SNAS682 March 2016 CDCM6208V2G
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematics
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Description (continued)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information, Airflow = 0 LFM
- 8.5 Thermal Information, Airflow = 150 LFM
- 8.6 Thermal Information, Airflow = 250 LFM
- 8.7 Thermal Information, Airflow = 500 LFM
- 8.8 Single Ended Input Characteristics
- 8.9 Single Ended Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.10 Differential Input Characteristics (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 8.11 Crystal Input Characteristics (SEC_REF)
- 8.12 Single Ended Output Characteristics (STATUS1, STATUS0, SDO, SDA)
- 8.13 PLL Characteristics
- 8.14 LVCMOS Output Characteristics
- 8.15 LVPECL (High-Swing CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.16 CML Output Characteristics
- 8.17 LVDS (Low-Power CML) Output Characteristics
- 8.18 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 8.19 Output Skew and Sync to Output Propagation Delay Characteristics
- 8.20 Device Individual Block Current Consumption
- 8.21 Worst Case Current Consumption
- 8.22 I2C TIMING
- 8.23 SPI Timing Requirements
- 8.24 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
- 10Detailed Description
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Applications
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 11.2.1.1 Device Block-level Description
- 11.2.1.2 Device Configuration Control
- 11.2.1.3 Configuring the RESETN Pin
- 11.2.1.4 Preventing False Output Frequencies in SPI/I2C Mode at Startup:
- 11.2.1.5 Power Down
- 11.2.1.6 Device Power Up Timing:
- 11.2.1.7 Input Mux and Smart Input Mux
- 11.2.1.8 Universal INPUT Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 11.2.1.9 VCO Calibration
- 11.2.1.10 Reference Divider (R)
- 11.2.1.11 Input Divider (M)
- 11.2.1.12 Feedback Divider (N)
- 11.2.1.13 Prescaler Dividers (PS_A, PS_B)
- 11.2.1.14 Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
- 11.2.1.15 Charge Pump (CP)
- 11.2.1.16
Programmable Loop Filter
- 11.2.1.16.1 Loop Filter Component Selection
- 11.2.1.16.2 Device Output Signaling
- 11.2.1.16.3 Integer Output Divider (IO)
- 11.2.1.16.4 Fractional Output Divider (FOD)
- 11.2.1.16.5 Output Synchronization
- 11.2.1.16.6 Output MUX on Y4 and Y5
- 11.2.1.16.7 Staggered CLK Output Powerup for Power Sequencing of a DSP
- 11.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 11.2.3 Application Performance Plots
- 11.2.1
Design Requirements
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
12 Power Supply Recommendations
12.1 Power Rail Sequencing, Power Supply Ramp Rate, and Mixing Supply Domains
Mixing Supplies: The CDCM6208V2G incorporates a very flexible power supply architecture. Each building block has its own power supply domain, and can be driven independently with 1.8 V, 2.5 V, or 3.3 V . This is especially of advantage to minimize total system cost by deploying multiple low-cost LDOs instead of one, more-expensive LDO. This also allows mixed IO supply voltages (e.g. one CMOS output with 1.8 V, another with 3.3 V) or interfacing to a SPI/I2C controller with 3.3 V supply while other blocks are driven from a lower supply voltage to minimize power consumption. The CDCM6208V2G current consumption is practically independent of the supply voltage, and therefore a lower supply voltage consumes lower device power. Also note that outputs Y3:0 if used for PECL swing will provide higher output swing if the according output domains are connected to 2.5 V or 3.3 V.
Power-on Reset: The CDCM6208V2G integrates a built-in POR circuit, that holds the device in powerdown until all input, digital, and PLL supplies have reached at least 1.06 V (min) to 1.24 V (max). After this power-on release, device internal counters start (see previous section on device power up timing) followed by device calibration. While the device digital circuit resets properly at this supply voltage level, the device is not ready to calibrate at such a low voltage. Therefore, for slow power up ramps, the counters expire before the supply voltage reaches the minimum voltage of 1.71 V. Hence for slow power-supply ramp rates, it is necessary to delay calibration further using the PDN input.
Slow power-up supply ramp: No particular power supply sequence is required for the CDCM6208V2G. However, it is necessary to ensure that device calibration occurs AFTER the DVDD supply as well as the VDD_PLL1, VDD_PLL2, VDD_PRI, and VDD_SEC supply are all operational, and the voltage on each supply is higher than 1.45. This is best realized by delaying the PDN low-to-high transition. The PDN input incorporates a 50 kΩ resistor to DVDD. Assuming the DVDD supply ramp has a fixed time relationship to the slowest of all PLL and input power supplies, a capacitor from PDN to GND can delay the PDN input signal sufficiently to toggle PDN low-to-high AFTER all other supplies are stable. However, if the DVDD supply ramps much sooner than the PLL or input supplies, additional means are necessary to prevent PDN from toggling too early. A premature toggling of PDN would possibly result in failed PLL calibration, which can only be corrected by re-calibrating the PLL by either toggling PDN or RESET high-low-high.
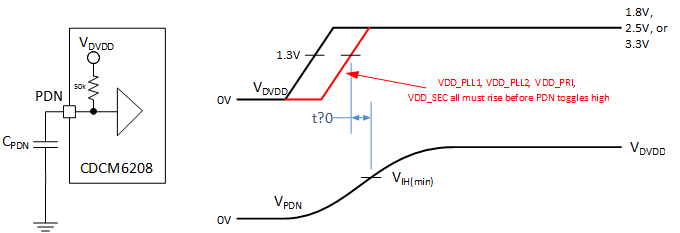 Figure 57. PDN Delay When Using Slow Ramping Power Supplies (Supply Ramp > 50 ms)
Figure 57. PDN Delay When Using Slow Ramping Power Supplies (Supply Ramp > 50 ms)
12.1.1 Fast Power-up Supply Ramp
If the supply ramp time for DVDD, VDD_PLL1, VDD_PLL2, VDD_PRI, and VDD_SEC are faster than 50 ms from 0 V to 1.8 V, no special provisions are necessary on PDN; the PDN pin can be left floating. Even an external capacitor to GND can be omitted in this circumstance, as the device delays calibration sufficiently by internal means.
12.1.2 Delaying VDD_Yx_Yy to Protect DSP IOs
DSPs and other highly integrated processors sometimes do not permit any clock signal to be present until the DSP power supply for the corresponding IO is also present. The CDCM6208V2G allows to either sequence output clock signals by writing to the corresponding output enable bit through SPI/I2C, or alternatively it is possible to connect the DSP IO supply and the CDCM6208V2G output supply together, in which case the CDCM6208V2G output will not turn on until the DSP supply is also valid. This second implementation avoids SPI/I2C programming.