SLAS748G March 2011 – January 2024 DAC3482
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics – DC Specifications
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics – Digital Specifications
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics – AC Specifications
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics - Phase-Locked Loop Specifications
- 5.9 Timing Requirements - Digital Specifications
- 5.10 Switching Characteristics – AC Specifications
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Serial Interface
- 6.3.2 Data Interface
- 6.3.3 Input FIFO
- 6.3.4 FIFO Modes of Operation
- 6.3.5 Clocking Modes
- 6.3.6 FIR Filters
- 6.3.7 Complex Signal Mixer
- 6.3.8 Quadrature Modulation Correction (QMC)
- 6.3.9 Temperature Sensor
- 6.3.10 Data Pattern Checker
- 6.3.11 Parity Check Test
- 6.3.12 DAC3482 Alarm Monitoring
- 6.3.13 LVPECL Inputs
- 6.3.14 LVDS Inputs
- 6.3.15 Unused LVDS Port Termination
- 6.3.16 CMOS Digital Inputs
- 6.3.17 Reference Operation
- 6.3.18 DAC Transfer Function
- 6.3.19 Analog Current Outputs
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Map
- 6.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 6.6.1.1 Register Name: config0 – Address: 0x00, Default: 0x049C
- 6.6.1.2 Register Name: config1 – Address: 0x01, Default: 0x050E
- 6.6.1.3 Register Name: config2 – Address: 0x02, Default: 0x7000
- 6.6.1.4 Register Name: config3 – Address: 0x03, Default: 0xF000
- 6.6.1.5 Register Name: config4 – Address: 0x04, Default: No RESET Value (WRITE TO CLEAR)
- 6.6.1.6 Register Name: config5 – Address: 0x05, Default: Setup and Power-Up Conditions Dependent (WRITE TO CLEAR)
- 6.6.1.7 Register Name: config6 – Address: 0x06, Default: No RESET Value (READ ONLY)
- 6.6.1.8 Register Name: config7 – Address: 0x07, Default: 0xFFFF
- 6.6.1.9 Register Name: config8 – Address: 0x08, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.10 Register Name: config9 – Address: 0x09, Default: 0x8000
- 6.6.1.11 Register Name: config10 – Address: 0x0A, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.12 Register Name: config11 – Address: 0x0B, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.13 Register Name: config12 – Address: 0x0C, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.14 Register Name: config13 – Address: 0x0D, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.15 Register Name: config14 – Address: 0x0E, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.16 Register Name: config15 – Address: 0x0F, Default: 0x0400
- 6.6.1.17 Register Name: config16 – Address: 0x10, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.18 Register Name: config17 – Address: 0x11, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.19 Register Name: config18 – Address: 0x12, Default: 0x0000 (CAUSES AUTO-SYNC)
- 6.6.1.20 Register Name: config19 – Address: 0x13, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.21 Register Name: config20 – Address: 0x14, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.22 Register Name: config21 – Address: 0x15, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.23 Register name: config22 – Address: 0x16, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.24 Register Name: config23 – Address: 0x17, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.25 Register Name: config24 – Address: 0x18, Default: NA
- 6.6.1.26 Register Name: config25 – Address: 0x19, Default: 0x0440
- 6.6.1.27 Register Name: config26 – Address: 0x1A, Default: 0x0020
- 6.6.1.28 Register Name: config27 – Address: 0x1B, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.29 Register Name: config28 – Address: 0x1C, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.30 Register Name: config29 – Address: 0x1D, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.31 Register Name: config30 – Address: 0x1E, Default: 0x1111
- 6.6.1.32 Register Name: config31 – Address: 0x1F, Default: 0x1140
- 6.6.1.33 Register Name: config32 – Address: 0x20, Default: 0x2400
- 6.6.1.34 Register Name: config33 – Address: 0x21, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.35 Register Name: config34 – Address: 0x22, Default: 0x1B1B
- 6.6.1.36 Register Name: config35 – Address: 0x23, Default: 0xFFFF
- 6.6.1.37 Register Name: config36 – Address: 0x24, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.38 Register Name: config37 – Address: 0x25, Default: 0x7A7A
- 6.6.1.39 Register Name: config38 – Address: 0x26, Default: 0xB6B6
- 6.6.1.40 Register Name: config39 – Address: 0x27, Default: 0xEAEA
- 6.6.1.41 Register Name: config40 – Address: 0x28, Default: 0x4545
- 6.6.1.42 Register Name: config41 – Address: 0x29, Default: 0x1A1A
- 6.6.1.43 Register Name: config42 – Address: 0x2A, Default: 0x1616
- 6.6.1.44 Register Name: config43 – Address: 0x2B, Default: 0xAAAA
- 6.6.1.45 Register Name: config44 – Address: 0x2C, Default: 0xC6C6
- 6.6.1.46 Register Name: config45 – Address: 0x2D, Default: 0x0004
- 6.6.1.47 Register Name: config46 – Address: 0x2E, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.48 Register Name: config47 – Address: 0x2F, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.49 Register Name: config48 – Address: 0x30, Default: 0x0000
- 6.6.1.50 Register Name: version– Address: 0x7F, Default: 0x540C (READ ONLY)
- 6.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RKD|88
Orderable Information
6.4.1.2 Multi-Device Synchronization: PLL Enabled with Dual Sync Sources Mode
The DAC3482 allows exact phase alignment between multiple devices even when operating with the internal PLL clock multiplier. In PLL clock mode, the PLL generates the DAC clock and an internal OSTR signal from the reference clock applied to the DACCLK inputs so there is no need to supply an additional LVPECL OSTR signal.
For this method to operate properly the SYNC signal should be set to reset the PLL N dividers to a known state by setting pll_ndivsync_ena in register config24 to 1b. The SYNC signal resets the PLL N dividers with a rising edge, and the timing relationship ts(SYNC_PLL) and th(SYNC_PLL) are relative to the reference clock presented on the DACCLK pin.
Both SYNC and DACCLK can be set as low frequency signals to greatly simplifying trace routing (SYNC can be just a pulse as a single rising edge is required, if using a periodic signal it is recommended to clear the pll_ndivsync_ena bit after resetting the PLL dividers). Besides the ts(SYNC_PLL) and th(SYNC_PLL) requirement between SYNC and DACCLK, there is no additional required timing relationship between the SYNC and FRAME signals or between DACCLK and DATACLK. The only restriction as in the PLL disabled case is that the DACCLK and SYNC signals are distributed from device to device with the lowest skew possible.
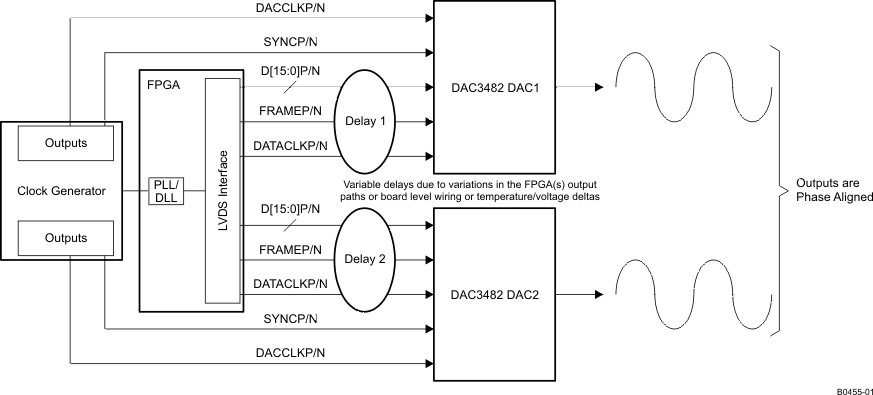 Figure 6-41 Synchronization System in Dual Sync Sources Mode with PLL Enabled
Figure 6-41 Synchronization System in Dual Sync Sources Mode with PLL EnabledThe following steps are required to make make sure the devices are fully synchronized. The procedure assumes all the DAC3482 devices have a DACCLK and OSTR signal and must be carried out on each device.
- Start-up the device as described in the power-up sequence. Set the DAC3482 in Dual Sync Sources mode and enable SYNC to reset the PLL dividers (set pll_ndivsync_ena in register config24 to 1b).
- Reset the PLL dividers with a rising edge on SYNC.
- Disable PLL dividers resetting.
- Sync the clock divider and FIFO pointers.
- Verify there are no FIFO alarms either through register config5 or through the ALARM pin.
- Disable clock divider sync by setting clkdiv_sync_ena to 0b in register config0.
After these steps all the DAC3482 outputs will be synchronized.