DLPS231B October 2021 – October 2024 DLPC3421
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Power Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Pin Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Internal Pullup and Pulldown Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 DMD Sub-LVDS Interface Electrical Characteristics
- 5.9 DMD Low-Speed Interface Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 System Oscillator Timing Requirements
- 5.11 Power Supply and Reset Timing Requirements
- 5.12 Parallel Interface Video Frame Timing Requirements
- 5.13 Parallel Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.14 DSI Host Timing Requirements
- 5.15 Flash Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.16 Other Timing Requirements
- 5.17 DMD Sub-LVDS Interface Switching Characteristics
- 5.18 DMD Parking Switching Characteristics
- 5.19 Chipset Component Usage Specification
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Features and System Configuration
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- 13Package Option Addendum
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZVB|176
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
8.2 System Power-Up and Power-Down Sequence
Although the DLPC3421 controller requires an array of power supply voltage pins (for example, VDD, VDDLP12, VDD_PLLM/D, VCC18, VCC_FLSH, and VCC_INTF) if VDDLP12 is tied to the 1.1V VDD supply (which is assumed to be the typical configuration), then there are no restrictions regarding the relative order of power supply sequencing to avoid damaging the DLPC3421 controller (this remains true for both power-up and power-down scenarios). The controller requires no minimum delay time between powering up and powering down the individual supplies if the VDDLP12 is tied to the 1.1V VDD supply.
However, if the VDDLP12 pin is not tied to the VDD supply, then the VDDLP12 pin must be powered on only after the VDD supply is powered on. In a similar sequence, the VDDLP12 pin must be powered off before the VDD supply is powered off. If the VDDLP12 pin is not tied to VDD, then the VDDLP12 pin and VDD supply pins must be powered on or powered off within 100ms of each other.
Although there is no risk of damaging the DLPC3421 controller when the above power sequencing rules are followed, these additional power sequencing recommendations must be considered to ensure proper system operation:
- To ensure that the DLPC3421 controller output signal states behave as expected, all controller I/O supplies are encouraged to remain applied while VDD core power is applied. If VDD core power is removed while the I/O supply (VCC_INTF) is applied, then the output signal states associated with the inactive I/O supply go to a high impedance state.
- Because additional power sequencing rules may exist for devices that share the supplies with the DLPC3421 controller (such as the PMIC and DMD), these devices may force additional system power sequencing requirements.
Figure 8-1, Figure 8-2, Figure 8-3, Figure 8-4, Figure 8-5, and Figure 8-6 show the waveforms for the corresponding power-up, power-down, normal park, and fast park sequences of the DLPC3421 for both nHD Mode and HD Mode.
When the VDD core power is applied, but I/O power is not applied, the controller may draw additional leakage current. This leakage current does not affect the normal DLPC3421 controller operation or reliability.
During a Normal Park, it is recommended to maintain SYSPWR within specification for at least 50ms after PROJ_ON goes low. Doing so allows the DMD to be parked and the power supply rails to safely power down. After 50ms, SYSPWR can be turned off. If a DLPA200x is used, it is also recommended that the 1.8V supply fed into the DLPA200x load switch be maintained within specification for at least 50ms after PROJ_ON goes low.
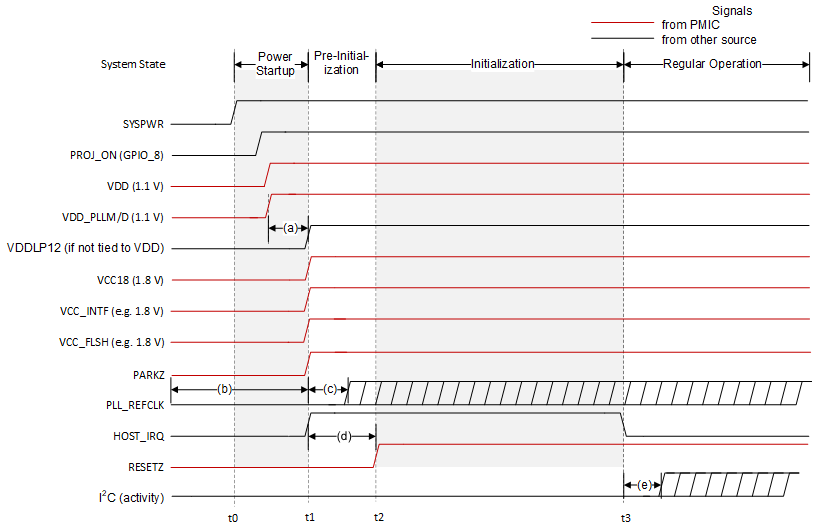
| t0: | SYSPWR applied to the PMIC. All other voltage rails are derived from SYSPWR. |
| t1: | All supplies reach 95% of their specified nominal value. Note HOST_IRQ may go high sooner if it is pulled up to a different external supply. |
| t2: | The point where RESETZ is deasserted (goes high). This indicates the beginning of the controller auto-initialization routine. |
| t3: | HOST_IRQ goes low to indicate initialization is complete. |
| (a): | VDDLP12 must be powered on after VDD if it is supplied from a separate source. |
| (b): | PLL_REFCLK is allowed to be active before power is applied. |
| (c): | PLL_REFCLK must be stable within 5ms of all power being applied. For external oscillator applications, this is oscillator dependent, and for crystal applications, this is crystal and controller oscillator cell dependent. |
| (d): | PARKZ must be high before RESETZ releases to support auto-initialization. RESETZ must also be held low for at least 5ms after the power supplies are in specification. |
| (e): | I2C activity cannot start until HOST_IRQ goes low to indicate auto-initialization completes. |
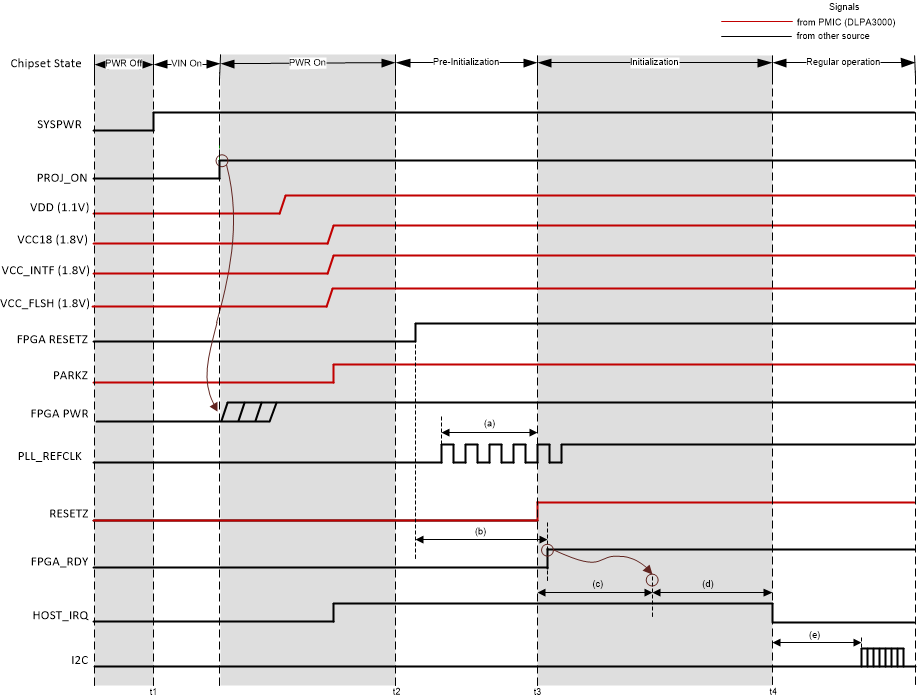
Figure 8-2 System Power-Up Waveforms for HD Mode
| t1: | SYSPWR (VIN) applied to the PMIC. All other voltage rails are derived from SYSPWR. |
| t2: | All supplies reach 95% of their specified nominal value. Note HOST_IRQ may go high sooner if it is pulled up to a different external supply. |
| t3: | The point where RESETZ is deasserted (goes high). This indicates the beginning of the controller auto-initialization routine. |
| t4: | HOST_IRQ goes low to indicate initialization is complete. I2C is now ready to accept commands. |
| (a): | The typical delay between the PLL reference clock becoming active and RESETZ being deasserted (going high) is less than 1ms. PLL_REFCLK must be stable within 5ms of all power being applied, and may be active before power is applied. |
| (b): | There is a typical delay of 1.5 s between FPGA RESETZ being deasserted and FPGA_RDY being asserted (going high). This duration is due to FPGA boot logic. |
| (c): | There is a typical controller boot time of 100ms. PARKZ must be high before RESETZ releases to support auto-initialization. RESETZ must also be held low for at least 5ms after the power supplies are in specification. |
| (d): | There is a typical FPGA setup time of 2.75ms before the system completes boot process. During this period, the DLPC3421 controller writes startup values to the FPGA registers. |
| (e): | After the FPGA setup is complete, I2C now accepts commands. |
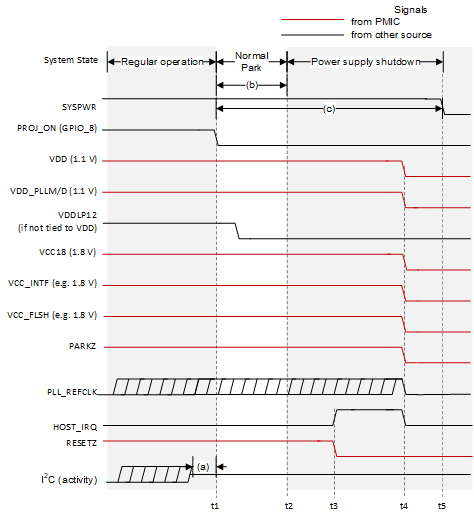
| t1: | PROJ_ON goes low to begin the power-down sequence. |
| t2: | The controller finishes parking the DMD. |
| t3: | RESETZ is asserted which causes HOST_IRQ to be pulled high. |
| t4: | All controller power supplies are turned off. |
| t5: | SYSPWR is removed now that all other supplies are turned off. |
| (a): | I2C activity must stop before PROJ_ON is deasserted (goes low). |
| (b): | The DMD will be parked within 20ms of PROJ_ON being deasserted (going low). VDD, VDD_PLLM/D, VCC18, VCC_INITF, and VCC_FLSH power supplies and the PLL_REFCLK must be held within specification for a minimum of 20ms after PROJ_ON is deasserted (goes low). However, 20ms does not satisfy the typical shutdown timing of the entire chipset. It is therefore recommended to follow note (c). |
| (c): | It is recommended that SYSPWR not be turned off for 50ms after PROJ_ON is deasserted (goes low). This time allows the DMD to be parked, the controller to turn off, and the PMIC supplies to shut down. |
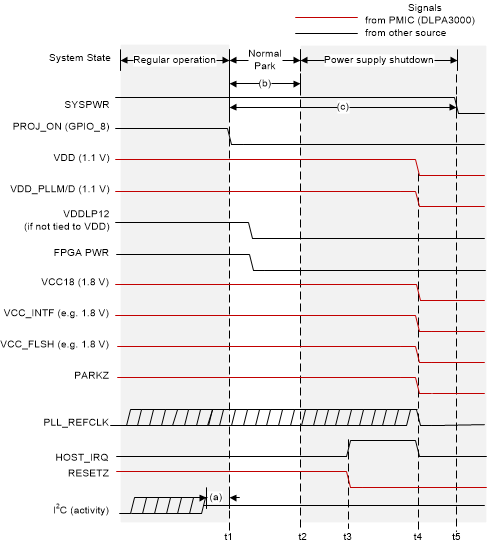
Figure 8-4 Normal Park Power-Down Waveforms for HD Mode
| t1: | PROJ_ON goes low to begin the power-down sequence. |
| t2: | The controller finishes parking the DMD. |
| t3: | Controller power supplies are turned off. |
| (a): | The DMD will be parked within 20ms of PROJ_ON being deasserted (going low). VDD, VDD_PLLM/D, VCC18, VCC_INITF, and VCC_FLSH power supplies and the PLL_REFCLK must be held within specification for a minimum of 20ms after PROJ_ON is deasserted (goes low). However, 20ms does not satisfy the typical shutdown timing of the entire chipset. It is therefore recommended to follow note (c). |
| (b): | DMD reset voltage regulation stops typically after 12ms of normal DMD park being completed. |
| (c): | It is recommended that SYSPWR not be turned off for 50ms after PROJ_ON is deasserted (goes low). This time allows the DMD to be parked, the controller to turn off, and the PMIC supplies to shut down. |
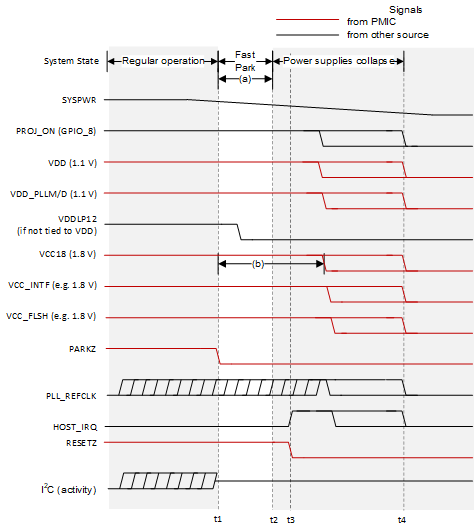
| t1: | A fault is detected (in this example the PMIC detects a UVLO condition) and PARKZ is asserted (goes low) to tell the controller to initiate a fast park of the DMD. |
| t2: | The controller finishes the fast park procedure. |
| t3: | RESETZ is asserted which puts the controller in a reset state which causes HOST_IRQ to be pulled high. |
| t4: | Eventually, all power supplies that were derived from SYSPWR collapse. |
| (a): | VDD, VDD_PLLM/D, VCC18, VCC_INITF, and VCC_FLSH power supplies and the PLL_REFCLK must be held within specification for a minimum of 32µs after PARKZ is asserted (goes low). |
| (b): | VCC18 must remain in specification long enough to satisfy DMD power sequencing requirements defined in the DMD data sheet. Also see the DLPA200x data sheets for more information. |
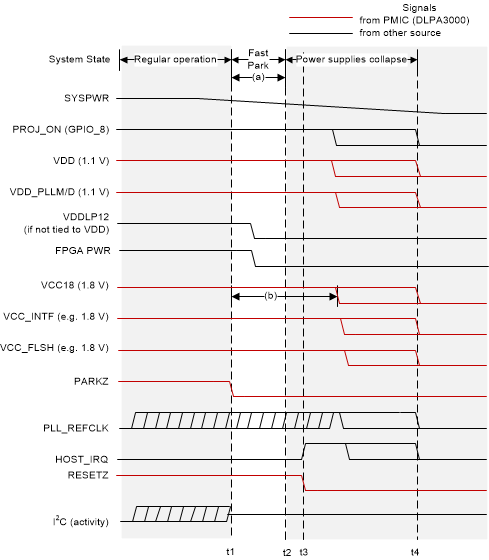
| t1: | A fault is detected and PARKZ is asserted (goes low) to tell the controller to initiate a fast park of the DMD. |
| t2: | The controller finishes the fast park procedure. |
| t3: | Eventually all power supplies that were derived from SYSPWR collapse. |
| t4: | System is completely turned off. |
| (a): | VDD, VDD_PLLM/D, VCC18, VCC_INTF, and VCC_FLSH power supplies and the PLL_REFCLK must be held within specification for a minimum of 32μs after PARKZ is asserted (goes low). |
| (b): | VCC18 must remain in specification long enough to satisfy DMD power sequencing requirements defined in the DMD datasheet. Also see the DLPAxxxx data sheets for more information. |