SBAS430F January 2009 – April 2018 DAC7568 , DAC8168 , DAC8568
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.2
Feature Description
- 8.2.1 Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 8.2.2 Resistor String
- 8.2.3 Output Amplifier
- 8.2.4 Internal Reference
- 8.2.5 Serial Interface
- 8.2.6 Input Shift Register
- 8.2.7 SYNC Interrupt
- 8.2.8 Power-on Reset to Zero Scale or Midscale
- 8.2.9 Clear Code Register and CLR Pin
- 8.2.10 Software Reset Function
- 8.2.11
Operating Examples: DAC7568/DAC8168/DAC8568
- Table 4. 1st: Write to Data Buffer A:
- Table 5. 2nd: Write to Data Buffer B:
- Table 6. 3rd: Write to Data Buffer G:
- Table 7. 4th: Write to Data Buffer H and Simultaneously Update all DACs:
- Table 8. 1st: Write to Data Buffer C and Load DAC C: DAC C Output Settles to Specified Value Upon Completion:
- Table 9. 2nd: Write to Data Buffer D and Load DAC D: DAC D Output Settles to Specified Value Upon Completion:
- Table 10. 3rd: Write to Data Buffer E and Load DAC E: DAC E Output Settles to Specified Value Upon Completion:
- Table 11. 4th: Write to Data Buffer F and Load DAC F: DAC F Output Settles to Specified Value Upon Completion:
- Table 12. 1st: Write Power-Down Command to DAC Channel A and DAC Channel B: DAC A and DAC B to 1kΩ.
- Table 13. 2nd: Write Power-Down Command to DAC Channel H: DAC H to 1kΩ.
- Table 14. 3rd: Write Power-Down Command to DAC Channel C and DAC Channel D: DAC C and DAC D to 100kΩ.
- Table 15. 4th: Write Power-Down Command to DAC Channel F: DAC F to 100kΩ.
- Table 16. 1st: Write Sequence for Enabling the DAC7568, DAC8168, and DAC8568 Internal Reference All the Time:
- Table 17. 2nd: Write Sequence to Power-Down All DACs to High-Impedance:
- Table 18. 1st: Write Sequence for Disabling the DAC7568, DAC8168, and DAC8568 Internal Reference All the Time (after this sequence, these devices require an external reference source to function):
- Table 19. 2nd: Write Sequence to Write Specified Data to All DACs:
- 8.3
Device Functional Modes
- 8.3.1
Enable/Disable Internal Reference
- 8.3.1.1 Static Mode
- 8.3.1.2
Flexible Mode
- Table 22. Write Sequence for Enabling Internal Reference (Flexible Mode) (Internal Reference Powered On—09080000h)
- Table 23. Write Sequence for Enabling Internal Reference (Flexible Mode) (Internal Reference Always Powered On—090A0000h)
- Table 24. Write Sequence for Disabling Internal Reference (Flexible Mode) (Internal Reference Always Powered Down—090C0000h)
- Table 25. Write Sequence for Switching from Flexible Mode to Static Mode for Internal Reference (Internal Reference Always Powered Down—09000000h)
- 8.3.2 LDAC Functionality
- 8.3.3 Power-Down Modes
- 8.3.1
Enable/Disable Internal Reference
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications - Microprocessor Interfacing
- 9.2.1 DAC7568/DAC8168/DAC8568 to an 8051 Interface
- 9.2.2 DAC7568/DAC8168/DAC8568 to Microwire Interface
- 9.2.3 DAC7568/DAC8168/DAC8568 to 68HC11 Interface
- 10Layout
-
11Device and Documentation Support
- 11.1
Device Support
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.1.1.1
Static Performance
- 11.1.1.1.1 Resolution
- 11.1.1.1.2 Least Significant Bit (LSB)
- 11.1.1.1.3 Most Significant Bit (MSB)
- 11.1.1.1.4 Relative Accuracy or Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
- 11.1.1.1.5 Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
- 11.1.1.1.6 Full-Scale Error
- 11.1.1.1.7 Offset Error
- 11.1.1.1.8 Zero-Code Error
- 11.1.1.1.9 Gain Error
- 11.1.1.1.10 Full-Scale Error Drift
- 11.1.1.1.11 Offset Error Drift
- 11.1.1.1.12 Zero-Code Error Drift
- 11.1.1.1.13 Gain Temperature Coefficient
- 11.1.1.1.14 Power-Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
- 11.1.1.1.15 Monotonicity
- 11.1.1.2
Dynamic Performance
- 11.1.1.2.1 Slew Rate
- 11.1.1.2.2 Output Voltage Settling Time
- 11.1.1.2.3 Code Change/Digital-to-Analog Glitch Energy
- 11.1.1.2.4 Digital Feedthrough
- 11.1.1.2.5 Channel-to-Channel DC Crosstalk
- 11.1.1.2.6 Channel-to-Channel AC Crosstalk
- 11.1.1.2.7 Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
- 11.1.1.2.8 Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
- 11.1.1.2.9 Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
- 11.1.1.2.10 Signal-to-Noise plus Distortion (SINAD)
- 11.1.1.2.11 DAC Output Noise Density
- 11.1.1.2.12 DAC Output Noise
- 11.1.1.2.13 Full-Scale Range (FSR)
- 11.1.1.1
Static Performance
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.2 Related Links
- 11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
- 11.4 Community Resources
- 11.5 Trademarks
- 11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 11.7 Glossary
- 11.1
Device Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.2 LDAC Functionality
The DAC7568, DAC8168, and DAC8568 offer both a software and hardware simultaneous update and control function. The DAC double-buffered architecture has been designed so that new data can be entered for each DAC without disturbing the analog outputs.
DAC7568, DAC8168, and DAC8568 data updates can be performed either in synchronous or in asynchronous mode.
In synchronous mode, data are updated with the falling edge of the 32nd SCLK cycle, which follows a falling edge of SYNC. For such synchronous updates, the LDAC pin is not required and it must be connected to GND permanently.
In asynchronous mode, the LDAC pin is used as a negative edge triggered timing signal for simultaneous DAC updates. Multiple single-channel updates can be done in order to set different channel buffers to desired values and then make a falling edge on LDAC pin to simultaneously update the DAC output registers. Data buffers of all channels must be loaded with desired data before an LDAC falling edge. After a high-to-low LDAC transition, all DACs are simultaneously updated with the last contents of the corresponding data buffers. If the content of a data buffer is not changed, the corresponding DAC output remains unchanged after the LDAC pin is triggered.
Alternatively, all DAC outputs can be updated simultaneously using the built-in software function of LDAC. The LDAC register offers additional flexibility and control by allowing the selection of which DAC channel(s) should be updated simultaneously when the LDAC pin is being brought low. The LDAC register is loaded with an 8-bit word (DB0 to DB7) using control bits C3, C2, C1, and C0 (see ). The default value for each bit, and therefore for each DAC channel, is zero. The external LDAC pin operates in normal mode. If the LDAC register bit is set to '1', it overrides the LDAC pin (the LDAC pin is internally tied low for that particular DAC channel) and this DAC channel updates synchronously after the falling edge of the 32nd SCLK cycle. However, if the LDAC register bit is set to '0', the DAC channel is controlled by the LDAC pin.
The combination of software and hardware simultaneous update functions is particularly useful in applications when updating only selective DAC channels simultaneously, while keeping the other channels unaffected and updating those channels synchronously; see for more information.
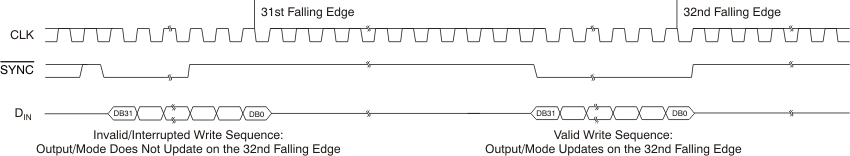 Figure 123. SYNC Interrupt Facility
Figure 123. SYNC Interrupt Facility