DLPS201E August 2020 – August 2024 DLPC230S-Q1 , DLPC231S-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics for Fixed Voltage I/O
- 5.7 DMD High-Speed SubLVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 DMD Low-Speed SubLVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 5.9 OpenLDI LVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 Power Dissipation Characterisics
- 5.11 System Oscillators Timing Requirements
- 5.12 Power Supply and Reset Timing Requirements
- 5.13 Parallel Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.14 OpenLDI Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.15 Parallel/OpenLDI Interface Frame Timing Requirements
- 5.16 Host/Diagnostic Port SPI Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.17 Host/Diagnostic Port I2C Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.18 Flash Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.19 TPS99000S-Q1 SPI Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.20 TPS99000S-Q1 AD3 Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.21 DLPC23xS-Q1 I2C Port Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.22 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Parallel Interface
- 7.3.2 OpenLDI Interface
- 7.3.3 DMD (SubLVDS) Interface
- 7.3.4 Serial Flash Interface
- 7.3.5 Serial Flash Programming
- 7.3.6 Host Command and Diagnostic Processor Interfaces
- 7.3.7 GPIO Supported Functionality
- 7.3.8 Built-In Self Test (BIST)
- 7.3.9 EEPROMs
- 7.3.10 Temperature Sensor
- 7.3.11 Debug Support
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4
Layout
- 8.4.1
Layout Guidelines
- 8.4.1.1 PCB Layout Guidelines for Internal ASIC PLL Power
- 8.4.1.2 DLPC23xS-Q1 Reference Clock
- 8.4.1.3 DMD Interface Layout Considerations
- 8.4.1.4 General PCB Recommendations
- 8.4.1.5 General Handling Guidelines for Unused CMOS-Type Pins
- 8.4.1.6 Maximum Pin-to-Pin, PCB Interconnects Etch Lengths
- 8.4.1.7 Number of Layer Changes
- 8.4.1.8 Stubs
- 8.4.1.9 Terminations
- 8.4.1.10 Routing Vias
- 8.4.2 Thermal Considerations
- 8.4.1
Layout Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZDQ|324
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
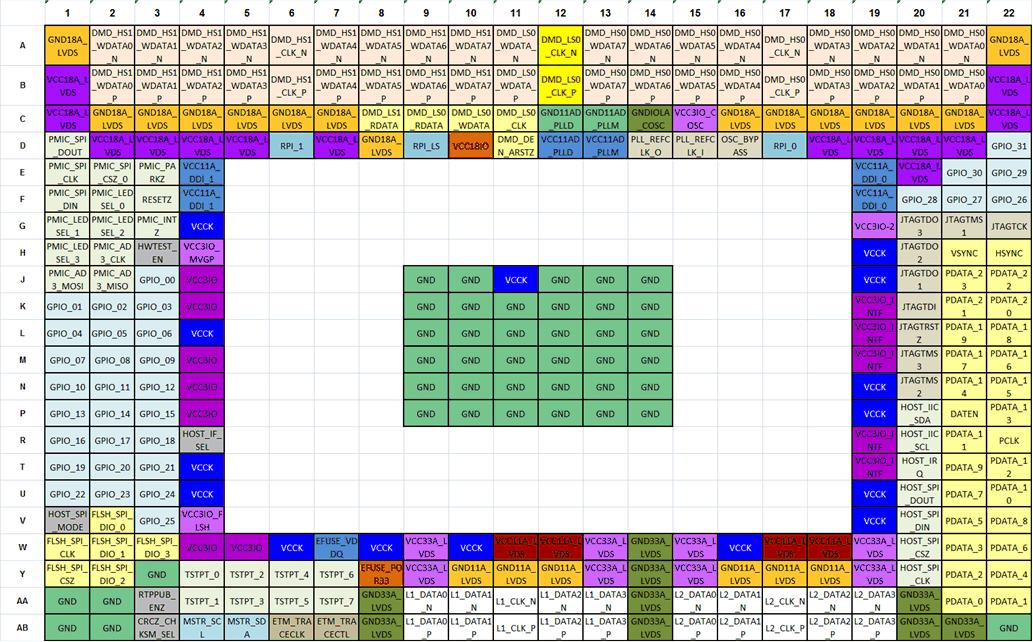
324-Pin BGA
Top View
 Figure 4-2 DLPC231 ZEK Package
Figure 4-2 DLPC231 ZEK Package324-Pin BGA
Top View
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME |
ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| RESETZ | F3 |
F3 |
I7 | Active low power-on reset for the DLPC23xS-Q1. A low-to-high transition starts
self-configuration and initialization of the ASIC. ('0' = Reset, '1' = Normal Operation) All ASIC power and input clocks must be stable before this reset is deasserted high. The signals listed below must be forced low by external pulldown, and will then be driven low as the power supplies stabilize with RESETZ asserted. PMIC_LEDSEL_0, PMIC_LEDSEL_1, PMIC_LEDSEL_2, PMIC_LEDSEL_3, DMD_DEN_ARSTZ, PMIC_AD3_CLK, and PMIC_AD3_MOSI All other bidirectional and output signals will be tristated while reset is asserted. External pullups or pulldowns must be added where necessary to protect external devices that can typically be driven by the ASIC to prevent device malfunction. This pin includes hysteresis. Specific timing requirements for this signal are shown in Section 5.12. |
| PMIC_PARKZ | E3 |
E4 |
I7 | DMD Park Control ('0' = Park, '1' = Un-Park) The TI TPS99000S-Q1 device is used to control this signal. As part of this function, it monitors power to the DLPC23xS-Q1 watching for an imminent power loss condition, upon which it will drive the PMIC_PARKZ signal accordingly. The specific timing requirements for this signal are shown in Section 5.12. |
| HOST_IF_SEL | R4 |
N1 |
B13,14 | Selects which input interface port will be used for Host Command
and Control. The port that is not selected as the Host Command and
Control port will be available as a Diagnostic Processor monitoring
port. ('0' = Host SPI, '1' = Host I2C) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. Tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for TI debug use after sampling. |
| HOST_SPI_MODE | V1 |
P2 |
B13,14 | Selects the SPI mode (clock phase and polarity) that will be used
with the HOST SPI interface. This value is applicable regardless of
whether the Host SPI interface is used for Host Command and Control,
or for the Diagnostic Processor monitoring port. ('0' = SPI Mode 0 or 3, '1' = SPI Mode 1 or 2) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. Tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for TI debug use after sampling. |
| RTPPUB_ENZ | AA3 |
U2 |
B13,14 | TI internal use. Must be left unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown |
| CRCZ_CHKSUM_SEL | AB3 |
V2 |
B13,14 | Selects whether the Host will use 8-bit CRC or checksum on the Host
Command and Control interface. This value is only applicable for the
Host Command and Control interface. The value for the Diagnostic
Processor monitoring port will be specified in Flash. ('0' = 8-bit CRC, '1' = 8-bit checksum) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. Tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for TI debug use after sampling. |
| ETM_TRACECLK | AB6 |
R10 |
O13 | TI internal use. Must be left unconnected (clock for Trace Debug) |
| ETM_TRACECTL | AB7 |
R9 |
O13 | TI internal use. Must be left unconnected (control for Trace Debug) |
| TSTPT_0 | Y4 |
R3 |
B13,14 | Test pin 0 / STAY-IN-BOOT: Selects whether the system must stay in the Boot Application, or proceed with the normal load of the Main Application. ('0' = Load Main Application, '1' = Stay in Boot Application) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is being used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. Tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for debug use after sampling as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_1 | AA4 |
R4 |
B13,14 | Test pin 1: This pin must be externally pulled down, left open or unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown. It can be driven as an output for debug use as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_2 | Y5 |
R5 |
B13,14 | Test pin 2: This pin must be externally pulled down, left open or unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown. It can be driven as an output for debug use as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_3 | AA5 |
R7 |
B13,14 | Test pin 3:
This pin must be externally pulled down, left open or unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown. It can be driven as an output for debug use as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_4 | Y6 |
P4 |
B13,14 | Test pin 4: This pin must be externally pulled down, left open or unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown. It can be driven as an output for debug use as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_5 | AA6 |
R8 |
B13,14 | Test pin 5 / Spread Spectrum Disable: Selects whether spread spectrum flash settings are used or whether spread spectrum clocking will be disabled. ('0' = Spread Spectrum Disabled, '1' = Use flash Spread Spectrum settings) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is being used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. This signal is tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for debug use after sampling as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_6 | Y7 |
P6 |
B13,14 | Test pin 6: An external pullup resistor must be used (≤ 8kΩ because pin includes a weak pulldown). This signal is tristated while RESETZ is asserted low, and is sampled as a host directive approximately 1.5µs after RESETZ is deasserted. It can be driven as an output for debug use after sampling as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| TSTPT_7 | AA7 |
P7 |
B13,14 | Test pin 7: This pin must be externally pulled down, left open or unconnected. Includes a weak pulldown. It can be driven as an output for debug use as described in Section 7.3.11. |
| HWTEST_EN | H3 |
J5 |
I14 | Manufacturing test enable signal. This signal must be connected directly to ground on the PCB. Includes a weak internal pulldown and hysteresis |
| JTAGTCK | G22 |
H17 |
I11 | JTAG Serial Data Clock Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTMS1 | G21 |
H16 |
I11 | JTAG Test Mode
Select Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTRSTZ | L20 |
G16 |
I11 | JTAG Reset
Includes a weak internal pullup and Hysteresis. For normal operation, this pin must be pulled to ground through an external 8kΩ or less resistor. Failure to pull this pin low during normal operation will cause start-up and initialization problems. For JTAG Boundary Scan, this pin must be pulled-up or left disconnected. |
| JTAGTDI | K20 |
G17 |
I11 | JTAG Serial Data In Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTDO1 | J20 |
G15 |
B10,11 | JTAG Serial Data
Out Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTDO2 | H20 | F18 | B10,11 | This pin must be left open or unconnected. Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTDO3 | G20 |
F17 |
B10,11 | This pin must be left open or unconnected. Includes a weak internal pullup |
| JTAGTMS2 | N20 | H15 | I11 | This pin must be left open or unconnected. Includes a weak internal pullup. See Section 7.3.11 for important debug access considerations. |
| JTAGTMS3 | M20 | G18 | I11 | This pin must be left open or unconnected. Includes a weak internal pullup. See Section 7.3.11 for important debug access considerations. |
| PIN (1) | I/O(2) | DESCRIPTION PARALLEL RGB MODE |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| PCLK | R22 |
M18 |
I11 | Pixel clock |
| VSYNC | H21 |
J18 |
I11 | Vsync(3) |
| HSYNC | H22 |
H18 |
I11 | Hsync(3) |
| DATEN | P21 |
M17 |
I11 | Data Valid |
| (TYPICAL RGB 888) | ||||
| PDATA_0 PDATA_1 PDATA_2 PDATA_3 PDATA_4 PDATA_5 PDATA_6 PDATA_7 |
AA21 AA22 Y21 W21 Y22 V21 W22 U21 |
V17 U17 U18 T17 T18 R17 R18 P17 |
I11 | Blue (bit weight 1) Blue (bit weight 2) Blue (bit weight 4) Blue (bit weight 8) Blue (bit weight 16) Blue (bit weight 32) Blue (bit weight 64) Blue (bit weight 128) |
| (TYPICAL RGB 888) | ||||
| PDATA_8 PDATA_9 PDATA_10 PDATA_11 PDATA_12 PDATA_13 PDATA_14 PDATA_15 |
V22 T21 U22 R21 T22 P22 N21 N22 |
P18 N18 P16 N16 N17 M16 L18 L17 |
I11 | Green (bit weight 1) Green (bit weight 2) Green (bit weight 4) Green (bit weight 8) Green (bit weight 16) Green (bit weight 32) Green (bit weight 64) Green (bit weight 128) |
| (TYPICAL RGB 888) | ||||
| PDATA_16 PDATA_17 PDATA_18 PDATA_19 PDATA_20 PDATA_21 PDATA_22 PDATA_23 |
M22 M21 L22 L21 K22 K21 J22 J21 |
L16 K18 K17 K16 K15 J17 J16 J15 |
I11 | Red (bit weight 1) Red (bit weight 2) Red (bit weight 4) Red (bit weight 8) Red (bit weight 16) Red (bit weight 32) Red (bit weight 64) Red (bit weight 128) |
| PIN (1)(2) | I/O(3) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK325 |
||
| L1_CLK_P L1_CLK_N |
AB11 AA11 |
V6 U6 |
I18 | OpenLDI (FPD Link I) Port 1 Clock Lane |
| L1_DATA0_P L1_DATA0_N L1_DATA1_P L1_DATA1_N L1_DATA2_P L1_DATA2_N L1_DATA3_P L1_DATA3_N |
AB9 AA9 AB10 AA10 AB12 AA12 AB13 AA13 |
V4 U4 V5 U5 V7 U7 V8 U8 |
I18 | OpenLDI (FPD Link I) Port 1 Data Lanes: Intraport data lane swapping can be done on a product configuration basis to support board considerations. |
| L2_CLK_P L2_CLK_N |
AB17 AA17 |
V12 U12 |
I18 | OpenLDI (FPD Link I) Port 2 Clock Lane |
| L2_DATA0_P L2_DATA0_N L2_DATA1_P L2_DATA1_N L2_DATA2_P L2_DATA2_N L2_DATA3_P L2_DATA3_N |
AB15 AA15 AB16 AA16 AB18 AA18 AB19 AA19 |
V10 U10 V11 U11 V13 U13 V14 U14 |
I18 | OpenLDI (FPD Link I) Port 2 Data Lanes: Intraport data lane swapping can be done on a product configuration basis to support board considerations. |
| PIN (1)(2) | I/O(3) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| DMD_DEN_ARSTZ | D11 |
D9 |
O1 | DMD driver enable signal ('1' = Enabled, '0' = Reset) This signal will be driven low after the DMD is parked and before power is removed from the DMD. If the 1.8V power to the DLPC23xS-Q1 is independent of the 1.8V power to the DMD, then an external pulldown resistor (≤ 2.2kΩ) must be used to hold the signal low in the event DLPC23xS-Q1 power is inactive while DMD power is applied. |
| DMD_LS0_CLK | C11 | C9 | O2 | TI internal use. Must be left unconnected |
| DMD_LS0_WDATA | C10 | D8 | O2 | TI internal use. Must be left unconnected |
| DMD_LS0_RDATA | C9 |
C7 |
I3 | DMD, low-speed single-ended serial read data |
| DMD_LS1_RDATA | C8 |
C8 |
I3 | DMD, low-speed single-ended serial read data (Training data response for second port of DMD) |
| DMD_LS0_CLK_P DMD_LS0_CLK_N |
B12 A12 |
B10 A10 |
O4 | DMD low-speed differential interface clock |
| DMD_LS0_WDATA_P DMD_LS0_WDATA_N |
B11 A11 |
B9 A9 |
O4 | DMD low-speed differential interface write data |
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| DMD_HS0_CLK_P DMD_HS0_CLK_N |
B17 A17 |
B15 A15 |
O4 | DMD high-speed interface, Port 0 Clock Lane. |
| DMD_HS0_WDATA0_P DMD_HS0_WDATA0_N DMD_HS0_WDATA1_P DMD_HS0_WDATA1_N DMD_HS0_WDATA2_P DMD_HS0_WDATA2_N DMD_HS0_WDATA3_P DMD_HS0_WDATA3_N DMD_HS0_WDATA4_P DMD_HS0_WDATA4_N DMD_HS0_WDATA5_P DMD_HS0_WDATA5_N DMD_HS0_WDATA6_P DMD_HS0_WDATA6_N DMD_HS0_WDATA7_P DMD_HS0_WDATA7_N |
B21 A21 B20 A20 B19 A19 B18 A18 B16 A16 B15 A15 B14 A14 B13 A13 |
D17 D18 C17 C18 B17 A17 B16 A16 B14 A14 B13 A13 B12 A12 B11 A11 |
O4 | DMD high-speed interface, Port 0 Data Lanes: The true numbering and application of the DMD_HS_DATA pins are software configuration dependent as discussed in Section 7.3.3. |
| DMD_HS1_CLK_P DMD_HS1_CLK_N |
B6 A6 |
B4 A4 |
O4 | DMD high-speed interface, Port 1 Clock Lane |
| DMD_HS1_WDATA0_P DMD_HS1_WDATA0_N DMD_HS1_WDATA1_P DMD_HS1_WDATA1_N DMD_HS1_WDATA2_P DMD_HS1_WDATA2_N DMD_HS1_WDATA3_P DMD_HS1_WDATA3_N DMD_HS1_WDATA4_P DMD_HS1_WDATA4_N DMD_HS1_WDATA5_P DMD_HS1_WDATA5_N DMD_HS1_WDATA6_P DMD_HS1_WDATA6_N DMD_HS1_WDATA7_P DMD_HS1_WDATA7_N |
B2 A2 B3 A3 B4 A4 B5 A5 B7 A7 B8 A8 B9 A9 B10 A10 |
D2 D1 C2 C1 B2 A2 B3 A3 B5 A5 B6 A6 B7 A7 B8 A8 |
O4 | DMD high-speed interface, Port 1 Data Lanes: The true numbering and application of the DMD_HS_DATA pins are software configuration dependent as discussed in Section 7.3.3. |
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| HOST_IRQ(2) | T20 |
N15 |
O10 | Host interrupt (output
active HIGH) This signal is used to indicate that the DLPC23xS-Q1 has detected a serious error for which the ASIC has initiated an Emergency Shutdown. This is discussed further in . The DLPC23xS-Q1 tristates this output during reset. An external pulldown (≤ 10kΩ) is required to drive this signal to its inactive state. |
| HOST_IIC_SCL | R20 |
M15 |
B12 | I2C Port, Host Command and Control to ASIC, SCL (bidirectional, open-drain): An external pullup is required. |
| HOST_IIC_SDA | P20 |
L15 |
B12 | I2C Port, Host Command and Control to ASIC, SDA (bidirectional, open-drain): An external pullup is required. |
| HOST_SPI_CLK | Y20 |
U16 |
I11 | SPI Port, Host Command and Control to ASIC, clock |
| HOST_SPI_CSZ | W20 |
T16 |
I11 | SPI Port, Host Command and
Control to ASIC, chip select (active low input) An external pullup resistor (≤ 2.2kΩ) is required to avoid a floating chip select input to the ASIC. |
| HOST_SPI_DIN | V20 |
R16 |
I11 | SPI Port, Host Command and Control to ASIC, receive data in |
| HOST_SPI_DOUT | U20 |
P15 |
O10 | SPI Port, Host Command and Control to ASIC, transmit data out |
| FLSH_SPI_CSZ | Y1 |
T1 |
O8 | SPI Port, Control Interface
to Flash device, chip select (active low output) An external pullup resistor (≤ 10kΩ) is required to avoid a floating chip select input to the Flash. |
| FLSH_SPI_CLK | W1 |
U1 |
O8 | SPI Port, Control Interface to Flash device, clock |
| FLSH_SPI_DIO_0 | V2 |
P1 |
B8,9 | SPI Port, Control Interface
to Flash device, transmit and receive data An external pullup resistor (≤ 10kΩ) is required. |
| FLSH_SPI_DIO_1 | W2 |
R2 |
B8,9 | SPI Port, Control Interface
to Flash device, transmit and receive data An external pullup resistor (≤ 10kΩ) is required. |
| FLSH_SPI_DIO_2 | Y2 |
R1 |
B8,9 | SPI Port, Control Interface
to Flash device, transmit and receive data An external pullup resistor (≤ 3.3kΩ) is required. |
| FLSH_SPI_DIO_3 | W3 |
T2 |
B8,9 | SPI Port, Control Interface
to Flash device, transmit and receive data An external pullup resistor (≤ 3.3kΩ) is required. |
| PMIC_INTZ(2) | G3 |
E2 |
I7 | TPS99000S-Q1 interrupt (input
with hysteresis) The ASIC provides a weak internal pullup. |
| PMIC_SPI_CLK | E1 |
F5 |
O6 | SPI Port, General Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1, clock |
| PMIC_SPI_CSZ0 | E2 |
G4 |
O6 | SPI Port, General Control
Interface to TPS99000S-Q1, chip
select 0 (active low output) An external pullup resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid floating chip select inputs to the external SPI device during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_SPI_DIN | F1 |
E3 |
I7 | SPI Port, General Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1, receive data in |
| PMIC_SPI_DOUT | D1 |
E5 |
O6 | SPI Port, General Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1, transmit data out |
| PMIC_AD3_CLK | H2 |
G1 |
O20 | Sequencer Clock / TPS99000S-Q1 primary system
clock An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled behavior during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_AD3_MISO | J2 |
G2 |
I14 | Measurement control interface to TPS99000S-Q1, receive data in |
| PMIC_AD3_MOSI | J1 |
G3 |
O20 | Measurement control
interface to TPS99000S-Q1,
transmit data out An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled behavior during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_LEDSEL_0 | F2 |
F4 |
O6 | LED Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1
An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled illumination during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_LEDSEL_1 | G1 |
E1 |
O6 | LED Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1
An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled illumination during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_LEDSEL_2 | G2 |
F2 |
O6 | LED Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1
An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled illumination during ASIC reset assertion. |
| PMIC_LEDSEL_3 | H1 |
F1 |
O6 | LED Control Interface to TPS99000S-Q1
An external pulldown resistor (≤ 10kΩ) must be used to avoid uncontrolled illumination during ASIC reset assertion. |
| MSTR_SDA | AB5 |
T7 |
B15 | I2C Port, SDA.
(bidirectional, open-drain) An external pullup is required. Typical use of the Master I2C port is communication with temperature sensing devices and an optional EEPROM. The Master I2C I/Os are powered by VCC3IO (3.3V only). |
| MSTR_SCL | AB4 |
R6 |
B15 | I2C Port, SCL.
(bidirectional, open-drain) An external pullup is required. Typical use of the Master I2C port is communication with temperature sensing devices and an optional EEPROM. The Master I2C I/Os are powered by VCC3IO (3.3V only). |
| PIN (1)(3) | I/O(2) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| GPIO_31 | D22 |
E15 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 31 |
| GPIO_30 | E21 |
E16 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 30 |
| GPIO_29 | E22 |
E17 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 29 |
| GPIO_28 | F20 |
E18 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 28 |
| GPIO_27 | F21 |
F15 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 27 |
| GPIO_26 | F22 |
F16 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 26 |
| GPIO_25 | V3 |
P3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 25 |
| GPIO_24 | U3 |
M5 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 24 |
| GPIO_23 | U2 |
N4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 23 |
| GPIO_22 | U1 |
N3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 22 |
| GPIO_21 | T3 |
N2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 21 |
| GPIO_20 | T2 |
M4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 20 |
| GPIO_19 | T1 |
M3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 19 |
| GPIO_18 | R3 |
M2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 18 |
| GPIO_17 | R2 |
M1 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 17 |
| GPIO_16 | R1 |
L4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 16 |
| GPIO_15 | P3 |
L3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 15 |
| GPIO_14 | P2 |
L2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 14 |
| GPIO_13 | P1 |
L1 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 13 |
| GPIO_12 | N3 |
K5 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 12 |
| GPIO_11 | N2 |
K4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 11 |
| GPIO_10 | N1 |
K3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 10 |
| GPIO_09 | M3 |
K2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 09 |
| GPIO_08 | M2 |
K1 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 08 |
| GPIO_07 | M1 |
J4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 07 |
| GPIO_06 | L3 |
J3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 06 |
| GPIO_05 | L2 |
H2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 05 |
| GPIO_04 | L1 |
H3 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 04 |
| GPIO_03 | K3 |
J2 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 03 |
| GPIO_02 | K2 |
H1 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 02 |
| GPIO_01 | K1 |
J1 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 01 |
| GPIO_00 | J3 |
H4 |
B20,14 | General purpose I/O 00 |
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 |
ZEK324 |
||
| PLL_REFCLK_I | D15 |
D12 |
I17 | Reference clock crystal input. If an external oscillator is used in place of a crystal, this pin must be left unconnected (floating with no added capacitive load). |
| PLL_REFCLK_O | D14 |
D13 |
B16,17 | Reference clock crystal return. If an external oscillator is used in place of a crystal, this pin must be used for the oscillator input. |
| OSC_BYPASS | D16 |
C13 |
I19 | Selects whether an external
crystal or external oscillator will be used to drive the internal
PLL. ('0' = Crystal, '1' = Oscillator) This pin includes a weak internal pulldown. If a pullup is used to obtain a '1' value, the pullup value must be ≤ 8kΩ. |
| PIN | I/O(1) | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | ZDQ324 | ZEK324 | ||
| VCC18A_LVDS | B1, B22, C1, C22, D2, D3, D4, D5, D7, D18, D19, D20, D21, E20 |
B1, B18, C4, C6, C15, D3, D5, D14, D16, E13, F7, F8, F10, F12 |
PWR | 1.8V Power for the differential High-Speed and Low-Speed DMD Interfaces |
| GND18A_LVDS | A1, A22, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C16, C17, C18, C19, C20, C21, D8 |
A1, A18, C3, C5, C14, C16, D6, E8, E10, E12, E14, F6 |
RTN | 1.8V GND for the differential High-Speed and Low-Speed DMD Interfaces |
| VCC18IO | D10 |
E9 |
PWR | 1.8V Power for 1.8V IO |
| VCC3IO_MVGP | H4 |
G5, H5 |
PWR | 3.3V Power for TPS99000S-Q1 Interfaces |
| VCC3IO_FLSH | V4 |
N5, P5 |
PWR | 3.3V Power for the Serial Flash Interface |
| VCC3IO_INTF | K19, L19, M19, R19, T19 |
H14, L14, J14, M14 |
PWR | 3.3V Power for the Parallel Data, JTAG, and Host Command Interfaces |
| VCC3IO_COSC | C15 |
E11 |
PWR | 3.3V I/O Power for the Crystal Oscillator |
| GNDIOLA_COSC | C14 |
C12 |
RTN | 3.3V I/O GND for the Crystal Oscillator |
| VCC3IO | J4, K4, M4, N4, P4, W4, W5, G19 |
F14, G14, K6, L5, M6, N7, P8 |
PWR | 3.3V I/O Power for all "other" I/O (such as GPIO, TSTPT, PMIC_AD3) |
| VCC33A_LVDS | W9, W13, W15, W19, Y9, Y13, Y15, Y19 |
T3, T4, T8, T10, R11, T12, R13, T14, R15, V16 |
PWR | 3.3V I/O Power for the OpenLDI Interface |
| GND33A_LVDS | W14, Y14, AA8, AA14, AA20, AB8, AB14, AB20, AB21 |
R12, R14, T5, T6, T9, T11, T13, T15, U3, U9, U15, V3, V9, V15 |
RTN | 3.3V I/O GND for the OpenLDI Interface |
| VCC11AD_PLLM | D13 |
D11 |
PWR | 1.1V Analog/Digital Power for MCG (Master Clock Generator) PLL |
| GND11AD_PLLM | C13 |
C11 |
RTN | 1.1V Analog/Digital GND for MCG (Master Clock Generator) PLL |
| VCC11AD_PLLD | D12 |
C10 |
PWR | 1.1V Analog/Digital Power for DCG (DMD Clock Generator) PLL |
| GND11AD_PLLD | C12 |
D10 |
RTN | 1.1V Analog/Digital GND for DCG (DMD Clock Generator) PLL |
| VCC11A_DDI_0 | E19, F19 |
F13, G13 |
PWR | 1.1V Filtered Core Power - External Filter Group A (HS DMD Interface 0) |
| VCC11A_DDI_1 | E4, F4 |
E6, E7 |
PWR | 1.1V Filtered Core Power - External Filter Group B (HS DMD Interface 1) |
| VCC11A_LVDS | W11, W12, W17, W18 |
N10, P11, P12, P13, P14 |
PWR | 1.1V Filtered Core Power - External Filter Group C (OpenLDI Interface) |
| VCCK | G4, H19, (J11), J19, L4, N19, P19, T4, U4, U19, V19, W6, W8, W10, W16 |
F9, F11, G6, H13, K13, L6, J6, M13, N6, N8, N9, N11 |
PWR | 1.1V Core Power (Ball numbers in parenthesis are also used as thermal ball and are located within the package center region) |
| GND | (J9, J10, J12, J13, J14, K9, K10, K11, K12, K13, K14, L9, L10, L11, L12, L13, L14, M9, M10, M11, M12, M13, M14, N9, N10, N11, N12, N13, N14, P9, P10, P11, P12, P13,P14), Y3, AA1, AA2, AB1, AB2, AB22, Y10, Y11, Y12, Y16, Y17, Y18 |
(G7, G8, G9, G10, G11, G12, H7, H8, H9, H10, H11, H12, J7, J8, J9, J10, J11, J12, K7, K8, K9, K10, K11, K12, L7, L8, L9, L10, L11, L12, M7, M8, M9, M10, M11, M12), H6, J13, K14, L13, N12, N13, N14, V1, V18 |
RTN | 1.1V Core GND (Ball numbers in parenthesis are also used as thermal ball and are located within the package center region) |
| EFUSE_VDDQ | W7 |
P9 |
Manufacturing use only. Must be tied to ground | |
| EFUSE_POR33 | Y8 |
P10 |
Manufacturing use only. Must be tied to ground | |
| RPI_0 | D17 |
D15 |
I5 | Bandgap Reference for SubLVDS drivers (Supports DMD_HS0_xxxx). Requires a resistor (1% Tolerance) to GND18A_LVDS - Value specified in Table 8-4. |
| RPI_1 | D6 |
D4 |
I5 | Bandgap Reference for SubLVDS drivers (Supports DMD_HS1_xxxx). Requires a resistor (1% Tolerance) to GND18A_LVDS - Value specified in Table 8-4. |
| RPI_LS | D9 |
D7 |
I5 | Bandgap References for SubLVDS drivers (Supports DMD_LS0_xxxx differential bus signals). Requires a resistor (1% Tolerance) to GND18A_LVDS - Value specified in Table 8-4. |
| I/O(1) | SUPPLY REFERENCE | ESD STRUCTURE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUBSCRIPT | DESCRIPTION | ||
| 1 | 1.8V LVCMOS Input | VCC18IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 2 | 1.8V LVCMOS Output | VCC18IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 3 | 1.8V LVCMOS Input | VCC18IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 4 | 1.8V SubLVDS Output | VCC18A_LVDS | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 5 | 1.8V SubLVDS Input | VCC18A_LVDS | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 6 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO_MVGP | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 7 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO_MVGP | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 8 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO_FLSH | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 9 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO_FLSH | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 10 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO_INTF | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 11 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO_INTF | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 12 | 3.3V I2C I/O | VCC3IO_INTF | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 13 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 14 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 15 | 3.3V I2C I/O with 3mA drive | VCC3IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 16 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO_OSC | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 17 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO_OSC | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 18 | 3.3V LVDS Input | VCC33A_LVDS | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 19 | 3.3V LVCMOS Input | VCC3IO_OSC | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| 20 | 3.3V LVCMOS Output | VCC3IO | ESD diode to GND and supply rail |
| TYPE | |||
| I | Input | N/A | |
| O | Output | ||
| B | Bidirectional | ||
| PWR | Power | ||
| RTN | Ground return | ||
| INTERNAL PULLUP AND PULLDOWN RESISTOR CHARACTERISTICS (1)(2) |
VCCIO | MIN | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak pullup resistance | 3.3V | 40 | 190 | kΩ |
| Weak pulldown resistance | 3.3V | 30 | 190 | kΩ |