SLAS749E March 2011 – November 2015 DAC3484
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal InformationZAY package information to Thermal InformationTJ row from top of thermal table
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Digital Specifications
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements - Digital Specifications
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Serial Interface
- 7.3.2 Data Interface
- 7.3.3 Input FIFO
- 7.3.4 FIFO Modes of Operation
- 7.3.5 Clocking Modes
- 7.3.6 FIR Filters
- 7.3.7 Complex Signal Mixer
- 7.3.8 Quadrature Modulation Correction (QMC)
- 7.3.9 Temperature Sensor
- 7.3.10 Data Pattern Checker
- 7.3.11 Parity Check Test
- 7.3.12 DAC3484 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.3.13 LVPECL Inputs
- 7.3.14 LVDS Inputs
- 7.3.15 Unused LVDS Port Termination
- 7.3.16 CMOS Digital Inputs
- 7.3.17 Reference Operation
- 7.3.18 DAC Transfer Function
- 7.3.19 Analog Current Outputs
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RKD|88
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage range(2) | DACVDD, DIGVDD, CLKVDD | –0.5 | 1.5 | V |
| VFUSE | –0.5 | 1.5 | V | |
| IOVDD | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| AVDD, PLLAVDD | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| Pin voltage range(2) | D[15..0]P/N, DATACLKP/N, FRAMEP/N, PARITYP/N, SYNCP/N | –0.5 | IOVDD + 0.5 | V |
| DACCLKP/N, OSTRP/N | –0.5 | CLKVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| ALARM, SDO, SDIO, SCLK, SDENB, SLEEP, RESETB, TESTMODE, TXENABLE | –0.5 | IOVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| IOUTAP/N, IOUTBP/N, IOUTCP/N, IOUTDP/N | –1.0 | AVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| EXTIO, BIASJ | –0.5 | AVDD + 0.5 | V | |
| LPF | 0.5 | PLLAVDD+0.5V | V | |
| Peak input current (any input) | 20 | mA | ||
| Peak total input current (all inputs) | –30 | mA | ||
| Operating free-air temperature range, TA: DAC3484 | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| Absolute maximum junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature range | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Measured with respect to GND.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TJ | Recommended operating junction temperature | 105 | °C | ||
| Maximum rated operating junction temperature(1) | 125 | ||||
| TA | Recommended free-air temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C |
(1) Prolonged use at this junction temperature may increase the device failure-in-time (FIT) rate.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DAC3484 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RKD (WQFN-MR) |
ZAY (NFBGA) |
|||
| 88 PINS | 196 BALLS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 22.1 | 37.6 | °C/W |
| RθJCtop | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 7.1 | 6.8 | °C/W |
| RθJCbot | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 0.6 | N/A | °C/W |
| θJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 4.7 | 16.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.1 | 0.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 4.6 | 16.4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
6.5 Electrical Characteristics – DC Specifications(1)
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, nominal supplies, IOUTFS = 20 mA (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 16 | Bits | ||||
| DC ACCURACY | ||||||
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | 1 LSB = IOUTFS/216 | ±2 | LSB | ||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | ±4 | LSB | |||
| ANALOG OUTPUT | ||||||
| Coarse gain linearity | ±0.04 | LSB | ||||
| Offset error | Mid code offset | ±0.001 | %FSR | |||
| Gain error | With external reference | ±2 | %FSR | |||
| With internal reference | ±2 | %FSR | ||||
| Gain mismatch | With internal reference | ±2 | %FSR | |||
| Full scale output current | 10 | 20 | 30 | mA | ||
| Output compliance range | –0.5 | 0.6 | V | |||
| Output resistance | 300 | kΩ | ||||
| Output capacitance | 5 | pF | ||||
| REFERENCE OUTPUT | ||||||
| VREF | Reference output voltage | 1.2 | V | |||
| Reference output current(2) | 100 | nA | ||||
| REFERENCE INPUT | ||||||
| VEXTIO | Input voltage range | External Reference Mode | 0.6 | 1.2 | 1.25 | V |
| Input resistance | 1 | MΩ | ||||
| Small signal bandwidth | 472 | kHz | ||||
| Input capacitance | 100 | pF | ||||
| TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS | ||||||
| Offset drift | ±1 | ppm/°C | ||||
| Gain drift | with external reference | ±15 | ppm/°C | |||
| with internal reference | ±30 | ppm/°C | ||||
| Reference voltage drift | ±8 | ppm/°C | ||||
| POWER SUPPLY(3) | ||||||
| AVDD, IOVDD, PLLAVDD | All Conditions | 3.14 | 3.3 | 3.46 | V | |
| DIGVDD | All Conditions | 1.14 | 1.2 | 1.32 | V | |
| CLKVDD, DACVDD | FDAC Sampling Rate ≤ 1.25 GSPS, PLL OFF FDAC Sampling Rate ≤ 1 GSPS, PLL ON |
1.14 | 1.2 | 1.32 | V | |
| FDAC Sampling Rate > 1 GSPS, PLL ON | 1.25 | 1.29 | 1.32 | |||
| PSRR | Power Supply Rejection Ratio | DC tested | ±0.2 | %FSR/V | ||
| POWER CONSUMPTION | ||||||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | MODE 1 fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, 4x interpolation, Mixer on, QMC on, invsinc on, PLL enabled, 20-mA FS output, IF = 200 MHz |
123 | 135 | mA | |
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 595 | 650 | mA | ||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 35 | 50 | mA | ||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 90 | 100 | mA | ||
| P | Power dissipation | 1270 | 1320 | mW | ||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | MODE 2 fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, 4x interpolation, Mixer on, QMC on, invsinc on, PLL disabled, 20-mA FS output, IF = 200 MHz |
107 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 595 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 38 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 71 | mA | |||
| P | Power dissipation | 1198 | mW | |||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | MODE 3 fDAC = 625 MSPS, 2x interpolation, Mixer on, QMC on, invsinc off, PLL disabled, 20-mA FS output, IF = 200 MHz |
107 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 282 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 20 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 41 | mA | |||
| P | Power dissipation | 765 | mW | |||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | MODE 4 fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, 4x interpolation, Mixer on, QMC on, invsinc on, PLL enabled, Channels A/B/C/D output sleep, IF = 200 MHz, |
35 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 595 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 38 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 90 | mA | |||
| P | Power dissipation | 984 | mW | |||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | Mode 5 Power-Down mode: No clock, DAC on sleep mode (clock receiver sleep), Channels A/B/C/D output sleep, static data pattern |
20 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 10 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 4 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 10 | mA | |||
| P | Power Dissipation | 95 | mW | |||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | Mode 6 fDAC = 1 GSPS, 8x interpolation, Mixer off, QMC on, invsinc off, PLL enabled, 20-mA FS output, IF = 200 MHz |
107 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 333 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 35 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 60 | mA | |||
| P | Power dissipation | 867 | mW | |||
| I(AVDD) | Analog supply current(4) | Mode 7 fDAC = 737.28 MSPS, 4x interpolation, Mixer on, QMC on, invsinc off, PLL enabled, 20-mA FS output, IF = 150 MHz |
123 | mA | ||
| I(DIGVDD) | Digital supply current | 323 | mA | |||
| I(DACVDD) | DAC supply current | 23 | mA | |||
| I(CLKVDD) | Clock supply current | 69 | mA | |||
| P | Power dissipation | 904 | mW | |||
(1) Measured differentially across IOUTP/N with 25 Ω each to GND.
(2) Use an external buffer amplifier with high impedance input to drive any external load.
(3) To ensure power supply accuracy and to account for power supply filter network loss at operating conditions, the use of the ATEST function in register config27 to check the internal power supply nodes is recommended.
(4) Includes AVDD, PLLAVDD, and IOVDD
6.6 Electrical Characteristics – Digital Specifications
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVDS INPUTS: D[15:0]P/N, DATACLKP/N, FRAMEP/N, SYNCP/N, PARITYP/N(1) | ||||||||
| VA,B+ | Logic high differential input voltage threshold | 200 | mV | |||||
| VA,B– | Logic low differential input voltage threshold | –200 | mV | |||||
| VCOM | Input Common Mode | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.6 | V | |||
| ZT | Internal termination | 85 | 110 | 135 | Ω | |||
| CL | LVDS Input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||||
| fINTERL | Interleaved LVDS data transfer rate | 1250 | MSPS | |||||
| fDATA | Input data rate | 312.5 | MSPS | |||||
| CLOCK INPUT (DACCLKP/N) | ||||||||
| Differential voltage(2) | |DACCLKP - DACCLKN| | 0.4 | 0.8 | V | ||||
| Internally biased common-mode voltage | 0.2 | V | ||||||
| Single-ended input level(3) | –0.4 | V | ||||||
| OUTPUT STROBE (OSTRP/N) | ||||||||
| Differential voltage | |OSTRP – OSTRN| | 0.4 | 0.8 | V | ||||
| Internally biased common-mode voltage | 0.2 | V | ||||||
| Single-ended input level(3) | –0.4 | V | ||||||
| CMOS INTERFACE: ALARM, SDO, SDIO, SCLK, SDENB, SLEEP, RESETB, TXENABLE | ||||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | V | |||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.8 | V | |||||
| IIH | High-level input current | -40 | 40 | µA | ||||
| IIL | Low-level input current | -40 | 40 | µA | ||||
| CI | CMOS Input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||||
| VOH | ALARM, SDO, SDIO | Iload = –100 μA | IOVDD – 0.2 | V | ||||
| Iload = –2 mA | 0.8 x IOVDD | V | ||||||
| VOL | ALARM, SDO, SDIO | Iload = 100 μA | 0.2 | V | ||||
| Iload = 2 mA | 0.5 | V | ||||||
(1) See LVDS Inputs section for terminology.
6.7 Electrical Characteristics – AC Specifications
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, nominal supplies, IOUTFS = 20mA (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG OUTPUT(1) | |||||||
| fDAC | Maximum DAC rate | 1250 | MSPS | ||||
| AC PERFORMANCE(2) | |||||||
| SFDR | Spurious free dynamic range (0 to fDAC/2) Tone at 0 dBFS |
fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 20 MHz | 82 | dBc | |||
| fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 50 MHz | 77 | ||||||
| fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 70 MHz | 72 | ||||||
| IMD3 | Third-order two-tone intermodulation distortion Each tone at –12 dBFS |
fDAC = 1.25 MSPS, fOUT = 30 ± 0.5 MHz | 81 | dBc | |||
| fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 50 ± 0.5 MHz | 79 | ||||||
| fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 100 ± 0.5 MHz | 77.5 | ||||||
| NSD | Noise Spectral Density Tone at 0dBFS |
fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 10 MHz | 160 | dBc/Hz | |||
| fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 80 MHz | 155 | ||||||
| ACLR(3) | Adjacent channel leakage ratio, single carrier | fDAC = 1.2288 GSPS, fOUT = 30.72 MHz | 77 | dBc | |||
| fDAC = 1.2288 GSPS, fOUT = 153.6 MHz | 74 | ||||||
| Alternate channel leakage ratio, single carrier | fDAC = 1.2288 GSPS, fOUT = 30.72 MHz | 82 | |||||
| fDAC = 1.2288 GSPS, fOUT = 153.6 MHz | 80 | ||||||
| Channel Isolation | fDAC = 1.25 GSPS, fOUT = 10 MHz | 84 | dBc | ||||
(1) Measured single ended into 50-Ω load.
(2) 4:1 transformer output termination, 50 Ω doubly terminated load.
(3) Single carrier, W-CDMA with 3.84-MHz BW, 5-MHz spacing, centered at IF, PAR = 12dB. TESTMODEL 1, 10 ms
6.8 Timing Requirements – Digital Specifications
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLOCK INPUT (DACCLKP/N) | ||||||||
| Duty cycle | 40% | 60% | ||||||
| DACCLKP/N input frequency | 1250 | MHz | ||||||
| OUTPUT STROBE (OSTRP/N) | ||||||||
| fOSTR | Frequency | fOSTR = fDACCLK / (n x 8 x Interp) where n is any positive integer, fDACCLK is DACCLK frequency in MHz | fDACCLK / (8 x interp) |
MHz | ||||
| Duty cycle | 50% | |||||||
| DIGITAL INPUT TIMING SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||||
| Timing LVDS inputs: D[15:0]P/N, FRAMEP/N, SYNCP/N, PARITYP/N, double edge latching | ||||||||
| ts(DATA) | Setup time, D[15:0]P/N, FRAMEP/N, SYNCP/N and PARITYP/N, valid to either edge of DATACLKP/N | FRAMEP/N reset and frame indicator latched on rising edge of DATACLKP/N. FRAMEP/N parity bit latched on falling edge of DATACLKP/N. |
Config36 Setting | |||||
| datadly | clkdly | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 150 | ps | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 100 | ||||||
| 0 | 2 | 50 | ||||||
| 0 | 3 | 0 | ||||||
| 0 | 4 | -50 | ||||||
| 0 | 5 | -100 | ||||||
| 0 | 6 | -150 | ||||||
| 0 | 7 | -200 | ||||||
| 1 | 0 | 200 | ||||||
| 2 | 0 | 250 | ||||||
| 3 | 0 | 300 | ||||||
| 4 | 0 | 350 | ||||||
| 5 | 0 | 400 | ||||||
| 6 | 0 | 450 | ||||||
| 7 | 0 | 500 | ||||||
| th(DATA) | Hold time, D[15:0]P/N, FRAMEP/N, SYNCP/N and PARITYP/N, valid after either edge of DATACLKP/N | FRAMEP/N reset and frame indicator latched on rising edge of DATACLKP/N. FRAMEP/N parity bit latched on falling edge of DATACLKP/N. |
Config36 Setting | ps | ||||
| datadly | clkdly | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 350 | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 400 | ||||||
| 0 | 2 | 450 | ||||||
| 0 | 3 | 500 | ||||||
| 0 | 4 | 550 | ||||||
| 0 | 5 | 600 | ||||||
| 0 | 6 | 650 | ||||||
| 0 | 7 | 700 | ||||||
| 1 | 0 | 300 | ||||||
| 2 | 0 | 250 | ||||||
| 3 | 0 | 200 | ||||||
| 4 | 0 | 150 | ||||||
| 5 | 0 | 100 | ||||||
| 6 | 0 | 50 | ||||||
| 7 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| t(FRAME_SYNC) | FRAMEP/N and SYNCP/N pulse width | fDATACLK is DATACLK frequency in MHz | 1/2fDATACLK | ns | ||||
| TIMING OUTPUT STROBE INPUT: DACCLKP/N rising edge LATCHING(1) | ||||||||
| ts(OSTR) | Setup time, OSTRP/N valid to rising edge of DACCLKP/N | 0 | ps | |||||
| th(OSTR) | Hold time, OSTRP/N valid after rising edge of DACCLKP/N | 300 | ps | |||||
| TIMING SYNC INPUT: DACCLKP/N rising edge LATCHING(2) | ||||||||
| ts(SYNC_PLL) | Setup time, SYNCP/N valid to rising edge of DACCLKP/N | 200 | ps | |||||
| th(SYNC_PLL) | Hold time, SYNCP/N valid after rising edge of DACCLKP/N | 300 | ps | |||||
| TIMING SERIAL PORT | ||||||||
| ts(SDENB) | Setup time, SDENB to rising edge of SCLK | 20 | ns | |||||
| ts(SDIO) | Setup time, SDIO valid to rising edge of SCLK | 10 | ns | |||||
| th(SDIO) | Hold time, SDIO valid to rising edge of SCLK | 5 | ns | |||||
| t(SCLK) | Period of SCLK | Register config6 read (temperature sensor read) | 1 | µs | ||||
| All other registers | 100 | ns | ||||||
| td(Data) | Data output delay after falling edge of SCLK | 10 | ns | |||||
| tRESET | Minimum RESETB pulse width | 25 | ns | |||||
(1) OSTR is required in Dual Sync Sources mode. In order to minimize the skew it is recommended to use the same clock distribution device such as Texas Instruments CDCE62005 or LMK0480x family to provide the DACCLK and OSTR signals to all the DAC3484 devices in the system. Swap the polarity of the DACCLK outputs with respect to the OSTR ones to establish proper phase relationship.
(2) SYNC is required to synchronize the PLL circuit in multiple devices. The SYNC signal must meet the timing relationship with respect to the reference clock (DACCLKP/N) of the on-chip PLL circuit.
6.9 Switching Characteristics – AC Specifications
over recommended operating free-air temperature range, nominal supplies, IOUTFS = 20 mA (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG OUTPUT(1) | |||||||
| ts(DAC) | Output settling time to 0.1% | Transition: Code 0x0000 to 0xFFFF | 10 | ns | |||
| tpd | Output propagation delay | DAC outputs are updated on the falling edge of DAC clock. Does not include Digital Latency (see below). | 2 | ns | |||
| tr(IOUT) | Output rise time 10% to 90% | 220 | ps | ||||
| tf(IOUT) | Output fall time 90% to 10% | 220 | ps | ||||
| Digital latency | No interpolation, FIFO on, Mixer off, QMC off, Inverse sinc off | 128 | DAC clock cycles | ||||
| 2x Interpolation | 216 | ||||||
| 4x Interpolation | 376 | ||||||
| 8x Interpolation | 726 | ||||||
| 16x Interpolation | 1427 | ||||||
| Fine mixer | 24 | ||||||
| QMC | 32 | ||||||
| Inverse sinc | 36 | ||||||
| Power-up Time |
DAC wake-up time | IOUT current settling to 1% of IOUTFS from output sleep | 2 | µs | |||
| DAC sleep time | IOUT current settling to less than 1% of IOUTFS in output sleep | 2 | |||||
(1) Measured single ended into 50-Ω load.
6.10 Typical Characteristics
All plots are at 25°C, nominal supply voltage, fDAC = 1250 MSPS, 4x interpolation, NCO enabled, Mixer Gain disabled, QMC enabled with gain set at 1446 for both I/Q channels, 0 dBFS digital input, 20-mA full-scale output current with 4:1 transformer (unless otherwise noted) Figure 1. Integral Nonlinearity
Figure 1. Integral Nonlinearity
 Figure 3. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
Figure 3. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
 Figure 5. Third Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
Figure 5. Third Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
 Figure 7. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over fDAC
Figure 7. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over fDAC
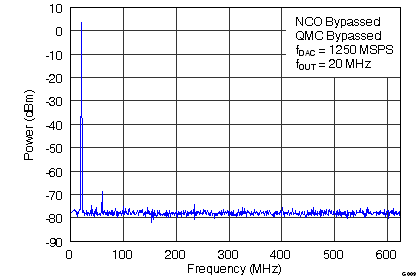 Figure 9. Single Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 9. Single Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 11. Single Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 11. Single Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 13. Single Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 13. Single Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 15. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over Interpolation
Figure 15. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over Interpolation
 Figure 17. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over IOUTFS
Figure 17. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over IOUTFS
 Figure 19. Two Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 19. Two Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 25. Single Carrier WCDMA ACLR (Adjacent) vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
Figure 25. Single Carrier WCDMA ACLR (Adjacent) vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
 Figure 27. Single Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
Figure 27. Single Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1

 Figure 31. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
Figure 31. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
 Figure 33. 10-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
Figure 33. 10-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
 Figure 35. 20-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
Figure 35. 20-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
 Figure 37. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Interpolation
Figure 37. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Interpolation
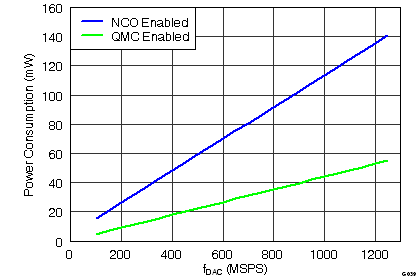 Figure 39. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Digital Processing Functions
Figure 39. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Digital Processing Functions
 Figure 41. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Interpolation
Figure 41. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Interpolation
 Figure 43. DACVDD Current vs fDAC
Figure 43. DACVDD Current vs fDAC
 Figure 45. AVDD Current vs fDAC
Figure 45. AVDD Current vs fDAC
 Figure 47. Channel Isolation vs Output Frequency
Figure 47. Channel Isolation vs Output Frequency
 Figure 2. Differential Nonlinearity
Figure 2. Differential Nonlinearity
 Figure 4. Second Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
Figure 4. Second Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
 Figure 6. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over Interpolation
Figure 6. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over Interpolation
 Figure 8. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over IOUTFS
Figure 8. SFDR vs Output Frequency Over IOUTFS
 Figure 10. Single Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 10. Single Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 12. Single Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 12. Single Tone Spectral Plot
 Figure 14. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
Figure 14. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over Input Scale
 Figure 16. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over fDAC
Figure 16. IMD3 vs Output Frequency Over fDAC
 Figure 18. Two Tone Spectral Plot
Figure 18. Two Tone Spectral Plot
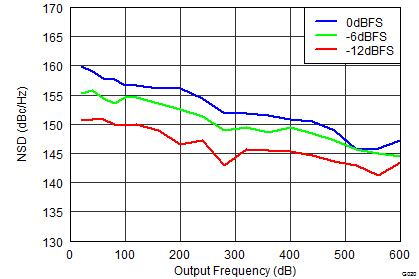
 Figure 24. NSD vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
Figure 24. NSD vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
 Figure 26. Single Carrier WCDMA ACLR (Alternate) vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
Figure 26. Single Carrier WCDMA ACLR (Alternate) vs Output Frequency Over Clocking Options
 Figure 28. Single Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
Figure 28. Single Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
 Figure 30. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
Figure 30. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
 Figure 32. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
Figure 32. Four Carrier W-CDMA Test Model 1
 Figure 34. 10-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
Figure 34. 10-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
 Figure 36. 20-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
Figure 36. 20-MHz Single Carrier LTE Test Model 3.1
 Figure 38. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Interpolation
Figure 38. Power Consumption vs fDAC Over Interpolation
 Figure 40. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Interpolation
Figure 40. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Interpolation
 Figure 42. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Digital Processing Functions
Figure 42. DIGVDD Current vs fDAC Over Digital Processing Functions
 Figure 44. CLKVDD Current vs fDAC
Figure 44. CLKVDD Current vs fDAC
 Figure 46. Channel Isolation vs Output Frequency
Figure 46. Channel Isolation vs Output Frequency