SNAS833A November 2021 – May 2022 CDCDB400
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
Figure 6-1 shows both the phase noise of the source as well as the output of the DUT (CDCDB400). It can be seen from the phase noise plot that the DUT has a very low phase noise profile with total jitter of 81.5 fs, rms. If we rms subtract the clock reference noise, the additive jitter of CDCDB400 under typical conditions would be lower than 81.5 fs, rms.
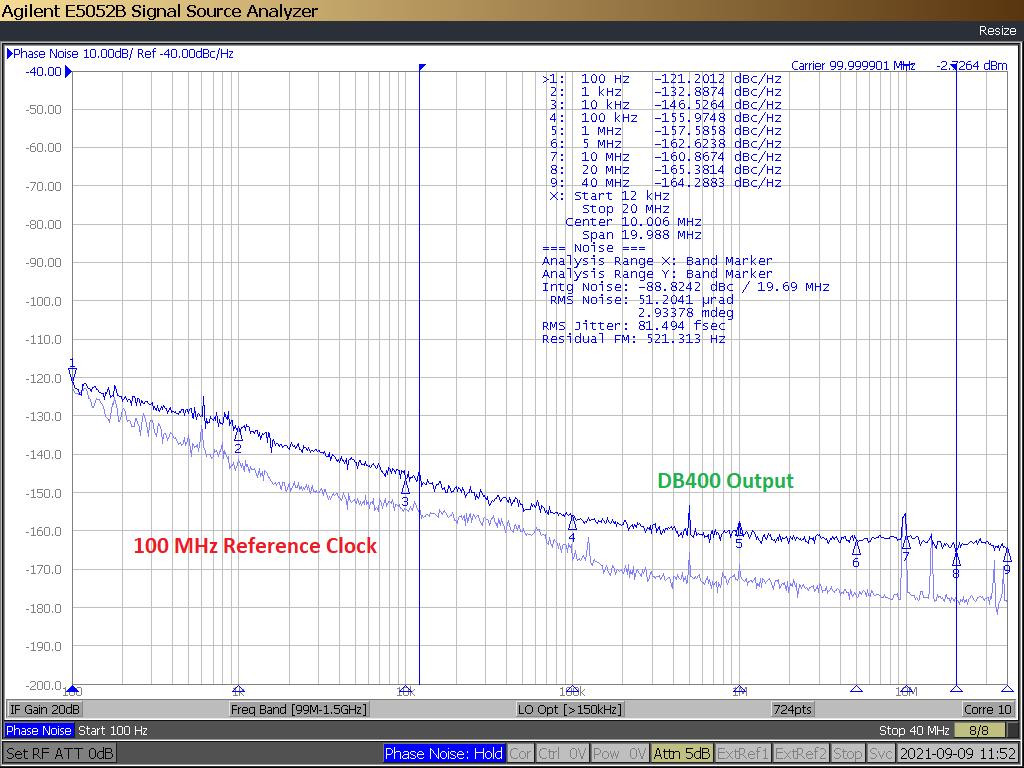 Figure 6-1 CDCDB400
Clock Out (CK0:4) Phase Noise
Figure 6-1 CDCDB400
Clock Out (CK0:4) Phase Noise