SNLS654C April 2021 – November 2024 DP83TC812R-Q1 , DP83TC812S-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|36
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|36
Orderable Information
7.4.12.1 Media Independent Interface
The Media Independent Interface (MII) is a synchronous 4-bit wide nibble data interface that connects the PHY to the MAC. The MII is fully compliant with IEEE 802.3-2015 clause 22. The PHY has internal series termination resistors on MII output pins including TX_CLK output when the PHY is operating in MII mode. In this mode, it is recommended to not leave the MII-TX pins floating or High-Z.
The MII signals are summarized in Table 7-4:
Table 7-4 MII Signals
| FUNCTION | PINS |
|---|---|
| Data Signals | TX_D[3:0] |
| RX_D[3:0] | |
| Control Signals | TX_EN, TX_ER |
| RX_DV, RX_ER | |
| Clock Signals | TX_CLK |
| RX_CLK |
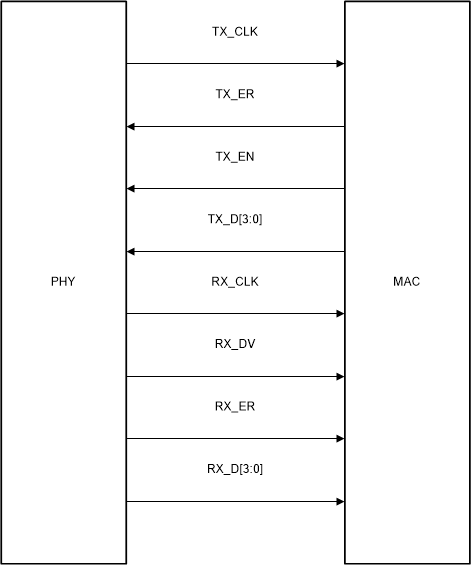 Figure 7-14 MII Signaling
Figure 7-14 MII SignalingTable 7-5 MII Transmit Encoding
| TX_EN | TX_ER | TX_D[3:0] | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0000 through 1111 | Normal Inter-Frame |
| 0 | 1 | 0000 through 1111 | Reserved |
| 1 | 0 | 0000 through 1111 | Normal Data Transmission |
| 1 | 1 | 0000 through 1111 | Transmit Error Propagation |
Table 7-6 MII Receive Encoding
| RX_DV | RX_ER | RX_D[3:0] | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0000 through 1111 | Normal Inter-Frame |
| 0 | 1 | 0000 | Normal Inter-Frame |
| 0 | 1 | 0001 through 1101 | Reserved |
| 0 | 1 | 1110 | False Carrier Indication |
| 0 | 1 | 1111 | Reserved |
| 1 | 0 | 0000 through 1111 | Normal Data Reception |
| 1 | 1 | 0000 through 1111 | Data Reception with Errors |