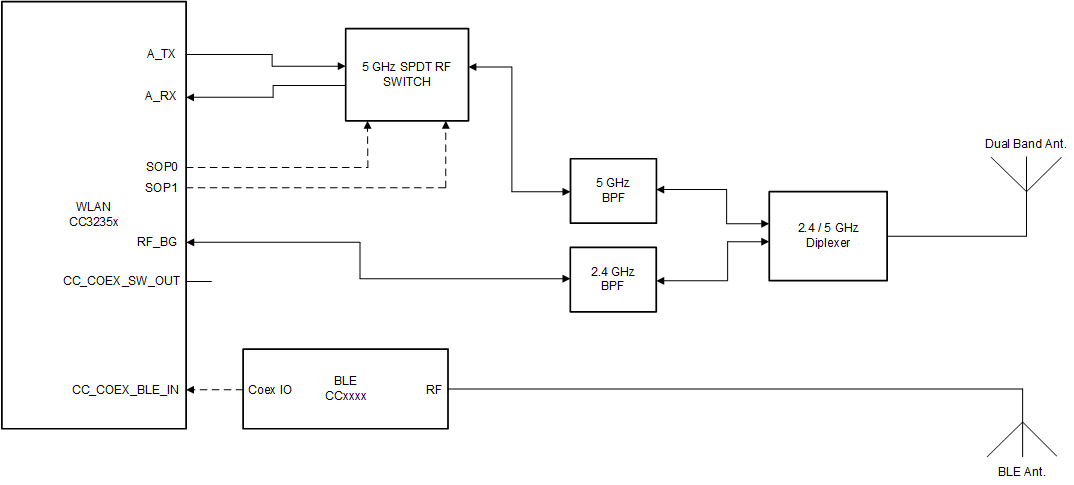 Figure 9-4 Dual Antenna Coexistence Solution with 5GHz Wi-Fi
Figure 9-4 Dual Antenna Coexistence Solution with 5GHz Wi-Fi