SLPS661 September 2017 CSD87503Q3E
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Features
- 2Applications
- 3Description
- 4Revision History
- 5 Specifications
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DTD|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Specifications
5.1 Electrical Characteristics
TA = 25°C (unless otherwise stated)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STATIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| BVDSS | Drain-to-source voltage(1) | VGS = 0 V, ID = 250 μA | 30 | V | |||
| IDSS | Drain-to-source leakage current(1) | VGS = 0 V, VDS = 24 V | 1 | μA | |||
| IGSS | Gate-to-source leakage current(1) | VDS = 0 V, VGS = 20 V | 100 | nA | |||
| VGS(th) | Gate-to-source threshold voltage(1) | VDS = VGS, ID = 250 μA | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.1 | V | |
| RDD(on) | Drain-to-drain on-resistance | VGS = 4.5 V, ID1D2 = 6 A | 17.3 | 21.9 | mΩ | ||
| VGS = 10 V, ID1D2 = 6 A | 13.5 | 16.9 | |||||
| gfs | Transconductance | VDS = 3 V, ID1D2 = 6 A | 24 | S | |||
| DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| CISS | Input capacitance | VGS = 0 V, VD1D2 = 15 V, ƒ = 1 MHz | 782 | 1020 | pF | ||
| COSS | Output capacitance | 157 | 204 | pF | |||
| CRSS | Reverse transfer capacitance | 149 | 194 | pF | |||
| Rg | Series gate resistance(1) | 1.5 | 3.0 | Ω | |||
| Qg | Gate charge total (4.5 V) | VD1D2 = 15 V, ID1D2 = 6 A | 13.4 | 17.4 | nC | ||
| Gate charge total (10 V) | 32.9 | 42.8 | |||||
| Qgd | Gate charge gate-to-drain | 5.8 | nC | ||||
| Qgs | Gate charge gate-to-source | 4.8 | nC | ||||
| Qg(th) | Gate charge at Vth | 1.0 | nC | ||||
| QOSS | Output charge | VD1D2 = 15 V, VGS = 0 V | 4.3 | nC | |||
| td(on) | Turnon delay time | VD1D2 = 15 V, VGS = 10 V, ID1D2 = 6 A, RG = 0 Ω |
10 | ns | |||
| tr | Rise time | 40 | ns | ||||
| td(off) | Turnoff delay time | 25 | ns | ||||
| tf | Fall time | 8 | ns | ||||
| DIODE CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VSD | Diode forward voltage(1) | ID = 0.5 A, VGS = 0 V | 0.75 | 0.95 | V | ||
| Qrr | Reverse recovery charge(1) | VDS = 15 V, IF = 6 A, di/dt = 300 A/μs | 9.2 | nC | |||
| trr | Reverse recovery time(1) | 14 | ns | ||||
(1) Parameter measured on both MOSFETs individually. Table values are for a single FET.
5.2 Thermal Information
TA = 25°C (unless otherwise stated)| THERMAL METRIC | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RθJC | Junction-to-case thermal resistance(1) | 8 | °C/W | ||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance(1)(2) | 60 | °C/W | ||
(1) RθJC is determined with the device mounted on a 1-in2 (6.45-cm2), 2-oz (0.071-mm) thick Cu pad on a 1.5-in × 1.5-in (3.81-cm × 3.81-cm), 0.06-in (1.52-mm) thick FR4 PCB. RθJC is specified by design, whereas RθJA is determined by the user’s board design.
(2) Device mounted on FR4 material with 1-in2 (6.45-cm2), 2-oz (0.071-mm) thick Cu.
 |
Max RθJA = 60°C/W when mounted on 1 in2 (6.45 cm2) of 2-oz (0.071-mm) thick Cu. |
 |
Max RθJA = 185°C/W when mounted on a minimum pad area of 2-oz (0.071-mm) thick Cu. |
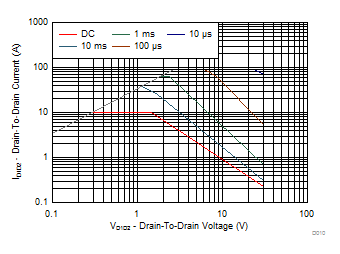
5.3 Typical MOSFET Characteristics
TA = 25°C (unless otherwise stated)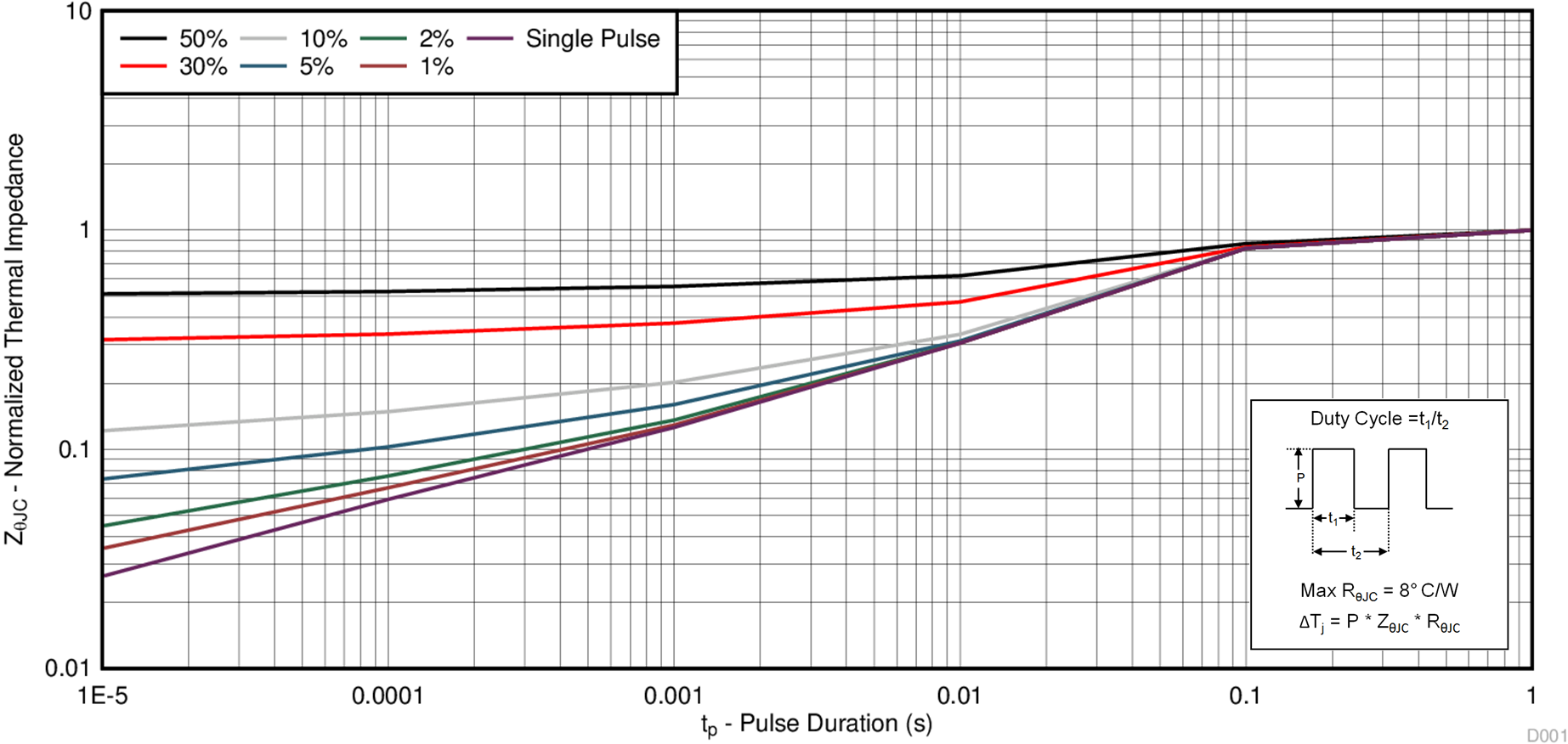

| Note: Measurement taken with both gates tied together | ||
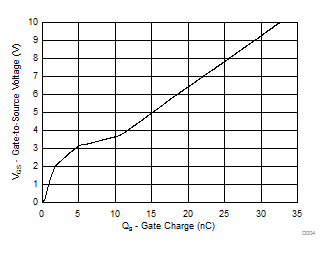
| ID1D2 = 6 A | VD1D2 = 15 V |

| ID = 250 µA |

| ID1D2 = 6 A | VD1D2 = 15 V | ||
| Note: Measurement taken with both gates tied together | |||
| Single pulse, max RθJC = 8°C/W | ||


| VD1D2 = 5 V | ||



