SLAS748G March 2011 – January 2024 DAC3482
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics – DC Specifications
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics – Digital Specifications
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics – AC Specifications
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics - Phase-Locked Loop Specifications
- 5.9 Timing Requirements - Digital Specifications
- 5.10 Switching Characteristics – AC Specifications
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Serial Interface
- 6.3.2 Data Interface
- 6.3.3 Input FIFO
- 6.3.4 FIFO Modes of Operation
- 6.3.5 Clocking Modes
- 6.3.6 FIR Filters
- 6.3.7 Complex Signal Mixer
- 6.3.8 Quadrature Modulation Correction (QMC)
- 6.3.9 Temperature Sensor
- 6.3.10 Data Pattern Checker
- 6.3.11 Parity Check Test
- 6.3.12 DAC3482 Alarm Monitoring
- 6.3.13 LVPECL Inputs
- 6.3.14 LVDS Inputs
- 6.3.15 Unused LVDS Port Termination
- 6.3.16 CMOS Digital Inputs
- 6.3.17 Reference Operation
- 6.3.18 DAC Transfer Function
- 6.3.19 Analog Current Outputs
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Map
- 6.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 6.6.1.1 Register Name: config0 – Address: 0x00, Default: 0x049C
- 6.6.1.2 Register Name: config1 – Address: 0x01, Default: 0x050E
- 6.6.1.3 Register Name: config2 – Address: 0x02, Default: 0x7000
- 6.6.1.4 Register Name: config3 – Address: 0x03, Default: 0xF000
- 6.6.1.5 Register Name: config4 – Address: 0x04, Default: No RESET Value (WRITE TO CLEAR)
- 6.6.1.6 Register Name: config5 – Address: 0x05, Default: Setup and Power-Up Conditions Dependent (WRITE TO CLEAR)
- 6.6.1.7 Register Name: config6 – Address: 0x06, Default: No RESET Value (READ ONLY)
- 6.6.1.8 Register Name: config7 – Address: 0x07, Default: 0xFFFF
- 6.6.1.9 Register Name: config8 – Address: 0x08, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.10 Register Name: config9 – Address: 0x09, Default: 0x8000
- 6.6.1.11 Register Name: config10 – Address: 0x0A, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.12 Register Name: config11 – Address: 0x0B, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.13 Register Name: config12 – Address: 0x0C, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.14 Register Name: config13 – Address: 0x0D, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.15 Register Name: config14 – Address: 0x0E, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.16 Register Name: config15 – Address: 0x0F, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.17 Register Name: config16 – Address: 0x10, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.18 Register Name: config17 – Address: 0x11, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.19 Register Name: config18 – Address: 0x12, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.20 Register Name: config19 – Address: 0x13, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.21 Register Name: config20 – Address: 0x14, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.22 Register Name: config21 – Address: 0x15, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.23 Register name: config22 – Address: 0x16, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.24 Register Name: config23 – Address: 0x17, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.25 Register Name: config24 – Address: 0x18, Default: NA
- 6.6.1.26 Register Name: config25 – Address: 0x19, Default: 0x0440
- 6.6.1.27 Register Name: config26 – Address: 0x1A, Default: 0x0020
- 6.6.1.28 Register Name: config27 – Address: 0x1B, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.29 Register Name: config28 – Address: 0x1C, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.30 Register Name: config29 – Address: 0x1D, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.31 Register Name: config30 – Address: 0x1E, Default: 0x1111
- 6.6.1.32 Register Name: config31 – Address: 0x1F, Default: 0x1140
- 6.6.1.33 Register Name: config32 – Address: 0x20, Default: 0x2400
- 6.6.1.34 Register Name: config33 – Address: 0x21, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.35 Register Name: config34 – Address: 0x22, Default: 0x1B1B
- 6.6.1.36 Register Name: config35 – Address: 0x23, Default: 0xFFFF
- 6.6.1.37 Register Name: config36 – Address: 0x24, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.38 Register Name: config37 – Address: 0x25, Default: 0x7A7A
- 6.6.1.39 Register Name: config38 – Address: 0x26, Default: 0xB6B6
- 6.6.1.40 Register Name: config39 – Address: 0x27, Default: 0xEAEA
- 6.6.1.41 Register Name: config40 – Address: 0x28, Default: 0x4545
- 6.6.1.42 Register Name: config41 – Address: 0x29, Default: 0x1A1A
- 6.6.1.43 Register Name: config42 – Address: 0x2A, Default: 0x1616
- 6.6.1.44 Register Name: config43 – Address: 0x2B, Default: 0xAAAA
- 6.6.1.45 Register Name: config44 – Address: 0x2C, Default: 0xC6C6
- 6.6.1.46 Register Name: config45 – Address: 0x2D, Default: 0x0004
- 6.6.1.47 Register Name: config46 – Address: 0x2E, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.48 Register Name: config47 – Address: 0x2F, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.49 Register Name: config48 – Address: 0x30, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.50 Register Name: version– Address: 0x7F, Default: 0x540C (READ ONLY)
- 6.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RKD|88
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
 Figure 4-1 RKD Package, 88-Pin WQFN-MR with Exposed Thermal Pad (Top View)
Figure 4-1 RKD Package, 88-Pin WQFN-MR with Exposed Thermal Pad (Top View)Table 4-1 RKD Package Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| AVDD | A36, A37, A38, A40, A41, A42, B31 | I | Analog supply voltage (3.3V) | |
| ALARM | B29 | O | CMOS output for ALARM condition. The ALARM output functionality is defined through the config7 register. Default polarity is active high, but can be changed to active low via config0 alarm_out_pol control bit. | |
| BIASJ | A33 | O | Full-scale output current bias. For 30-mA full-scale output current, connect 1.28kΩ to ground. Change the full-scale output current through coarse_dac(3:0) in config3, bit<15:12>. | |
| CLKVDD | A4 | I | Internal clock buffer supply voltage. (1.2 V) It is recommended to isolate this supply from DIGVDD and DACVDD. | |
| D[15..0]P | A7, A8, B9, B10, A12, A13, A14, A15, B17, B18, B19, B20, A23, A24, B23, B24 | I | LVDS positive input data bits 0 through 15. Internal 100Ω termination resistor. Data format relative to DATACLKP/N clock is Double Data Rate (DDR) and can be transferred in either byte-wide or word-wide mode. In byte-wide mode the unused pins can be left unconnected. | |
| D15P is most significant data bit (MSB) in word-wide mode D7P is most significant data bit (MSB) in byte-wide mode D0P is least significant data bit (LSB) | ||||
| The order of the bus can be reversed via config2 revbus bit. | ||||
| D[15..0]N | B7, B8, A10, A11, B11, B12, B13, B14, A19, A20, A21, A22, B21, B22, A26, A27 | I | LVDS negative input data bits 0 through 15. (See D[15:0]P description above.) | |
| DACCLKP | A3 | I | Positive external LVPECL clock input for DAC core with a self-bias. | |
| DACCLKN | B3 | I | Complementary external LVPECL clock input for DAC core. (see the DACCLKP description above.) | |
| DACVDD | A35, A39, A43 | I | DAC core supply voltage. (1.2V). It is recommended to isolate this supply from CLKVDD and DIGVDD. | |
| DATACLKP | A16 | I | LVDS positive input data clock. Internal 100-Ω termination resistor. Input data D[15:0]P/N is latched on both edges of DATACLKP/N (Double Data Rate). | |
| DATACLKN | B15 | I | LVDS negative input data clock. (See DATACLKP description above.) | |
| DIGVDD | A6, A9, A25, A28 | I | Digital supply voltage. (1.2V). It is recommended to isolate this supply from CLKVDD and DACVDD. | |
| EXTIO | A34 | I/O | Used as external reference input when internal reference is disabled through config27 extref_ena = 1b. Used as internal reference output when config27 extref_ena = 0b (default). Requires a 0.1μF decoupling capacitor to AGND when used as reference output. | |
| FRAMEP | B16 | I | LVDS frame indicator positive input. Internal 100-Ω termination resistor. The main functions of this input are to reset the FIFO or to be used as a syncing source. These two functions are captured with the rising edge of DATACLKP/N. The signal captured by the falling edge of DATACLKP/N can be used as a block parity bit. The FRAMEP/N signal should be edge-aligned with D[15:0]P/N. | |
| FRAMEN | A18 | I | LVDS frame indicator negative input. (See the FRAMEP description above.) | |
| GND | C1, C2, C3, C4, B32, B33, B38, B39, Thermal Pad | I | These pins are ground for all supplies. | |
| IOUTIP | B36 | O | I-Channel DAC current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTIN | B37 | O | I-Channel DAC complementary current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTQP | B35 | O | Q-Channel DAC current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTQN | B34 | O | Q-Channel DAC complementary current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOVDD | B6, A17, B25 | I | Supply voltage for all digital I/O. (3.3V) | |
| LPF | A1 | I/O | PLL loop filter connection. If not using the clock multiplying PLL, the LPF pin can be left unconnected. | |
| OSTRP | A2 | I | LVPECL output strobe positive input. This positive/negative pair is captured with the rising edge of DACCLKP/N. It is used to sync the divided-down clocks and FIFO output pointer in Dual Sync Sources Mode. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| OSTRN | B2 | I | LVPECL output strobe negative input. (See the OSTRP description) | |
| PARITYP | B26 | I | Optional LVDS positive input parity bit. The PARITYP/N LVDS pair has an internal 100Ω termination resistor. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| PARITYN | A29 | I | Optional LVDS negative input parity bit. | |
| PLLAVDD | B1 | I | PLL analog supply voltage. (3.3V) | |
| SCLK | A31 | I | Serial interface clock. Internal pull-down. | |
| SDENB | B28 | I | Active low serial data enable, always an input to the DAC3482. Internal pull-up. | |
| SDIO | A30 | I/O | Serial interface data. Bi-directional in 3-pin mode (default) and uni-directional in 4-pin mode. Internal pull-down. | |
| SDO | B27 | O | Uni-directional serial interface data in 4-pin mode. The SDO pin is tri-stated in 3-pin interface mode (default). | |
| SLEEP | B40 | I | Active high asynchronous hardware power-down input. Internal pull-down. If SLEEP pin is set to logic HIGH before and during device power-up and initialization, the fuse_sleep bit in register 0x1B, bit 11 must be written after register 0x23 during device initialization register setup. | |
| SYNCP | A5 | I | Optional LVDS SYNC positive input. The SYNCP/N LVDS pair has an internal 100Ω termination resistor. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| SYNCN | B5 | I | Optional LVDS SYNC negative input. | |
| RESETB | B30 | I | Active low input for chip RESET, which resets all the programming registers to their default state. Internal pull-up. | |
| TXENABLE | A32 | I | Transmit enable active high input. Internal pull-down. To enable analog output data transmission, set sif_txenable in register config3 to 1b or pull CMOS TXENABLE pin to high. To disable analog output, set sif_txenable to 0b and pull CMOS TXENABLE pin to low. The digital logic section is forced to all 0, and any input data is ignored. | |
| TESTMODE | A44 | I | This pin is used for factory testing. Internal pull-down. Leave unconnected for normal operation. | |
| VFUSE | B4 | I | Digital supply voltage. This supply pin is also used for factory fuse programming. Connect to DACVDD for normal operation. | |
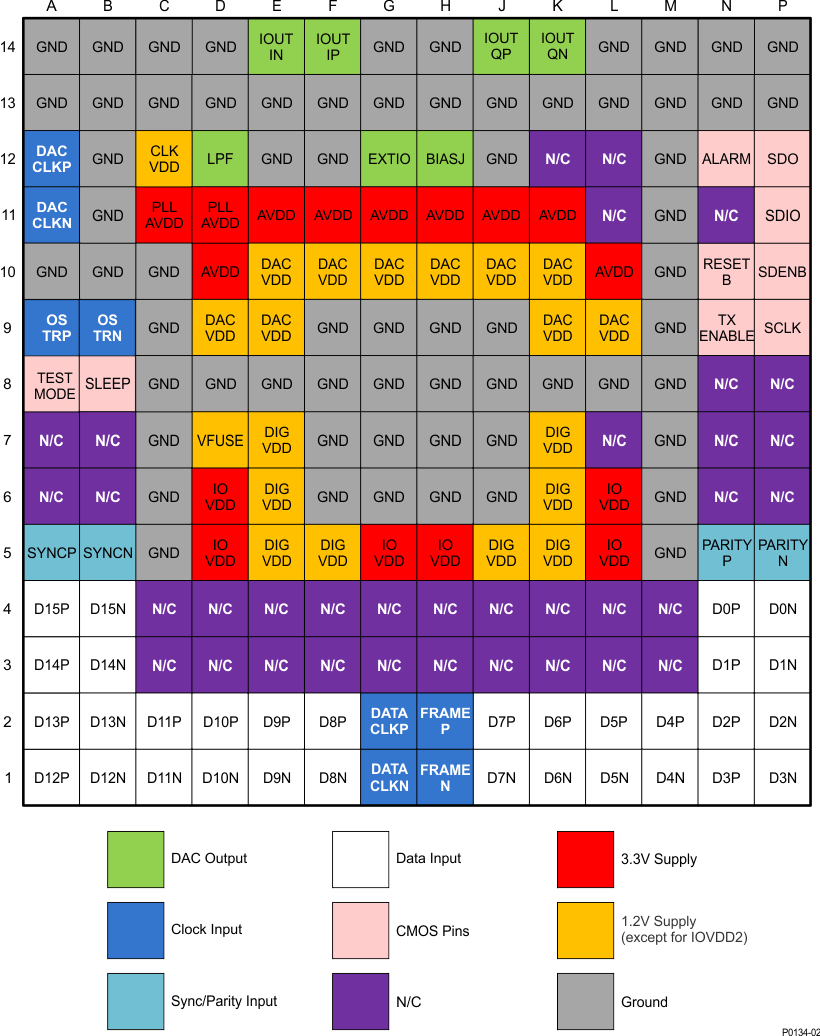 Figure 4-2 ZAY Package, 196-Ball NFBGA (Top View)
Figure 4-2 ZAY Package, 196-Ball NFBGA (Top View)Table 4-2 ZAY Package Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| AVDD | D10, E11, F11, G11, H11, J11, K11, L10 | I | Analog supply voltage (3.3V) | |
| ALARM | N12 | O | CMOS output for ALARM condition. The ALARM output functionality is defined through the config7 register. Default polarity is active low, but can be changed to active high via config0 alarm_out_pol control bit. | |
| BIASJ | H12 | O | Full-scale output current bias. For 30mA full-scale output current, connect 1.28kΩ to ground. Change the full-scale output current through coarse_dac(3:0) in config3, bit<15:12>. | |
| CLKVDD | C12 | I | Internal clock buffer supply voltage. (1.2V) It is recommended to isolate this supply from DIGVDD and DACVDD. | |
| D[15..0]P | N4, N3, N2, N1, M2, L2, K2, J2, F2, E2, D2, C2, A1, A2, A3, A4 | I | LVDS positive input data bits 0 through 15. Internal 100Ω termination resistor. Data format relative to DATACLKP/N clock is Double Data Rate (DDR). | |
| D15P is most significant data bit (MSB) D0P is least significant data bit (LSB) | ||||
| The order of the bus can be reversed via config2 revbus bit. | ||||
| D[15..0]N | P4, P3, P2, P1, M1, L1, K1, J1, F1, E1, D1, C1, B1, B2, B3, B4 | I | LVDS negative input data bits 0 through 15. (See D[15:0]P description above.) | |
| DACCLKP | A12 | I | Positive external LVPECL clock input for DAC core with a self-bias. | |
| DACCLKN | A11 | I | Complementary external LVPECL clock input for DAC core. (see the DACCLKP description above.) | |
| DACVDD | D9, E9, E10, F10, G10, H10, J10, K9, K10, L9 | I | DAC core supply voltage. (1.2V). It is recommended to isolate this supply from CLKVDD and DIGVDD. | |
| DATACLKP | G2 | I | LVDS positive input data clock. Internal 100Ω termination resistor. Input data D[15:0]P/N is latched on both edges of DATACLKP/N (Double Data Rate). | |
| DATACLKN | G1 | I | LVDS negative input data clock. (See DATACLKP description above.) | |
| DIGVDD | E5, E6, E7, F5, J5, K5, K6, K7 | I | Digital supply voltage. (1.2V). It is recommended to isolate this supply from CLKVDD and DACVDD. | |
| EXTIO | G12 | I/O | Used as external reference input when internal reference is disabled through config27 extref_ena = 1b. Used as internal reference output when config27 extref_ena = 0b (default). Requires a 0.1-μF decoupling capacitor to AGND when used as reference output. | |
| FRAMEP | H2 | I | LVDS frame indicator positive input. Internal 100-Ω termination resistor. The main functions of this input are to reset the FIFO pointer or to be used as a syncing source. These two functions are captured with the rising edge of DATACLKP/N. The signal captured by the falling edge of DATACLKP/N can be used as a block parity bit. The FRAMEP/N signal should be edge-aligned with D[15:0]P/N. Additionally it is used to indicate the beginning of the frame. | |
| FRAMEN | H1 | I | LVDS frame indicator negative input. (See the FRAMEP description above.) | |
| GND | A10, A13, A14, B10, B11, B12, B13, B14, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10, C13, C14, D8, D13, D14, E8, E12, E13, F6, F7, F8, F9, F12, F13, G6, G7, G8, G9, G13, G14, H6, H7, H8, H9, H13, H14, J6, J7, J8, J9, J12, J13, K8, K13, L8, L13, L14, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, N13, N14, P13, P14 | I | These pins are ground for all supplies. | |
| IOUTIP | F14 | O | I-Channel DAC current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTIN | E14 | O | I-Channel DAC complementary current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTQP | J14 | O | Q-Channel DAC current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOUTQN | K14 | O | Q-Channel DAC complementary current output. Connect directly to ground if unused. | |
| IOVDD | D5, D6, G5, H5, L5, L6 | I | Supply voltage for all digital I/O. (3.3V) | |
| LPF | D12 | I | PLL loop filter connection. If not using the clock multiplying PLL, the LPF pin can be left unconnected. | |
| OSTRP | A9 | I | LVPECL output strobe positive input. This positive/negative pair is captured with the rising edge of DACCLKP/N. It is used for multiple DAC synchronization. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| OSTRN | B9 | I | LVPECL output strobe negative input. (See the OSTRP description above.) | |
| PARITYP | N5 | I | Optional LVDS positive input parity bit. The PARITYP/N LVDS pair has an internal 100-Ω termination resistor. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| PARITYN | P5 | I | Optional LVDS negative input parity bit. | |
| PLLAVDD | C11, D11 | I | PLL analog supply voltage. (3.3V) | |
| SCLK | P9 | I | Serial interface clock. Internal pull-down. | |
| SDENB | P10 | I | Active low serial data enable, always an input to the DAC3482. Internal pull-up. | |
| SDIO | P11 | I/O | Serial interface data. Bi-directional in 3-pin mode (default) and 4-pin mode. Internal pull-down. | |
| SDO | P12 | O | Uni-directional serial interface data in 4-pin mode. The SDO pin is three-stated in 3-pin interface mode (default). | |
| SLEEP | B8 | I | Active high asynchronous hardware power-down input. Internal pull-down. If SLEEP pin is set to logic HIGH before and during device power-up and initialization, the fuse_sleep bit in register 0x1B, bit 11 must be written after register 0x23 during device initialization register setup. | |
| SYNCP | A5 | I | Optional LVDS SYNC positive input. The SYNCP/N LVDS pair has an internal 100-Ω termination resistor. If unused it can be left unconnected. | |
| SYNCN | B5 | I | LVDS SYNC negative input. | |
| RESETB | N10 | I | Active low input for chip RESET, which resets all the programming registers to their default state. Internal pull-up. | |
| TXENABLE | N9 | I | Transmit enable active high input. Internal pull-down. To enable analog output data transmission, set sif_txenable in register config3 to 1b or pull CMOS TXENABLE pin to high. To disable analog output, set sif_txenable to 0b and pull CMOS TXENABLE pin to low. The DAC output is forced to midscale. | |
| TESTMODE | A8 | O | This pin is used for factory testing. Internal pull-down. Leave unconnected for normal operation. | |
| VFUSE | D7 | I | Digital supply voltage. This supply pin is also used for factory fuse programming. Connect to DACVDD for normal operation. | |