SLVSFZ0A June 2021 – July 2021 DRV8212P
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
9.2.3.2.1 Shunt Resistor Sizing
The Absolute Maximum Ratings for the INx pins set the maximum voltage across the shunt resistor. If the signal on the INx pin is low, referenced at the board ground, then the INx pins are at a negative voltage with respect to the GND pin voltage. This sets the maximum sense voltage/GND pin voltage to 0.5 V. Figure 9-12 shows the relative pin voltages.
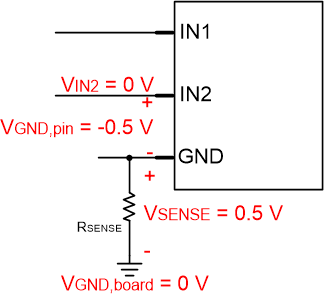 Figure 9-12 Pin voltages with respect to board ground using current sense
resistor
Figure 9-12 Pin voltages with respect to board ground using current sense
resistorThis example uses 150 mV for the maximum VSENSE, which is less than 0.5 V and provides some margin for safety or error. The maximum current through the motor will be the stall current, which is 1 A for this example. With this information, the sense resistance RSENSE can be calculated from the equation below.
Because the device GND pin voltage will vary with current through the sense resistor, the designers must also ensure that the logic pins meet VIL and VIH parameters,and the supply remains above VUVLO for proper operation.