DLPS242A March 2023 – March 2024 DLP781TE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 Storage Conditions
- 5.3 ESD Ratings
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 11
- 5.5 Thermal Information
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Timing Requirements
- 15
- 5.8 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 17
- 5.9 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 19
- 5.10 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 21
- 5.11 Window Characteristics
- 5.12 Chipset Component Usage Specification
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Optical Interface and System Image Quality Considerations
- 6.6 Micromirror Array Temperature Calculation
- 6.7 Micromirror Power Density Calculation
- 6.8 Window Aperture Illumination Overfill Calculation
- 6.9 Micromirror Landed-On/Landed-Off Duty Cycle
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FYU|350
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.8 Window Aperture Illumination Overfill Calculation
The amount of optical overfill on the critical area of the window aperture cannot be measured directly. For systems with uniform illumination on the array the amount is determined using the total measured incident optical power on the DMD, and the ratio of the total optical power on the DMD that is on the defined critical area. The optical model is used to determine the percent of optical power on the window aperture critical area and estimate the size of the area.
- QAP-ILL = [QINCIDENT × OPAP_ILL_RATIO] ÷ AAP_ILL (W/cm2)
where:
- QAP-ILL = window aperture illumination overfill (W/cm2)
- QINCIDENT = total incident optical power on the DMD (Watts) (measured)
- OPAP_ILL_RATIO = ratio of the optical power on the critical area of the window aperture to the total optical power on the DMD (optical model)
- AAP-ILL = size of the window aperture critical area (cm2) (datasheet)
- OPCA_RATIO = percent of the window aperture critical area with incident optical power (%) (optical model)
Sample calculation:
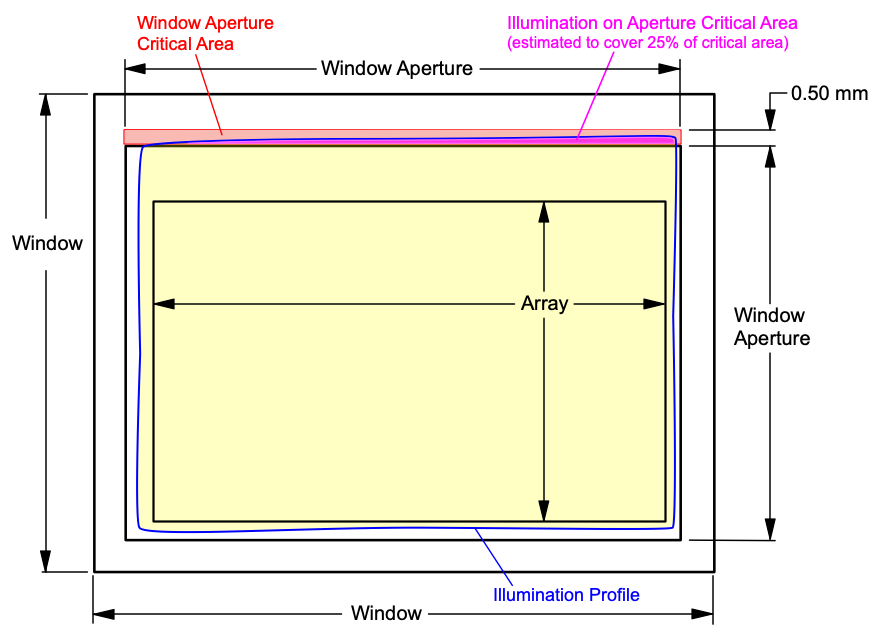
Figure 6-2 Window Aperture Overfill Example
See the figure for the length of the critical aperture.
Equation 22. QINCIDENT = 80W (measured)
Equation 23. OPAP_ILL_RATIO = 0.312% (optical
model)
Equation 24. OVCA_RATIO = 25% (optical
model)
Equation 25. Length
of the window aperture for critical area = 1.8613cm (data
sheet)
Equation 26. Width
of critical area =
0.050cm (data
sheet)
Equation 27. AAP-ILL = 1.8613cm × 0.050cm = 0.093065
(cm2)
Equation 28. QAP-ILL = (80W × 0.00312) ÷ (0.093065cm2 × 0.25) =
10.7 (W/cm2)