SNLS504E October 2015 – May 2024 DP83867CS , DP83867E , DP83867IS
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Power-Up Timing
- 6.7 Reset Timing
- 6.8 MII Serial Management Timing
- 6.9 SGMII Timing
- 6.10 RGMII Timing
- 6.11 DP83867E Start of Frame Detection Timing
- 6.12 DP83867IS/CS Start of Frame Detection Timing
- 6.13 Timing Diagrams
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 MAC Interfaces
- 7.4.2
Serial Management Interface
- 7.4.2.1
Extended Address Space Access
- 7.4.2.1.1 Write Address Operation
- 7.4.2.1.2 Read Address Operation
- 7.4.2.1.3 Write (No Post Increment) Operation
- 7.4.2.1.4 Read (No Post Increment) Operation
- 7.4.2.1.5 Write (Post Increment) Operation
- 7.4.2.1.6 Read (Post Increment) Operation
- 7.4.2.1.7 Example of Read Operation Using Indirect Register Access
- 7.4.2.1.8 Example of Write Operation Using Indirect Register Access
- 7.4.2.1
Extended Address Space Access
- 7.4.3
Auto-Negotiation
- 7.4.3.1 Speed and Duplex Selection - Priority Resolution
- 7.4.3.2 Master and Slave Resolution
- 7.4.3.3 Pause and Asymmetrical Pause Resolution
- 7.4.3.4 Next Page Support
- 7.4.3.5 Parallel Detection
- 7.4.3.6 Restart Auto-Negotiation
- 7.4.3.7 Enabling Auto-Negotiation Through Software
- 7.4.3.8 Auto-Negotiation Complete Time
- 7.4.3.9 Auto-MDIX Resolution
- 7.4.4 Loopback Mode
- 7.4.5 BIST Configuration
- 7.4.6 Cable Diagnostics
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Basic Mode Control Register (BMCR)
- 7.6.2 Basic Mode Status Register (BMSR)
- 7.6.3 PHY Identifier Register #1 (PHYIDR1)
- 7.6.4 PHY Identifier Register #2 (PHYIDR2)
- 7.6.5 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (ANAR)
- 7.6.6 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (ANLPAR) (BASE Page)
- 7.6.7 Auto-Negotiate Expansion Register (ANER)
- 7.6.8 Auto-Negotiation Next Page Transmit Register (ANNPTR)
- 7.6.9 Auto-Negotiation Next Page Receive Register (ANNPRR)
- 7.6.10 1000BASE-T Configuration Register (CFG1)
- 7.6.11 Status Register 1 (STS1)
- 7.6.12 Extended Register Addressing
- 7.6.13 1000BASE-T Status Register (1KSCR)
- 7.6.14 PHY Control Register (PHYCR)
- 7.6.15 PHY Status Register (PHYSTS)
- 7.6.16 MII Interrupt Control Register (MICR)
- 7.6.17 Interrupt Status Register (ISR)
- 7.6.18 Configuration Register 2 (CFG2)
- 7.6.19 Receiver Error Counter Register (RECR)
- 7.6.20 BIST Control Register (BISCR)
- 7.6.21 Status Register 2 (STS2)
- 7.6.22 LED Configuration Register 1 (LEDCR1)
- 7.6.23 LED Configuration Register 2 (LEDCR2)
- 7.6.24 LED Configuration Register (LEDCR3)
- 7.6.25 Configuration Register 3 (CFG3)
- 7.6.26 Control Register (CTRL)
- 7.6.27 Testmode Channel Control (TMCH_CTRL)
- 7.6.28 Robust Auto MDIX Timer Configuration Register (AMDIX_TMR_CFG)
- 7.6.29 Fast Link Drop Configuration Register (FLD_CFG)
- 7.6.30 Fast Link Drop Threshold Configuration Register (FLD_THR_CFG)
- 7.6.31 Configuration Register 4 (CFG4)
- 7.6.32 RGMII Control Register (RGMIICTL)
- 7.6.33 RGMII Control Register 2 (RGMIICTL2)
- 7.6.34 SGMII Auto-Negotiation Status (SGMII_ANEG_STS)
- 7.6.35 100BASE-TX Configuration (100CR)
- 7.6.36 Viterbi Module Configuration (VTM_CFG)
- 7.6.37 Skew FIFO Status (SKEW_FIFO)
- 7.6.38 Strap Configuration Status Register 1 (STRAP_STS1)
- 7.6.39 Strap Configuration Status Register 2 (STRAP_STS2)
- 7.6.40 BIST Control and Status Register 1 (BICSR1)
- 7.6.41 BIST Control and Status Register 2 (BICSR2)
- 7.6.42 BIST Control and Status Register 3 (BICSR3)
- 7.6.43 BIST Control and Status Register 4 (BICSR4)
- 7.6.44 Configuration for Receiver's Equalizer (CRE)
- 7.6.45 RGMII Delay Control Register (RGMIIDCTL)
- 7.6.46 ANA_LD_TXG_FINE_GAINSEL_AB (ALTFGAB)
- 7.6.47 ANA_LD_TXG_FINE_GAINSEL_CD (ALTFGCD)
- 7.6.48 ANA_LD_FILTER_TUNE_AB (ALFTAB)
- 7.6.49 ANA_LD_FILTER_TUNE_CD (ALFTCD)
- 7.6.50 Configuration of Receiver's LPF (CRLPF)
- 7.6.51 Enable Control of Receiver's Equalizer (ECRE)
- 7.6.52 PLL Clock-out Control Register (PLLCTL)
- 7.6.53 SGMII Control Register 1 (SGMIICTL1)
- 7.6.54 Sync FIFO Control (SYNC_FIFO_CTRL)
- 7.6.55 Loopback Configuration Register (LOOPCR)
- 7.6.56 DSP Configuration (DSP_CONFIG)
- 7.6.57 DSP Feedforward Equalizer Configuration (DSP_FFE_CFG)
- 7.6.58 Receive Configuration Register (RXFCFG)
- 7.6.59 Receive Status Register (RXFSTS)
- 7.6.60 Pattern Match Data Register 1 (RXFPMD1)
- 7.6.61 Pattern Match Data Register 2 (RXFPMD2)
- 7.6.62 Pattern Match Data Register 3 (RXFPMD3)
- 7.6.63 SecureOn Pass Register 2 (RXFSOP1)
- 7.6.64 SecureOn Pass Register 2 (RXFSOP2)
- 7.6.65 SecureOn Pass Register 3 (RXFSOP3)
- 7.6.66 Receive Pattern Register 1 (RXFPAT1)
- 7.6.67 Receive Pattern Register 2 (RXFPAT2)
- 7.6.68 Receive Pattern Register 3 (RXFPAT3)
- 7.6.69 Receive Pattern Register 4 (RXFPAT4)
- 7.6.70 Receive Pattern Register 5 (RXFPAT5)
- 7.6.71 Receive Pattern Register 6 (RXFPAT6)
- 7.6.72 Receive Pattern Register 7 (RXFPAT7)
- 7.6.73 Receive Pattern Register 8 (RXFPAT8)
- 7.6.74 Receive Pattern Register 9 (RXFPAT9)
- 7.6.75 Receive Pattern Register 10 (RXFPAT10)
- 7.6.76 Receive Pattern Register 11 (RXFPAT11)
- 7.6.77 Receive Pattern Register 12 (RXFPAT12)
- 7.6.78 Receive Pattern Register 13 (RXFPAT13)
- 7.6.79 Receive Pattern Register 14 (RXFPAT14)
- 7.6.80 Receive Pattern Register 15 (RXFPAT15)
- 7.6.81 Receive Pattern Register 16 (RXFPAT16)
- 7.6.82 Receive Pattern Register 17 (RXFPAT17)
- 7.6.83 Receive Pattern Register 18 (RXFPAT18)
- 7.6.84 Receive Pattern Register 19 (RXFPAT19)
- 7.6.85 Receive Pattern Register 20 (RXFPAT20)
- 7.6.86 Receive Pattern Register 21 (RXFPAT21)
- 7.6.87 Receive Pattern Register 22 (RXFPAT22)
- 7.6.88 Receive Pattern Register 23 (RXFPAT23)
- 7.6.89 Receive Pattern Register 24 (RXFPAT24)
- 7.6.90 Receive Pattern Register 25 (RXFPAT25)
- 7.6.91 Receive Pattern Register 26 (RXFPAT26)
- 7.6.92 Receive Pattern Register 27 (RXFPAT27)
- 7.6.93 Receive Pattern Register 28 (RXFPAT28)
- 7.6.94 Receive Pattern Register 29 (RXFPAT29)
- 7.6.95 Receive Pattern Register 30 (RXFPAT30)
- 7.6.96 Receive Pattern Register 31 (RXFPAT31)
- 7.6.97 Receive Pattern Register 32 (RXFPAT32)
- 7.6.98 Receive Pattern Byte Mask Register 1 (RXFPBM1)
- 7.6.99 Receive Pattern Byte Mask Register 2 (RXFPBM2)
- 7.6.100 Receive Pattern Byte Mask Register 3 (RXFPBM3)
- 7.6.101 Receive Pattern Byte Mask Register 4 (RXFPBM4)
- 7.6.102 Receive Pattern Control (RXFPATC)
- 7.6.103 10M SGMII Configuration (10M_SGMII_CFG)
- 7.6.104 I/O Configuration (IO_MUX_CFG)
- 7.6.105 GPIO Mux Control Register (GPIO_MUX_CTRL)
- 7.6.106 TDR General Configuration Register 1 (TDR_GEN_CFG1)
- 7.6.107 TDR Peak Locations Register 1 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_1)
- 7.6.108 TDR Peak Locations Register 2 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_2)
- 7.6.109 TDR Peak Locations Register 3 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_3)
- 7.6.110 TDR Peak Locations Register 4 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_4)
- 7.6.111 TDR Peak Locations Register 5 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_5)
- 7.6.112 TDR Peak Locations Register 6 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_6)
- 7.6.113 TDR Peak Locations Register 7 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_7)
- 7.6.114 TDR Peak Locations Register 8 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_8)
- 7.6.115 TDR Peak Locations Register 9 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_9)
- 7.6.116 TDR Peak Locations Register 10 (TDR_PEAKS_LOC_10)
- 7.6.117 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 1 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_1)
- 7.6.118 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 2 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_2)
- 7.6.119 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 3 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_3)
- 7.6.120 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 4 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_4)
- 7.6.121 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 5 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_5)
- 7.6.122 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 6 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_6)
- 7.6.123 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 7 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_7)
- 7.6.124 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 8 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_8)
- 7.6.125 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 9 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_9)
- 7.6.126 TDR Peak Amplitudes Register 10 (TDR_PEAKS_AMP_10)
- 7.6.127 TDR General Status (TDR_GEN_STATUS)
- 7.6.128 TDR Peak Sign AB (TDR_PEAK_SIGN_A_B)
- 7.6.129 TDR Peak Sign CD (TDR_PEAK_SIGN_C_D)
- 7.6.130 Programmable Gain Register (PROG_GAIN)
- 7.6.131 MMD3 PCS Control Register (MMD3_PCS_CTRL)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGZ|48
Orderable Information
7.5.1 Strap Configuration
The DP83867 uses many of the functional pins as strap options to place the device into specific modes of operation. The values of these pins are sampled at power up or hard reset. During software resets, the strap options are internally reloaded from the values sampled at power up or hard reset. The strap option pin assignments are defined below. The functional pin name is indicated in parentheses.
The strap pins supported are 4-level straps, which are described in greater detail below.
Because strap pins may have alternate functions after reset is deasserted, they should not be connected directly to VDD or GND.
Configuration of the device may be done through the 4-level strap pins or through the management register interface. A pullup resistor and a pulldown resistor of suggested values may be used to set the voltage ratio of the 4-level strap pin input and the supply to select one of the possible selected modes.
The MAC interface pins must support I/O voltages of 3.3V, 2.5V, and 1.8V. As the strap inputs are implemented on these pins, the straps must also support operation at 3.3V, 2.5V, and 1.8V supplies.
For more information about configuring 4-level straps, see the Configuring Ethernet Devices with 4-Level Straps application report (SNLA258).
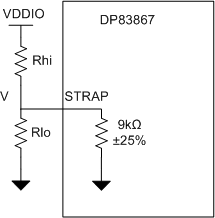 Figure 7-10 Strap Circuit
Figure 7-10 Strap Circuit| MODE | TARGET VOLTAGE | IDEAL Rhi (kΩ) | IDEAL Rlo (kΩ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vmin (V) | Vtyp (V) | Vmax (V) | |||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.098 × VDDIO | OPEN | OPEN |
| 2 | 0.140 × VDDIO | 0.165 × VDDIO | 0.191 × VDDIO | 10 | 2.49 |
| 3 | 0.225 × VDDIO | 0.255 × VDDIO | 0.284 × VDDIO | 5.76 | 2.49 |
| 4 | 0.694 × VDDIO | 0.783 × VDDIO | 0.888 × VDDIO | 2.49 | OPEN |
For SGMII Mode 4 strap, TI recommends using Rhi = 4kΩ and Rlo = 10kΩ on RX_D0 and RX_D1 , RX_D2 and RX_D3.
All straps have a 9kΩ ±25% internal pulldown resistor. The voltage at strap pins should be between the Vmin and Vmax mentioned in the Target Voltage column in Table 7-5. Strap resistors with 1% tolerance are recommended.
The following tables describes the DP83867 configuration straps:
| PIN NAME | 48VQFN PIN # | DEFAULT | STRAP FUNCTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RX_D0 | 33 | [00] | MODE | PHY_ADD1 | PHY_ADD0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| RX_D2 | 35 | [00] | MODE | PHY_ADD3 | PHY_ADD2 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| RX_CTRL (1) | 38 | [00] | MODE | Autoneg Disable | |
| 1 | N/A | ||||
| 2 | N/A | ||||
| 3 | 0 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | ||||
| GPIO_0 (2) | 39 | [00] | MODE | RGMII Clock Skew RX[0] | |
| 1 | 0 | ||||
| 2 | Not Applicable | ||||
| 3 | 1 | ||||
| 4 | Not Applicable | ||||
| GPIO_1 | 40 | [00] | MODE | RGMII Clock Skew RX[2] | RGMII Clock Skew RX[1] |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| LED_2 | 45 | [00] | MODE | RGMII Clock Skew TX[1] | RGMII Clock Skew TX[0] |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| LED_1 | 46 | [00] | MODE | ANEG_SEL | RGMII Clock Skew TX[2] |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| LED_0 | 47 | [00] | MODE | Mirror Enable | SGMII Enable |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 1 | 0 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
RX_D1 is not a strap input, but this pin must be populated with the same strap resistors chosen for RX_D0. RX_D0 and RX_D1 form an SGMII differential pair. The dummy straps on RX_D1 are required to provide a balanced load for this SGMII differential pair.
RX_D3 is not a strap input, but this pin must be populated with the same strap resistors chosen for RX_D2. RX_D2 and RX_D3 form an SGMII differential pair. The dummy straps on RX_D3 are required to provide a balanced load for this SGMII differential pair.
| MODE | ANEG_SEL | REMARKS |
|---|---|---|
| 10/100/1000 | 0 | advertise ability of 10/100/1000 |
| 100/1000 | 1 | advertise ability of 100/1000 only |
| MODE | RGMII CLOCK SKEW TX[2] | RGMII CLOCK SKEW TX[1] | RGMII CLOCK SKEW TX[0] | RGMII TX CLOCK SKEW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0ns |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.5ns |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1.0ns |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5ns |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0ns |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3.5ns |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3.0ns |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2.5ns |
| MODE | RGMII CLOCK SKEW RX[2] | RGMII CLOCK SKEW RX[1] | RGMII CLOCK SKEW RX[0] | RGMII RX CLOCK SKEW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0ns |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.5ns |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1.0ns |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5ns |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0ns |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3.5ns |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3.0ns |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2.5ns |