SBAS538D December 2013 – December 2021 DAC7750 , DAC8750
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.10 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
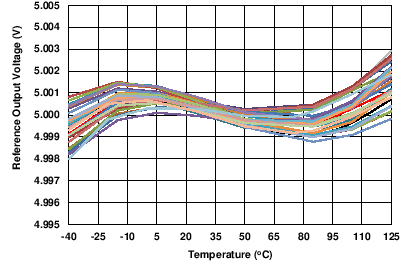
| 30 units shown | AVDD = 24 V | |

| AVDD = 24 V |
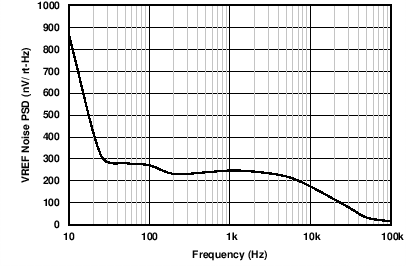
| AVDD = 24 V |
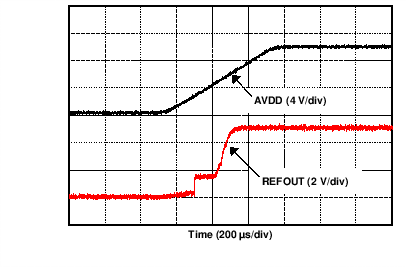
| AVDD = 10 V | ||
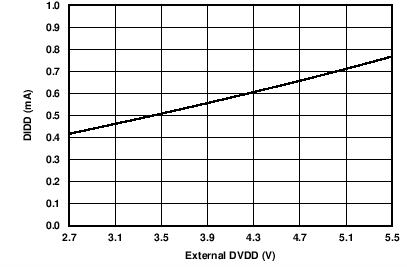
| TA = 25°C | External DVDD | |

| AVDD = 18 V | CLOAD = 100 nF | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
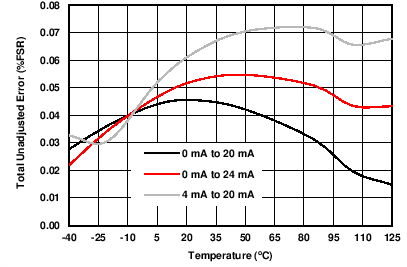
| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
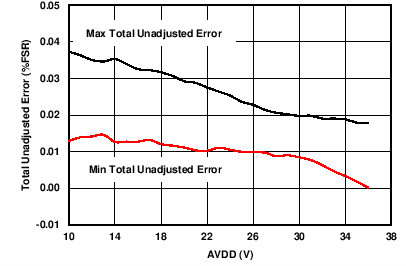
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
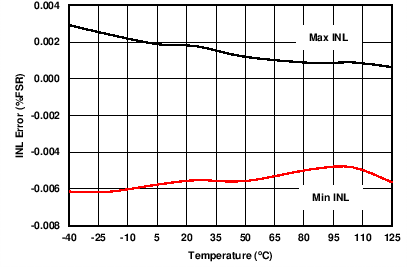
| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | All IOUT ranges |

| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |
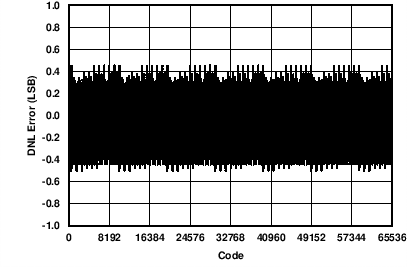
| AVDD = 24 V | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | ||

| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | All IOUT ranges |
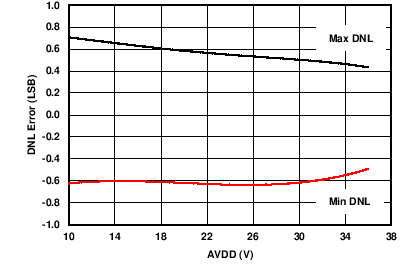
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |

| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
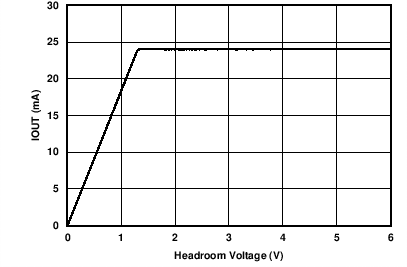
| AVDD = 36 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
| DAC configured to deliver 24 mA | ||
| NOTE: Compliance voltage headroom is defined as the drop from the AVDD pin to the IOUT pin. | ||
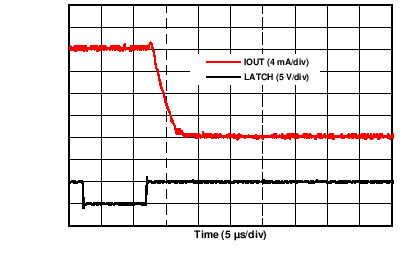
| AVDD = 24 V | 4-mA to 20-mA range | |
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | From code: 0x0000 | To code: 0xFFFF |
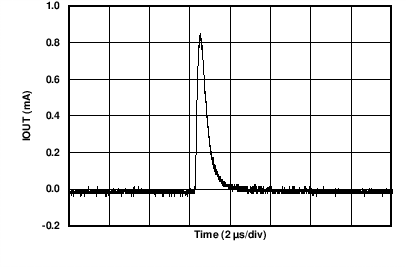
| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | All IOUT ranges |

| AVDD = 36 V | Output disabled | |
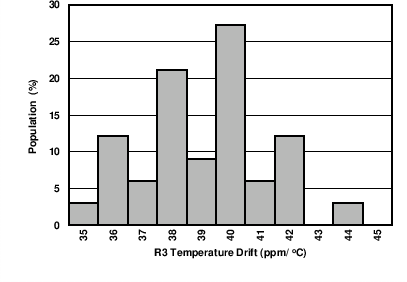
 Figure 7-4 Internal Reference Temperature Drift Histogram
Figure 7-4 Internal Reference Temperature Drift Histogram
| TA = 25°C |

| AVDD = 24 V |

| External DVDD | IOUT = 0 mA | |

| TA = 25°C | Internal DVDD | |
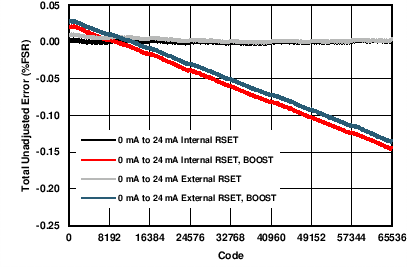
| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
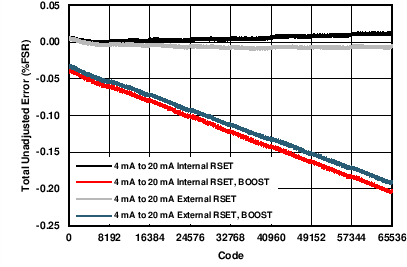
| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
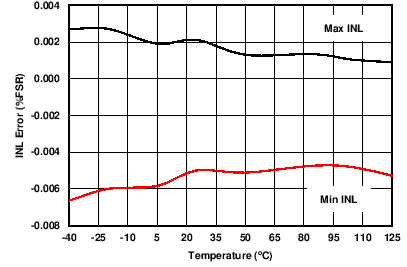
| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | All IOUT ranges |

| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |

| AVDD = 24 V | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | ||
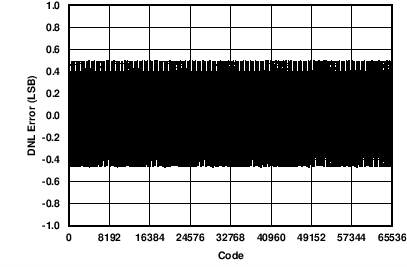
| AVDD = 24 V | 4-mA to 24-mA range | |
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | ||
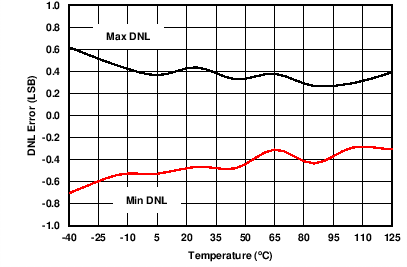
| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | All IOUT ranges |
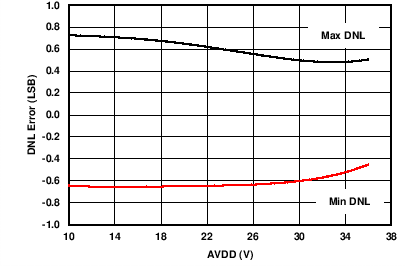
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | 0-mA to 24-mA range | |

| AVDD = 10 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |
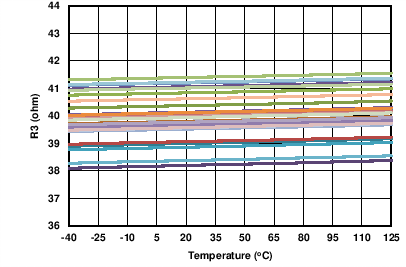
| 33 units shown | ||

| AVDD = 36 V | IOUT = 24 mA | RLOAD = 300 Ω |
| NOTE: Compliance voltage headroom is defined as the drop from the AVDD pin to the IOUT pin. | ||

| AVDD = 24 V | 4-mA to 20-mA range | |
| RLOAD = 300 Ω | From code: 0x0000 | To code: 0xFFFF |
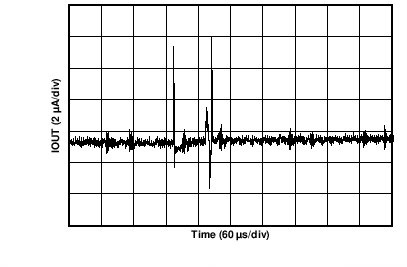
| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 300 Ω | |

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 250 Ω | |

| AVDD = 24 V | 0-mA to 20-mA range | |
| DAC = midscale | ||

| AVDD = 24 V | RLOAD = 250 Ω | All IOUT ranges |