SCAS897A July 2010 – October 2016 CDCLVD1213
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
7 Parameter Measurement Information
 Figure 3. LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 3. LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test
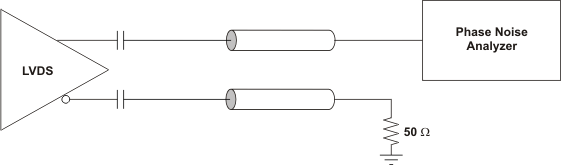 Figure 4. LVDS Output AC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 4. LVDS Output AC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 5. Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
Figure 5. Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
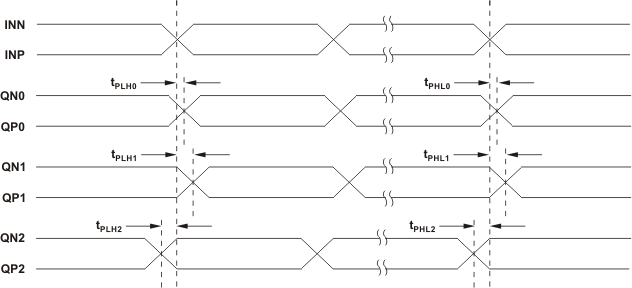
1. Output skew is calculated as the greater of the following: As the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPLHn or the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn (n = 0, 1, 2).
2. Part-to-part skew is calculated as the greater of the following: As the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPLHn or the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn across multiple devices (n = 0, 1, 2).
Figure 6. Output and Part-to-Part Skew
 Figure 7. Output Overshoot and Undershoot
Figure 7. Output Overshoot and Undershoot
 Figure 8. Output AC Common Mode
Figure 8. Output AC Common Mode