DLPS271 April 2024 DLPC7530
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Power Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 Pin Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 DMD HSSI Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 DMD Low-Speed LVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 5.9 V-by-One Interface Electrical Characteristics
- 5.10 FPD-Link LVDS Electrical Characteristics
- 5.11 USB Electrical Characteristics
- 5.12 System Oscillator Timing Requirements
- 5.13 Power Supply and Reset Timing Requirements
- 5.14 DMD HSSI Timing Requirements
- 5.15 DMD Low-Speed LVDS Timing Requirements
- 5.16 V-by-One Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.17 FPD-Link Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.18 Parallel Interface General Timing Requirements
- 5.19 Source Frame Timing Requirements
- 5.20 Synchronous Serial Port Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.21 Controller and Target I2C Interface Timing Requirements
- 5.22 Programmable Output Clock Timing Requirements
- 5.23 JTAG Boundary Scan Interface Timing Requirements (Debug Only)
- 5.24 JTAG ARM Multi-Ice Interface Timing Requirements (Debug Only)
- 5.25 Multi-Trace ETM Interface Timing Requirements
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
-
9 Layout
- 9.1
Layout Guidelines
- 9.1.1 General Layout Guidelines
- 9.1.2 Power Supply Layout Guidelines
- 9.1.3 Layout Guidelines for Internal Controller PLL Power
- 9.1.4 Layout Guideline for DLPC7530 Reference Clock
- 9.1.5 V-by-One Interface Layout Considerations
- 9.1.6 FPD-Link Interface Layout Considerations
- 9.1.7 USB Interface Layout Considerations
- 9.1.8 DMD Interface Layout Considerations
- 9.1.9 General Handling Guidelines for Unused CMOS-Type Pins
- 9.1.10 Maximum Pin-to-Pin, PCB Interconnects Etch Lengths
- 9.2 Thermal Considerations
- 9.1
Layout Guidelines
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- ZDC|676
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.2 Power Supply Layout Guidelines
The following filtering circuits are recommended for the power supply inputs listed below.
- VAD115_VX1
- VAD18_VX1
- VAD115_FPD
- VDD33_FPD
- VAD33_USB
- VDD18_SCS
Because the PBC layout is critical to the performance of the interfaces associated with these power supplies, it is vital that these power supplies be treated like an analog signal. Specifically:
- Place high-frequency components (such as ferrites and capacitors) as close to the power ball(s) as possible.
- Choose high-frequency ceramic capacitors (such as those with a value of 0.1 µF, 0.01 µF, and 100 nF) that have low ESR and ESL values. Design the leads as short as possible, and as such, place these capacitors under the package on the opposite side of the board.
- For each power pin, a single trace (as wide as possible) must be used from the controller to the capacitor and then through the series ferrite to the power source.
- For each power pin, add a 100-nF decoupling capacitor placed near the escape via. Add this decoupling capacitance to the capacitance recommended for filters. These are minimum recommendations, so different layouts could require additional capacitance.
- See Table 9-1 for the recommended series ferrite component for these supplies.
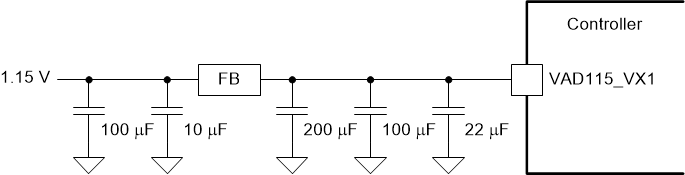 Figure 9-1 VAD115_VX1
(V-by-One) Recommended Filter
Figure 9-1 VAD115_VX1
(V-by-One) Recommended Filter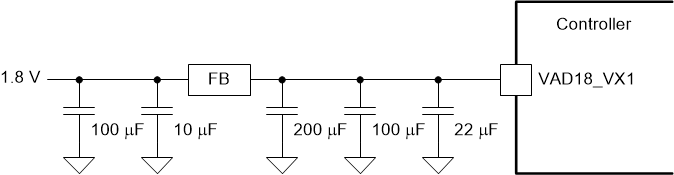 Figure 9-2 VAD18_VX1
(V-by-One) Recommended Filter
Figure 9-2 VAD18_VX1
(V-by-One) Recommended Filter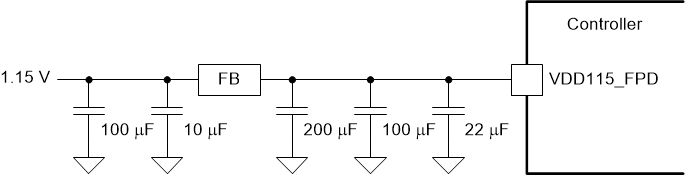 Figure 9-3 VAD115_FPD
(FPD-Link) Recommended Filter
Figure 9-3 VAD115_FPD
(FPD-Link) Recommended Filter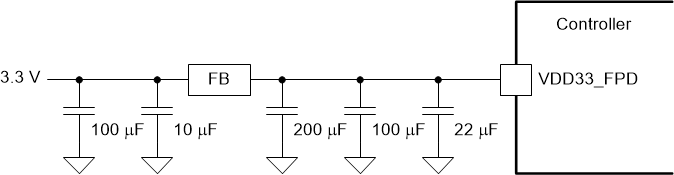 Figure 9-4 VDD33_FPD
(FPD-Link) Recommended Filter
Figure 9-4 VDD33_FPD
(FPD-Link) Recommended Filter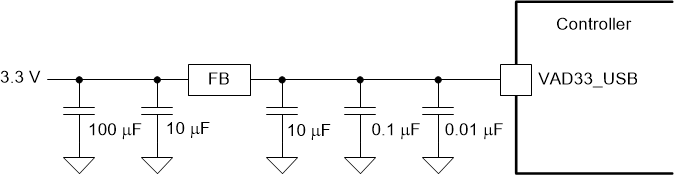 Figure 9-5 VAD33_USB (USB)
Recommended Filter
Figure 9-5 VAD33_USB (USB)
Recommended Filter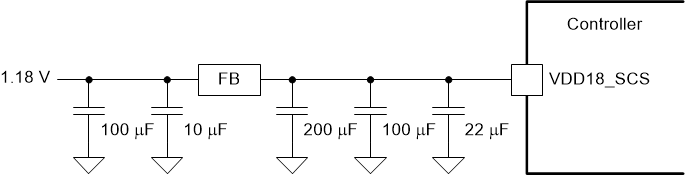 Figure 9-6 VDD18_SCS (SCS
DRAM) Recommended Filter
Figure 9-6 VDD18_SCS (SCS
DRAM) Recommended Filter