SLVSFY9B June 2021 – August 2021 DRV8212
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
9.2.2.3 Application Curves
The figures below show waveform examples of high-side and low-side driving in half-bridge mode. Figure 9-15 and Figure 9-16 show example waveforms of driving a motor unidirectionally using high-side and low-side driving. Figure 9-17 and Figure 9-18 show example waveforms of driving a solenoid using high-side and low-side driving. Figure 9-19 and Figure 9-20 show examples of driving a motor using high-side and low-side driving when the OUTx pins are paralleled together to create a single half bridge.
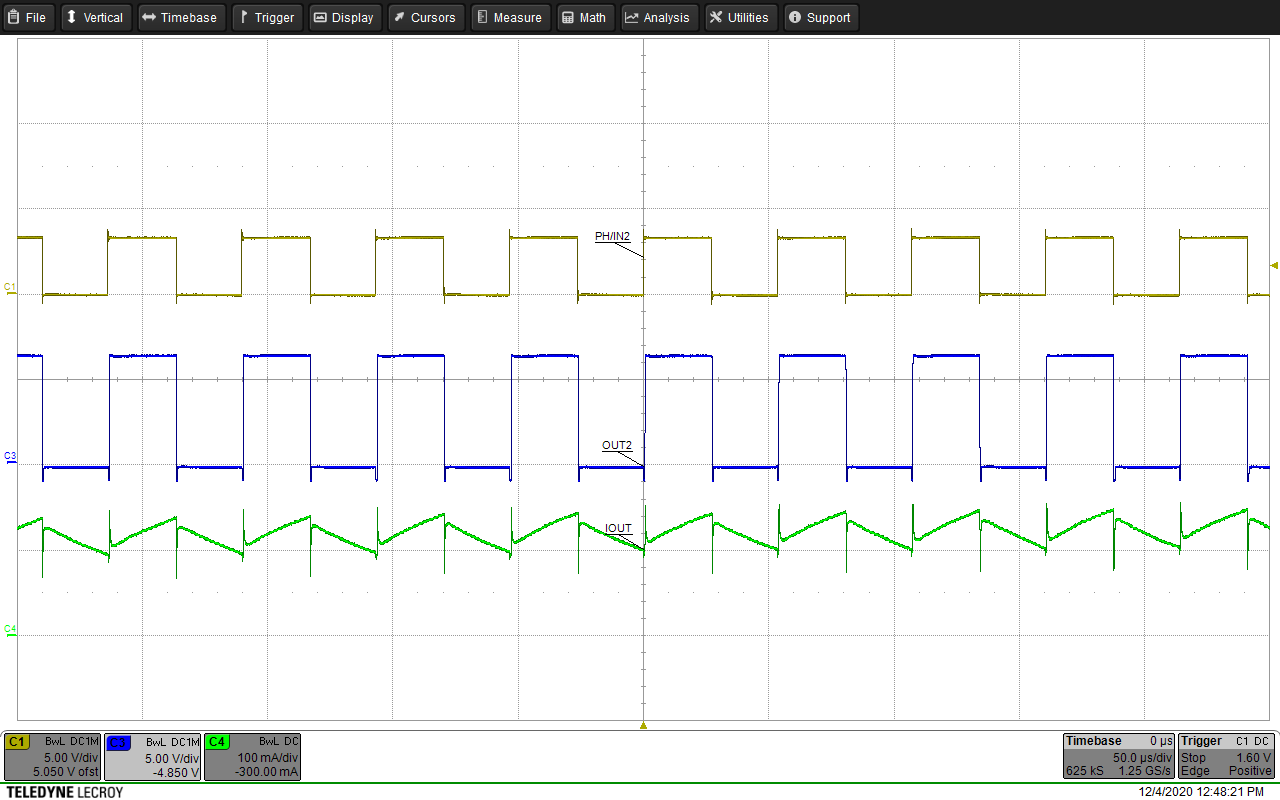
| Channel 1 = IN2 | Channel 2 = VOUT2 | Channel 4 = Motor Current |
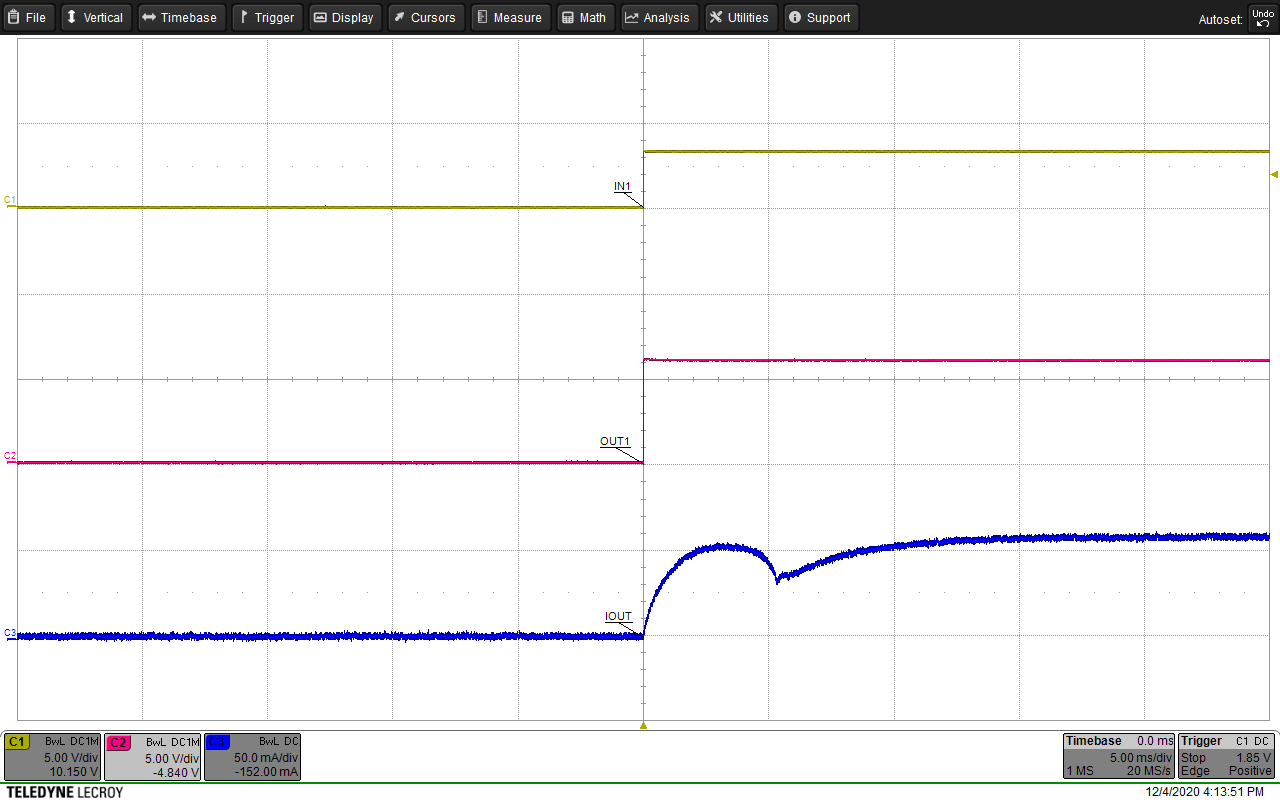
| Channel 1 = IN1 | Channel 2 = VOUT1 | Channel 4 = Solenoid Current |
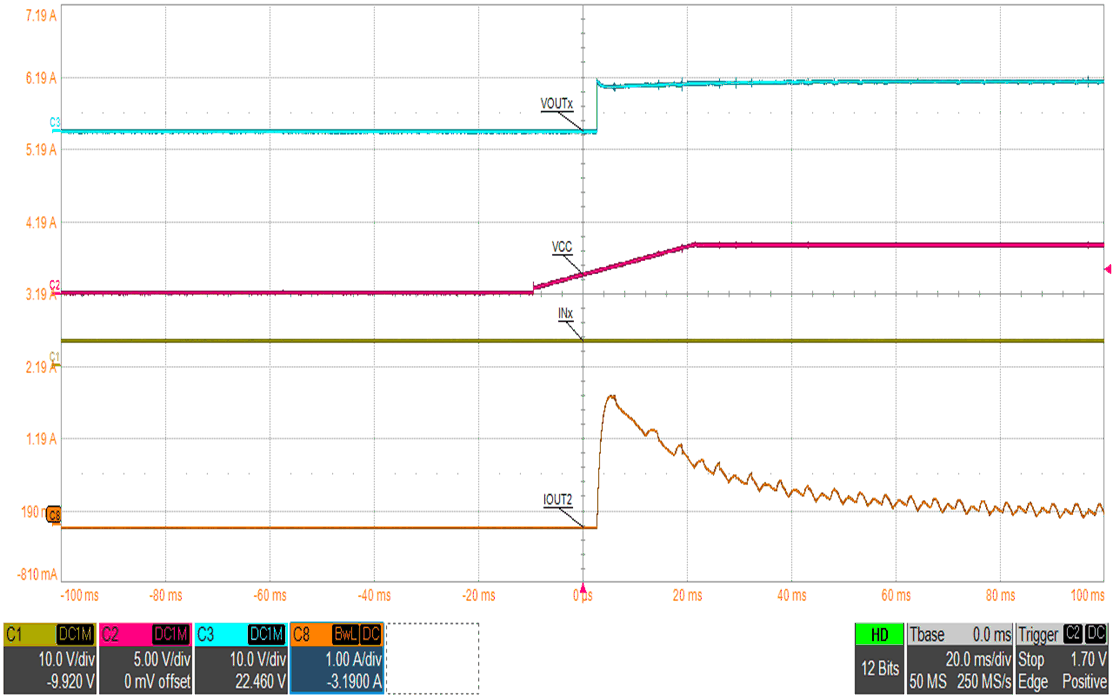
| Channel 1 = IN1, IN2 (paralleled) | Channel 2 = VVCC | Channel 3 = VOUT (OUT1/2 paralleled) |
| Channel 8 = Motor Current |
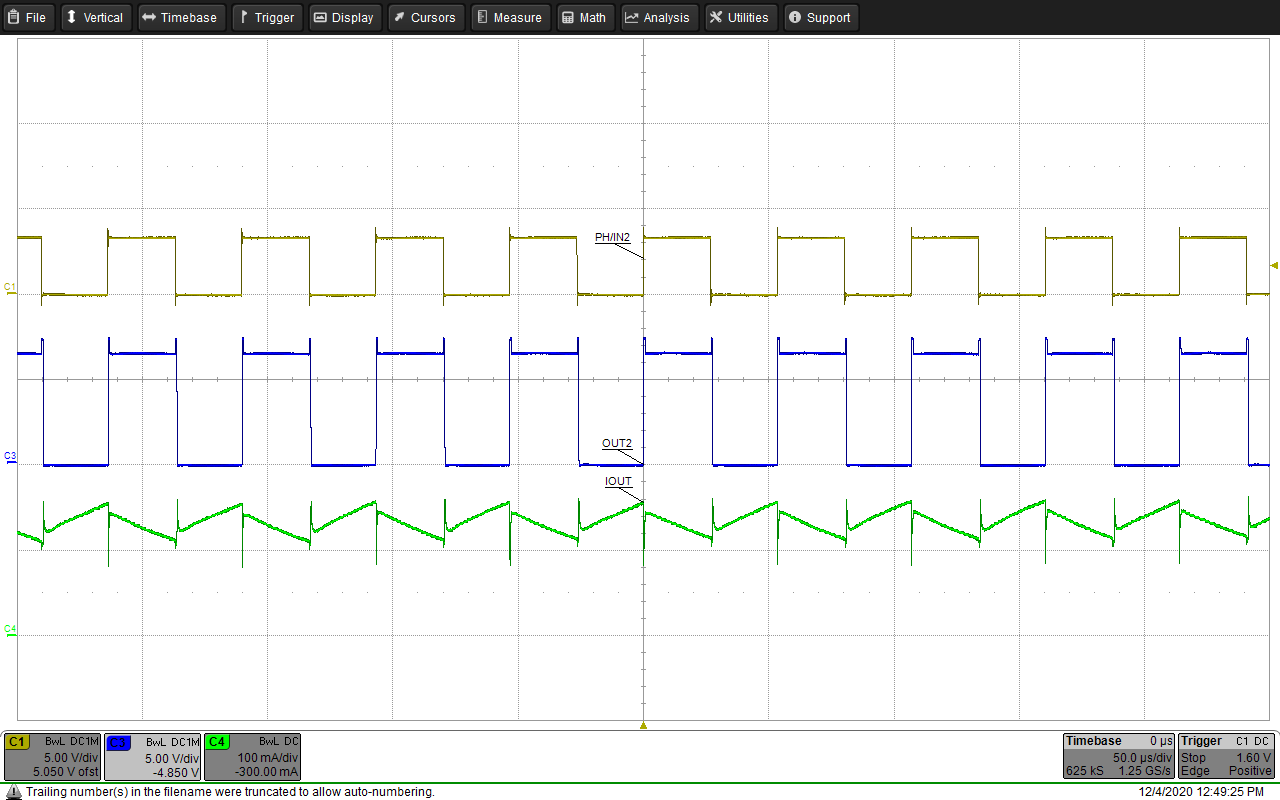
| Channel 1 = IN2 | Channel 2 = VOUT2 | Channel 4 = Motor Current |
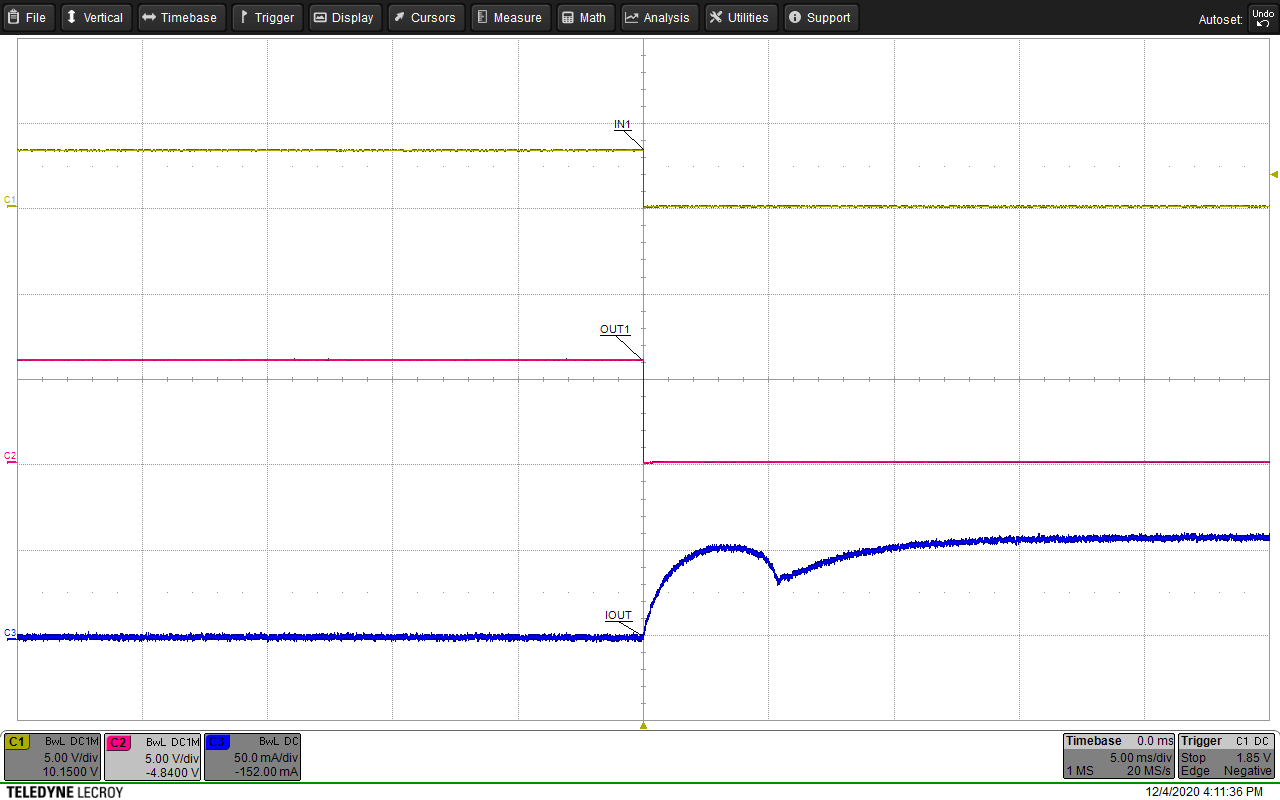
| Channel 1 = IN1 | Channel 2 = VOUT1 | Channel 4 = Solenoid Current |
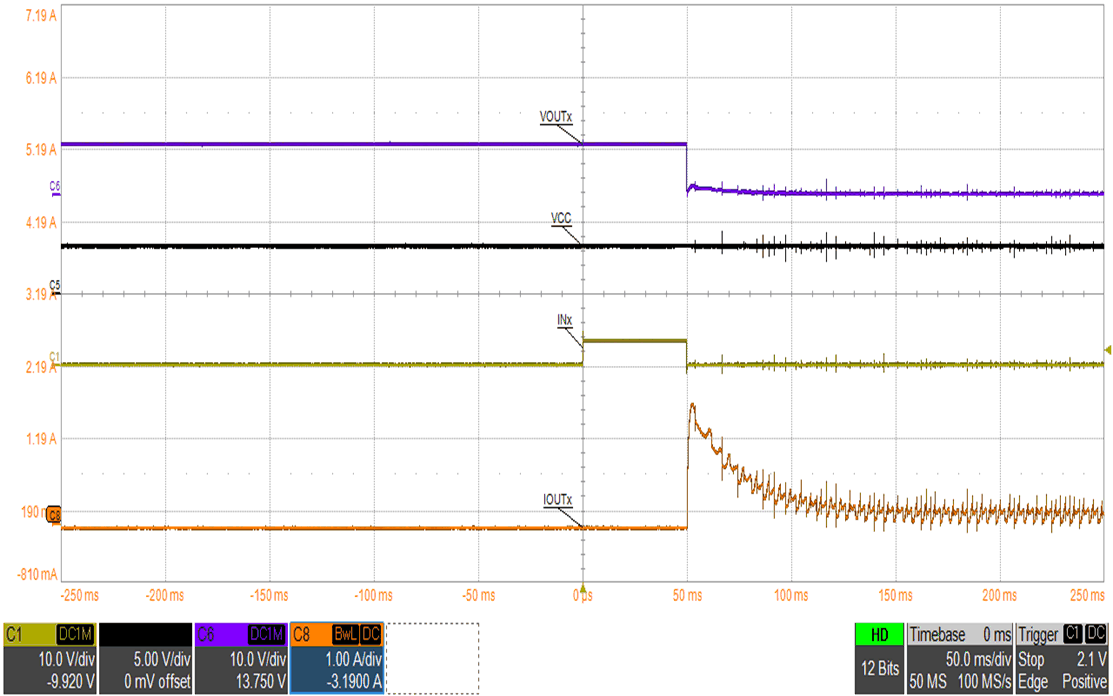
| Channel 1 = IN1, IN2 (paralleled) | Channel 5 = VVCC | Channel 6 = VOUT (OUT1/2 paralleled) |
| Channel 8 = Motor Current |